How To Stay In Shape At 70
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Questions and Answers at 10almonds
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
This newsletter has been growing a lot lately, and so have the questions/requests, and we love that! In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
I have a question: what are the pros and cons of older people (60+) taking creatine every day?
It depends what else you’re doing, as creatine mostly helps the muscles recover after exercise. So:
- iff you’re doing resistance training (such as weights or bodyweight training), or HIIT (High Intensity Interval Training), then creatine monohydrate may help you keep at that and keep doing well.
- if you’re just doing light-to-moderate exercises, you might not get much benefit from creatine!
The topic merits diving deeper though, so we’ll queue that for one of our “Research Review Monday” days!
I wanted to ask if you think marine collagen is decent to take. I’ve heard a lot of bad press about it
We don’t know what you’ve heard, but generally speaking it’s been found to be very beneficial to bones, joints, and skin! We wrote about it quite recently on a “Research Review Monday”:
See: We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Natural alternatives to medication for depression?
Great question! We did a mean feature a while back, but we definitely have much more to say! We’ll do another main feature soon, but in the meantime, here’s what we previously wrote:
See: The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
^This covers not just the obvious, but also why the most common advice is not helpful, and practical tips to actually make manageable steps back to wellness, on days when “literally just survive the day” is one’s default goal.
I am now in the “aging” population. A great concern for me is Alzheimers. My father had it and I am so worried. What is the latest research on prevention?
One good thing to note is that while Alzheimer’s has a genetic component, it doesn’t appear to be hereditary per se. Still, good to be on top of these things, and it’s never too early to start with preventive measures!
You might like a main feature we did on this recently:
See: How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
Side effects of statins, are they worth it? Depression, are antidepressants worth it?
About statins, that depends a lot on you, your circumstances, and—as it happens—your gender. We covered this in a main feature recently, but a short answer is: for most people, they may not be the best first choice, and could even make things worse. For some people, however, they really are just what’s needed.
- Factors that make them more likely better for you: being a man, or having atherosclerosis
- Factors that make them more likely worse for you: being a woman in general
Check out the main feature we did: Statins: His & Hers?
As for antidepressants? That depends a lot on you, your physiology, your depression, your circumstances, and more. We’ll definitely do a main feature on that sometime soon, as there’s a lot that most people don’t know!
I am interested in the following: Aging, Exercise, Diet, Relationships, Purpose, Lowering Stress
You’re going to love our Psychology Sunday editions of 10almonds!
You may particularly like some of these:
- Seriously Useful Communication Skills! ← this is about relationship stuff
- Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How) ← about “the stress hormone”
- How To Set Your Anxiety Aside ← these methods work for stress too
(This coming Psychology Sunday will have a feature specifically on stress, so do make sure to read that when it comes out!)
Hair growth strategies for men combing caffeine and minoxidil?
Well, the strategy for that is to use caffeine and minoxidil! Some more specific tips, though:
- Both of those things need to be massaged (gently!) into your scalp especially around your hairline.
- In the case of caffeine, that boosts hair growth. No extra thought or care needed for that one.
- In the case of minoxidil, it reboots the hair growth cycle, so if you’ve only recently started, don’t be surprised (or worried) if you see more shedding in the first three months. It’s jettisoning your old hairs because new ones were just prompted (by the minoxidil) to start growing behind them. So: it will get briefly worse before it gets better, but then it’ll stay better… provided you keep using it.
- If you’d like other options besides minoxidil, finasteride is a commonly prescribed oral drug that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which latter is what tells your hairline to recede.
- If you’d like other options besides prescription drugs, saw palmetto performs comparably to finasteride (and works the same way).
- You may also want to consider biotin supplementation if you don’t already enjoy that
- Consider also using a dermaroller on your scalp. If you’re unfamiliar, this is a device that looks like a tiny lawn aerator, with many tiny needles, and you roll it gently across your skin.
- It can be used for promoting hair growth, as well as for reducing wrinkles and (more slowly) healing scars.
- It works by breaking up the sebum that may be blocking new hair growth, and also makes the skin healthier by stimulating production of collagen and elastin (in response to the thousands of microscopic wounds that the needles make).
- Sounds drastic, but it doesn’t hurt and doesn’t leave any visible marks—the needles are that tiny. Still, practise good sterilization and ensure your skin is clean when using it.
See: How To Use A Dermaroller ← also explains more of the science of it
PS: this question was asked in the context of men, but the information goes the same for women suffering from androgenic alepoceia—which is a lot more common than most people think!
How to get to sleep at night as fast and as naturally as possible? Thank you!
We’ll definitely write more on that! You might like these articles we wrote already, meanwhile:
- Beating The Insomnia Blues ← this one is general advice and tips
- Time For Some Pillow Talk ← this one compares and reviews some popular sleep apps
- Insomnia? High Blood Pressure? Try these! ← this one tackles the matter from a dietary angle
Q: How to be your best self after 60: Self motivation / Avoiding or limiting salt, sugar & alcohol: Alternatives / Ways to sneak in more movements/exercise
…and, from a different subscriber…
Q: Inflammation & over 60 weight loss. Thanks!
Here are some of our greatest hits on those topics:
- Where Nutrition Meets Habits ← focusing on food that’s all three of: healthy + easy + cheap
- How To Keep On Keeping On ← exercise tips for when the motivation wanes
- Keep Inflammation At Bay ← science-based tips and advice
Also, while we’ve recommended a couple of books on stopping (or reducing) drinking, we’ve not done a main feature on that, so we definitely will one of these days!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Keep Cellulite At Bay
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Does anything actually get rid of cellulite? Nothing seems to❞
Let’s get the bad news over with in one go:
Nothing (that the scientific world currently knows of) can get rid of cellulite permanently, nor completely guard against it proactively. Which, given that it affects up to 98% of women to some degree, and often shows up not long after puberty (though it can appear at any time and often increases later in life), any pre-emptive health regime would need to be started as a child in any case.
As with many things that predominantly affect women, the world of medicine isn’t entirely sure what causes it, let alone how to effectively treat it.
Obviously hormones are implicated, namely estrogen.
Obviously adiposity is implicated, because one can’t have dimples in one’s fat if one doesn’t have enough fat to dimple.
Other hypothesized contributory factors include genetics, poor diet, inactivity, unhealthy lifestyle (in ways not previously mentioned, e.g. use of alcohol, tobacco, etc), accumulated toxins, and pregnancy.
Here’s an old paper (from 2004); today’s reviews say pretty much the same thing, but we love how succinctly (albeit, somewhat depressingly) this abstract states how little we know and how little we can do:
Cellulite: a review of its physiology and treatment
However, all is not lost!
There are some things that can affect how much cellulite we get, and there are some things that can reduce it, and even some things that can get rid of it completely—albeit temporarily.
First, a quick refresher on what it actually is, physiologically speaking: cellulite occurs when connective tissue bands pull the skin down in places, where fat tissue has been able to squeeze through. One of the reasons it is hypothesized women get this more than men is because our fat is not merely different in distribution and overall percentage, but also in how the fat cells stack up; we generally have have of a vertical stacking structure going on, while men generally have a more horizontal structure. This means that it can be easier for ours to get moved about differently, causing the connective tissue to pull on the skin unevenly in places.
With that in mind…
Prevention is, as we say, probably impossible if your body is running on estrogen. However, those contributory factors we mentioned above? Most of those are modifiable, including these things that it is hypothesized can reduce it:
Diet: as it seems to be worsened by inflammation (what isn’t?), an anti-inflammatory diet is recommended.
Exercise: there are three things here: 1) exercises to improve circulation and thus the body’s ability to sort things out by itself 2) HIIT exercise to reduce body fat percentage, if one has a high enough starting body fat percentage for that to be a healthy goal 3) mobility exercises, to ensure our connective tissues are the right amount of mobile.
Creams and lotions
These reduce the superficial appearance of cellulite, without actually treating the thing itself. Mostly they are caffeine-based, which when used topically increases blood flow and works as a local diuretic, reducing the water content of the fat cells, diminishing the appearance of the cellulite by making each fat cell physically smaller (while still containing the same amount of fat, and it’ll bounce back in size as soon as the body can restore osmotic balance).
Medical procedures
There are too many of these to discuss them all separately, but they all work on the principle of breaking up the tough bands of connective tissue to eliminate the dimpling of cellulite.
The methods they use vary from ultrasound to cryolipolysis to lasers to “vacuum-assisted precise tissue release”, which involves a suction pump and a multipronged robotic assembly with needles to administer anaesthetic as it goes and small blades to cut the connective tissues under the skin:
Tissue Stabilized–Guided Subcision for the Treatment of Cellulite
That last one definitely sounds like the least fun, but it’s also the only one that doesn’t take months to maybe see results.
Cellulite can and almost certainly will come back after all of these.
Home remedies
Aside from at-home versions of the above (not the robots with vacuum pumps and needles and microblades, hopefully, but for example homemade caffeine creams), and of course diet and exercise which can be considered “home remedies”, there are two more things worth mentioning:
Dry brushing: using a body brush to, as the name suggests, simply brush one’s skin. The “dry” aspect here is simply that it’s not done in the bath or shower; it’s done while dry. It can improve local circulation of blood and lymph, allowing for better detoxification and redistribution of needed bodily resources.
Here’s an example dry brushing body brush on Amazon; this writer has one and hates it, but I’ve also tried with other kinds of brush and hate them too, so it seems to be a me thing rather than a brush thing, and I have desisted in trying, now. Maybe you will like it better; many people do.
Self-massage: or massage by someone else, if that’s an option for you and you prefer. In this case, it works by a different mechanism than dry brushing; this time it’s working by the same principle as the medical techniques described in the previous section; it’s physically breaking down the toughened bits of connective tissue.
Here’s an example wooden massage roller on Amazon; this writer has one and loves it; it’s sooooooo good. I got it as a matter of general maintenance for my fascia, but it’s also very good if I get a muscular pain now and again. As for cellulite, I personally get just a little cellulite sometimes (in the backs of my thighs), and whenever I use this regularly, it goes away for at least a while.
A quick note in closing
Cellulite is normal for women and is not unhealthy. Much like gray hair for example, it’s something that can be increased by poor health, but the thing itself isn’t intrinsically unhealthy, and most of us get it to some degree at some point.
Nevertheless, aesthetic factors can also have a role to play in mental health, and we tend to feel best when we like the way our body looks. If for you that means wanting less/no cellulite, then the above are some ways towards that.
As a bonus, most of the nonmedical options are directly good for the physical health anyway, so doing them is of course good.
In particular that last one (the wooden massage roller), because that connective tissue we talked about? It matters for a lot more than just cellulite, and is heavily implicated in a lot of kinds of chronic pain, so it pays to keep it in good health:
Fascia: Why (And How) You Should Take Care Of Yours
(that article, also written by this same writer by the way, suggests a vibrating foam roller—those are very popular; I just really love my wooden one, and find it more effective)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why Adult ADHD Often Leads To Anxiety & Depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ADHD’s Knock-On Effects On Mental Health
We’ve written before about ADHD in adult life, often late-diagnosed because it’s not quite what people think it is:
In women in particular, it can get missed and/or misdiagnosed:
Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
…but what we’re really here to talk about today is:
It’s the comorbidities that get you
When it comes to physical health conditions:
- if you have one serious condition, it will (usually) be taken seriously
- if you have two, they will still be taken seriously, but people (friends and family members, as well as yes, medical professionals) will start to back off, as it starts to get too complicated for comfort
- if you have three, people will think you are making at least one of them up for attention now
- if you have more than three, you are considered a hypochondriac and pathological liar
Yet, the reality is: having one serious condition increases your chances of having others, and this chance-increasing feature compounds with each extra condition.
Illustrative example: you have fibromyalgia (ouch) which makes it difficult for you to exercise much, shop around when grocery shopping, and do much cooking at home. You do your best, but your diet slips and it’s hard to care when you just want the pain to stop; you put on some weight, and get diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, which in time becomes diabetes with high cardiovascular risk factors. Your diabetes is immunocompromising; you get COVID and find it’s now Long COVID, which brings about Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, when you barely had the spoons to function in the first place. At this point you’ve lost count of conditions and are just trying to get through the day.
If this is you, by the way, we hope at least something in the following might ease things for you a bit:
- Stop Pain Spreading
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue (While Having The Limitations Of Chronic Fatigue)
- When Painkillers Aren’t Helping, These Things Might
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
It’s the same for mental health
In the case of ADHD as a common starting point (because it’s quite common, may or may not be diagnosed until later in life, and doesn’t require any external cause to appear), it is very common that it will lead to anxiety and/or depression, to the point that it’s perhaps more common to also have one or more of them than not, if you have ADHD.
(Of course, anxiety and/or depression can both pop up for completely unrelated reasons too, and those reasons may be physiological, environmental, or a combination of the above).
Why?
Because all the good advice that goes for good mental health (and/or life in general), gets harder to actuate when one had ADHD.
- “Strong habits are the core of a good life”, but good luck with that if your brain doesn’t register dopamine in the same way as most people’s do, making intentional habit-forming harder on a physiological level.
- “Plan things carefully and stick to the plan”, but good luck with that if you are neurologically impeded from forming plans.
- “Just do it”, but oops you have the tendency-to-overcommitment disorder and now you are seriously overwhelmed with all the things you tried to do, when each of them alone were already going to be a challenge.
Overwhelm and breakdown are almost inevitable.
And when they happen, chances are you will alienate people, and/or simply alienate yourself. You will hide away, you will avoid inflicting yourself on others, you will brood alone in frustration—or distract yourself with something mind-numbing.
Before you know it, you’re too anxious to try to do things with other people or generally show your face to the world (because how will they react, and won’t you just mess things up anyway?), and/or too depressed to leave your depression-lair (because maybe if you keep playing Kingdom Vegetables 2, you can find a crumb of dopamine somewhere).
What to do about it
How to tackle the many-headed beast? By the heads! With your eyes open. Recognize and acknowledge each of the heads; you can’t beat those heads by sticking your own in the sand.
Also, get help. Those words are often used to mean therapy, but in this case we mean, any help. Enlist your partner or close friend as your support in your mental health journey. Enlist a cleaner as your support in taking that one thing off your plate, if that’s an option and a relevant thing for you. Set low but meaningful goals for deciding what constitutes “good enough” for each life area. Decide in advance what you can safely half-ass, and what things in life truly require your whole ass.
Here’s a good starting point for that kind of thing:
When You Know What You “Should” Do (But Knowing Isn’t The Problem)
And this is an excellent way to “get the ball rolling” if you’re already in a bit of a prison of your own making:
Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
If things are already bad, then you might also consider:
- How To Set Anxiety Aside and
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need ← this is about getting out of depression
And if things are truly at the worst they can possibly be, then:
How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How Your Exercise Today Gives A Brain Boost Tomorrow
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Regular 10almonds readers may remember we not long back wrote about a study that showed how daily activity levels, in aggregate, make a difference to brain health over the course of 1–2 weeks (in fact, it was a 9-day study):
Daily Activity Levels & The Measurable Difference They Make To Brain Health
Today, we’re going to talk about a new (published today, at time of writing) study that shows the associations between daily exercise levels (amongst other things) and how well people performed in cognitive tests the next day.
By this we mean: they recorded exercise vs sedentary behavior vs sleep on a daily basis (using wearable tech to track it), and tested them daily with cognitive tests, and looked at how the previous day’s activities (or lack thereof) impacted the next day’s test results.
Notably, the sample was of older adults (aged 50–83). The sample size wasn’t huge but was statistically significant (n=76) and the researchers are of course calling for more studies to be done with more people.
What they found
To put their findings into few words:
- Consistent light exercise boosts general cognitive performance not just for hours (which was already known) but through the next day.
- More moderate or vigorous activity than usual in particular led to better working memory and episodic memory the next day.
- More sleep (especially slow-wave deep sleep) improved episodic memory and psychomotor speed.
- Sedentary behavior was associated with poorer working memory.
Let’s define some terms:
- general cognitive performance = average of scores across the different tests
- working memory = very short term memory, such as remembering what you came into this room for, or (as an example of a test format) being able to take down a multi-digit number in one go without it being broken down (and then, testing with longer lengths of number until failure)
- episodic memory = memory of events in a narrative context, where and when they happened, etc
- psychomotor speed = the speed of connection between perception and reaction in quick-response tests
These are, of course, all useful things to have, which means the general advice here is to:
- move more, generally
- exercise more, specifically
- sit less, whenever reasonably possible
- sleep well
You can read the study itself here:
Want to know the best kind of exercise for brain health?
Check out our article about neuroscientist Dr. Suzuki, and what she has to say about it:
The Exercise That Protects Your Brain
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Avoid Self-Hatred & Learn To Love Oneself More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Alain de Botton gives a compassionate, but realistic, explanation in this video:
The enemy within
Or rather, the collaborator within. Because there’s usually first an enemy without—those who are critical of us, who consider that we are bad people in some fashion, and may indeed get quite colorful in their expressions of this.
Sometimes, their words will bounce straight off us; sometimes, their words will stick. So what’s the difference, and can we do anything about it?
The difference is: when their words stick, it’s usually because on some level we believe their words may be true. That doesn’t mean they necessarily are true!
They could be (and it would be a special kind of hubris to assume no detractor could ever find a valid criticism of us), but very often the reason we have that belief, or at least that fear/insecurity, is simply because it was taught to us at an early age, often by harsh words/actions of those around us; perhaps our parents, perhaps our schoolteachers, perhaps our classmates, and so forth.
The problem—and solution—is that we learn emotions much the same way that we learn language; only in part by reasoned thought, and rather for the most part, by immersion and repetition.
It can take a lot of conscious self-talk to undo the harm of decades of unconscious self-talk based on what was probably a few years of external criticisms when we were small and very impressionable… But, having missed the opportunity to start fixing this sooner, the next best time to do it is now.
We cannot, of course, simply do what a kind friend might do and expect any better results; if a kind friend tells us something nice that we do not believe is true, then however much they mean it, we’re not going to internalize it. So instead, we must simply chip away at those unhelpful longstanding counterproductive beliefs, and simply build up the habit of viewing ourselves in a kinder light.
For more on all this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Escape From The Clutches Of Shame
- To Err Is Human; To Forgive, Healthy
- How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Brazil Nuts vs Hazelnuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Brazil nuts to hazelnuts, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
In terms of macros, Brazil nuts have more fats (including more omega-3, and/but also including more saturated fat) while hazelnuts have more fiber, carbs, and protein. So, which one wins this round is a little subjective; we’d say it’s the fiber for hazelnuts that cinch it, but we could also reasonably declare this round a tie.
In the category of vitamins, Brazil nuts are not higher in any vitamins, while hazelnuts are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline. And the margins of difference are large in most cases. An easy win for hazelnuts here.
When it comes to minerals, things get interesting: Brazil nuts have more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and selenium, while hazelnuts have more iron, manganese, and potassium, but!
Before we crown Brazil nuts with a 4:3 win in this category, though, let’s take a closer look at those selenium levels:
- A cup of hazelnuts contains 13% of the RDA of selenium. Your hair will be luscious and shiny.
- A cup of Brazil nuts contains 10,456% of the RDA of selenium. This is way past the point of selenium toxicity, and your (luscious, shiny) hair will fall out.
For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
We consider that a point against Brazil nuts.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall win for hazelnuts, but by all means enjoy either or both, we just recommend to practise moderation when it comes to the Brazil nuts!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Some women’s breasts can’t make enough milk, and the effects can be devastating
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many new mothers worry about their milk supply. For some, support from a breastfeeding counsellor or lactation consultant helps.
Others cannot make enough milk no matter how hard they try. These are women whose breasts are not physically capable of producing enough milk.
Our recently published research gives us clues about breast features that might make it difficult for some women to produce enough milk. Another of our studies shows the devastating consequences for women who dream of breastfeeding but find they cannot.
Some breasts just don’t develop
Unlike other organs, breasts are not fully developed at birth. There are key developmental stages as an embryo, then again during puberty and pregnancy.
At birth, the breast consists of a simple network of ducts. Usually during puberty, the glandular (milk-making) tissue part of the breast begins to develop and the ductal network expands. Then typically, further growth of the ductal network and glandular tissue during pregnancy prepares the breast for lactation.
But our online survey of women who report low milk supply gives us clues to anomalies in how some women’s breasts develop.
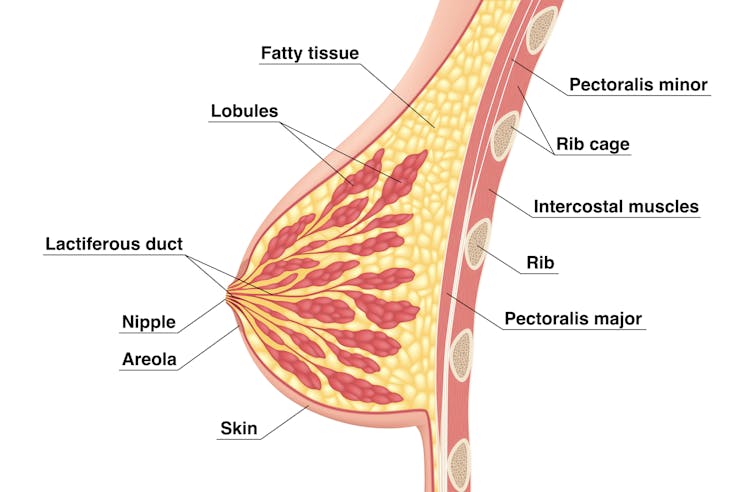
We’re not talking about women with small breasts, but women whose glandular tissue (shown in this diagram as “lobules”) is underdeveloped and have a condition called breast hypoplasia.
Sometimes not enough glandular tissue, shown here as lobules, develop.
Tsuyna/ShutterstockWe don’t know how common this is. But it has been linked with lower rates of exclusive breastfeeding.
We also don’t know what causes it, with much of the research conducted in animals and not humans.
However, certain health conditions have been associated with it, including polycystic ovary syndrome and other endocrine (hormonal) conditions. A high body-mass index around the time of puberty may be another indicator.
Could I have breast hypoplasia?
Our survey and other research give clues about who may have breast hypoplasia.
But it’s important to note these characteristics are indicators and do not mean women exhibiting them will definitely be unable to exclusively breastfeed.
Indicators include:
- a wider than usual gap between the breasts
- tubular-shaped (rather than round) breasts
- asymmetric breasts (where the breasts are different sizes or shapes)
- lack of breast growth in pregnancy
- a delay in or absence of breast fullness in the days after giving birth
In our survey, 72% of women with low milk supply had breasts that did not change appearance during pregnancy, and about 70% reported at least one irregular-shaped breast.
The effects
Mothers with low milk supply – whether or not they have breast hyoplasia or some other condition that limits their ability to produce enough milk – report a range of emotions.
Research, including our own, shows this ranges from frustration, confusion and surprise to intense or profound feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair.
Some mothers describe “breastfeeding grief” – a prolonged sense of loss or failure, due to being unable to connect with and nourish their baby through breastfeeding in the way they had hoped.
These feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair can trigger symptoms of anxiety and depression for some women.
Feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair were common.
Bricolage/ShutterstockOne woman told us:
[I became] so angry and upset with my body for not being able to produce enough milk.
Many women’s emotions intensified when they discovered that despite all their hard work, they were still unable to breastfeed their babies as planned. A few women described reaching their “breaking point”, and their experience felt “like death”, “the worst day of [my] life” or “hell”.
One participant told us:
I finally learned that ‘all women make enough milk’ was a lie. No amount of education or determination would make my breasts work. I felt deceived and let down by all my medical providers. How dare they have no answers for me when I desperately just wanted to feed my child naturally.
Others told us how they learned to accept their situation. Some women said they were relieved their infant was “finally satisfied” when they began supplementing with formula. One resolved to:
prioritise time with [my] baby over pumping for such little amounts.
Where to go for help
If you are struggling with low milk supply, it can help to see a lactation consultant for support and to determine the possible cause.
This will involve helping you try different strategies, such as optimising positioning and attachment during breastfeeding, or breastfeeding/expressing more frequently. You may need to consider taking a medication, such as domperidone, to see if your supply increases.
If these strategies do not help, there may be an underlying reason why you can’t make enough milk, such as insufficient glandular tissue (a confirmed inability to make a full supply due to breast hypoplasia).
Even if you have breast hypoplasia, you can still breastfeed by giving your baby extra milk (donor milk or formula) via a bottle or using a supplementer (which involves delivering milk at the breast via a tube linked to a bottle).
More resources
The following websites offer further information and support:
- Australian Breastfeeding Association
- Lactation Consultants of Australia and New Zealand
- Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne
- Supply Line Breastfeeders Support Group of Australia Facebook support group
- IGT And Low Milk Supply Support Group Facebook support group
- Breastfeeding Medicine Network Australia/New Zealand
- Supporting breastfeeding grief (a collection of resources).
Shannon Bennetts, a research fellow at La Trobe University, contributed to this article.
Renee Kam, PhD candidate and research officer, La Trobe University and Lisa Amir, Professor in Breastfeeding Research, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: