Why ’10almonds’? Newsletter Name Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: Why is your newsletter called 10almonds? Maybe I missed it in the intro email, but my curiosity wants to know the significance. Thanks!”
It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was online… So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a tongue-in-cheek reference to that story… but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Heart Health vs Systemic Stress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At The Heart Of Good Health
This is Dr. Michelle Albert. She’s a cardiologist with a decades-long impressive career, recently including a term as the president of the American Heart Association. She’s the current Admissions Dean at UCSF Medical School. She’s accumulated enough awards and honors that if we list them, this email will not fit in your inbox without getting clipped.
What does she want us to know?
First, lifestyle
Although Dr. Albert is also known for her work with statins (which found that pravastatin may have anti-inflammatory effects in addition to lipid-lowering effects, which is especially good news for women, for whom the lipid-lowering effects may be less useful than for men), she is keen to emphasize that they should not be anyone’s first port-of-call unless “first” here means “didn’t see the risk until it was too late and now LDL levels are already ≥190 mg/dL”.
Instead, she recommends taking seriously the guidelines on:
- getting plenty of fruit, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein
- avoiding red meat, processed meats, refined carbohydrates, and sweetened beverages
- getting your 150 minutes per week of moderate exercise
- avoiding alcohol, and definitely abstaining from smoking
See also: These Top Five Things Make The Biggest Difference To Health
Next, get your house in order
No, not your home gym—though sure, that too!
But rather: after the “Top Five Things” we linked just above, the sixth on the list would be “reduce stress”. Indeed, as Dr. Albert says:
❝Heart health is not just about the physical heart but also about emotional well-being. Stress management is crucial for a healthy heart❞
~ Dr. Michelle Albert
This is where a lot of people would advise mindfulness meditation, CBT, somatic therapies, and the like. And these things are useful! See for example:
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
…and:
However, Dr. Albert also advocates for awareness of what some professionals have called “Shit Life Syndrome”.
This is more about socioeconomic factors. There are many of those that can’t be controlled by the individual, for example:
❝Adverse maternal experiences such as depression, economic issues and low social status can lead to poor cognitive outcomes as well as cardiovascular disease.
Many jarring statistics illuminate a marked wealth gap by race and ethnicity… You might be thinking education could help bridge that gap. But it is not that simple.
While education does increase wealth, the returns are not the same for everyone. Black persons need a post-graduate degree just to attain similar wealth as white individuals with a high school degree.❞
~ Dr. Michelle Albert
Read in full: AHA president: The connection between economic adversity and cardiovascular health
What this means in practical terms (besides advocating for structural change to tackle the things such as the racism that has been baked into a lot of systems for generations) is:
Be aware not just of your obvious health risk factors, but also your socioeconomic risk factors, if you want to have good general health outcomes.
So for example, let’s say that you, dear reader, are wealthy and white, in which case you have some very big things in your favor, but are you also a woman? Because if so…
Women and Minorities Bear the Brunt of Medical Misdiagnosis
See also, relevant for some: Obesity Discrimination In Healthcare Settings ← you’ll need to scroll to the penultimate section for this one.
In other words… If you are one of the majority of people who is a woman and/or some kind of minority, things are already stacked against you, and not only will this have its own direct harmful effect, but also, it’s going to make your life harder and that stress increases CVD risk more than salt.
In short…
This means: tackle not just your stress, but also the things that cause that. Look after your finances, gather social support, know your rights and be prepared to self-advocate / have someone advocate for you, and go into medical appointments with calm well-prepared confidence.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Feminist narratives are being hijacked to market medical tests not backed by evidence
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Corporations have used feminist language to promote their products for decades. In the 1980s, companies co-opted messaging about female autonomy to encourage women’s consumption of unhealthy commodities, such as tobacco and alcohol.
Today, feminist narratives around empowerment and women’s rights are being co-opted to market interventions that are not backed by evidence across many areas of women’s health. This includes by commercial companies, industry, mass media and well-intentioned advocacy groups.
Some of these health technologies, tests and treatments are useful in certain situations and can be very beneficial to some women.
However, promoting them to a large group of asymptomatic healthy women that are unlikely to benefit, or without being transparent about the limitations, runs the risk of causing more harm than good. This includes inappropriate medicalisation, overdiagnosis and overtreatment.
In our analysis published today in the BMJ, we examine this phenomenon in two current examples: the anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) test and breast density notification.
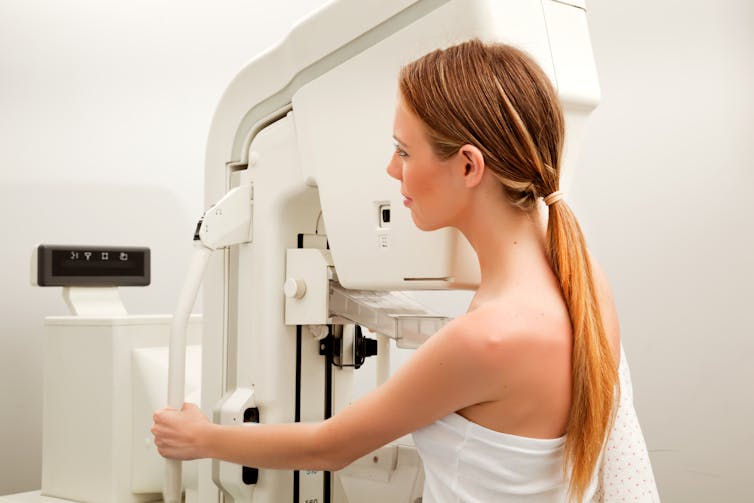
The AMH test
The AMH test is a blood test associated with the number of eggs in a woman’s ovaries and is sometimes referred to as the “egg timer” test.
Although often used in fertility treatment, the AMH test cannot reliably predict the likelihood of pregnancy, timing to pregnancy or specific age of menopause. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists therefore strongly discourages testing for women not seeking fertility treatment.
The AMH test can’t predict your chance of getting pregnant.
Anastasia Vityukova/UnsplashDespite this, several fertility clinics and online companies market the AMH test to women not even trying to get pregnant. Some use feminist rhetoric promising empowerment, selling the test as a way to gain personalised insights into your fertility. For example, “you deserve to know your reproductive potential”, “be proactive about your fertility” and “knowing your numbers will empower you to make the best decisions when family planning”.
The use of feminist marketing makes these companies appear socially progressive and champions of female health. But they are selling a test that has no proven benefit outside of IVF and cannot inform women about their current or future fertility.
Our recent study found around 30% of women having an AMH test in Australia may be having it for these reasons.
Misleading women to believe that the test can reliably predict fertility can create a false sense of security about delaying pregnancy. It can also create unnecessary anxiety, pressure to freeze eggs, conceive earlier than desired, or start fertility treatment when it may not be needed.
While some companies mention the test’s limitations if you read on, they are glossed over and contradicted by the calls to be proactive and messages of empowerment.
Breast density notification
Breast density is one of several independent risk factors for breast cancer. It’s also harder to see cancer on a mammogram image of breasts with high amounts of dense tissue than breasts with a greater proportion of fatty tissue.
While estimates vary, approximately 25–50% of women in the breast screening population have dense breasts.
Dense breasts can make it harder to detect cancer.
Tyler Olsen/ShutterstockStemming from valid concerns about the increased risk of cancer, advocacy efforts have used feminist language around women’s right to know such as “women need to know the truth” and “women can handle the truth” to argue for widespread breast density notification.
However, this simplistic messaging overlooks that this is a complex issue and that more data is still needed on whether the benefits of notifying and providing additional screening or tests to women with dense breasts outweigh the harms.
Additional tests (ultrasound or MRI) are now being recommended for women with dense breasts as they have the ability to detect more cancer. Yet, there is no or little mention of the lack of robust evidence showing that it prevents breast cancer deaths. These extra tests also have out-of-pocket costs and high rates of false-positive results.
Large international advocacy groups are also sponsored by companies that will financially benefit from women being notified.
While stronger patient autonomy is vital, campaigning for breast density notification without stating the limitations or unclear evidence of benefit may go against the empowerment being sought.
Ensuring feminism isn’t hijacked
Increased awareness and advocacy in women’s health are key to overcoming sex inequalities in health care.
But we need to ensure the goals of feminist health advocacy aren’t undermined through commercially driven use of feminist language pushing care that isn’t based on evidence. This includes more transparency about the risks and uncertainties of health technologies, tests and treatments and greater scrutiny of conflicts of interests.
Health professionals and governments must also ensure that easily understood, balanced information based on high quality scientific evidence is available. This will enable women to make more informed decisions about their health.
Brooke Nickel, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, University of Sydney and Tessa Copp, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Understanding Cellulitis: Skin And Soft Tissue Infections
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference between a minor passing skin complaint, and a skin condition that’s indicative of something more serious? Dr. Thomas Watchman explains:
More than skin-deep
Cellulitis sounds benign enough, like having a little cellulite perhaps, but in fact it means an infection of the skin and—critically—the underlying soft tissues.
Normally, the skin acts as a barrier against infections, but this barrier can be breached by physical trauma (i.e. an injury that broke the skin), eczema, fungal nail infections, skin ulcers, and other similar things that disrupt the skin’s ability to protect us.
Things to watch out for: Dr. Watchman advises we keep an eye out for warm, reddened skin, swelling, and blisters. Specifically, a golden-yellow crust to these likely indicates a Staphylococcus aureus infection (hence the name).
There’s a scale of degrees of severity:
- Class 1: No systemic toxicity or comorbidities
- Class 2: Systemic toxicity or comorbidities present
- Class 3: Significant systemic toxicity or comorbidities with risk of significant deterioration
- Class 4: Sepsis or life-threatening infection
…with antibiotics being recommended in the latter two cases there, or in other cases for frail, young, old, or immunocompromised patients. Given the rather “scorched earth” results of antibiotics (they cause a lot of collateral iatrogenic damage), this can be taken as a sign of how seriously such infections should be taken.
For more about all this, including visual guides, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Of Brains & Breakouts: The Brain-Skin Doctor
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- Antibiotics? You Might Want To Think Thrice
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Your Health Audit, From Head To Toe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health Audit Time
Here at 10almonds, we often cover quite specific things, ranging from “the effect of sodium on organs other than your heart” to “make this one small change to save your knees while driving”.
But, we’re each a whole person, and we need to take care of the whole organism that makes up the wonderful being that we each are. If we let one part of it drop in health too much, the others will soon follow suit because of the knock-on effects.
So, let’s do a quick self-check-up, and see what can be done for each! How’s your…
Mental Health
We’re doing this audit head-to-to, so let’s start it here, because mental health is also just health, and it’s difficult to tackle the others without having this one at least under control!
Are you experiencing chronic stress? Anxiety? Depression? Joy?
If you answered “no” to “joy” but also “no” to “depression”, you might want to rethink your answer to “depression”, by the way. Life should be a joyous thing!
Some resources to address your mental health:
Brain Health
Your brain is a big, powerful organ. It uses more of your daily energy (in the physiological sense of the word, we’re talking calories and mitochondria and ATP) than any other organ, by far.
And when it comes to organ failure, if your brain fails, then having the best joints in the world won’t help you, for example.
Some resources to address your brain health:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It
- How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
- The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
Heart Health
Everything depends on your heart, head to toe. Tirelessly pumping blood with oxygen, nutrients, and agents of your immune system all around your body, all day every day for your entire life.
What’s your resting heart rate like? How about your blood pressure? And while we’re on the topic of blood… how’s your blood sugar health?
These are all important things to a) know about and b) keep on top of!
Some resources to address your heart health:
- 1-Minute Heart Health Check-Up Tips
- A Five-Point Plan For Heart Health
- High Blood Pressure? Try These!
Gut Health
By cell count, we’re about 10% human and 90% bacteria. By gene count, also. Pretty important, therefore, that we look after our trillions of tiny friends that keep our organism working.
Most people in N. America, for example, get vastly under the recommended daily amount of fiber, and that’s just the most basic courtesy we could do for these bugs that keep us alive (they need that fiber to live, and their process of consuming it is beneficial to us in a stack of ways).
Some resources to address your gut health:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- The Surprising Link Between Gut Health And Serotonin
- The Vagus Nerve: The Brain-Gut Highway!
Hormonal Health
Hormones are weird and wonderful and affect so much more than the obvious sex-related functions (but yes, those too). A lot of people don’t realize it, but having our hormones in good order or not can make the difference between abject misery and a happy, fulfilling life.
Some resources to address your hormonal health:
- What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
- Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them
- Too Much Or Too Little Testosterone?
Bone/Joint Health
Fear nothing! For you are a ghost operating a skeleton clad in flesh. But also, you know, look after that skeleton; you only get one! Being animals, we’re all about movement, and being humans, we’ve ended up with some lifestyle situations that aren’t great for that mobility. We sit too much; we walk too little; we cramp ourselves into weird positions (driving, anyone?), and we forget the range of motion we’re supposed to have. But let’s remember…
Some resources to address your bone/joint health:
- Collagen’s benefits are more than skin deep
- Cool As A Cucumber (Move Over, Glucosamine + Chondroitin)
- 5 Best Bodyweight Exercises For Incredible Mobility
Lastly…
While it’s good to do a little self-audit like this every now and again, it’s even better to get a professional check-up!
As engineers say: if you don’t schedule time for maintenance, your equipment will schedule it for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do Breathe – by Michael Williams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever felt you could get everything in your life in order, if you could just get a little breathing room first?
Notwithstanding the title, this is mostly not a book about breathing exercises. It does cover that too, but there’s a lot more.
The author’s advices draw from a variety of high quality sources. Well-read readers will certainly recognise sections that are straight from David Allen’s “Getting Things Done”, and Mihaly Czikszentmihalyi’s “Flow”, for example, as well as Francesco Cirillo’s “Pomodoro Technique”, and James Clear’s “Atomic Habits”.
We also learn about how even simple yoga can help us, and good sleep, and a healthy diet.
In short, if you’ve been reading 10almonds for a while, you might not actually learn much new! But it’s very nice to have all these things in one book, for sure, and it’s a pleasant, easy read too.
Bottom line: if you’d like to streamline your life and not have to buy a whole stack of different books to do it, this book is a great composite that will enable you to get the job done efficiently.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Proteinaholic – by Dr. Garth Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein is important, yes. However, you can have too much of a good thing, and you can also get it from bad sources that do more harm than good.
That’s what this book is about, and how to go about understanding the science in a world where marketing has outstripped the conclusions of research scientists.
Firstly, let’s mention that Dr. Davis’ main issue here is (as the subtitle suggests) about animal proteins, not plant-based proteins. The former are associated with very many health risks that the latter are not. And yes, even just the lean protein, not considering the animal fat.
He does not argue that the reader must, or even necessarily needs to, adopt a vegan diet. However, he does argue for minimizing animal proteins, and getting more plants in.
A lot of the book is about the research to back this approach, and specifically, it’s largely a polemic against animal protein. He also shares anecdotes throughout, about his own health journey—from an overweight cheeseburger-fueled heart attack machine with exciting cholesterol levels, to a healthy, muscular, plant-fueled advocate for healthier eating.
He talks us through the science at hand, including chapters for each of the main health risks associated with meat consumption, as well as how the science got misrepresented by popular marketing for [not necessarily, but usually] meat-heavy diets such as Atkins and Paleo. That yes, they will give short term weight loss, but bring extra health risks in the longer term, and how.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut down your meat consumption but worry “will I get enough protein?”, this book will set your mind at ease with an abundance of science.
Click here to check out Proteinaholic, and give your body better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: