Apples vs Bananas – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apples to bananas, we picked the bananas.
Why?
Both apples and bananas contain lots of vitamins, but bananas contain far more of Vitamins A, B, and C.
Apples beat bananas only for vitamins E and K.
This may seem like “well that’s 2 vs 3; that’s pretty close” until one remembers that vitamin B is actually eight vitamins in a trenchcoat. Bananas have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9.
If you’re wondering about the other numbers: neither fruit contains vitamins B7 (biotin) or B12 (cobalamins of various kinds). Vitamins B4, B8, B10, and B11 do not exist as such (due to changes in how vitamins are classified).
Both apples and bananas contain lots of minerals, but bananas contain far more of iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium.
Apples beat bananas only for calcium (and then, only very marginally)
Both apples and bananas have plenty of fiber.
Apples have marginally less sugar, but given the fiber content, this is pretty much moot when it comes to health considerations, and apples are higher in fructose in any case.
In short, both are wonderful fruits (and we encourage you to enjoy both!), and/but bananas beat apples healthwise in almost all measures.
PS: top tip if you find it challenging to get bananas at the right level of ripeness for eating… Try sun-dried! Not those hard chip kinds (those are mechanically and/or chemically dried, and usually have added sugar and preservatives), but sun-dried.
Here’s an example product on Amazon
Warning: since there aren’t many sun-dried bananas available on Amazon, double-check you haven’t been redirected to mechanically/chemically dried ones, as Amazon will try that sometimes!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What does it mean to be immunocompromised?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our immune systems help us fight off disease, but certain health conditions and medications can weaken our immune systems. People whose immune systems don’t work as well as they should are considered immunocompromised.
Read on to learn more about how the immune system works, what causes people to be immunocompromised, and how we can protect ourselves and the immunocompromised people around us from illness.
What is the immune system?
The immune system is a network of cells, organs, and chemicals that helps our bodies fight off infections caused by invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Some important parts of the immune system include:
- White blood cells, which attack and kill germs that don’t belong inside our bodies.
- Lymph nodes, which help our bodies filter out germs.
- Antibodies, which help our bodies recognize invaders.
- Cytokines, which tell our immune cells what to do.
What causes people to be immunocompromised?
Some health conditions and medications can prevent our immune systems from functioning optimally, which makes us more vulnerable to infection. Health conditions that compromise the immune system fall into two categories: primary immunodeficiency and secondary immunodeficiency.
Primary immunodeficiency
People with primary immunodeficiency are born with genetic mutations that prevent their immune systems from functioning as they should. There are hundreds of types of primary immunodeficiencies. Since these mutations affect the immune system to varying degrees, some people may experience symptoms and get diagnosed early in life, while others may not know they’re immunocompromised until adulthood.
Secondary immunodeficiency
Secondary immunodeficiency happens later in life due to an infection like HIV, which weakens the immune system over time, or certain types of cancer, which prevent the body from producing enough white blood cells to adequately fight off infection. Studies have also shown that getting infected with COVID-19 may cause immunodeficiency by reducing our production of “killer T-cells,” which help fight off infections.
Sometimes necessary treatments for certain medical conditions can also cause secondary immunodeficiency. For example, people with autoimmune disorders—which cause the immune system to become overactive and attack healthy cells—may need to take immunosuppressant drugs to manage their symptoms. However, the drugs can make them more vulnerable to infection.
People who receive organ transplants may also need to take immunosuppressant medications for life to prevent their body from rejecting the new organ. (Given the risk of infection, scientists continue to research alternative ways for the immune system to tolerate transplantation.)
Chemotherapy for cancer patients can also cause secondary immunodeficiency because it kills the immune system’s white blood cells as it’s trying to kill cancer cells.
What are the symptoms of a compromised immune system?
People who are immunocompromised may become sick more frequently than others or may experience more severe or longer-term symptoms than others who contract the same disease.
Other symptoms of a compromised immune system may include fatigue; digestive problems like cramping, nausea, and diarrhea; and slow wound healing.
How can I find out if I’m immunocompromised?
If you think you may be immunocompromised, talk to your health care provider about your medical history, your symptoms, and any medications you take. Blood tests can determine whether your immune system is producing adequate proteins and cells to fight off infection.
I’m immunocompromised—how can I protect myself from infection?
If you’re immunocompromised, take precautions to protect yourself from illness.
Wash your hands regularly, wear a well-fitting mask around others to protect against respiratory viruses, and ensure that you’re up to date on recommended vaccines.
Immunocompromised people may need more doses of vaccines than people who are not immunocompromised—including COVID-19 vaccines. Talk to your health care provider about which vaccines you need.
How can I protect the immunocompromised people around me?
You never know who may be immunocompromised. The best way to protect immunocompromised people around you is to avoid spreading illnesses.
If you know you’re sick, isolate whenever possible. Wear a well-fitting mask around others—especially if you know that you’re sick or that you’ve been exposed to germs. Make sure you’re up to date on recommended vaccines, and practice regular hand-washing.
If you’re planning to spend time with someone who is immunocompromised, ask them what steps you can take to keep them safe.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
The Healthiest Bread Recipe You’ll Probably Find
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝[About accidental scalding with water] Is cold water actually the best immediate treatment for a burn? Maybe there is something better, or something I should apply after the cold water.❞
If this is a case of spilled tea or similar—as in your story, which (apologies) we clipped for brevity—indeed, cold running water is best, and nothing else should be needed. It’s up to you whether you want to invest the time based on the extent of the scalding, but 10 minutes is recommended to minimize tissue damage.
If it’s a more severe scalding or burning, seek medical attention immediately. If it’s a burn to anywhere other than the airway, cold running water is still best for 10 minutes, but if you have to choose between that and professional medical attention, don’t delay the help.
If it’s a burn you’ve given 10 minutes of cold running water and it still hurts and/or has blistered, cover it in a sterile, non-adhesive dressing that extends well beyond the visible burn (because the actual damage probably extends further, and you don’t want to find this out the hard way later). If the burn is to the face, do still irrigate but not cover it; wait for help.
Do not apply any kind of cream, lotion, oil, etc. No matter how tempting, no matter where the burn is.
All of the above also goes for splashed oil, chemical burns, and electrical burns too (but obviously, make sure to get away from the electricity first).
Source: this ex-military writer was trained for this sort of thing and, suffice it to say, has dealt with more serious things than spilled tea before now.
Legal note: notwithstanding the above, we are a health science newsletter, not paramedics. Also, circumstances may differ, and best practices may change. In the case of serious injury, call emergency services first, and follow their instructions over ours.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
4 things ancient Greeks and Romans got right about mental health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
According to the World Health Organization, about 280 million people worldwide have depression and about one billion have a mental health problem of any kind.
People living in the ancient world also had mental health problems. So, how did they deal with them?
As we’ll see, some of their insights about mental health are still relevant today, even though we might question some of their methods.
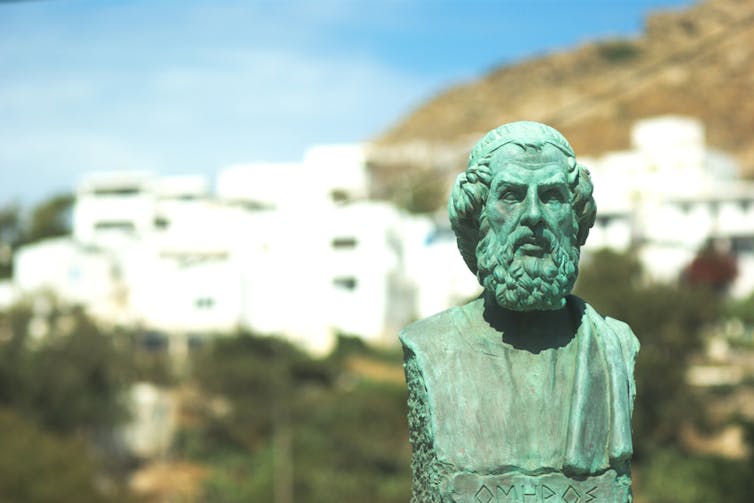
Jr Morty/Shutterstock 1. Our mental state is important
Mental health problems such as depression were familiar to people in the ancient world. Homer, the poet famous for the Iliad and Odyssey who lived around the eighth century BC, apparently died after wasting away from depression.
Already in the late fifth century BC, ancient Greek doctors recognised that our health partly depends on the state of our thoughts.
In the Epidemics, a medical text written in around 400BC, an anonymous doctor wrote that our habits about our thinking (as well as our lifestyle, clothing and housing, physical activity and sex) are the main determinants of our health.
Homer, the ancient Greek poet, had depression. Thirasia/Shutterstock 2. Mental health problems can make us ill
Also writing in the Epidemics, an anonymous doctor described one of his patients, Parmeniscus, whose mental state became so bad he grew delirious, and eventually could not speak. He stayed in bed for 14 days before he was cured. We’re not told how.
Later, the famous doctor Galen of Pergamum (129-216AD) observed that people often become sick because of a bad mental state:
It may be that under certain circumstances ‘thinking’ is one of the causes that bring about health or disease because people who get angry about everything and become confused, distressed and frightened for the slightest reason often fall ill for this reason and have a hard time getting over these illnesses.
Galen also described some of his patients who suffered with their mental health, including some who became seriously ill and died. One man had lost money:
He developed a fever that stayed with him for a long time. In his sleep he scolded himself for his loss, regretted it and was agitated until he woke up. While he was awake he continued to waste away from grief. He then became delirious and developed brain fever. He finally fell into a delirium that was obvious from what he said, and he remained in this state until he died.
3. Mental illness can be prevented and treated
In the ancient world, people had many different ways to prevent or treat mental illness.
The philosopher Aristippus, who lived in the fifth century BC, used to advise people to focus on the present to avoid mental disturbance:
concentrate one’s mind on the day, and indeed on that part of the day in which one is acting or thinking. Only the present belongs to us, not the past nor what is anticipated. The former has ceased to exist, and it is uncertain if the latter will exist.
The philosopher Clinias, who lived in the fourth century BC, said that whenever he realised he was becoming angry, he would go and play music on his lyre to calm himself.
Doctors had their own approaches to dealing with mental health problems. Many recommended patients change their lifestyles to adjust their mental states. They advised people to take up a new regime of exercise, adopt a different diet, go travelling by sea, listen to the lectures of philosophers, play games (such as draughts/checkers), and do mental exercises equivalent to the modern crossword or sudoku.
Galen, a famous doctor, believed mental problems were caused by some idea that had taken hold of the mind. Pierre Roche Vigneron/Wikimedia For instance, the physician Caelius Aurelianus (fifth century AD) thought patients suffering from insanity could benefit from a varied diet including fruit and mild wine.
Doctors also advised people to take plant-based medications. For example, the herb hellebore was given to people suffering from paranoia. However, ancient doctors recognised that hellebore could be dangerous as it sometimes induced toxic spasms, killing patients.
Other doctors, such as Galen, had a slightly different view. He believed mental problems were caused by some idea that had taken hold of the mind. He believed mental problems could be cured if this idea was removed from the mind and wrote:
a person whose illness is caused by thinking is only cured by taking care of the false idea that has taken over his mind, not by foods, drinks, [clothing, housing], baths, walking and other such (measures).
Galen thought it was best to deflect his patients’ thoughts away from these false ideas by putting new ideas and emotions in their minds:
I put fear of losing money, political intrigue, drinking poison or other such things in the hearts of others to deflect their thoughts to these things […] In others one should arouse indignation about an injustice, love of rivalry, and the desire to beat others depending on each person’s interest.
4. Addressing mental health needs effort
Generally speaking, the ancients believed keeping our mental state healthy required effort. If we were anxious or angry or despondent, then we needed to do something that brought us the opposite of those emotions.
Watch some comedy, said physician Caelius Aurelianus. VCU Tompkins-McCaw Library/Flickr, CC BY-NC-SA This can be achieved, they thought, by doing some activity that directly countered the emotions we are experiencing.
For example, Caelius Aurelianus said people suffering from depression should do activities that caused them to laugh and be happy, such as going to see a comedy at the theatre.
However, the ancients did not believe any single activity was enough to make our mental state become healthy. The important thing was to make a wholesale change to one’s way of living and thinking.
When it comes to experiencing mental health problems, we clearly have a lot in common with our ancient ancestors. Much of what they said seems as relevant now as it did 2,000 years ago, even if we use different methods and medicines today.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Konstantine Panegyres, McKenzie Postdoctoral Fellow, researching Greco-Roman antiquity, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Brown Rice vs Russet Potatoes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing brown rice to russet potatoes, we picked the rice.
Why?
First we’ll note: for brevity and to avoid undue repetitiveness, we’re henceforth going to just say “rice” and “potato”, respectively, but values and conclusions are still for brown rice and russet potatoes. Also, we are including the flesh and skin into the metrics for the potato (without the skin, many nutrients are no longer present).
In terms of macros, the rice has more fiber, carbs, and protein. It’s difficult to compare glycemic indices in this case, because they both need cooking before eating, and how one cooks them (and whether one cools them) along with other preparatory methods will change the GI considerably. Thus, we’ll simply go with the more nutritionally dense option, and that’s the rice.
In the category of vitamins, the rice has much more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, E, and choline, while the potato has more of vitamins C and K. A clear win for rice (and by the way, that’s 60x the vitamin E, but as potatoes don’t have much vitamin E, in practical terms, it’s actually the B-vitamins where rice’s strengths really show, as potatoes aren’t a bad source but rice is amazing).
When it comes to minerals, rice has a lot more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while potato has more calcium and potassium. Another easy win for rice.
You may be wondering about phytic acid: brown rice contains this by default, and it is something of an antinutrient (i.e., if left as-is, it reduces the bioavailability of other nutrients), and/but the phytic acid content is reduced to negligible by two things: soaking and heating (especially if those two things are combined) ← doing this the way described results in bioavailability of nutrients that’s even better than if there were just no phytic acid, albeit it requires you having the time to soak, and do so at temperature.
All in all, adding up the sections makes for an overall win for brown rice, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong? Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Your Health Audit, From Head To Toe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health Audit Time
Here at 10almonds, we often cover quite specific things, ranging from “the effect of sodium on organs other than your heart” to “make this one small change to save your knees while driving”.
But, we’re each a whole person, and we need to take care of the whole organism that makes up the wonderful being that we each are. If we let one part of it drop in health too much, the others will soon follow suit because of the knock-on effects.
So, let’s do a quick self-check-up, and see what can be done for each! How’s your…
Mental Health
We’re doing this audit head-to-to, so let’s start it here, because mental health is also just health, and it’s difficult to tackle the others without having this one at least under control!
Are you experiencing chronic stress? Anxiety? Depression? Joy?
If you answered “no” to “joy” but also “no” to “depression”, you might want to rethink your answer to “depression”, by the way. Life should be a joyous thing!
Some resources to address your mental health:
Brain Health
Your brain is a big, powerful organ. It uses more of your daily energy (in the physiological sense of the word, we’re talking calories and mitochondria and ATP) than any other organ, by far.
And when it comes to organ failure, if your brain fails, then having the best joints in the world won’t help you, for example.
Some resources to address your brain health:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It
- How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
- The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
Heart Health
Everything depends on your heart, head to toe. Tirelessly pumping blood with oxygen, nutrients, and agents of your immune system all around your body, all day every day for your entire life.
What’s your resting heart rate like? How about your blood pressure? And while we’re on the topic of blood… how’s your blood sugar health?
These are all important things to a) know about and b) keep on top of!
Some resources to address your heart health:
- 1-Minute Heart Health Check-Up Tips
- A Five-Point Plan For Heart Health
- High Blood Pressure? Try These!
Gut Health
By cell count, we’re about 10% human and 90% bacteria. By gene count, also. Pretty important, therefore, that we look after our trillions of tiny friends that keep our organism working.
Most people in N. America, for example, get vastly under the recommended daily amount of fiber, and that’s just the most basic courtesy we could do for these bugs that keep us alive (they need that fiber to live, and their process of consuming it is beneficial to us in a stack of ways).
Some resources to address your gut health:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- The Surprising Link Between Gut Health And Serotonin
- The Vagus Nerve: The Brain-Gut Highway!
Hormonal Health
Hormones are weird and wonderful and affect so much more than the obvious sex-related functions (but yes, those too). A lot of people don’t realize it, but having our hormones in good order or not can make the difference between abject misery and a happy, fulfilling life.
Some resources to address your hormonal health:
- What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
- Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them
- Too Much Or Too Little Testosterone?
Bone/Joint Health
Fear nothing! For you are a ghost operating a skeleton clad in flesh. But also, you know, look after that skeleton; you only get one! Being animals, we’re all about movement, and being humans, we’ve ended up with some lifestyle situations that aren’t great for that mobility. We sit too much; we walk too little; we cramp ourselves into weird positions (driving, anyone?), and we forget the range of motion we’re supposed to have. But let’s remember…
Some resources to address your bone/joint health:
- Collagen’s benefits are more than skin deep
- Cool As A Cucumber (Move Over, Glucosamine + Chondroitin)
- 5 Best Bodyweight Exercises For Incredible Mobility
Lastly…
While it’s good to do a little self-audit like this every now and again, it’s even better to get a professional check-up!
As engineers say: if you don’t schedule time for maintenance, your equipment will schedule it for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cherries vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cherries to cranberries, we picked the cherries.
Why?
In terms of macros, cherries have a little more protein (but it’s not much) while cranberries have a little more fiber. Despite this, cherries have the lower glycemic index—about half that of cranberries.
In the category of vitamins, cherries have a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B9, and a little more choline, while cranberries have more of vitamins B5, B6, C, E, and K. A modest win for cherries here.
When it comes to minerals, things are more divided: cherries have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while cranberries have more manganese. An easy win for cherries here.
This all adds up to a total win for cherries, but both of these fruits are great and both have their own beneficial properties (see our main features below!)
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
- Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: