Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
This is Dr. Michael Greger, M.D. FACLM, of “Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen” and “How Not To Die” fame, and he wants us to protect our brains (and while we’re at it, our eyesight).
And the secret is…
Lutein.
This is a carotenoid, which is super important for the eyes and brain. Not to be confused with carrots, which despite the name are usually not a good source of carotenoids!
They do however contain lots of beta-carotene, a form of vitamin A, but that (and the famous WW2-era myth born of deliberate disinformation by the British government) isn’t what we’re covering today.
We say “eyes and brain” but really, the eyes are just an extension of the brain in any case.
Pedantry aside, what Dr. Greger wants you to know about lutein is how important it is for the protection of your brain/eyes, both against cognitive decline and against age-related macular degeneration (the most common cause of eyesight loss in old age).
Important take-away info:
- Two things that hasten brain aging are inflammation and oxidative stress. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory foods mitigate those.
- Researchers investigated eight different dietary antioxidants, including vitamins A and E. Only lutein was “significantly related to better cognition”.
- The macula in the middle of our retina is packed with lutein, and levels in the retina correspond to levels in the rest of our brain.
- Alzheimer’s patients have significantly less lutein in their eyes and in their blood, and a higher occurrence of macular degeneration.
- Dark green leafy vegetables are lutein superstars. A half cup of kale has 50 times more lutein than an egg.
Want to know more about the Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen approach to health?
See the Website / Get the App (Android & iOS) / Get the Science Book / Get the Cookbook!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
It’s A Wrap
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We hope all our readers have had a great and healthy week! Here are some selections from health news from around the world:
A lack of transparency
Thousands of chemicals blanket-approved for food contact in packaging, under the FDA’s “Generally Recognized As Safe” umbrella, have been found in humans.
This highlights a gap in the safeguarding system, because the GRAS classification is given when there’s no known significant association with disease—but in this case, a problem can occur when the build-up in the blood and brain cause problems much later.
Read in full: Thousands of toxins from food packaging found in humans – research
Learn more: We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of (It’s Not Fantastic To Be Plastic)
Cafestol for weight loss?
Most coffee intervention studies use instant coffee. Which is understandable; they are scientists on a budget, not coffee shop baristas. But, instant coffee is low in some of coffee’s important compounds, such as cafestol—which as it turns out, can lower not only overall body fat, but also (importantly!) visceral fat.
Read in full: 12-week coffee compound study shows promising results for weight and fat reduction in at-risk individuals
Learn more: The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Doing something is better than doing nothing
While a lot of the bad news both locally and around the world can be infuriating and/or depressing, turning a blind eye may not be the best approach for dealing with it. This study was in teens, but it’s likely that the benefits are similar for other ages too:
Read in full: Racial justice activism, advocacy found to reduce depression, anxiety in some teens
Learn more: Make Social Media Work For Your Mental Health
A ray of hope!
Sometimes, the topic of sun and sunscreens can seem like “damned if you do; damned if you don’t”, with regard to the harmful effects of the sun, and in some cases, potentially harmful effects of some sunscreen chemicals. We’ve argued ultimately in favor of sunscreens in this tug-of-war, but it’s nice to see improvements being made, in this case, with lignin-based sunscreen (a plant-based by-product of the pulp industry).
Read in full: Researchers create high-performing, eco-friendly sunscreen
Learn more: Who Screens The Sunscreens?
All about the pores
Researchers have identified a protein, and from that, a stack of protein fragments, that are involved in the formation of large pores. This is important, as it’s pointing to a means of relief for a lot of inflammatory diseases.
Read in full: Scientists unravel the process of pore formation in cells
Learn more: Why Do We Have Pores, And Could We Not?
Getting to the bottom of Crohn’s
If you have Crohn’s, or perhaps someone close to you has it, then you’ll be familiar with the common medical refrain of “we don’t know”. While this honesty is laudable, it’s not reassuring. So, it’s good that researchers are making progress in understanding why many people with Crohn’s may respond differently not only to lifestyle interventions, but also to various relevant drugs—allowing doctors to prescribe the right treatment for the right person.
Read in full: Patient-derived gut organoids reveal new insights into Crohn’s disease subtypes
Learn more: Diet Tips for Crohn’s Disease
Another carotenoid that holds back Alzheimer’s
Phytoene is a carotenoid that is found in many red, orange, or yellow foods, including tomatoes, carrots, apricots, red peppers, oranges, mandarins and passion fruit, among others. Researchers have found that it slows the onset of symptoms associated with the formation of amyloid plaques, by 30–40%, and increases longevity by 10–19%:
Read in full: Carotenoid phytoene shows potential in slowing Alzheimer’s plaque formation and increasing lifespan
Learn more: Brain Food? The Eyes Have It! ← this is about a different carotenoid, lutein, found mostly in dark green leafy vegetables, but it’s best to enjoy both 😎
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Move – by Caroline Williams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
- Get 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, says the American Heart Association
- There are over 10,000 minutes per week, says the pocket calculator
Is 150/10,000 really the goal here? Really?
For Caroline Williams, the answer is no.
In this book that’s practically a manifesto, she outlines the case that:
- Humans evolved to move
- Industrialization and capitalism scuppered that
- We now spend far too long each day without movement
Furthermore, for Williams this isn’t just an anthropological observation, it’s a problem to be solved, because:
- Our lack of movement is crippling us—literally
- Our stagnation affects not just our bodies, but also our minds
- (again literally—there’s a direct correlation with mental health)
- We urgently need to fix this
So, what now, do we need to move in to the gym and become full-time athletes to clock up enough hours of movement? No.
Williams convincingly argues the case (using data from supercentenarian “blue zones” around the world) that even non-exertive movement is sufficient. In other words, you don’t have to be running; walking is great. You don’t have to be lifting weights; doing the housework or gardening will suffice.
From that foundational axiom, she calls on us to find ways to build our life around movement… rather than production-efficiency and/or convenience. She gives plenty of tips for such too!
Bottom line: some books are “I couldn’t put it down!” books. This one’s more of a “I got the urge to get up and get moving!” book.
Get your get-up-and-go up and going with “Move”—order yours from Amazon today!
Share This Post
-
Are You A Calorie-Burning Machine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burn, Calorie, Burn
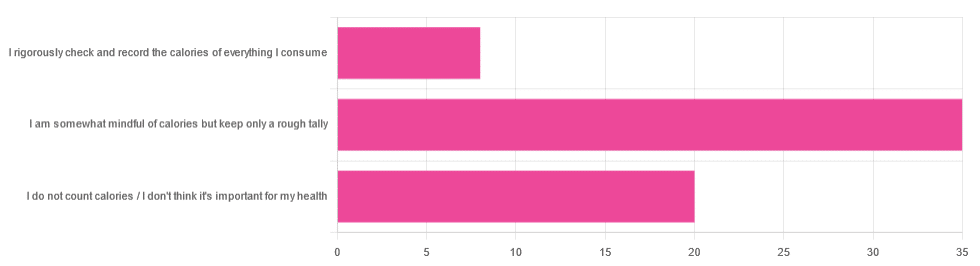
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you whether you count calories, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of answers:
- About 56% said “I am somewhat mindful of calories but keep only a rough tally”
- About 32% said “I do not count calories / I don’t think it’s important for my health”
- About 13% said “I rigorously check and record the calories of everything I consume”
So what does the science say, about the merits of all these positions?
A food’s calorie count is a good measure of how much energy we will, upon consuming the food, have to use or store: True or False?
False, broadly. It can be, at best, a rough guideline. Do you know what a calorie actually is, by the way? Most people don’t.
One thing to know before we get to that: there’s “cal” vs “kcal”. The latter is generally used when it comes to foodstuffs, and it’s what we’ll be meaning whenever we say “calorie” here. 1cal is 1/1000th of a kcal, that’s all.
Now, for what a calorie actually is:
A calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃
Question: so, how to we measure how much food is needed to do that?
Answer: by using a bomb calorimeter! Which is the exciting name for the apparatus used to literally burn food and capture the heat produced to indeed raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃.
If you’re having trouble imagining such equipment, here it is:
Bomb Calorimeter: Definition, Construction, & Operation (with diagram and FAQs)
The unfortunate implication of the above information
A kilogram of sawdust contains about a 1000 kcal, give or take what wood was used and various other conditions.
However, that does not mean you can usefully eat the sawdust. In other words:
Calorie count tells us only how good something is at raising the temperature of water if physically burned.
Now do you see why oils and sugars have such comparably high calorie counts?
And while we may talk about “burning calories” as a metaphor, we do not, in fact, have a little wood stove inside us burning the food we eat.
A calorie is a calorie: True or False?
Definitely False! Building on from the above… We will get very little energy from sawdust; it’s not just that we can’t use it; we can’t store it either; it’ll mostly pass through as fiber.
(however, please do not use sawdust to get your daily dose of fiber either, as it is not safe for human consumption and may give you diseases, depending on what is lurking in it)
But let’s look at oil and sugar, two very high-calorie categories of food, because they’re really easy to physically burn and they give off a good flame.
A bomb calorimeter may treat them quite equally, but to our body, they are metabolically very different indeed.
For a start, most sugars will get absorbed and processed much more quickly than most oils, and that can overwhelm the liver (responsible for glycogen management), and lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes, and more. Metabolic syndrome in general, and if you keep it up too much and you may find it’s now a lottery between dying of NAFLD, diabetes, or heart disease (it’ll usually be the heart disease that kills).
See also:
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Meanwhile, we know all about the different kinds of nutritional profiles that oils can have, and some can promote having high energy without putting on fat, while others can strain the heart. Not even “a fat is a fat”, so “a calorie is a calorie” doesn’t get much mileage outside of a bomb calorimeter!
See also:
A calorie-controlled / calorie-restricted diet is an effective weight loss strategy: True or False?
True, usually! Surprise!
- On the one hand: calories are a wildly imprecise way to reckon the value of food, and using them as a guide to health can be dangerously misleading
- On the other hand: the very activity of calorie-counting itself promotes mindful eating, which is very good for the health
There is a strong difference between the mind of somebody who is carefully logging their pre-bedtime piece of chocolate and reflecting on its nutritional value, vs someone who isn’t sure whether this is their second or third glass of wine, nor how much the glass contained.
So if you want to get most of the benefits of a calorie-controlled diet without counting calories, you may try taking a “mindful eating” approach to diet.
However! If you want to do this for weight loss, be aware, that you will have to practice it all the time, not just for one meal here and there.
You can read more on how to do “mindful eating” here:
Dr. Rupy Aujla: The Kitchen Doctor | Mindful Eating & Interoception
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cool As A Cucumber
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
Do you take glucosamine & chondroitin supplements for your bone-and-joint health?
Or perhaps, like many, you take them intermittently because they mean taking several large tablets a day. Or maybe you don’t take them at all because they generally contain ingredients derived from shellfish?
Cucumber extract has your back! (and your knees, and your hips, and…)
It’s plant-derived (being from botanical cucumbers, not sea cucumbers, the aquatic animal!) and requires only 1/135th of the dosage to produce twice the benefits!
Distilling the study to its absolute bare bones for your convenience:
- Cucumber extract (10mg) was pitted against glucosamine & chondroitin (1350mg)
- Cucumber extract performed around 50% better than G&C after 30 days
- Cucumber extract performed more than 200% better than G&C after 180 days
In conclusion, this study indicates that, in very lay terms:
Cucumber extract blows glucosamine & chondroitin out of the water as a treatment and preventative for joint pain
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Immunostimulant Superfood
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat These Greens!
Chlorella vulgaris, henceforth “chlorella”, is a simple green algae that has a lot of health benefits.
Note: most of the studies here are for Chlorella vulgaris specifically. However, some are for other species of the Chlorella genus, of which Chlorella vulgaris is by far the most common, hence the name (vulgaris = common). The relevant phytochemical properties appear to be the same regardless.
Superfood
While people generally take it as a supplement rather than a food item in any kind of bulk, it is more than 50% protein and contains all 9 essential amino acids.
As you might expect of a green superfood, it’s also full of many antioxidants, most of them carotenoids, and these pack a punch, for example against cancer:
It also has a lot of vitamins and minerals, and even omega-3.
Which latter also means it helps improve lipids and is thus particularly…
Heart healthy
❝Daily consumption of Chlorella supplements provided the potential of health benefits reducing serum lipid risk factors, mainly triglycerides and total cholesterol❞
Its heart-healthy benefits don’t stop at lipids though, and include blood pressure management, as in this study that found…
❝GABA-rich Chlorella significantly decreased high-normal blood pressure and borderline hypertension, and is a beneficial dietary supplement for prevention of the development of hypertension. ❞
About that GABA, if you’re curious about that, check out:
GABA Against Stress, Anxiety, & More
May remove heavy metals
We’re going with “may” for this one as we could only find animal studies so far (probably because most humans don’t have megadoses of heavy metals in them, which makes testing harder).
Here’s an example animal study, though:
Enhanced elimination of tissue methyl mercury in [Chlorella]-fed mice
Immunostimulant
This one’s clearer, for example in this 8-week study (with humans) that found…
❝Serum concentrations of interferon-γ (p<0.05) and interleukin-1β (p<0.001) significantly increased and that of interleukin-12 (p<0.1) tended to increase in the Chlorella group.
The increments of these cytokines after the intervention were significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than those in the placebo group. In addition, NK cell activities (%) were significantly increased in Chlorella group, but not in Placebo group.
The increments of NK cell activities (%) were also significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than the placebo group.
Additionally, changed levels of NK cell activity were positively correlated with those of serum interleukin-1β (r=0.280, p=0.047) and interferon-γ (r=0.271, p<0.005).❞
tl;dr = it boosts numerous different kinds of immune cells
PS, if you click though to the study, you may be momentarily alarmed by the first paragraph of the abstract that says “However, there were no direct evidences for the effect of Chlorella supplementation on immune/inflammation response in healthy humans“
this is from the “Background” section of the abstract, so what they are saying is “before we did this study, nobody had done this yet”.
So, be assured that the results are worthwhile and compelling.
Is it safe?
Based on the studies, it has a good safety profile. However, as it boosts the immune system, you may want to check with your doctor if you have an autoimmune disorder, and/or you are on immunosuppressants.
And in general, of course always check with your doctor/pharmacist if unsure about any potential drug interactions.
Want some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Immediately after we stop drinking is rarely when we feel our best. But how long is it before we can expect to see benefits, instead of just suffering?
Timeline
After stopping drinking alcohol for…
- Seconds: the liver starts making progress filtering out toxins and sugars; ethanol starts to leave the system
- 1 hour: fatigue sets in as the body uses a lot of energy to metabolize and eliminate alcohol. However, sleep quality (if one goes to sleep now) is low because alcohol disrupts the brain patterns required for restful sleep
- 6–12 hours: the immune system starts recovering from the suppression caused by alcohol
- 24 hours: immune system is back to normal; withdrawal symptoms may occur in the case of heavy drinkers
- 3–5 days: resting blood pressure begins to drop, as stress levels decrease (alcohol may seem anxiolytic, but it is actually anxiogenic; it just masks its own effect in this regard). Also, because of insulin responses improving, appetite reduces. The liver, once it has finished dealing your last drinking session (if you used to drink all the time, it probably had a backlog to clear), can now begin to make repairs on itself.
- 1 week: skin will start looking better, as antidiuretic hormone levels neutralize, leading to a healthier maintenance of hydration
- 2 weeks: cognitive abilities improve as the brain begins to make progress in repairing itself. At the same time, kidneys start to heal.
- 3–4 weeks: the liver begins to regenerate in earnest. You may wonder what took it so long given the liver’s famous regenerative abilities, but in this case, the liver was also the organ that took the most damage from drinking, so its regeneration gets off to a slow start (in contrast, if the liver had “merely” suffered physical trauma, such as being shot, stabbed,
or eaten by eagles,it’d start regenerating vigorously as soon as the immediate wound-response had been tended to). Once it is able to pick up the pace though, overall health improves, as the liver can focus on breaking down other toxins. - 1–2 months: the heart is able to repair itself, and start to become stronger again (dependent on other lifestyle factors, of course).
- 3 months and more: bodily repairs continue (for example, the damage to the liver is often so severe that it can take quite a bit longer to recover completely, and repairs in the brain are always slow, for reasons beyond the scope of this article). Looking at the big picture, at this point we also see other benefits, such as reduced cancer risks.
In short… It’s never too soon to stop, but it’s also never too late, unless you are going to die in the next few days. So long as you’ll be in the land of the living for a few days yet, there’s time to enjoy the benefits of stopping.
Most importantly: the timeline for the most important repairs is not as long as many people might think, and that itself can be very motivating.
For more detail on much of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Can We Drink To Good Health?
- How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
- Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: