Here’s Looking At Ya!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This Main Feature Should Take You Two Minutes (and 18 Seconds) To Read*
*Or at least, that’s what we’re told by this software that checks things for readability!
There’s a problem nobody wants to talk about when it comes to speed-reading
If you’re not very conscientious in your method, information does get lost. Especially, anything over 500 words per minute is almost certainly skimming and not true speed-reading.
One of the reasons information gets lost is because of a weird and wonderful feature of our eyes and brain: saccades.
Basically, our eyes can either collect visual information or they can move; they can’t do both at once. And as you may know, our eyes are almost always moving. So why aren’t we blind most of the time?
We actually are.
Did you know: your eyes take two upside-down 2D images and your brain presents you one 3D image the right way around instead? You probably did know that. So: it’s a bit like that.
Your brain takes a series of snapshots from whenever your eyes weren’t moving, and mentally fills in the blanks for you, just like a studio animation. We have a “frame rate” of about 60 frames per second, by the way—that’s why many computer monitors use that frequency. Lower frequencies can result in a noticeable flicker, and higher frequencies are wasted on us mere mortals!
Our eyes do some super-speedy movements called saccades (up to 500º per second! Happily no, our eyes don’t rotate 500º, but that’s the “per second” rate) and our brain fills in the gaps with its best guesses. The more you push it, the more it’ll guess wrong.
We’re not making this up, by the way! See for yourself:
Eye Movements In Reading And Information Processing: 20 Years Of Research
Fortunately, it is possible to use your eyes in a way that reduces the brain’s need to guess. That also means it has more processing power left over to guess correctly when it does need to.
Yes, There’s An App For That
Actually there are a few! But we’re going to recommend Spreeder as a top-tier option, with very rapid improvement right from day one.
It works by presenting the text with a single unmoving focal point. This is the opposite of traditional speed-reading methods that involve a rapidly moving pacer (such as your finger on the page, or a dot on the screen).
This unmoving focal point (while the words move instead) greatly reduces the number of saccades needed, and so a lot less information is lost to optical illusions and guesswork.
Try Spreeder (any platform) Here Now!
If you find that easy to use and would like something with a few more features, you might like another app that works on the same principle: Spritz.
It can take a bit more getting-used-to, but allows for greater integrations with all your favourite content in the long-run:
Check Out Spritz: Android App / iOS App / Free Chrome Extension
Lastly, if you don’t want any of those fancy apps and would just like to read more quickly and easily with less eye-strain, Beeline has you covered.
For free, unless you want to unlock some premium features!
How Beeline works is by adding a color gradient to text on websites and in documents. This makes it a lot easier for the eye to track without going off-piste, skipping a line, or re-reading the same bit again, etc.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
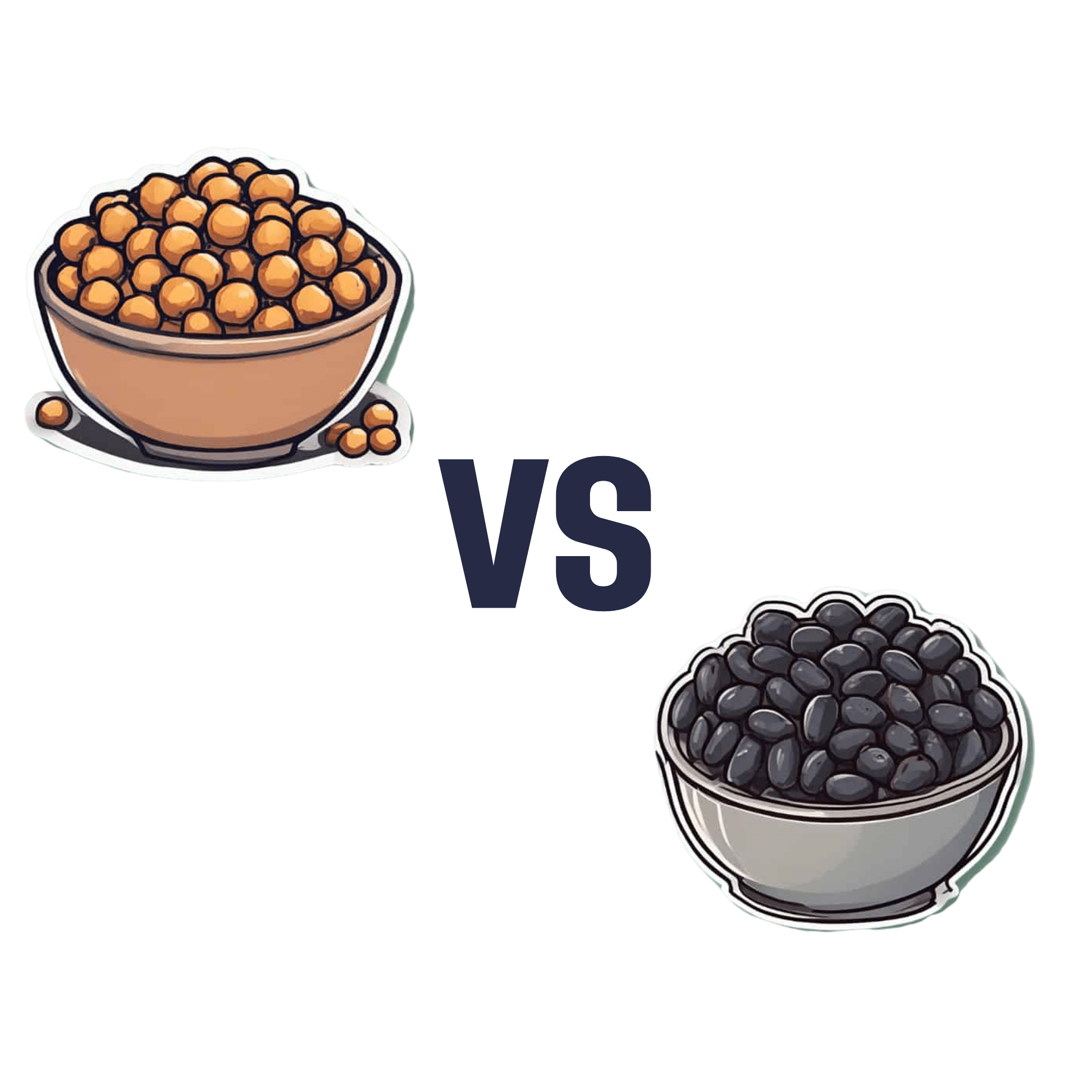
Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing chickpeas to black beans, we picked the black beans.
Why?
They’re both great! But we consider the nutritional profile of black beans to be better:
In terms of macros, black beans have a little more protein, while chickpeas have more carbohydrates. Generally speaking, people are not usually short of carbs in their diet, so we’ll go with the one with more protein. Black beans also have more fiber, which is important for heart health and more.
In the category of micronutrients, black beans have twice as much potassium and twice as much calcium, as well as twice as much magnesium. Chickpeas, meanwhile are better for manganese and slightly higher in B vitamins, but B vitamins are everywhere (especially vitamin B5, pantothenic acid; that’s literally where its name comes from, it means “from everywhere”), so we don’t consider that as much of a plus as the black beans doubling up on potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
So, do enjoy both, but if you’re going to pick, or lean more heavily on one, we recommend the black beans
Further reading
See also:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Easily Digestible Vegetarian Protein Sources
- What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The China Study – by Dr. T Colin Campbell and Dr. Thomas M. Campbell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not the newest book we’ve reviewed (originally published 2005; this revised and expanded edition 2016), but it is a seminal one.
You’ve probably heard it referenced, and maybe you’ve wondered what the fuss is about. Now you can know!
The titular study itself was huge. We tend to think “oh there was one study” and look to discount it, but it literally looked at the population of China. That’s a large study.
And because China is relatively ethnically homogenous, especially per region, it was easier to isolate what dietary factors made what differences to health. Of course, that did also create a limitation: follow-up studies would be needed to see if the results were the same for non-Chinese people. But even for the rest of us (this reviewer is not Chinese), it already pointed science in the right direction. And sure enough, smaller follow-up studies elsewhere found the same.
But enough about the research; what about the book? This is a book review, not a research review, after all.
The book itself is easy for a lay reader to understand. It explains how the study was conducted (no small feat), and how the data was examined. It also discusses the results, and the conclusions drawn from those results.
In light of all this, it also offers simple actionable advices, on how to eat to avoid disease in general, and cancer in particular. In especially that latter case, one take-home conclusion was: get more of your protein from plants for a big reduction in cancer risk, for example.
Bottom line: this book is an incredible blend of “comprehensive” and “readable” that we don’t often find in the same book! It contains not just a lot of science, but also an insight into how the science works, on a research level. And, of course, its results and conclusions have strong implications for all our lives.
Click here to check out The China Study, to know more about it!
Share This Post
-
The Surprising Link Between Type 2 Diabetes & Alzheimer’s
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Surprising Link Between Type 2 Diabetes & Alzheimer’s
This is Dr. Rhonda Patrick. She’s a biomedical scientist with expertise in the areas of aging, cancer, and nutrition. In the past five years she has expanded her research of aging to focus more on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, as she has a genetic predisposition to both.
What does that genetic predisposition look like? People who (like her) have the APOE-ε4 allele have a twofold increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease—and if you have two copies (i.e., one from each of two parents), the risk can be up to tenfold. Globally, 13.7% of people have at least one copy of this allele.
So while getting Alzheimer’s or not is not, per se, hereditary… The predisposition to it can be passed on.
What’s on her mind?
Dr. Patrick has noted that, while we don’t know for sure the causes of Alzheimer’s disease, and can make educated guesses only from correlations, the majority of current science seems to be focusing on just one: amyloid plaques in the brain.
This is a worthy area of research, but ignores the fact that there are many potential Alzheimer’s disease mechanisms to explore, including (to count only mainstream scientific ideas):
- The amyloid hypothesis
- The tau hypothesis
- The inflammatory hypothesis
- The cholinergic hypothesis
- The cholesterol hypothesis
- The Reelin hypothesis
- The large gene instability hypothesis
…as well as other strongly correlated factors such as glucose hypometabolism, insulin signalling, and oxidative stress.
If you lost your keys and were looking for them, and knew at least half a dozen places they might be, how often would you check the same place without paying any attention to the others?
To this end, she notes about those latter-mentioned correlated factors:
❝50–80% of people with Alzheimer’s disease have type 2 diabetes; there is definitely something going on❞
There’s another “smoking gun” for this too, because dysfunction in the blood vessels and capillaries that line the blood-brain barrier seem to be a very early event that is common between all types of dementia (including Alzheimer’s) and between type 2 diabetes and APOE-ε4.
Research is ongoing, and Dr. Patrick is at the forefront of that. However, there’s a practical take-away here meanwhile…
What can we do about it?
Dr. Patrick hypothesizes that if we can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, we may reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s with it.
Obviously, avoiding diabetes if possible is a good thing to do anyway, but if we’re aware of an added risk factor for Alzheimer’s, it becomes yet more important.
Of course, all the usual advices apply here, including a Mediterranean diet and regular moderate exercise.
Three other things Dr. Patrick specifically recommends (to reduce both type 2 diabetes risk and to reduce Alzheimer’s risk) include:
(links are to her blog, with lots of relevant science for each)
You can also hear more from Dr. Patrick personally, as a guest on Dr. Peter Attia’s podcast recently. She discusses these topics in much greater detail than we have room for in our newsletter:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Younger – by Dr. Sara Gottfried
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does this do the things it says in the subtitle? In honestly, not really, no, but what it does do (if implemented) is modify your gene expression, slow aging, and extend healthspan. Which is all good stuff, even if it’s not the snappy SEO-oriented keywords in the subtitle.
A lot of the book pertains to turning certain genes (e.g. SIRT1, mTOR, VDR, APOE4, etc) on or off per what is sensible in each case, noting that while genes are relatively fixed (technically they can be changed, but the science is young and we can’t do much yet), gene expression is something we can control quite a bit. And while it may be unsettling to have the loaded gun that is the APOE4 gene being held against your head, at the end of the day there are things we can do that influence whether the trigger gets pulled, and when. Same goes for other undesirable genes, and also for the desirable ones that are useless if they never actually get expressed.
She offers (contained within the book, not as an upsell) a 7-week program that aims to set the reader up with good healthy habits to do just that and thus help keep age-related maladies at bay, and if we slip up, perhaps later in the year or so, we can always recommence the program.
The advice is also just good health advice, even without taking gene expression into account, because there are a stack of benefits to each of the things in her protocol.
The style is personable without being padded with fluff, accessible without dumbing down, and information-dense without being a challenging read. The formatting helps a lot also; a clear instructional layout is a lot better than a wall of text.
Bottom line: if you’d like to tweak your genes for healthy longevity, this book can help you do just that!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is it good to eat farm raised fish?❞
We’ll answer this as a purely health-related question (and thus not considering economy, ecology, ethics, or taste).
It’s certainly not as good as wild-caught fish, for several reasons, some more serious than others:
Farmed fish can have quite a different nutritional profile to wild-caught fish, and also contain more contaminants, including heavy metals.
For example, farmed fish tend to have much higher fat content for the same amount of protein, but lower levels of minerals and other nutrients. Here are two side-by-side:
Wild-caught salmon | Farmed salmon
See also:
Quantitative analysis of the benefits and risks of consuming farmed and wild salmon
Additionally, because fish in fish farms tend to be very susceptible to diseases (because of the artificially cramped and overcrowded environment), fish farms tend to make heavy use of antibiotics, which can cause all sorts of problems down the line:
So definitely, “let the buyer beware”!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nori vs Wakame – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing nori to wakame, we picked the nori.
Why?
It was close, and both of these seaweed options are great!
In terms of macros, nori has more protein while wakame has more carbs; they’re about equal on fiber. While the difference in protein and carbs isn’t big, out of the two we’ll prioritize protein, and thus say nori gets a notional win here—but as it’s so close, one could just as easily call it a tie.
In the category of vitamins both are very rich in many minerals, but nori has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, B12*, and C, while wakame has more of vitamins B5, B9, K, and choline. Thus, a 6:4 victory for nori.
*Yes, nori is one of those rare vegan foods that naturally contain vitamin B12; it’s because of the composition of the algae that this seaweed is made of, which includes some beneficial B12-making bacteria. Meanwhile, wakame is “just” a kelp, so it doesn’t have B12.
When it comes to minerals, nori has more potassium and zinc, while wakame has more calcium and magnesium. They’re equal on other minerals, except: it’s worth noting that wakame is moderately high in sodium, while nori has very little sodium. So, either a tie-breaking win for nori, or just a tie.
Adding up the sections gives nori the overall win; it’s only the margin of the win that’s reasonably debatable. Still, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- A Deeper Dive Into Seaweed
- Spirulina vs Nori – Which is Healthier? ← guess which won!
- 21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nori and wakame both feature (very favorably) in this case study
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: