Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong?
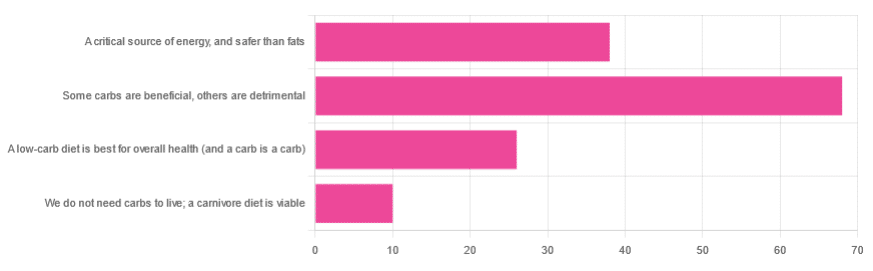
We asked you for your health-related view of carbs, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses
- About 48% said “Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental”
- About 27% said “Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats”
- About 18% said “A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb)”
- About 7% said “We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable”
But what does the science say?
Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats: True or False?
True and False, respectively! That is: they are a critical source of energy, and carbs and fats both have an important place in our diet.
❝Diets that focus too heavily on a single macronutrient, whether extreme protein, carbohydrate, or fat intake, may adversely impact health.❞
Source: Low carb or high carb? Everything in moderation … until further notice
(the aforementioned lead author Dr. de Souza, by the way, served as an external advisor to the World Health Organization’s Nutrition Guidelines Advisory Committee)
Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental: True or False?
True! Glycemic index is important here. There’s a big difference between eating a raw carrot and drinking high-fructose corn syrup:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
While some say grains and/or starchy vegetables are bad, best current science recommends:
- Eat some whole grains regularly, but they should not be the main bulk of your meal (non-wheat grains are generally better)
- Starchy vegetables are not a critical food group, but in moderation they are fine.
To this end, the Mediterranean Diet is the current gold standard of healthful eating, per general scientific consensus:
A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb): True or False?
True-ish and False, respectively. We covered the “a carb is a carb” falsehood earlier, so we’ll look at “a low-carb diet is best”.
Simply put: it can be. One of the biggest problems facing the low-carb diet though is that adherence tends to be poor—that is to say, people crave their carby comfort foods and eat more carbs again. As for the efficacy of a low-carb diet in the context of goals such as weight loss and glycemic control, the evidence is mixed:
❝There is probably little to no difference in weight reduction and changes in cardiovascular risk factors up to two years’ follow-up, when overweight and obese participants without and with T2DM are randomised to either low-carbohydrate or balanced-carbohydrate weight-reducing diets❞
Source: Low-carbohydrate versus balanced-carbohydrate diets for reducing weight and cardiovascular risk
❝On the basis of moderate to low certainty evidence, patients adhering to an LCD for six months may experience remission of diabetes without adverse consequences.
Limitations include continued debate around what constitutes remission of diabetes, as well as the efficacy, safety, and dietary satisfaction of longer term LCDs❞
~ Dr. Joshua Goldenberg et al.
Source: Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission
❝There should be no “one-size-fits-all” eating pattern for different patient´s profiles with diabetes.
It is clinically complex to suggest an ideal percentage of calories from carbohydrates, protein and lipids recommended for all patients with diabetes.❞
Source: Current Evidence Regarding Low-carb Diets for The Metabolic Control of Type-2 Diabetes
We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable: True or False?
False. For a simple explanation:
The Carnivore Diet: Can You Have Too Much Meat?
There isn’t a lot of science studying the effects of consuming no plant products, largely because such a study, if anything other than observational population studies, would be unethical. Observational population studies, meanwhile, are not practical because there are so few people who try this, and those who do, do not persist after their first few hospitalizations.
Putting aside the “Carnivore Diet” as a dangerous unscientific fad, if you are inclined to meat-eating, there is some merit to the Paleo Diet, at least for short-term weight loss even if not necessarily long-term health:
What’s The Real Deal With The Paleo Diet?
For longer-term health, we refer you back up to the aforementioned Mediterranean Diet.
Enjoy!





