Resistance Beyond Weights
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resistance, Your Way
We’ve talked before about the importance of resistance training:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And we’ve even talked about how to make resistance training more effective:
(High Intensity Interval Training, but make it High Intensity Resistance Training)
Which resistance training exercises are best?
There are two reasonable correct answers here:
- The resistance training exercises that you will actually do (because it’s no good knowing the best exercise ever if you’re not going to do it because it is in some way offputting to you)
- The resistance training exercises that will prevent you from getting a broken bone in the event of some accident or incident
This latter is interesting, because when people think resistance training, the usually immediate go-to exercises are often things like the bench press, or the chest machine in the gym.
But ask yourself: how often do we hear about some friend or relative who in their old age has broken their humerus?
It can happen, for sure, but it’s not as often as breaking a hip, a tarsal (ankle bones), or a carpal (wrist bones).
So, how can we train to make those bones strong?
Strong bones grow under strong muscles
When archaeologists dig up a skeleton from a thousand years ago, one of the occupations that’s easy to recognize is an archer. Why?
An archer has an unusual frequent exercise: pushing with their left arm while pulling with their right arm. This will strengthen different muscles on each side, and thus, increase bone density in different places on each arm. The left first metacarpal and right first and second metacarpals and phalanges are also a giveaway.
This is because: one cannot grow strong muscles on weak bones (or else the muscles would just break the bones), so training muscles will force the body to strengthen the relevant bones.
So: if you want strong bones, train the muscles attached to those bones
This answers the question of “how am I supposed to exercise my hips” etc.
Weights, bodyweight, resistance bands
If you go to the gym, there’s a machine for everything, and a member of gym staff will be able to advise which of their machines will strengthen which muscles.
If you train with free weights at home:
- Wrist curls (forearm supported and stationary, lifting a dumbbell in your hand, palm-upwards) will strengthen the wrist
- The farmer’s walk (carrying a heavy weight in each hand) will also strengthen your wrist
- A modified version of this involves holding the weight with just your fingertips, and then raising and lowering it by curling and uncurling your fingers)
- Lateral leg raises (you will need ankle-weights for this) will strengthen your ankles and your hips, as will hip abductions (as in today’s featured video), especially with a weight attached.
- Ankle raises (going up on your tip-toes and down again, repeat) while holding weights in your hands will strengthen your ankles
If you don’t like weights:
- Press-ups will strengthen your wrists
- Fingertip press-ups are even better: to do these, do your press-ups as normal, except that the only parts of your hands in contact with the ground are your fingertips
- This same exercise can be done the other way around, by doing pull-ups
- And that same “even better” works by doing pull-ups, but holding the bar only with one’s fingertips, and curling one’s fingers to raise oneself up
- Lateral leg raises and hip abductions can be done with a resistance band instead of with weights. The great thing about these is that whereas weights are a fixed weight, resistance bands will always provide the right amount of resistance (because if it’s too easy, you just raise your leg further until it becomes difficult again, since the resistance offered is proportional to how much tension the band is under).
Remember, resistance training is still resistance training even if “all” you’re resisting is gravity!
If it fells like work, then it’s working
As for the rest of preparing to get older?
Check out:
Training Mobility Ready For Later Life
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Forever Strong – by Dr. Gabrielle Lyon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Obesity kills a lot of people (as does medical neglect and malpractice when it comes to obese patients, but that is another matter), but often the biggest problem is not “too much fat” but rather “too little muscle”. This gets disguised a bit, because these factors often appear in the same people, but it’s a distinction that’s worthy of note.
Dr. Lyon lays out a lot of good hard science in this work, generally in the field of protein metabolism, but also with a keen eye on all manner of blood metrics (triglycerides, LDL/HDL, fasting blood sugars, assorted other biomarkers of metabolic health).
The style of this book is two books in one. It’s a very accessible pop-science book in its primary tone, with an extra layer of precise science and lots of references, for those who wish to dive into that.
In the category of criticism, the diet plan section of the book is rather meat-centric, but the goal of this is protein content, not meat per se, so substitutions can easily be made. That’s just one small section of the book, though, and it’s little enough a downside that even Dr. Mark Hyman (a popular proponent of plant-based nutrition) highly recommends the book.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be less merely fighting decline and more actually becoming healthier as you age, then this book will help you do just that.
Click here to check out Forever Strong, and level up your wellness as you age!
Share This Post
-
What Mattress Is Best, By Science?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Foundations of Good Sleep
You probably know the importance of good sleep for good health. If not, here’s a quick refresher:
- Why You Probably Need More Sleep
- How Sleep-Deprived Are You, Really?
- The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
You should also definitely check out this quite famous book on the topic:
Why We Sleep – by Dr Matthew Walker
What helps, to get that good sleep
We’ve covered this a little before too, for example:
- Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors
- Sleep Better With Better Air
- How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
How to level-up from there
One of the biggest barriers to good sleep for many people is obstructive sleep apea:
Healthier, Natural Sleep Without Obstruction!
We covered (in the above article) a whole lot of ways of mitigating/managing obstructive sleep apnea. One of the things we mentioned as beneficial was avoiding sleeping on one’s back, and this is something Mayo Clinic’s Dr. Somers agreed with:
Back Sleeping, And Sleeping Differently After 50
“But side-sleeping is uncomfortable”
If this is you, then chances are you have the wrong mattress.
If your mattress is too firm, you can get around it by using this “five pillow” method:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
If your mattress is too soft, then sorry, you really just have to throw that thing out and start again.
The Goldilocks mattress
While different people will have different subjective preferences, the science is quite clear on what is actually best for people’s spines. As this review of 39 qualified scholarly articles concluded:
❝Results of this systematic review show that a medium-firm mattress promotes comfort, sleep quality and rachis alignment❞
~ Dr. Gianfilippo Caggiari et al.
Read in full: What type of mattress should be chosen to avoid back pain and improve sleep quality? Review of the literature
Note: to achieve “medium-firm” that remains “medium firm” has generally been assumed to require a memory-foam mattress.
How memory-foam works: memory-foam is a moderately thermosoftening material, designed to slightly soften at the touch of human body temperature, and be firmer at room temperature. This will result in it molding itself to the form of a human body, providing what amounts to personalized support for your personal shape and size, meaning your spine can stay exactly as it’s supposed to when you’re sleeping on your side, instead of (for example) your hips being wider meaning that your lumbar vertebrae are raised higher than your thoracic vertebrae, giving you the equivalent of a special nocturnal scoliosis.
It will, therefore, stop working if
- the ambient temperature is comparable to human body temperature (as happens in some places sometimes, and increasingly often these days)
- you die, and thus lose your body temperature (but in that case, your spinal alignment will be the least of your concerns)
Here’s a good explanation of the mechanics of memory foam from the Sleep Foundation:
Sleep Foundation | What is Memory Foam?
An alternative to memory foam?
If you don’t like memory foam (one criticism is that it doesn’t allow good ventilation underneath the body), there is an alterative, the grid mattress.
It’s very much “the new kid on the block” and the science is young for this, but for example this recent (April 2024) study that concluded:
❝The grid mattress is a simple, noninvasive, and nonpharmacological intervention that improved adults sleep quality and health. Controlled trials are encouraged to examine the effects of this mattress in a variety of populations and environments.❞
~ Dr. Heather Hausenblas et al.
Read in full: Effectiveness of a grid mattress on adults’ sleep quality and health: A quasi-experimental intervention study
However, that was a small (n=39) uncontrolled (i.e. there was no control group) study, and the conflict of interest statement is, well, interesting:
❝Heather A. Hausenblas, Stephanie L. Hooper, Martin Barragan, and Tarah Lynch declare no conflict of interest. Michael Breus served as a former consultant for Purple, LLC.❞
~ Ibid.
…which is a fabulous way of distracting from the mention in the “Acknowledgements” section to follow, that…
❝Purple, LLC, provided financial support for the study❞
~ Ibid.
Purple is the company that invented the mattress being tested. So while this doesn’t mean the study is necessarily dishonest and/or corrupt, it does at the very least raise a red flag for a potential instance of publication bias (because Purple may have funded multiple studies and then pulled funding of the ones that weren’t going their way).
If you are interested in Purple’s mattress and how it works, you can check it out here ← this is a link for your interest and information; not an advertisement or an endorsement. We look forward to seeing more science for this though, and echo their own call for randomized controlled trials!
Summary
Sleep is important, and while it’s a popular myth that we need less as we get older, the truth is that we merely get less on average, while still needing the same amount.
A medium-firm memory-foam mattress is a very good, well-evidenced way to support that (both figuratively and literally!).
A grid mattress is an interesting innovation, and/but we’d like to see more science for it.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Chiropractors have been banned again from manipulating babies’ spines. Here’s what the evidence actually says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chiropractors in Australia will not be able to perform spinal manipulation on children under the age of two once more, following health concerns from doctors and politicians.
But what is the spinal treatment at the centre of the controversy? Does it work? Is there evidence of harm?
We’re a team of researchers who specialise in evidence-based musculoskeletal health. I (Matt) am a registered chiropractor, Joshua is a registered physiotherapist and Giovanni trained as a physiotherapist.
Here’s what the evidence says.
Dmitry Naumov/Shutterstock Remind me, how did this all come about?
A Melbourne-based chiropractor posted a video on social media in 2018 using a spring-loaded device (known as the Activator) to manipulate the spine of a two-week-old baby suspended upside down by the ankles.
The video sparked widespread concerns among the public, medical associations and politicians. It prompted a ban on the procedure in young children. The Victorian health minister commissioned Safer Care Victoria to conduct an independent review of spinal manipulation techniques on children.
Recently, the Chiropractic Board of Australia reinstated chiropractors’ authorisation to perform spinal manipulation on babies under two years old. But this week, it backflipped, following heavy criticism from medical associations and politicians.
What is spinal manipulation?
Spinal manipulation is a treatment used by chiropractors and other health professionals such as doctors, osteopaths and physiotherapists.
It is an umbrella term that includes popular “back cracking” techniques.
It also includes more gentle forms of treatment, such as massage or joint mobilisations. These involve applying pressure to joints without generating a “cracking” sound.
Does spinal manipulation in babies work?
Several international guidelines for health-care professionals recommend spinal manipulation to treat adults with conditions such as back pain and headache as there is an abundance of evidence on the topic. For example, spinal manipulation for back pain is supported by data from nearly 10,000 adults.
For children, it’s a different story. Safer Care Victoria’s 2019 review of spinal manipulation found very few studies testing whether this treatment was safe and effective in children.
Studies were generally small and were of poor quality. Some of those small, poor-quality studies, suggest spinal manipulation provides a very small benefit for back pain, colic and potentially bedwetting – some common reasons for parents to take their child to see a chiropractor. But overall, the review found the overall body of evidence was very poor.
Spinal manipulation doesn’t seem to help young children with an ear infection. MIA Studio/Shutterstock However, for most other children’s conditions chiropractors treat – such as headache, asthma, otitis media (a type of ear infection), cerebral palsy, hyperactivity and torticollis (“twisted neck”) – there did not appear to be a benefit.
The number of studies investigating the effectiveness of spinal manipulation on babies under two years of age was even smaller.
There was one high-quality study and two small, poor quality studies. These did not show an appreciable benefit of spinal manipulation on colic, otitis media with effusion (known as glue ear) or twisted neck in babies.
Is spinal manipulation on babies safe?
In terms of safety, most studies in the review found serious complications were extremely rare. The review noted one baby or child dying (a report from Germany in 2001 after spinal manipulation by a physiotherapist). The most common complications were mild in nature such as increased crying and soreness.
However, because studies were very small, they cannot tell us anything about the safety of spinal manipulation in a reliable way. Studies that are designed to properly investigate if a treatment is safe typically include thousands of patients. And these studies have not yet been done.
Why do people see chiropractors?
Safer Care Victoria also conducted surveys with more than 20,000 people living in Australia who had taken their children under 12 years old to a chiropractor in the past ten years.
Nearly three-quarters said that was for treatment of a child aged two years or younger.
Nearly all people surveyed reported a positive experience when they took their child to a chiropractor and reported that their child’s condition improved with chiropractic care. Only a small number of people (0.3%) reported a negative experience, and this was mostly related to cost of treatment, lack of improvement in their child’s condition, excessive use of x-rays, and perceived pressure to avoid medications.
Many of the respondents had also consulted their GP or maternity/child health nurse.
What now for spinal manipulation in children?
At the request of state and federal ministers, the Chiropractic Board of Australia confirmed that spinal manipulation on babies under two years old will continue to be banned until it discusses the issue further with health ministers.
Many chiropractors believe this is unfair, especially considering the strong consumer support for chiropractic care outlined in the Safer Care Victoria report, and the rarity of serious reported harms in children.
Others believe that in the absence of evidence of benefit and uncertainty around whether spinal manipulation is safe in children and babies, the precautionary principle should apply and children and babies should not receive spinal manipulation.
Ultimately, high quality research is urgently needed to better understand whether spinal manipulation is beneficial for the range of conditions chiropractors provide it for, and whether the benefit outweighs the extremely small chance of a serious complication.
This will help parents make an informed choice about health care for their child.
Matt Fernandez, Senior lecturer and researcher in chiropractic, CQUniversity Australia; Giovanni E. Ferreira, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, Institute of Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney, and Joshua Zadro, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, Sydney Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Toe-Tapping Tip For Better Balance
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Balance is critical for health especially in older age, since it’s amazing how much else can go dramatically and suddenly wrong after a fall. So, here’s an exercise to give great balance and stability:
How to do it
You will need:
- Something to hold onto, such as a countertop
- A target on the floor, such as a mark or a coin
The steps:
- Lift one leg up, bring your foot forward, and tap the object in front of you.
- Then, bring that foot back to where it started.
- Next, switch to the other leg and tap.
- Alternate between your right and left legs, shifting back and forth.
- Your goal is to do this for 10 repetitions on each leg without holding on.
How it works:
Whenever you tap, you have to lift one leg up and reach it out in front of you. Doing this requires you to stand on one leg while moving a weight (namely: your other leg), which is something many people, especially upon getting older, are hesitant to do. If you’re unable to stand on one leg, let alone move your center of gravity (per the counterbalance of the other leg) while doing so, you may end up shuffling and walking with your feet sliding across the ground—something you really want to avoid.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fall Special ← this is about not falling, or, failing that, minimizing injury if you do
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Your Health Audit, From Head To Toe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health Audit Time
Here at 10almonds, we often cover quite specific things, ranging from “the effect of sodium on organs other than your heart” to “make this one small change to save your knees while driving”.
But, we’re each a whole person, and we need to take care of the whole organism that makes up the wonderful being that we each are. If we let one part of it drop in health too much, the others will soon follow suit because of the knock-on effects.
So, let’s do a quick self-check-up, and see what can be done for each! How’s your…
Mental Health
We’re doing this audit head-to-to, so let’s start it here, because mental health is also just health, and it’s difficult to tackle the others without having this one at least under control!
Are you experiencing chronic stress? Anxiety? Depression? Joy?
If you answered “no” to “joy” but also “no” to “depression”, you might want to rethink your answer to “depression”, by the way. Life should be a joyous thing!
Some resources to address your mental health:
Brain Health
Your brain is a big, powerful organ. It uses more of your daily energy (in the physiological sense of the word, we’re talking calories and mitochondria and ATP) than any other organ, by far.
And when it comes to organ failure, if your brain fails, then having the best joints in the world won’t help you, for example.
Some resources to address your brain health:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It
- How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
- The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
Heart Health
Everything depends on your heart, head to toe. Tirelessly pumping blood with oxygen, nutrients, and agents of your immune system all around your body, all day every day for your entire life.
What’s your resting heart rate like? How about your blood pressure? And while we’re on the topic of blood… how’s your blood sugar health?
These are all important things to a) know about and b) keep on top of!
Some resources to address your heart health:
- 1-Minute Heart Health Check-Up Tips
- A Five-Point Plan For Heart Health
- High Blood Pressure? Try These!
Gut Health
By cell count, we’re about 10% human and 90% bacteria. By gene count, also. Pretty important, therefore, that we look after our trillions of tiny friends that keep our organism working.
Most people in N. America, for example, get vastly under the recommended daily amount of fiber, and that’s just the most basic courtesy we could do for these bugs that keep us alive (they need that fiber to live, and their process of consuming it is beneficial to us in a stack of ways).
Some resources to address your gut health:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- The Surprising Link Between Gut Health And Serotonin
- The Vagus Nerve: The Brain-Gut Highway!
Hormonal Health
Hormones are weird and wonderful and affect so much more than the obvious sex-related functions (but yes, those too). A lot of people don’t realize it, but having our hormones in good order or not can make the difference between abject misery and a happy, fulfilling life.
Some resources to address your hormonal health:
- What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
- Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them
- Too Much Or Too Little Testosterone?
Bone/Joint Health
Fear nothing! For you are a ghost operating a skeleton clad in flesh. But also, you know, look after that skeleton; you only get one! Being animals, we’re all about movement, and being humans, we’ve ended up with some lifestyle situations that aren’t great for that mobility. We sit too much; we walk too little; we cramp ourselves into weird positions (driving, anyone?), and we forget the range of motion we’re supposed to have. But let’s remember…
Some resources to address your bone/joint health:
- Collagen’s benefits are more than skin deep
- Cool As A Cucumber (Move Over, Glucosamine + Chondroitin)
- 5 Best Bodyweight Exercises For Incredible Mobility
Lastly…
While it’s good to do a little self-audit like this every now and again, it’s even better to get a professional check-up!
As engineers say: if you don’t schedule time for maintenance, your equipment will schedule it for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
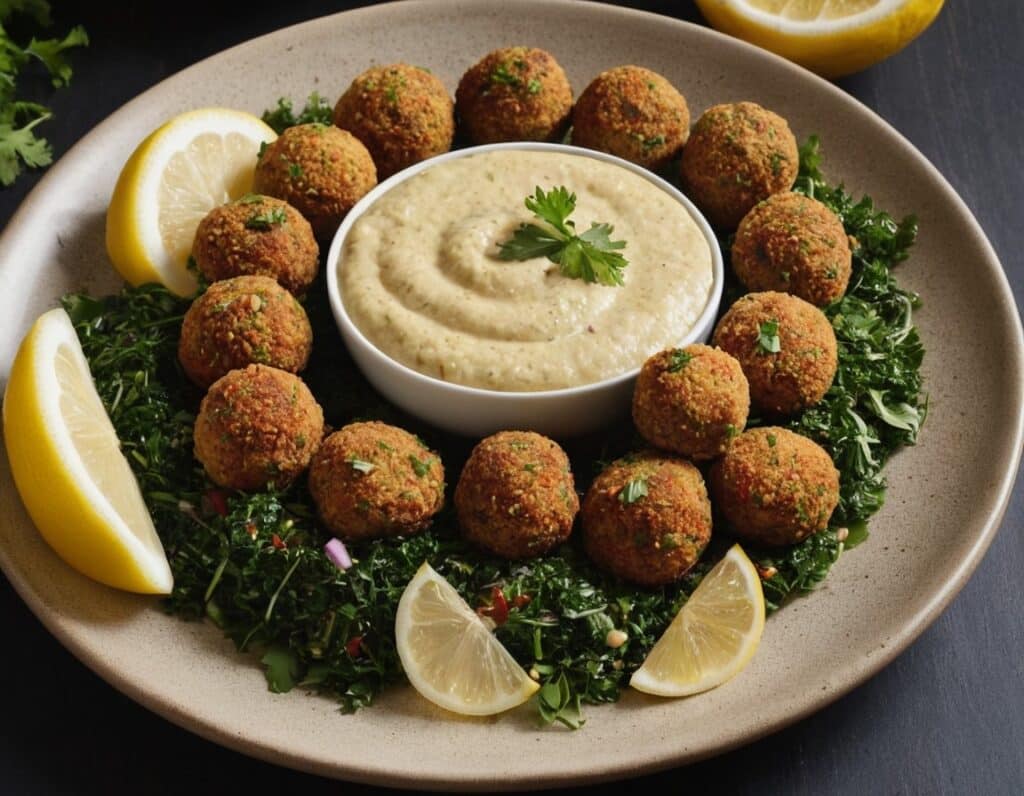
Easy Quinoa Falafel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Falafel is a wonderful snack or accompaniment to a main, and if you’ve only had shop-bought, you’re missing out. Plus, with this quinoa-based recipe, it’s almost impossible to accidentally make them dry.
You will need
- 1 cup cooked quinoa
- 1 cup chopped fresh parsley
- ½ cup wholewheat breadcrumbs (or rye breadcrumbs if you’re avoiding wheat/gluten)
- 1 can chickpeas, drained
- 4 green onions, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for frying
- 2 tbsp tomato paste
- 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp dried thyme
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend all the ingredients in a food processor until it has an even, but still moderately coarse, texture.
2) Shape into 1″ balls, and put them in the fridge to chill for about 20 minutes.
3) Fry the balls over a medium-high heat until evenly browned—just do a few at a time, taking care to not overcrowd the pan.
4) Serve! Great with salad, hummus, and other such tasty healthy snack items:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in more of what we have going on today:
- Cilantro vs Parsley – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Hero Homemade Hummus Recipe ← perfect accompaniment!
- Tasty Tabbouleh with Tahini Recipe ← also a great option!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: