Train For The Event Of Your Life!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mobility As A Sporting Pursuit
As we get older, it becomes increasingly important to treat life like a sporting event. By this we mean:
As an “athlete of life”, there are always events coming up for which we need to train. Many of these events will be surprise tests!
Such events/tests might include:
- Not slipping in the shower and breaking a hip (or worse)
- Reaching an item from a high shelf without tearing a ligament
- Getting out of the car at an awkward angle without popping a vertebra
- Climbing stairs without passing out light-headed at the top
- Descending stairs without making it a sled-ride-without-a-sled
…and many more.
Train for these athletic events now
Not necessarily this very second; we appreciate you finishing reading first. But, now generally in your life, not after the first time you fail such a test; it can (and if we’re not attentive: will) indeed happen to us all.
With regard to falling, you might like to revisit our…
…which covers how to not fall, and to not injure yourself if you do.
You’ll also want to be able to keep control of your legs (without them buckling) all the way between standing and being on the ground.
Slav squats or sitting squats (same exercise, different names, amongst others) are great for building and maintaining this kind of strength and suppleness:
(Click here for a refresher if you haven’t recently seen Zuzka’s excellent video explaining how to do this, especially if it’s initially difficult for you, “The Most Anti-Aging Exercise”)
this exercise is, by the way, great for pretty much everything below the waist!
You will also want to do resistance exercises to keep your body robust:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And as for those shoulders? If it is convenient for you to go swimming, then backstroke is awesome for increasing and maintaining shoulder mobility (and strength).
If swimming isn’t a viable option for you, then doing the same motion with your arms, while standing, will build the same flexibility. If you do it while holding a small weight (even just 1kg is fine, but feel free to increase if you so wish and safely can) in each hand will build the necessary strength as you go too.
As for why even just 1kg is fine: read on
About that “and strength”, by the way…
Stretching is not everything. Stretching is great, but mobility without strength (in that joint!) is just asking for dislocation.
You don’t have to be built like the Terminator, but you do need to have the structural integrity to move your body and then a little bit more weight than that (or else any extra physical work could be enough to tip you to breaking point) without incurring damage from the strain. So, it needs to not be a strain! See again, the aforementioned resistance exercises.
That said, even very gentle exercise helps too; see for example the impact of walking on osteoporosis:
Living near green spaces linked to higher bone density and lower osteoporosis risk
and…
So you don’t have to run marathons—although you can if you want:
Marathons in Mid- and Later-Life
…to keep your hips and more in good order.
Want to test yourself now?
Check out:
Building & Maintaining Mobility
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ice Cream vs Fruit Sorbet – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing ice cream to fruit sorbet, we picked the ice cream.
Why?
Well, neither are great!
But the deciding factor is simple: ice cream has more nutrients to go with its sugar.
While “fruit is good” is a very reliable truism in and of itself, sorbet tends to be made with fruit juice (or at best, purée, which for these purposes is more or less the same) and sugar. The small vitamin content is nowhere near enough to make up for this. The fiber having been removed by juicing or puréeing, the fruit juice with added sugar is basically shooting glucose and fructose into your veins while doing little else.
Fruit juice (even freshly-pressed) is nowhere near in the same league of healthiness as actual fruit!
See also: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Ice cream, meanwhile, is also not exactly a health food. But it has at least some minerals worth speaking of (mostly: calcium, potassium, phosphorus), and some fat that a) can be used b) helps slightly slow the absorption of the sugars.
In short: please do not consider either of these things to be a health food. But if you’re going to choose one or the other (and are not lactose-intolerant), then ice cream has some small positives to go with its negatives.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Hazelnuts vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hazelnuts to cashews, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
It’s close! This one’s interesting…
In terms of macros, hazelnuts have more fiber and fats, while cashews have more protein and carbs. All in all, all good stuff all around; maybe a win for one or the other depending on your priorities. We’d pick hazelnuts here, but your preference may vary.
When it comes to vitamins, hazelnuts have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and E, while cashews have more vitamin K. An easy win for hazelnuts here, and the margins weren’t close.
In the category of minerals, hazelnuts have more calcium, manganese, and potassium, while cashews have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. This is a win for cashews, but it’s worth noting that cup for cup, both of these nuts provide more than the daily requirement of most of those minerals. This means that in practical terms, it doesn’t matter too much that (for example), while cashews provide 732% of the daily requirement for copper, hazelnuts “only” provide 575%. So while this category remains a victory for cashews, it’s something of a “on paper” thing for the most part.
Adding up the sections (ambivalent + clear win for hazelnuts + nominal win for cashews) means that in total today we’re calling it in favour of hazelnuts… But as ever, enjoy both, because both are good and so is diversity!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
CBD Against Diabetes!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝CBD for diabetes! I’ve taken CBD for body pain. Did no good. Didn’t pay attention as to diabetes. I’m type 1 for 62 years. Any ideas?❞
Thanks for asking! First up, for reference, here’s our previous main feature on the topic of CBD:
CBD Oil: What Does The Science Say?
There, we touched on CBD’s effects re diabetes:
in mice / in vitro / in humans
In summary, according to the above studies, it…
- lowered incidence of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. By this they mean that pancreatic function improved (reduced insulitis and reduced inflammatory Th1-associated cytokine production). Obviously this has strong implications for Type 1 Diabetes in humans—but so far, just that, implications (because you are not a mouse).
- attenuated high glucose-induced endothelial cell inflammatory response and barrier disruption. Again, this is promising, but it was an in vitro study in very controlled lab conditions, and sometimes “what happens in the Petri dish, stays in the Petri dish”—in order words, these results may or may not translate to actual living humans.
- Improved insulin response ← is the main take-away that we got from reading through their numerical results, since there was no convenient conclusion given. Superficially, this may be of more interest to those with type 2 diabetes, but then again, if you have T1D and then acquire insulin resistance on top of that, you stand a good chance of dying on account of your exogenous insulin no longer working. In the case of T2D, “the pancreas will provide” (more or less), T1D, not so much.
So, what else is there out there?
The American Diabetes Association does not give a glowing review:
❝There’s a lot of hype surrounding CBD oil and diabetes. There is no noticeable effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers continue to study the effects of CBD on diabetes in animal studies. ❞
~ American Diabetes Association
Source: ADA | CBD & Diabetes
Of course, that’s type 2, but most research out there is for type 2, or else have been in vitro or rodent studies (and not many of those, at that).
Here’s a relatively more recent study that echoes the results of the previous mouse study we mentioned; it found:
❝CBD-treated non-obese diabetic mice developed T1D later and showed significantly reduced leukocyte activation and increased FCD in the pancreatic microcirculation.
Conclusions: Experimental CBD treatment reduced markers of inflammation in the microcirculation of the pancreas studied by intravital microscopy. ❞
~ Dr. Christian Lehmann et al.
Read more: Experimental cannabidiol treatment reduces early pancreatic inflammation in type 1 diabetes
…and here’s a 2020 study (so, more recent again) that was this time rats, and/but still more promising, insofar as it was with rats that had full-blown T1D already:
Read in full: Two-weeks treatment with cannabidiol improves biophysical and behavioral deficits associated with experimental type-1 diabetes
Finally, a paper in July 2023 (so, since our previous article about CBD), looked at the benefits of CBD against diabetes-related complications (so, applicable to most people with any kind of diabetes), and concluded:
❝CBDis of great value in the treatment of diabetes and its complications. CBD can improve pancreatic islet function, reduce pancreatic inflammation and improve insulin resistance. For diabetic complications, CBD not only has a preventive effect but also has a therapeutic value for existing diabetic complications and improves the function of target organs❞
…before continuing:
❝However, the safety and effectiveness of CBD are still needed to prove. It should be acknowledged that the clinical application of CBD in the treatment of diabetes and its complications has a long way to go.
The dissecting of the pharmacology and therapeutic role of CBD in diabetes would guide the future development of CBD-based therapeutics for treating diabetes and diabetic complications❞
~ Ibid.
Now, the first part of that is standard ass-covering, and the second part of that is standard “please fund more studies please”. Nevertheless, we must also not fail to take heed—little is guaranteed, especially when it comes to an area of research where the science is still very young.
In summary…
It seems well worth a try, and with ostensibly nothing to lose except the financial cost of the CBD.
If you do, you might want to keep careful track of a) your usual diabetes metrics (blood sugar levels before and after meals, insulin taken), and b) when you took CBD, what dose, etc, so you can do some citizen science here.
Lastly: please remember our standard disclaimer; we are not doctors, let alone your doctors, so please do check with your endocrinologist before undertaking any such changes!
Want to read more?
You might like our previous main feature:
How To Prevent And Reverse Type 2 Diabetes ← obviously this will not prevent or reverse Type 1 Diabetes, but avoiding insulin resistance is good in any case!
If you’re not diabetic and you’ve perhaps been confused throughout this article, then firstly thank you for your patience, and secondly you might like this quick primer:
The Sweet Truth About Diabetes: Debunking Diabetes Myths! ← this gives a simplified but fair overview of types 1 & 2
(for space, we didn’t cover the much less common types 3 & 4; perhaps another time we will)
Meanwhile, take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How light tells you when to sleep, focus and poo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
Exposure to light is crucial for our physical and mental health, as this and future articles in the series will show.
But the timing of that light exposure is also crucial. This tells our body to wake up in the morning, when to poo and the time of day to best focus or be alert. When we’re exposed to light also controls our body temperature, blood pressure and even chemical reactions in our body.
But how does our body know when it’s time to do all this? And what’s light got to do with it?
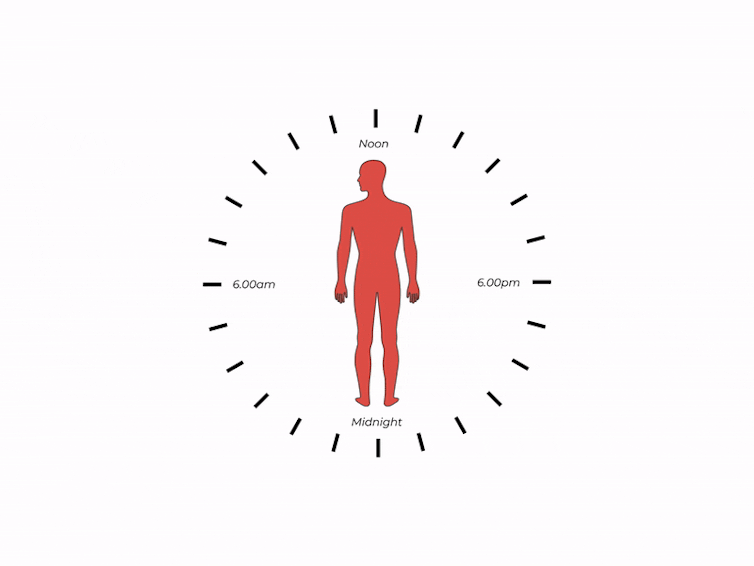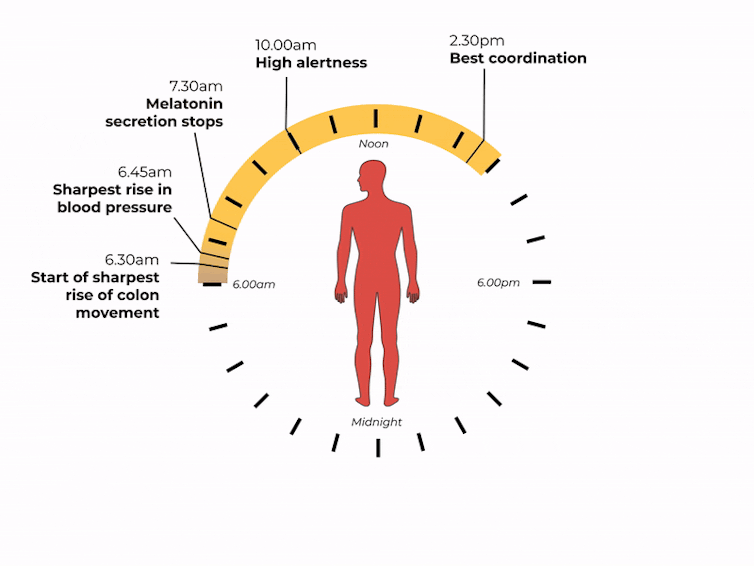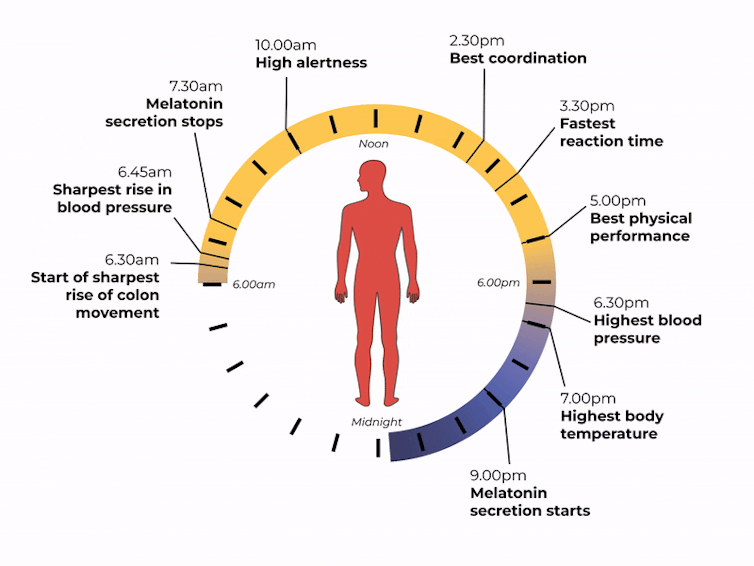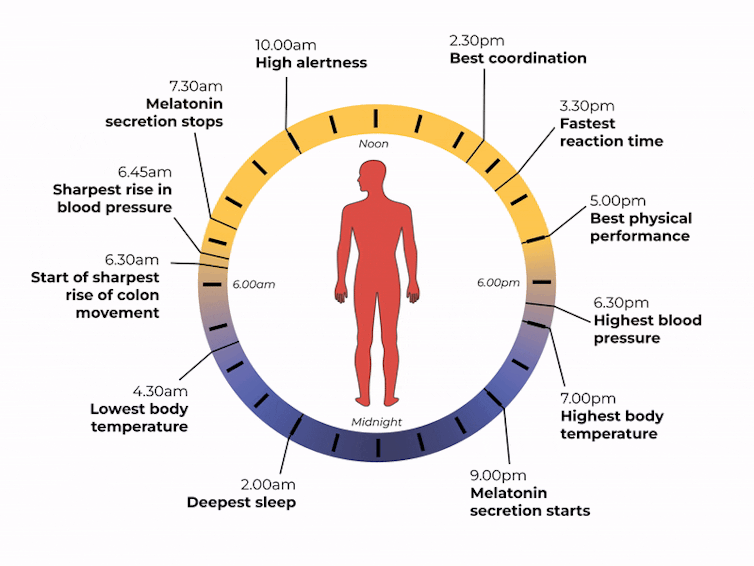
nymphoenix/Shutterstock What is the body clock, actually?
One of the key roles of light is to re-set our body clock, also known as the circadian clock. This works like an internal oscillator, similar to an actual clock, ticking away as you read this article.
But rather than ticking you can hear, the body clock is a network of genes and proteins that regulate each other. This network sends signals to organs via hormones and the nervous system. These complex loops of interactions and communications have a rhythm of about 24 hours.
In fact, we don’t have one clock, we have trillions of body clocks throughout the body. The central clock is in the hypothalamus region of the brain, and each cell in every organ has its own. These clocks work in concert to help us adapt to the daily cycle of light and dark, aligning our body’s functions with the time of day.
However, our body clock is not precise and works to a rhythm of about 24 hours (24 hours 30 minutes on average). So every morning, the central clock needs to be reset, signalling the start of a new day. This is why light is so important.
The central clock is directly connected to light-sensing cells in our retinas (the back of the eye). This daily re-setting of the body clock with morning light is essential for ensuring our body works well, in sync with our environment.
In parallel, when we eat food also plays a role in re-setting the body clock, but this time the clock in organs other than the brain, such as the liver, kidneys or the gut.
So it’s easy to see how our daily routines are closely linked with our body clocks. And in turn, our body clocks shape how our body works at set times of the day.
What time of day?
Matt Garrow/The Conversation. Adapted from Delos, CC BY Let’s take a closer look at sleep
The naturally occurring brain hormone melatonin is linked to our central clock and makes us feel sleepy at certain times of day. When it’s light, our body stops making melatonin (its production is inhibited) and we are alert. Closer to bedtime, the hormone is made, then secreted, making us feel drowsy.
Our sleep is also partly controlled by our genes, which are part of our central clock. These genes influence our chronotype – whether we are a “lark” (early riser), “night owl” (late sleeper) or a “dove” (somewhere in between).
But exposure to light at night when we are supposed to be sleeping can have harmful effects. Even dim light from light pollution can impair our heart rate and how we metabolise sugar (glucose), may lead to psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder, and increases the overall risk of premature death.
The main reason for these harmful effects is that light “at the wrong time” disturbs the body clock, and these effects are more pronounced for “night owls”.
This “misaligned” exposure to light is also connected to the detrimental health effects we often see in people who work night shifts, such as an increased risk of cancer, diabetes and heart disease.
How about the gut?
Digestion also follows a circadian rhythm. Muscles in the colon that help move waste are more active during the day and slow down at night.
The most significant increase in colon movement starts at 6.30am. This is one of the reasons why most people feel the urge to poo in the early morning rather than at night.
The gut’s day-night rhythm is a direct result of the action of the gut’s own clock and the central clock (which synchronises the gut with the rest of the body). It’s also influenced by when we eat.
At 6.30am, your gut really begins to get going for the day. Rendra Dria Septia Aji/Shutterstock How about focusing?
Our body clock also helps control our attention and alertness levels by changing how our brain functions at certain times of day. Attention and alertness levels improve in the afternoon and evening but dip during the night and early morning.
Those fluctuations impact performance and can lead to decreased productivity and an increased risk of errors and accidents during the less-alert hours.
So it’s important to perform certain tasks that require our attention at certain times of day. That includes driving. In fact, disruption of the circadian clock at the start of daylight savings – when our body hasn’t had a chance to adapt to the clocks changing – increases the risk of a car accident, particularly in the morning.
What else does our body clock control?
Our body clock influences many other aspects of our biology, including:
- physical performance by controlling the activity of our muscles
- blood pressure by controlling the system of hormones involved in regulating our blood volume and blood vessels
- body temperature by controlling our metabolism and our level of physical activity
- how our body handles drugs and toxins by controlling enzymes involved in how the liver and kidneys eliminate these substances from the body.
If you can, avoid driving long distances at night, as you’ll be less alert. trendobjects/Shutterstock Morning light is important
But what does this all mean for us? Exposure to light, especially in the morning, is crucial for synchronising our circadian clock and bodily functions.
As well as setting us up for a good night’s sleep, increased morning light exposure benefits our mental health and reduces the risk of obesity. So boosting our exposure to morning light – for example, by going for a walk, or having breakfast outside – can directly benefit our mental and metabolic health.
However, there are other aspects about which we have less control, including the genes that control our body clock.
Frederic Gachon, Associate Professor, Physiology of Circadian Rhythms, Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland and Benjamin Weger, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
This is Dr. Elissa Epel, whose work has for the past 20 years specialized in the effect of stress on aging. She’s led groundbreaking research on cortisol, telomeres, and telomerase, all in the context of aging, especially in women, as well as the relationship between stress and weight gain. She was elected member of the National Academy of Medicine for her work on stress pathways, and has been recognized as a key “Influencer in Aging” by the Alliance for Aging Research.
Indeed, she’s also been named in the top 0.1% of researchers globally, in terms of publication impact.
What’s that about stress and aging?
In her words,
❝Women with the highest levels of perceived stress have telomeres shorter on average by the equivalent of at least one decade of additional aging compared to low stress women❞
Source: Accelerated telomere shortening in response to life stress
We say “in her words”, as she is the top-listed author on this paper—an honour reserved for the lead researcher of any given study/paper.
However, we’d be remiss not to note that the second-listed author is Nobel Prize Laureate Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn. What a team! Maybe we’ll do a spotlight feature on Dr. Blackburn’s work one of these days, but for now, back to Dr. Epel…
What does she want us to do about it?
She has the following advice for us:
Let go of what we can’t control
This one is simple enough, and can be as simple as learning how to set anxiety aside, and taking up the practice of radical acceptance of what we cannot control.
Be challenged, not afraid
This is about eustress, and being the lion, not the gazelle. Dr. Epel uses the example of how when lions are hunting gazelles, both are stressed, but both are feeling the physiological effects of that stress in terms of the augmentation to their immediate abilities, but only one of them is suffering by it.
We’ll let her explain how to leverage this:
TED ideas | Here’s how you can handle stress like a lion, not a gazelle | Dr. Elissa Epel
Build resilience through controlled discomfort
Don’t worry, you don’t have to get chased by lions. A cold shower will do it! This is about making use of hormesis, the body’s ability to build resilience to stressors by small doses of controlled cortisol release—as for example when one undergoes thermal shock, which sounds drastic, but for most people, a cold shower (or even an ice bath) is safe enough.
You can read more about this here:
A Cold Shower A Day Keeps The Doctor Away
Connect with nature
You don’t have to hug a tree, but you do have get to a natural (or at least, natural-seeming) environment once in a while. Simply put, we did not evolve to be in the urban or even suburban settings where most of us spend most of our time. Getting to be around greenery with at least some kind of regularity is hugely beneficial. It doesn’t have to be a national park; a nice garden or local park can suffice, and potted plants at home are better than nothing. Even spending time in virtual reality “nature” is an option:
(you can see an example there, of the kind of scenery this study used)
Breathe deeply, and rest deeply
Mindful breathing, and good quality sleep, are very strongly evidence-based approaches to reduce stress, for example:
Practice gratitude to build optimism
Optimism has a huge positive impact on health outcomes, even when other factors (including socioeconomic factors, pre-existing conditions, and general reasons for one person to be more optimistic than another) are controlled for.
Read: Optimism and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study
There are various ways to increase optimism, and practising gratitude is one of them—but that doesn’t necessarily mean abandoning realism, either:
How To Practise (Non-Toxic) Positivity
There are other ways too, though, and Dr. Epel discusses some with her friend and colleague, Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn, here:
Want to learn more from Dr. Epel?
We reviewed one of her books, The Telomere Effect, previously. It’s about what we can do to lengthen our telomeres (a key factor in health aging; effectively, being biologically younger). You also might enjoy her newer book, The Stress Prescription, as well as her blog.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Gut-Healthy Tacos
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Full of prebiotics and probiotics, healthy fats, colorful salad boasting vitamins and minerals aplenty, and of course satisfying protein too, these tacos are also boasting generous flavors to keep you coming back for more…
You will need
- 24 sardines—canned is fine (if vegetarian/vegan, substitute tempeh and season generously; marinade if you have time)
- 12 small wholewheat tortillas
- 1 14oz/400g can black beans, drained
- 1 ripe avocado, stoned and cut into small chunks
- 1 red onion, thinly sliced
- 1 little gem lettuce, shredded
- 12 cherry tomatoes, halved
- 1 bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 lemon, sliced
- 4 tbsp plain unsweetened yogurt (your choice what kind, but something with a live culture is best)
- 3oz pickled jalapeños, roughly chopped
- 1oz cilantro (or substitute parsley if you have the cilantro-tastes-like-soap gene), finely chopped
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- Juice of 1 lime
- Optional: Tabasco sauce, or similar hot sauce
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat your oven to a low temperature; 200℉ or just under 100℃ is fine
2) Place the lemon slices on top of the sardines on top of foil on a baking tray; you want the foil to be twice as much as you’d expect to need, because now you’re going to fold it over and make a sort of sealed envelope. You could use a dish with a lid yes, but this way is better because there’s going to be less air inside. Upturn the edges of the envelope slightly so that juices won’t run out, and make sure the foil is imperfectly sealed so a little steam can escape but not much at a time. This will ensure it doesn’t dry out, while also ensuring your house doesn’t smell of fish. Put all this into the oven on a middle shelf.
3) Mix the lime juice with the onion in a bowl, and add the avocado and tomatoes, mixing gently. Add half the cilantro, and set aside.
4) Put the black beans in a sieve and pour boiling water over them to refresh and slightly warm them. Tip them into a bowl and add the olive oil, black pepper, and paprika. Mix thoroughly with a fork, and no need to be gentle this time; in fact, deliberately break the beans a little in this case.
5) Mix the yogurt, jalapeños, garlic, and remaining cilantro in a small bowl.
6) Get the warmed sardines from the oven; discard the lemon slices.
7) Assemble! We recommend the order: tortilla, lettuce, fish (2 per taco), black bean mixture, salad mixture, garlic jalapeño yogurt mixture. You can also add a splash of the hot sauce per your preference, or if catering for more people, let people add their own.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Enjoy Pungent Polyphenols For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: