The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Good Is Your Sleep, Really?
This is Dr. Marie-Pierre St-Onge, Director of Columbia University’s Center of Excellence for Sleep and Circadian Research.
The focus of Dr. St-Onge’s research is the study of the impact of lifestyle, especially sleep and diet, on cardio-metabolic risk factors.
She conducts clinical research combining her expertise on sleep, nutrition, and energy regulation.
What kind of things do her studies look at?
Her work focuses on questions about…
- The role of circadian rhythms (including sleep duration and timing)
- Meal timing and eating patterns
…and their impact on cardio-metabolic risk.
What does she want us to know?
First things first, when not to worry:
❝Getting a bad night’s sleep once in a while isn’t anything to worry about. That’s what we would describe as transient insomnia. Chronic insomnia occurs when you spend three months or more without regular sleep, and that is when I would start to be concerned.❞
But… as prevention is (as ever) better than cure, she also advises that we do pay attention to our sleep! And, as for how to do that…
The Six Dimensions of Sleep
One useful definition of overall sleep health is the RU-Sated framework, which assesses six key dimensions of sleep that have been consistently associated with better health outcomes. These are:
- regularity
- satisfaction with sleep
- alertness during waking hours
- timing of sleep
- efficiency of sleep
- duration of sleep
You’ll notice that some of these things you can only really know if you use a sleep-monitoring app. She does recommend the use of those, and so do we!
We reviewed and compared some of the most popular sleep-monitoring apps! You can check them out here: Time For Some Pillow Talk
You also might like…
We’re not all the same with regard to when is the best time for us to sleep, so:
Use This Sleep Cycle Calculator To Figure Out the Optimal Time for You To Go to Bed and Wake Up
AROUND THE WEB
What’s happening in the health world…
- Aspirin may make your breathing worse
- Taking naps for more than 30 minutes may raise your metabolic disease risk
- How to ease back into exercise after surgery
- Study provides evidence that breathing exercises may reduce your Alzheimer’s risk
- No one in movies knows how to swallow a pill
More to come tomorrow!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Take Care Of Your “Unwanted” Parts Too!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Meet The Family…
If you’ve heard talk of “healing your inner child” or similar ideas, then today’s featured type of therapy takes that to several extra levels, in a way that helps many people.
It’s called Internal Family Systems therapy, often “IFS” for short.
Here’s a quick overview:
Psychology Today | Internal Family Systems Therapy
Note: if you are delusional, paranoid, schizophrenic, or have some other related disorder*, then IFS would probably be a bad idea for you as it could worsen your symptoms, and/or play into them badly.
*but bipolar disorder, in its various forms, is not usually a problem for IFS. Do check with your own relevant healthcare provider(s), of course, to be sure.
What is IFS?
The main premise of IFS is that your “self” can be modelled as a system, and its constituent parts can be examined, questioned, given what they need, and integrated into a healthy whole.
For example…
- Exile is the name given to parts that could be, for example, the “inner child” referenced in a lot of pop-psychology, but it could also be some other ignored and pushed-down part of oneself, often from some kind of trauma. The defining characteristic of an exile is that it’s a part of ourself that we don’t consciously allow ourselves to see as a current part of ourself.
- Protector is the name given to a part of us that looks to keep us safe, and can do this in an adaptive (healthy) or maladaptive (unhealthy) way, for example:
- Firefighter is the name given to a part of us that will do whatever is necessary in the moment to deal with an exile that is otherwise coming to the surface—sometimes with drastic actions/reactions that may not be great for us.
- Manager is the name given to a part of us that has a more nurturing protective role, keeping us from harm in what’s often a more prophylactic manner.
To give a simple illustration…
A person was criticized a lot as a child, told she was useless, and treated as a disappointment. Consequently, as an adult she now has an exile “the useless child”, something she strives to leave well behind in her past, because it was a painful experience for her. However, sometimes when someone questions and/or advises her, she will get defensive as her firefighter “the hero” will vigorously speak up for her competence, like nobody did when she was a child. This vigor, however, manifests as rude abrasiveness and overcompensation. Finally, she has a manager, “the advocate”, who will do the same job, but in a more quietly confident fashion.
This person’s therapy will look at transferring the protector job from the firefighter to the manager, which will involve examining, questioning, and addressing all three parts.
The above example is fictional and created for simplicity and clarity; here’s a real-world case study if you’d like a more in-depth overview of how it can work:
How it all fits together in practice
IFS looks to make sure all the parts’ needs are met, even the “bad” ones, because they all have their functions.
Good IFS therapy, however, can make sure a part is heard, and then reassure that part in a way that effectively allows that part to “retire”, safe and secure in the knowledge that it has done what it needed to, and/or the job is being done by another part now.
That can involve, for example, thanking the firefighter for looking after our exile for all these years, but that our exile is safe and in good hands now, so it can put that fire-axe away.
See also: On Being Reactive vs Being Responsive
Questions you might ask yourself
While IFS therapy is best given by a skilled practitioner, we can take some of the ideas of it for self-therapy too. For example…
- What is a secret about yourself that you will take to the grave? And now, why did that part of you (now an exile) come to exist?
- What does that exile need, that it didn’t get? What parts of us try to give it that nowadays?
- What could we do, with all that information in mind, to assign the “protection” job to the part of us best-suited to healthy integration?
Want to know more?
We’ve only had the space of a small article to give a brief introduction to Family Systems therapy, so check out the “resources” tab at:
IFS Institute | What Is Internal Family Systems Therapy?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Seven Steps to Managing Your Memory – by Dr. Andrew Budson & Dr. Maureen O’Connor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this is not: a “how to improve your memory” book of the kind marketed to students and/or people who want to do memory-themed party tricks.
What this book actually is: exactly what the title and subtitle claim it to be: seven steps to managing your memory: what’s normal, what’s not, and what to do about it.
Drs. Budson & O’Connor cover:
- which memory errors can (and usually do) happen at any age
- how memory changes with normal aging, and
- what kinds of memory problems are not normal.
One thing that sets this book aside from a lot of its genre is that it also covers which kinds of memory loss are reversible—and, where appropriate, what can be undertaken to effect such a reversal.
The authors talk about what things have (and what things haven’t!) been shown to strengthen memory and reduce cognitive decline, and in the worst case scenario, what medications can help against Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
The style is halfway between pop-science and a science textbook. The structure of the book, with its headings, subheadings, bullet points, summaries, etc, helps the reader to process and remember the information.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get on top of managing your memory before you forget, then this book is for you.
Share This Post
-
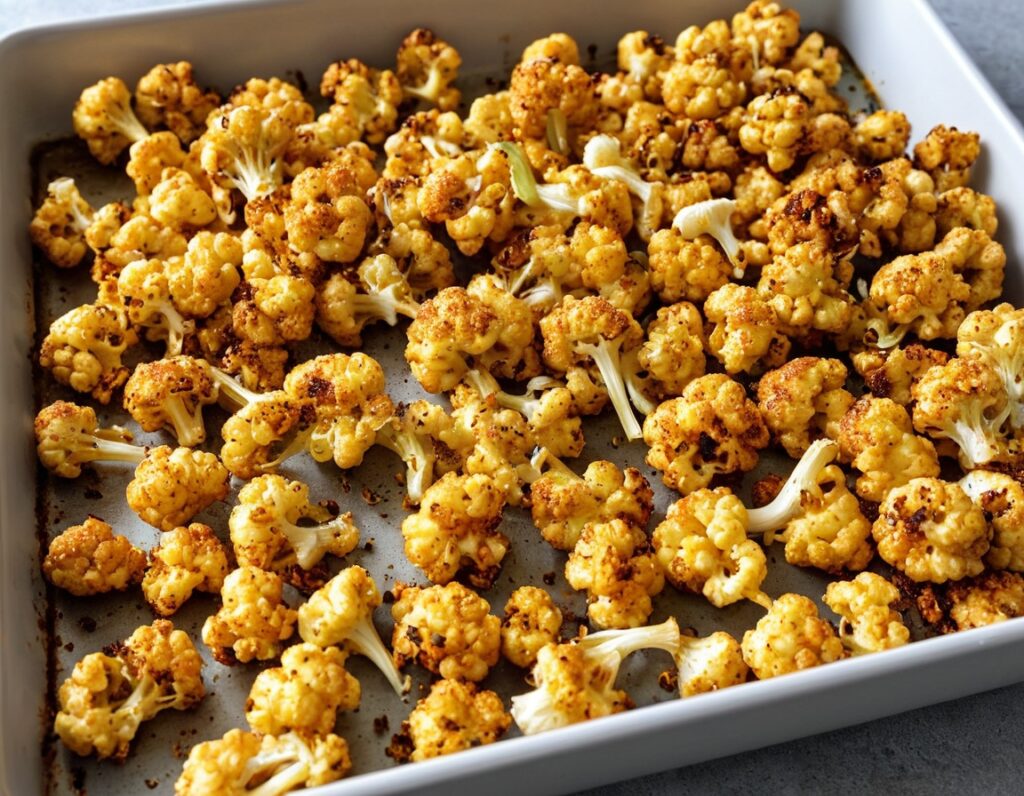
Lime-Charred Cauliflower Popcorn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Called “popcorn” for its appearance and tasty-snackness, this one otherwise bears little relation to the usual movie theater snack, and it’s both tastier and healthier. All that said, it can be eaten on its own as a snack (even with a movie, if you so wish), or served as one part of a many-dish banquet, or (this writer’s favorite) as a delicious appetizer that also puts down a healthy bed of fiber ready for the main course to follow it.
You will need
- 1 cauliflower, cut into small (popcorn-sized) florets
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp lime pickle
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp ground turmeric
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat your oven as hot as it will go
2) Mix all the ingredients in a small bowl except the cauliflower, to form a marinade
3) Drizzle the marinade over the cauliflower in a larger bowl (i.e. big enough for the cauliflower), and mix well until the cauliflower is entirely, or at least almost entirely, coated. Yes, it’s not a lot of marinade but unless you picked a truly huge cauliflower, the proportions we gave will be enough, and you want the end result to be crisp, not dripping.
4) Spread the marinaded cauliflower florets out on a baking tray lined with baking paper. Put it in the oven on the middle shelf, so it doesn’t cook unevenly, but keeping the temperature as high as it goes.
5) When it is charred and crispy golden, it’s done—this should take about 20 minutes, but we’ll say ±5 minutes depending on your oven, so do check on it periodically—and time to serve (it is best enjoyed warm).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- We must do a main feature on the merits of cruciferous vegetables! Watch this space.
- All About Olive Oils (Extra Virgin & Otherwise)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Stick with It – by Dr. Sean Young
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us know the theory when it comes to building new habits and/or replacing old ones, and maybe we even implement those ideas. So why is our success rate still not as high as we think it should be?
Dr. Sean Young is here to do science to it!
This book comes with advice and explanations that rely a lot less on “that sounds reasonable” and a lot more on “in this recent high-quality study, researchers found…”
And, at 10almonds, we love that. We’re all for trying new things that sound reasonable in general… but we definitely prefer when there’s a stack of solid science to point to, and that’s the kind of thing we recommend!
Dr. Young is big on using that science to find ways to trick our brains and get them working the way we want.
Each chapter has lots of science, lots of explanations, and lots of actionable step-by-step advice.
Bottom line: if you’re all over “Atomic Habits”, this one’s the science-based heavy-artillery for your practical neurohacking.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dating apps could have negative effects on body image and mental health, our research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around 350 million people globally use dating apps, and they amass an estimated annual revenue of more than US$5 billion. In Australia, 49% of adults report using at least one online dating app or website, with a further 27% having done so in the past.
But while dating apps have helped many people find romantic partners, they’re not all good news.
In a recent review, my colleagues and I found using dating apps may be linked to poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Dikushin Dmitry/Shutterstock We collated the evidence
Our study was a systematic review, where we collated the results of 45 studies that looked at dating app use and how this was linked to body image, mental health or wellbeing.
Body image refers to the perceptions or feelings a person has towards their own appearance, often relating to body size, shape and attractiveness.
Most of the studies we included were published in 2020 onwards. The majority were carried out in Western countries (such as the United States, the United Kingdom and Australia). Just under half of studies included participants of all genders. Interestingly, 44% of studies observed men exclusively, while only 7% included just women.
Of the 45 studies, 29 looked at the impact of dating apps on mental health and wellbeing and 22 considered the impact on body image (some looked at both). Some studies examined differences between users and non-users of dating apps, while others looked at whether intensity of dating app use (how often they’re used, how many apps are used, and so on) makes a difference.
More than 85% of studies (19 of 22) looking at body image found significant negative relationships between dating app use and body image. Just under half of studies (14 of 29) observed negative relationships with mental health and wellbeing.
The studies noted links with problems including body dissatisfaction, disordered eating, depression, anxiety and low self-esteem.
Dating apps are becoming increasingly common. But could their use harm mental health? Rachata Teyparsit/Shutterstock It’s important to note our research has a few limitations. For example, almost all studies included in the review were cross-sectional – studies that analyse data at a particular point in time.
This means researchers were unable to discern whether dating apps actually cause body image, mental health and wellbeing concerns over time, or whether there is simply a correlation. They can’t rule out that in some cases the relationship may go the other way, meaning poor mental health or body image increases a person’s likelihood of using dating apps.
Also, the studies included in the review were mostly conducted in Western regions with predominantly white participants, limiting our ability to generalise the findings to all populations.
Why are dating apps linked to poor body image and mental health?
Despite these limitations, there are plausible reasons to expect there may be a link between dating apps and poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Like a lot of social media, dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric, meaning they have an emphasis on pictures or videos. Dating app users are initially exposed primarily to photos when browsing, with information such as interests or hobbies accessible only after manually clicking through to profiles.
Because of this, users often evaluate profiles based primarily on the photos attached. Even when a user does click through to another person’s profile, whether or not they “like” someone may still often be determined primarily on the basis of physical appearance.
This emphasis on visual content on dating apps can, in turn, cause users to view their appearance as more important than who they are as a person. This process is called self-objectification.
People who experience self-objectification are more likely to scrutinise their appearance, potentially leading to body dissatisfaction, body shame, or other issues pertaining to body image.
Dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric. Studio Romantic/Shutterstock There could be several reasons why mental health and wellbeing may be impacted by dating apps, many of which may centre around rejection.
Rejection can come in many forms on dating apps. It can be implied, such as having a lack of matches, or it can be explicit, such as discrimination or abuse. Users who encounter rejection frequently on dating apps may be more likely to experience poorer self-esteem, depressive symptoms or anxiety.
And if rejection is perceived to be based on appearance, this could lead again to body image concerns.
What’s more, the convenience and game-like nature of dating apps may lead people who could benefit from taking a break to keep swiping.
What can app developers do? What can you do?
Developers of dating apps should be seeking ways to protect users against these possible harms. This could, for example, include reducing the prominence of photos on user profiles, and increasing the moderation of discrimination and abuse on their platforms.
The Australian government has developed a code of conduct – to be enforced from April 1 this year – to help moderate and reduce discrimination and abuse on online dating platforms. This is a positive step.
Despite the possible negatives, research has also found dating apps can help build confidence and help users meet new people.
If you use dating apps, my colleagues and I recommend choosing profile images you feel display your personality or interests, or photos with friends, rather than semi-clothed images and selfies. Engage in positive conversations with other users, and block and report anyone who is abusive or discriminatory.
It’s also sensible to take breaks from the apps, particularly if you’re feeling overwhelmed or dejected.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14. The Butterfly Foundation provides support for eating disorders and body image issues, and can be reached on 1800 334 673.
Zac Bowman, PhD Candidate, College of Education, Psychology & Social Work, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Adult ADHD Often Leads To Anxiety & Depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ADHD’s Knock-On Effects On Mental Health
We’ve written before about ADHD in adult life, often late-diagnosed because it’s not quite what people think it is:
In women in particular, it can get missed and/or misdiagnosed:
Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
…but what we’re really here to talk about today is:
It’s the comorbidities that get you
When it comes to physical health conditions:
- if you have one serious condition, it will (usually) be taken seriously
- if you have two, they will still be taken seriously, but people (friends and family members, as well as yes, medical professionals) will start to back off, as it starts to get too complicated for comfort
- if you have three, people will think you are making at least one of them up for attention now
- if you have more than three, you are considered a hypochondriac and pathological liar
Yet, the reality is: having one serious condition increases your chances of having others, and this chance-increasing feature compounds with each extra condition.
Illustrative example: you have fibromyalgia (ouch) which makes it difficult for you to exercise much, shop around when grocery shopping, and do much cooking at home. You do your best, but your diet slips and it’s hard to care when you just want the pain to stop; you put on some weight, and get diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, which in time becomes diabetes with high cardiovascular risk factors. Your diabetes is immunocompromising; you get COVID and find it’s now Long COVID, which brings about Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, when you barely had the spoons to function in the first place. At this point you’ve lost count of conditions and are just trying to get through the day.
If this is you, by the way, we hope at least something in the following might ease things for you a bit:
- Stop Pain Spreading
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue (While Having The Limitations Of Chronic Fatigue)
- When Painkillers Aren’t Helping, These Things Might
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
It’s the same for mental health
In the case of ADHD as a common starting point (because it’s quite common, may or may not be diagnosed until later in life, and doesn’t require any external cause to appear), it is very common that it will lead to anxiety and/or depression, to the point that it’s perhaps more common to also have one or more of them than not, if you have ADHD.
(Of course, anxiety and/or depression can both pop up for completely unrelated reasons too, and those reasons may be physiological, environmental, or a combination of the above).
Why?
Because all the good advice that goes for good mental health (and/or life in general), gets harder to actuate when one had ADHD.
- “Strong habits are the core of a good life”, but good luck with that if your brain doesn’t register dopamine in the same way as most people’s do, making intentional habit-forming harder on a physiological level.
- “Plan things carefully and stick to the plan”, but good luck with that if you are neurologically impeded from forming plans.
- “Just do it”, but oops you have the tendency-to-overcommitment disorder and now you are seriously overwhelmed with all the things you tried to do, when each of them alone were already going to be a challenge.
Overwhelm and breakdown are almost inevitable.
And when they happen, chances are you will alienate people, and/or simply alienate yourself. You will hide away, you will avoid inflicting yourself on others, you will brood alone in frustration—or distract yourself with something mind-numbing.
Before you know it, you’re too anxious to try to do things with other people or generally show your face to the world (because how will they react, and won’t you just mess things up anyway?), and/or too depressed to leave your depression-lair (because maybe if you keep playing Kingdom Vegetables 2, you can find a crumb of dopamine somewhere).
What to do about it
How to tackle the many-headed beast? By the heads! With your eyes open. Recognize and acknowledge each of the heads; you can’t beat those heads by sticking your own in the sand.
Also, get help. Those words are often used to mean therapy, but in this case we mean, any help. Enlist your partner or close friend as your support in your mental health journey. Enlist a cleaner as your support in taking that one thing off your plate, if that’s an option and a relevant thing for you. Set low but meaningful goals for deciding what constitutes “good enough” for each life area. Decide in advance what you can safely half-ass, and what things in life truly require your whole ass.
Here’s a good starting point for that kind of thing:
When You Know What You “Should” Do (But Knowing Isn’t The Problem)
And this is an excellent way to “get the ball rolling” if you’re already in a bit of a prison of your own making:
Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
If things are already bad, then you might also consider:
- How To Set Anxiety Aside and
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need ← this is about getting out of depression
And if things are truly at the worst they can possibly be, then:
How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: