Basic Baked Tofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One of the main criticisms of tofu is that it is tasteless. Well, so is flour, but you’re not supposed to eat it plain, and the same goes for tofu. It’s a blank canvas that you get to decide what to do with—not to mention, it’s a canvas that’s very high in protein, and is a complete protein too, containing all essential amino acids. Anyway, here’s a starter recipe that elevates tofu from “nutrition” to “nutritious tasty snack”!
We were going to do a fancier recipe today, but considered that it might be judicious to cover this basic element first, that can be incorporated into a larger recipe later, a bit like we have done with recipes such as our Tasty Versatile Rice, and Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese (amongst others).
You will need
- 1 block of extra-firm tofu; these are quite standardized in size; it should be about 12oz; don’t worry if it’s a little more or less.
- 2 tbsp arrowroot powder (or potato starch if you don’t have arrowroot)
- 1½ tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: ½ tsp garlic powder
- Optional: ½ tsp ground turmeric
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 425ºF / 220ºC.
2) Press the tofu for about 15 minutes (to remove excess moisture), using a tofu press if you have one. If you don’t, then here is an example product on Amazon, or alternatively, you can go with the time-honored tradition of cutting the tofu lengthways into slabs, and wrapping it in a lint-free kitchen towel or muslin cloth, and pressing it with heavy books. We don’t recommend pressing for more than about 15 minutes, as you are going to bake the tofu so you don’t want it too dry going in.
3) Cut the tofu into cubes. Size is up to you, but half-inch cubes are very respectable.
4) Combine the tofu cubes in a big bowl with the oil and seasonings, including the nutritional yeast but not the arrowroot powder or potato starch yet. You will need to toss them gently (very gently; they are fragile!) to combine.
5) Add the arrowroot powder or potato starch, and again toss gently to combine. We do this last, because it would stop the other things from sticking properly if we did it earlier.
6) Arrange the tofu on a baking tray lined with baking paper, in a single layer so that the cubes don’t touch. Bake for 15 minutes, turn them over, and bake for a further 15 minutes on the other side. They should now be golden and crisp, but if they’re not, just give them a little more time.
7) Serve as a snack, or set aside for whatever else you’re going to do with them in a larger more complex recipe.
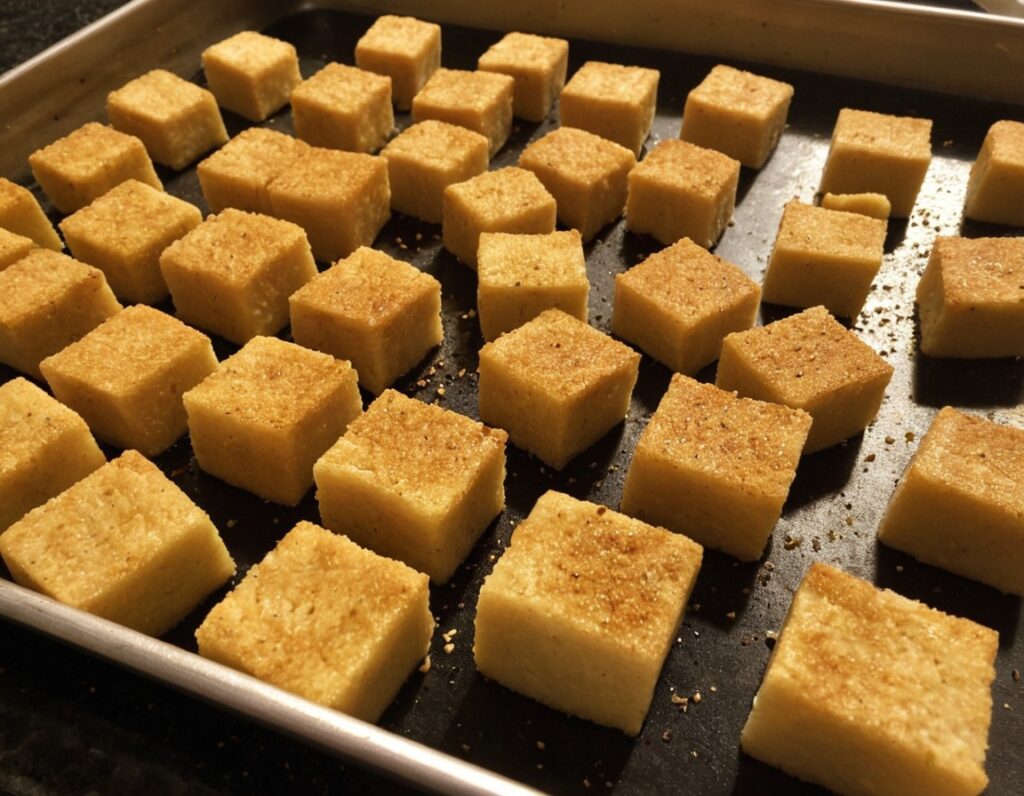

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
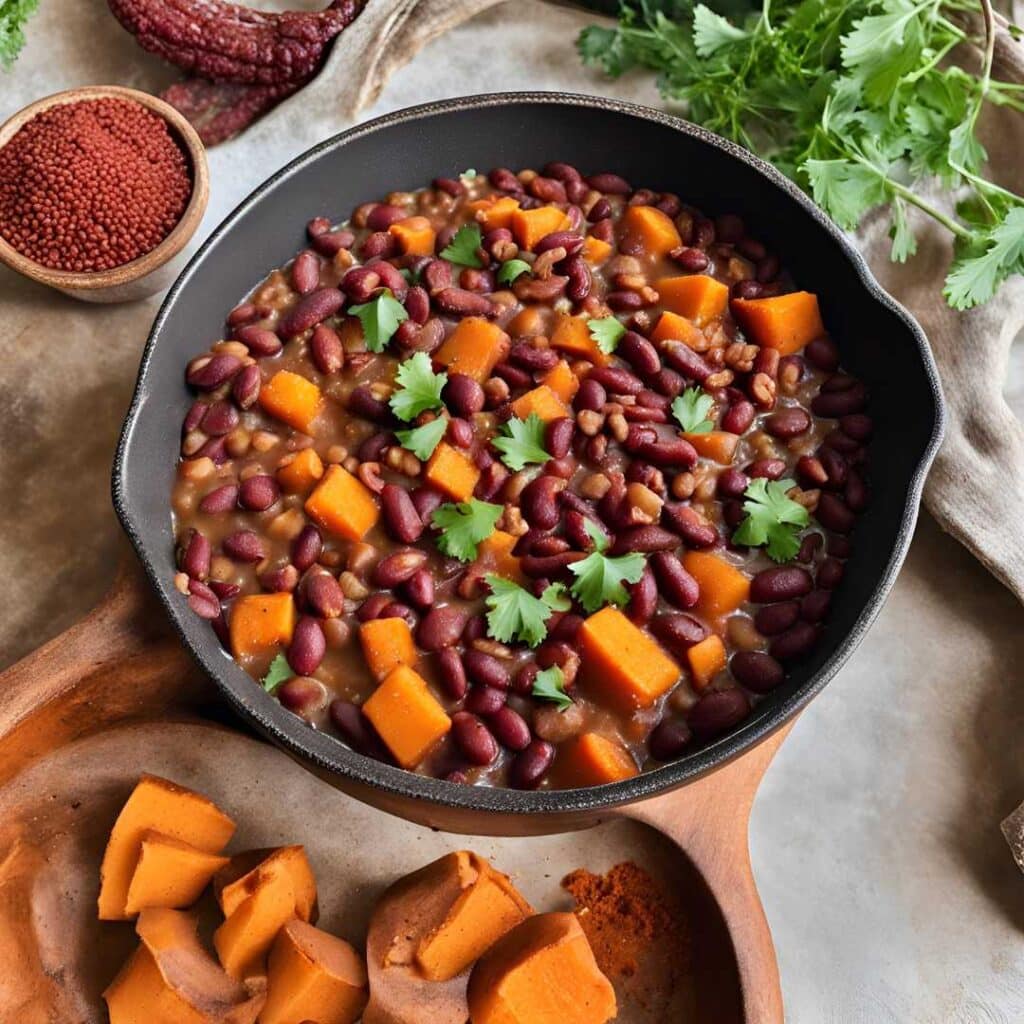
Ghanaian Red Bean & Sweet Potato Groundnut Stew
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a dish popular in principle throughout West Africa. We say “in principle” because that’s a big place, and there is a lot of regional variation. The archetypal peanut stew is from Senegal (as maafe) or Mali (as tigadèguèna), but for its more balanced nutritional profile we’ve chosen one from Ghana—and since there are regional variations within Ghana too, we should specify that this one is from the south.
If you are allergic to nuts, you can substitute a seed butter (or tahini) for the nut butter, and omit the nuts—this will work in culinary terms and be fine healthwise, but we can’t claim it would be the same dish, having lost its defining ingredient. If your allergy is solely to peanuts, then substituting with any oily nut would work. So, not almonds for example, but cashews or even walnuts would be fine.
You will need
- 1½ lbs sweet potatoes, peeled and cut into ½” cubes
- 2 cups low-sodium vegetable stock
- 2 cans kidney beans, drained, cooked, and rinsed (or 2 cups same; cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- 1 can chopped tomatoes
- ½ cup unsalted dry-roasted peanuts
- 1 onion, chopped
- 1 red bell pepper, deseeded and chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 heaped tbsp unsalted peanut butter, minimal (ideally: no) additives
- 2 tsp white miso paste
- 2 tsp grated fresh ginger
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp cayenne pepper
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- ½ tsp coarsely ground nigella seeds
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a sauté pan, or other pan suitable for both frying and fitting the entire stew in. Fry the onions until softened, turn the heat down low, and add the garlic, ginger, red bell pepper, cumin, cayenne, black pepper, and MSG/salt.
2) Add ¼ cup of the vegetable stock, and the sweet potato, and turn the heat back up, on high for about 30 seconds to get it to temperature, and then take it down to a simmer.
3) Stir in the miso paste and chopped tomatoes.
4) Add most of the rest of the vegetable stock, keeping ¼ cup aside. Simmer for about 20 minutes.
5) Stir in the kidney beans, and simmer for about 30 minutes more—the sweet potato should be soft now; if it isn’t, let it simmer a while longer until it is.
6) Combine the peanut butter with the remaining ¼ cup vegetable stock, and blend until smooth. Stir it into the stew.
7) If the stew is looking more like a soup than a stew, take out 1 cup and blend this 1 cup to a purée, adding it back in.
8) Add half the peanuts unto the stew. Taste, and adjust the seasonings if necessary.
9) Crush the remaining peanuts using a pestle and mortar; not too much though; you want them broken into bits, not pulverised.
10) Garnish with the crushed nuts and nigella seeds, and serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we used 4/5 today!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mythbusting Protein!
Yesterday, we asked you for your policy on protein consumption. The distribution of responses was as follows:
- A marginal majority (about 55%) voted for “Protein is very important, but we can eat too much of it”
- A large minority (about 35%) voted for “We need lots of protein; the more, the better!”
- A handful (about 4%) voted for “We should go as light on protein as possible”
- A handful (6%) voted for “If we don’t eat protein, our body will create it from other foods”
So, what does the science say?
If we don’t eat protein, our body will create it from other foods: True or False?
Contingently True on an absurd technicality, but for all practical purposes False.
Our body requires 20 amino acids (the building blocks of protein), 9 of which it can’t synthesize and absolutely must get from food. Normally, we get those amino acids from protein in our diet, and we can also supplement them by buying amino acid supplements.
Specifically, we require (per kg of bodyweight) a daily average of:
- Histidine: 10 mg
- Isoleucine: 20 mg
- Leucine: 39 mg
- Lysine: 30 mg
- Methionine: 10.4 mg
- Phenylalanine*: 25 mg
- Threonine: 15 mg
- Tryptophan: 4 mg
- Valine: 26 mg
*combined with the non-essential amino acid tyrosine
Source: Protein and Amino Acid Requirements In Human Nutrition: WHO Technical Report
However, to get the requisite amino acid amounts, without consuming actual protein, would require gargantuan amounts of supplementation (bearing in mind bioavailability will never be 100%, so you’ll always need to take more than it seems), using supplements that will have been made by breaking down proteins anyway.
So unless you live in a laboratory and have access to endless amounts of all of the required amino acids (you can’t miss even one; you will die), and are willing to do that for the sake of proving a point, then you do really need to eat protein.
Your body cannot, for example, simply break down sugar and use it to make the protein you need.
On another technical note… Do bear in mind that many foods that we don’t necessarily think of as being sources of protein, are sources of protein.
Grains and grain products, for example, all contain protein; we just don’t think of them as that because their macronutritional profile is heavily weighted towards carbohydrates.
For that matter, even celery contains protein. How much, you may ask? Almost none! But if something has DNA, it has protein. Which means all plants and animals (at least in their unrefined forms).
So again, to even try to live without protein would very much require living in a laboratory.
We can eat too much protein: True or False?
True. First on an easy technicality; anything in excess is toxic. Even water, or oxygen. But also, in practical terms, there is such a thing as too much protein. The bar is quite high, though:
❝Based on short-term nitrogen balance studies, the Recommended Dietary Allowance of protein for a healthy adult with minimal physical activity is currently 0.8 g protein per kg bodyweight per day❞
❝To meet the functional needs such as promoting skeletal-muscle protein accretion and physical strength, dietary intake of 1.0, 1.3, and 1.6 g protein per kg bodyweight per day is recommended for individuals with minimal, moderate, and intense physical activity, respectively❞
❝Long-term consumption of protein at 2 g per kg bodyweight per day is safe for healthy adults, and the tolerable upper limit is 3.5 g per kg bodyweight per day for well-adapted subjects❞
❝Chronic high protein intake (>2 g per kg bodyweight per day for adults) may result in digestive, renal, and vascular abnormalities and should be avoided❞
Source: Dietary protein intake and human health
To put this into perspective, if you weigh about 160lbs (about 72kg), this would mean eating more than 144g protein per day, which grabbing a calculator means about 560g of lean beef, or 20oz, or 1¼lb.
If you’re eating quarter-pounder burgers though, that’s not usually so lean, so you’d need to eat more than nine quarter-pounder burgers per day to get too much protein.
High protein intake damages the kidneys: True or False?
True if you have kidney damage already; False if you are healthy. See for example:
- Effects of dietary protein restriction on the progression of advanced renal disease in the modification of diet in renal disease study
- A high protein diet has no harmful effects: a one-year crossover study in healthy male athletes
High protein intake increases cancer risk: True or False?
True or False depending on the source of the protein, so functionally false:
- Eating protein from red meat sources has been associated with higher risk for many cancers
- Eating protein from other sources has been associated with lower risk for many cancers
Source: Red Meat Consumption and Mortality Results From 2 Prospective Cohort Studies
High protein intake increase risk of heart disease: True or False?
True or False depending on the source of the protein, so, functionally false:
- Eating protein from red meat sources has been associated with higher risk of heart disease
- Eating protein from other sources has been associated with lower risk of heart disease
Source: Major Dietary Protein Sources and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Women
In summary…
Getting a good amount of good quality protein is important to health.
One can get too much, but one would have to go to extremes to do so.
The source of protein matters:
- Red meat is associated with many health risks, but that’s not necessarily the protein’s fault.
- Getting plenty of protein from (ideally: unprocessed) sources such as poultry, fish, and/or plants, is critical to good health.
- Consuming “whole proteins” (that contain all 9 amino acids that we can’t synthesize) are best.
Learn more: Complete proteins vs. incomplete proteins (explanation and examples)
Share This Post
-
HBD: The Human Being Diet – by Petronella Ravenshear
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We don’t often review diet books, so why did this one catch our attention? The answer lies in its comprehensive nature without being excessively long and complex.
Ravenshear (a nutritionist) brings a focus on metabolic balance, and what will and won’t work for keeping it healthy.
The first part of the book is mostly informational; covering such things as blood sugar balance, gut health, hormones, and circadian rhythm considerations, amongst others.
The second, larger part of the book is mostly instructional; do this and that, don’t do the other, guidelines on quantities and timings, and what things may be different for some people, and what to do about those.
The style is conversational and light, but well-grounded in good science.
Bottom line: if you’d like a “one-stop shop” for giving your diet an overhaul, this book is a fine choice.
Click here to check out the Human Being Diet, and enjoy the best of health!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Most adults will gain half a kilo this year – and every year. Here’s how to stop ‘weight creep’
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we enter a new year armed with resolutions to improve our lives, there’s a good chance we’ll also be carrying something less helpful: extra kilos. At least half a kilogram, to be precise.
“Weight creep” doesn’t have to be inevitable. Here’s what’s behind this sneaky annual occurrence and some practical steps to prevent it.
Allgo/Unsplash Small gains add up
Adults tend to gain weight progressively as they age and typically gain an average of 0.5 to 1kg every year.
While this doesn’t seem like much each year, it amounts to 5kg over a decade. The slow-but-steady nature of weight creep is why many of us won’t notice the extra weight gained until we’re in our fifties.
Why do we gain weight?
Subtle, gradual lifestyle shifts as we progress through life and age-related biological changes cause us to gain weight. Our:
- activity levels decline. Longer work hours and family commitments can see us become more sedentary and have less time for exercise, which means we burn fewer calories
- diets worsen. With frenetic work and family schedules, we sometimes turn to pre-packaged and fast foods. These processed and discretionary foods are loaded with hidden sugars, salts and unhealthy fats. A better financial position later in life can also result in more dining out, which is associated with a higher total energy intake
- sleep decreases. Busy lives and screen use can mean we don’t get enough sleep. This disturbs our body’s energy balance, increasing our feelings of hunger, triggering cravings and decreasing our energy
Insufficient sleep can increase our appetite. Craig Adderley/Pexels - stress increases. Financial, relationship and work-related stress increases our body’s production of cortisol, triggering food cravings and promoting fat storage
- metabolism slows. Around the age of 40, our muscle mass naturally declines, and our body fat starts increasing. Muscle mass helps determine our metabolic rate, so when our muscle mass decreases, our bodies start to burn fewer calories at rest.
We also tend to gain a small amount of weight during festive periods – times filled with calorie-rich foods and drinks, when exercise and sleep are often overlooked. One study of Australian adults found participants gained 0.5 kilograms on average over the Christmas/New Year period and an average of 0.25 kilograms around Easter.
Why we need to prevent weight creep
It’s important to prevent weight creep for two key reasons:
1. Weight creep resets our body’s set point
Set-point theory suggests we each have a predetermined weight or set point. Our body works to keep our weight around this set point, adjusting our biological systems to regulate how much we eat, how we store fat and expend energy.
When we gain weight, our set point resets to the new, higher weight. Our body adapts to protect this new weight, making it challenging to lose the weight we’ve gained.
But it’s also possible to lower your set point if you lose weight gradually and with an interval weight loss approach. Specifically, losing weight in small manageable chunks you can sustain – periods of weight loss, followed by periods of weight maintenance, and so on, until you achieve your goal weight.
Holidays can also come with weight gain. Zan Lazarevic/Unsplash 2. Weight creep can lead to obesity and health issues
Undetected and unmanaged weight creep can result in obesity which can increase our risk of heart disease, strokes, type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis and several types of cancers (including breast, colorectal, oesophageal, kidney, gallbladder, uterine, pancreatic and liver).
A large study examined the link between weight gain from early to middle adulthood and health outcomes later in life, following people for around 15 years. It found those who gained 2.5 to 10kg over this period had an increased incidence of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, strokes, obesity-related cancer and death compared to participants who had maintained a stable weight.
Fortunately, there are steps we can take to build lasting habits that will make weight creep a thing of the past.
7 practical steps to prevent weight creep
1. Eat from big to small
Aim to consume most of your food earlier in the day and taper your meal sizes to ensure dinner is the smallest meal you eat.
A low-calorie or small breakfast leads to increased feelings of hunger, specifically appetite for sweets, across the course of the day.
We burn the calories from a meal 2.5 times more efficiently in the morning than in the evening. So emphasising breakfast over dinner is also good for weight management.
Aim to consume bigger breakfasts and smaller dinners. Michael Burrows/Pexels 2. Use chopsticks, a teaspoon or an oyster fork
Sit at the table for dinner and use different utensils to encourage eating more slowly.
This gives your brain time to recognise and adapt to signals from your stomach telling you you’re full.
3. Eat the full rainbow
Fill your plate with vegetables and fruits of different colours first to support eating a high-fibre, nutrient-dense diet that will keep you feeling full and satisfied.
Meals also need to be balanced and include a source of protein, wholegrain carbohydrates and healthy fat to meet our dietary needs – for example, eggs on wholegrain toast with avocado.
4. Reach for nature first
Retrain your brain to rely on nature’s treats – fresh vegetables, fruit, honey, nuts and seeds. In their natural state, these foods release the same pleasure response in the brain as ultra-processed and fast foods, helping you avoid unnecessary calories, sugar, salt and unhealthy fats.
5. Choose to move
Look for ways to incorporate incidental activity into your daily routine – such as taking the stairs instead of the lift – and boost your exercise by challenging yourself to try a new activity.
Just be sure to include variety, as doing the same activities every day often results in boredom and avoidance.
Try new activities or sports to keep your interest up. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels 6. Prioritise sleep
Set yourself a goal of getting a minimum of seven hours of uninterrupted sleep each night, and help yourself achieve it by avoiding screens for an hour or two before bed.
7. Weigh yourself regularly
Getting into the habit of weighing yourself weekly is a guaranteed way to help avoid the kilos creeping up on us. Aim to weigh yourself on the same day, at the same time and in the same environment each week and use the best quality scales you can afford.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Clinical Trials Director, Department of Endocrinology, RPA Hospital, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How old do you want to be?
We asked you how old you are, and got an interesting spread of answers. This wasn’t too surprising; of course we have a general idea of who our readership is and we write accordingly.
What’s interesting is the gap for “40s”.
And, this wasn’t the case of a broken poll button, it’s something that crops up a lot in health-related sociological research. People who are most interested in taking extra care of their body are often:
- Younger people full of optimism about maintaining this perfectly healthy body forever
- Older people realizing “if I don’t want to suffer avoidable parts of age-related decline, now is the time to address these things”
In between, we often have a gap whereby people no longer have the optimism of youth, but do not yet feel the pressure of older age.
Which is not to say there aren’t 40-somethings who do care! Indeed, we know for a fact we have some subscribers in their 40s (and some in their 90s, too), just, they evidently didn’t vote in this poll.
Anyway, let’s bust some myths…
Aging is inevitable: True or False?
False, probably. That seems like a bold (and fortune-telling) claim, so let’s flip it to deconstruct it more logically:
Aging is, and always will be, unstoppable: True or False?
That has to be “False, probably”. To say “true” now sounds like an even bolder claim. Just like “the moon will always be out of reach”.
- When CPR was first developed, first-aiders were arrested for “interfering with a corpse”.
- Many diseases used to be death sentences that are now “take one of these in the morning”
- If you think this is an appeal to distant history, HIV+ status was a death sentence in the 90s. Now it’s “take one of these in the morning”.
But, this is an appeal to the past, and that’s not always a guarantee of the future. Where does the science stand currently? How is the research and development doing on slowing, halting, reversing aging?
We can slow aging: True or False?
True! There’s a difference between chronological age (i.e., how much time has passed while we’ve been alive) and biological age (i.e., what our diverse markers of aging look like).
Biological age often gets talked about as a simplified number, but it’s more complex than that, as we can age in different ways at different rates, for example:
- Visual markers of aging (e.g. wrinkles, graying hair)
- Performative markers of aging (e.g. mobility tests)
- Internal functional markers of aging (e.g. tests for cognitive decline, eyesight, hearing, etc)
- Cellular markers or aging (e.g. telomere length)
- …and more, but we only have so much room here
There are things we can do to slow most of those, including:
- Good nutrition (e.g. collagen and lutein, to keep specific parts of the body functioning “like those of a younger person” ranging from the joints to the eyes and brain)
- Anti-oxidant activity (e.g. eating anti-oxidant foods, supplementing with anti-oxidants or other things that mitigate oxidative stress, and avoiding foods that hasten oxidative stress which causes many kinds of aging)
- Getting good sleep (not to be underestimated for its restorative importance)
- Taking care of our cognitive health
- Taking care of our mental health (especially: reducing stress)
- Taking care of our mobility (prevention is better than cure!)
In the case of cognitive decline particularly, check out our previous article:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
It’s too early to worry about… / It’s too late to do anything about… True or False?
False and False!
Many things that affect our health later in life are based on early-life choices and events. So it’s important for young people to take advantage of that. The earlier one adopts a healthy lifestyle, the better, because, and hold onto your hats for the shocker here: aging is cumulative.
However, that doesn’t mean that taking up healthy practices (or dropping unhealthy ones) is pointless later in life, even in one’s 70s and beyond!
Read about this and more from the National Institute of Aging:
What Do We Know About Healthy Aging?
We can halt aging: True or False?
False, for now at least. Our bodies are not statues; they are living organisms, constantly rebuilding themselves, constantly changing, every second of every day, for better or for worse. Every healthy or unhealthy choice you make, every beneficial or adverse experience you encounter, affects your body on a cellular level.
Your body never, ever, stops changing for as long as you live.
But…
We can reverse aging: True or False?
True! Contingently and with limitations, for now at least.
Remember what we said about your body constantly rebuilding itself? That goes for making itself better as well as making itself worse.
- If yesterday you couldn’t touch your toes and today you can, congratulations, you just got younger by a biological marker of aging.
- If you stopped drinking/smoking/eating a certain way last year, and this year your skin has fewer wrinkles, congratulations, you got younger by a biological marker of aging.
- If you’ve been exercising and now your heart rate variability and VO2 max are better than last month, congratulations, you got younger by a biological marker aging.
- If you took supplements that reduce and/or mitigate oxidative stress (e.g. resveratrol, CoQ10, l-theanine, etc), and you took up intermittent fasting, and now your telomeres are longer than they were six months ago, congratulations, you got younger by a biological marker of aging.
But those aren’t really being younger, we’ll still die when our time is up: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
Those kinds of things are really being younger, biologically. What else do you think being biologically younger is?
We may indeed die when our time is up, but (unless we suffer fatal accident or incident first) “when our time is up” is something that is decided mostly by the above factors.
Genetics—the closest thing we have to biological “fate”—accounts for only about 25% of our longevity-related health*.
Genes predispose, but they don’t predetermine.
*Read more: Human longevity: Genetics or Lifestyle? It takes two to tango
(from the Journal of Immunity and Ageing)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
HIIT, But Make It HIRT
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This May HIRT A Bit
This is Ingrid Clay. She’s a professional athlete, personal trainer, chef*, and science writer.
*A vegan bodybuilding chef, no less:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
For those who prefer reading…
This writer does too 😉
We’ve previously reviewed her book, “Science of HIIT”, and we’re going to be talking a bit about High Intensity Interval Training today.
If you’d like to know a little more about the woman herself first, then…
Centr | Meet Ingrid: Your HIIT HIRT trainer
Yes, that is Centr, as in Chris Hemsworth’s personal training app, where Clay is the resident HIIT & HIRT expert & trainer.
What’s this HIIT & HIRT?
“HIIT” is High Intensity Interval Training, which we’ve written about before:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Basically, it’s a super-efficient way of working out, that gets better results than working out for longer with other methods, especially because of how it raises the metabolism for a couple of hours after training (this effect is called EPOC, by the way—Excessive Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption), and is a good thing.
You can read more about the science of it, in the above-linked main feature.
And HIRT?
“HIRT” is High Intensity Resistance Training, and is resistance training performed with HIIT principles.
See also: Chris Hemsworth’s Trainer Ingrid Clay Explains HIRT
An example is doing 10 reps of a resistance exercise (e.g., a dumbbell press) every minute on odd-numbered minutes, and 10 reps of a different resistance exercise (e.g. dumbbell squats) on even-numbered minutes.
If dumbbells aren’t your thing, it could be resistance bands, or even the floor (press-ups are a resistance exercise!)
For HIRT that’s not also a cardio exercise, gaps between different exercises can be quite minimal, as we only need to confuse the muscles, not the heart. So, effectively, it becomes a specially focused kind of circuit training!
If doing planks though, you might want to check out Clay’s troubleshooting guide:
Want more from Clay?
Here she gives a full 20-minute full-body HIIT HIRT workout:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: