An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
You’ve probably heard of people drinking apple cider vinegar for its health benefits. It’s not very intuitive, so today we’re going to see what the science has to say…
Apple cider vinegar for managing blood sugars
Whether diabetic, prediabetic, or not at all, blood sugar spikes aren’t good for us, so anything that evens that out is worth checking out. As for apple cider vinegar…
Diabetes Control: Is Vinegar a Promising Candidate to Help Achieve Targets?
…the answer found by this study was “yes”, but their study was small, and they concluded that more research would be worthwhile. So…
…was also a small study, with the same (positive) results.
But! We then found a much larger systematic review was conducted, examining 744 previously-published papers, adding in another 14 they found via those. After removing 47 duplicates, and removing another 15 for not having a clinical trial or not having an adequate control, they concluded:
❝In this systematic review and meta-analyses, the effect of vinegar consumption on postprandial glucose and insulin responses were evaluated through pooled analysis of glucose and insulin AUC in clinical trials. Vinegar consumption was associated with a statistically significant reduction in postprandial glucose and insulin responses in both healthy participants and participants with glucose disorder.❞
~ Sishehbor, Mansoori, & Shirani
Check it out:
Apple cider vinegar for weight loss?
Yep! It appears to be an appetite suppressant, probably moderating ghrelin and leptin levels.
But…
As a bonus, it also lowers triglycerides and total cholesterol, while raising HDL (good cholesterol), and that’s in addition to doubling the weight loss compared to control:
How much to take?
Most of these studies were done with 1–2 tbsp of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water, at mealtime.
Obviously, if you want to enjoy the appetite-suppressant effects, take it before the meal! If you forget and/or choose to take it after though, it’ll still help keep your blood sugars even and still give you the cholesterol-moderating benefits.
Where to get it?
Your local supermarket will surely have it. Or if you buy it online, you can even get it in capsule form!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Kava vs Anxiety
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Kava, sometimes also called “kava kava” but we’re just going to call it kava once for the sake of brevity, is a heart-shaped herb that
bestows the powers of the Black Pantheris popularly enjoyed for its anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects. Despite the similarity of the name in many languages, it is unrelated to coffee (except insofar as they are both plants), and its botanical name is Piper methysticum.Does it work?
Yes! At least in the short-term; more on that later.
Firstly, you may be wondering how it works; it works by its potentiation of GABA receptors in the brain. GABA (or gamma-aminobutyric acid, to give it its full name), as you may recall, is a neurotransmitter that is associated with feelings of calm; we wrote about it here:
So, what does “potentiation of GABA receptors” mean? It means… Scientists don’t for 100% sure know how it works yet, but it does make GABA receptors fire more. It’s possible that to some degree GABA fits the “molecular lock” of the receptors and causes them to say “GABA is here”; it’s also possible that they just make them more sensitive to the real GABA that is there, or there could be another explanation as yet undiscovered. Either way, it means that taking kava has a similar effect to having increased GABA levels in the brain:
As for how much to use, 20–300mg appears to be an effective dose, and most sources recommend 80–250mg:
Kava as a Clinical Nutrient: Promises and Challenges
This review of clinical trials found that it was more effective than placebo in only 3 of 7 trials; specifically, it was beneficial in the short-term and not in the long-term. For these reasons, the researchers concluded:
❝Kava Kava appears to be a short-term treatment for anxiety, but not a replacement for prolonged anti-anxiety use. Although not witnessed in this review, liver toxicity is especially possible if taken longer than 8 weeks.❞
Another review of clinical trials found better results over the course of 11 clinical trials, though again, short-term treatment only was considered to be where the “safe and effective” claim can be placed:
❝Compared with placebo, kava extract appears to be an effective symptomatic treatment option for anxiety. The data available from the reviewed studies suggest that kava is relatively safe for short-term treatment (1 to 24 weeks), although more information is required. Further rigorous investigations, particularly into the long-term safety profile of kava are warrant❞
Source: Kava extract for treating anxiety
Is it safe?
Nope! It has been associated with liver damage:
The likely main mechanism of toxicity is that it simply monopolizes the liver’s metabolic abilities, meaning that while it’s metabolizing the kava, it’s not metabolizing other things (such as alcohol or other medications), which will then build up, and potentially overwhelm the liver:
Constituents in kava extracts potentially involved in hepatotoxicity: a review
However, traditionally-prepared kava has not had the same effect as modern extracts; at first it seemed the difference was the traditional aqueous extracts vs modern acetonic/ethanolic extracts, but eventually that was found not to be the case, as toxicity occurred with industrial aqueous extracts too. The conclusion so far is that it is about the quality of the source ingredients, and the problems inherent to mass-production:
Meanwhile, short-term use doesn’t seem to have this problem, if you’re not drinking alcohol or taking medications that affect the liver:
Mechanisms/risk factors – kava-associated hepatotoxicity ← you’ll need to scroll down to 4.2.4 to read about this
Want to try it?
If the potential for hepatotoxicity doesn’t put you off, here’s an example product on Amazon ← we do not recommend it, but we are not the boss of you, and maybe you’re confident about your liver and want to use it only very short-term?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
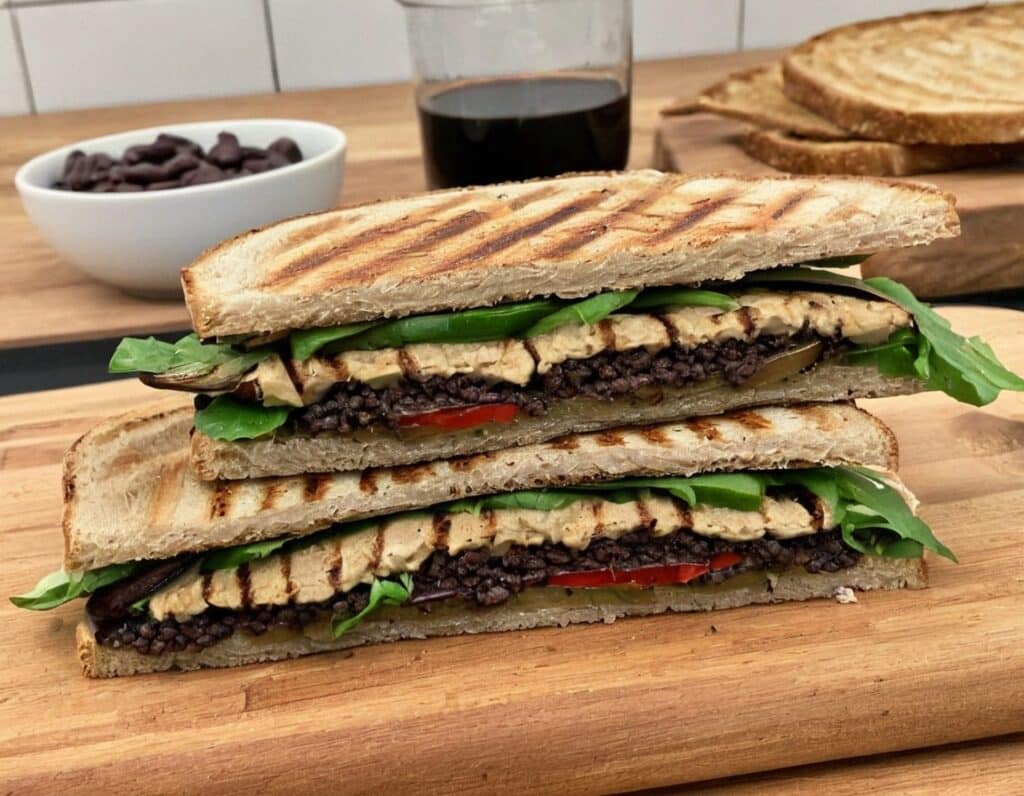
Black Bean Hummus Panini
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A recipe for a sandwich? Try it once, and you’ll see why. Welcome to your new favorite!
You will need
- 1 cup cooked-and-rinsed black beans (canned is fine)
- ⅓ cup hummus (you can use our Hero Homemade Hummus recipe)
- 4 thin slices of eggplant (or more if you like it meaty)
- 4 sun-dried tomatoes
- 2 slices of your favorite bread (you can use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe)
- A little olive oil, ideally sprayable
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Grill the eggplant slices until soft.
2) Spread hummus generously on one side of both slices of bread.
2) Add the black beans on top of one slice (the hummus will help them stay in place), followed by the sun-dried tomatoes and then the eggplant. Top with the other slice of bread, hummus-side down.
3) Coat (carefully, please) the inside of the panini press (both interior sides) with olive oil. If you don’t have sprayable oil, using a sheet of kitchen roll to apply the oil is a good way to do it without making a mess.
4) Grill the assembled sandwich, until the bread starts to brown and the insides are warm; this should take about 4 minutes.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Nicotine Benefits (That We Don’t Recommend)!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Does nicotine have any benefits at all? I know it’s incredibly addictive but if you exclude the addiction, does it do anything?❞
Good news: yes, nicotine is a stimulant and can be considered a performance enhancer, for example:
❝Compared with the placebo group, the nicotine group exhibited enhanced motor reaction times, grooved pegboard test (GPT) results on cognitive function, and baseball-hitting performance, and small effect sizes were noted (d = 0.47, 0.46 and 0.41, respectively).❞
Read in full: Acute Effects of Nicotine on Physiological Responses and Sport Performance in Healthy Baseball Players
However, another study found that its use as a cognitive enhancer was only of benefit when there was already a cognitive impairment:
❝Studies of the effects of nicotinic systems and/or nicotinic receptor stimulation in pathological disease states such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and schizophrenia show the potential for therapeutic utility of nicotinic drugs.
In contrast to studies in pathological states, studies of nicotine in normal-non-smokers tend to show deleterious effects.
This contradiction can be resolved by consideration of cognitive and biological baseline dependency differences between study populations in terms of the relationship of optimal cognitive performance to nicotinic receptor activity.
Although normal individuals are unlikely to show cognitive benefits after nicotinic stimulation except under extreme task conditions, individuals with a variety of disease states can benefit from nicotinic drugs❞
Read in full: Effects of nicotinic stimulation on cognitive performance
Bad news: its addictive qualities wipe out those benefits due to tolerance and thus normalization in short order. So you may get those benefits briefly, but then you’re addicted and also lose the benefits, as well as also ruining your health—making it a lose/lose/lose situation quite quickly.
As an aside, while nicotine is poisonous per se, in the quantities taken by most users, the nicotine itself is not usually what kills. It’s mostly the other stuff that comes with it (smoking is by far and away the worst of all; vaping is relatively less bad, but that’s not a strong statement in this case) that causes problems.
See also: Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
However, this is still not an argument for, say, getting nicotine gum and thinking “no harmful effects” because then you’ll be get a brief performance boost yes before it runs out and being addicted to it and now being in a position whereby if you stop, your performance will be lower than before you started (since you now got used to it, and it became your new normal), before eventually recovering:
In summary
We recommend against using nicotine in the first place, and for those who are addicted, we recommend quitting immediately if not contraindicated (check with your doctor if unsure; there are some situations where it is inadvisable to take away something your body is dependent on, until you correct some other thing first).
For more on quitting in general, see:
Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What’s So Special About Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Access-All-Areas Antioxidant
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA) is one of the most bioavailable antioxidants in existence. A bold claim, but most antioxidants are only water-soluble or fat-soluble, whereas ALA is both. This has far-reaching implications—and we mean that literally, because its “go everywhere” status means that it can access (and operate in) all living cells of the human body.
We make it inside our body, and we can also get it in our diet, or take it as a supplement.
What foods contain it?
The richest food sources are:
- For the meat-eaters: organ meats
- For everyone: broccoli, tomatoes, & spinach
However, supplements are more efficient at delivering it, by several orders of magnitude:
Read more: Lipoic acid – biological activity and therapeutic potential
What are its benefits?
Most of its benefits are the usual benefits you would expect from any antioxidant, just, more of it. In particular, reduced inflammation and slowed skin aging are common reasons that people take ALA as a supplement.
Does it really reduce inflammation?
Yes, it does. This one’s not at all controversial, as this systematic review of studies shows:
(C-reactive protein is a marker of inflammation)
Does it really reduce skin aging?
Again yes—which again is not surprising for such a potent antioxidant; remember that oxidative stress is one of the main agonists of cellular aging:
As a special feature, ALA shows particular strength against sun-related skin aging, because of how it protects against UV radiation and increases levels of gluthianone, which also helps:
- Photochemical stability of lipoic acid and its impact on skin ageing
- Modern approach to topical treatment of aging skin
Where can I get some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Age Later – by Dr. Nir Barzilai
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Barzilai discusses why we age, why supercentenarians age more slowly, and even, why it is so often the case that supercentenarians outside of Blue Zones have poor lifestyles (their longevity is because of protective genes that mitigate the harmful effects of those poor lifestyles—the ultimate in “survivorship bias”).
He also talks not just genetics, but also epigenetics, and thus gene expression. Bearing in mind, there’s a scale of modifiability there: with current tech, we can’t easily change a bad gene… But we often can just switch it off (or at least downregulate its expression). This is where studies in supercentenarians are helpful even for those who don’t have such fortunate genes—the supercentenarian studies show us which genes we want on or off, what gene expressions to aim for, etc. Further clinical studies can then show us what lifestyle interventions (exercise, diet, nutraceuticals, etc) can do that for us.
With regard to those lifestyle interventions, he does cover many, and that’s where a lot of the practical value of the book comes from. But it’s not just “do this, do that”; understanding the reasons behind why things work the way they do is important, so as to be more likely to do it right, and also to enjoy greater adherence (we tend to do things we understand more readily than things we have just been told to do).
There are areas definitely within the author’s blind spots—for example, when talking about menopausal HRT, he discusses at great length the results of the discredited WHI study, and considers it the only study of relevance. So, this is a reminder to not believe everything said by someone who sounds confident (Dr. Barzilai’s professional background is mostly in treating diabetes).
In terms of style, it is very much narrative; somewhat pop-science, but more “this doctor wants to tell stories”. So many stories. Now, the stories all have informational value, so this isn’t padding, but it is the style, so we mention it as such. As for citations, there aren’t any, so if you want to look up the science he mentions, you’re going to need a bit of digital sleuthery to find the papers from the clues in the stories.
Bottom line: if you’re interested in the science of aging and how that has been progressing for the past decades and where we’re at, this book will give you so many jumping-off points, and is an engaging read.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Your Brain on Art – by Susan Magsamen & Ivy Ross
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The notion of art therapy is popularly considered a little wishy-washy. As it turns out, however, there are thousands of studies showing its effectiveness.
Nor is this just a matter of self-expression. As authors Magsamen and Ross explore, different kinds of engagement with art can convey different benefits.
That’s one of the greatest strengths of this book: “this form of engagement with art will give these benefits, according to these studies”
With benefits ranging from reducing stress and anxiety, to overcoming psychological trauma or physical pain, there’s a lot to be said for art!
And because the book covers many kinds of art, if you can’t imagine yourself taking paintbrush to canvas, that’s fine too. We learn of the very specific cognitive benefits of coloring in mandalas (yes, really), of sculpting something terrible in clay, or even just of repainting the kitchen, and more. Each thing has its set of benefits.
The book’s main goal is to encourage the reader to cultivate what the authors call an aesthetic mindset, which involves four key attributes:
- a high level of curiosity
- a love of playful, open-ended exploration
- a keen sensory awareness
- a drive to engage in creative activities
And, that latter? It’s as a maker and/or a beholder. We learn about what we can gain just by engaging with art that someone else made, too.
Bottom line: come for the evidence-based cognitive benefits; stay for the childlike wonder of the universe. If you already love art, or have thought it’s just “not for you”, then this book is for you.
Click here to check out Your Brain On Art, and open up whole new worlds of experience!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: