No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s on your mind, really?
We hear a lot about “the evidence-based benefits of mindfulness”, but what actually are they? And what is the evidence? And, perhaps most importantly: how do we do it?
What are the benefits?
The benefits of mindfulness are many, and include:
- reducing stress
- reducing pain
- improving quality of life
- reducing fatigue
- providing relief from digestive disorders
- reducing symptoms of sleep disorders
- improving immune response
- providing support for caregivers
The evidence is also abundant, and includes:
- Effects of mindfulness exercises as stand-alone intervention on symptoms of anxiety and depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Fusing character strengths and mindfulness interventions: Benefits for satisfaction and performance
- Evidence for the Role of Mindfulness in Cancer: Benefits and Techniques
- Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on anxiety symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The benefits of meditation and mindfulness practices during times of crisis such as COVID-19
Sounds great… What actually is it, though?
Mindfulness is the state of being attentive to one’s mind. This is at its heart a meditative practice, but that doesn’t necessarily mean you have to be sitting in the lotus position with candles—mindfulness can be built into any daily activity, or even no activity at all.
An exercise you can try right now:
Take a moment to notice everything you can hear. For this writer, that includes:
- The noise of my keystrokes as I type
- The ticking of the clock on the wall
- The gentle humming of my computer’s processor
- The higher-pitched noise of my computer’s monitor
- Birdsong outside
- Traffic further away
- My own breathing
- The sound of my eyelids as I blink
Whatever it is for you, notice how much you can notice that you had previously taken for granted.
You can repeat this exercise with other senses, by the way! For example:
- Notice five things you can see in your immediate environment that you’ve never noticed before. If you’re at home reading this, you probably think you’re very familiar with everything around you, but now see that mark on the wall you’d never noticed before, or a quirk of some electrical wiring, or the stitching on some furnishing, for example.
- Notice the textures of your clothes, or your face, or perhaps an object you’ve never paid attention to touching before. Your fingertips, unless you have some special reason this doesn’t apply to you, are far more sensitive than you probably give them credit for, and can notice the tiniest differentiation in textures, so take a moment to do that now.
- Mindful eating can be an especially healthful practice because it requires that we pay every attention to what we’re putting in our mouth, tasting, chewing, swallowing. No more thoughtlessly downing a box of cookies; every bite is now an experience. On the one hand, you’ll probably eat less at a sitting. On the other hand, what a sensory experience! It really reminds one that life is for living, not just for zipping through at a speed-run pace!
What about mindfulness as a meditative practice?
Well, those are meditative practices! But yes, mindfulness goes for more formal meditation too. For example:
Sit comfortably, with good posture, whatever that means to you. No need to get too caught up in the physical mechanics here—it’d take a whole article. For now, if you’re sitting and comfortable, that’s enough.
Notice your breathing. No need to try to control it—that’s not what this is about today. Just notice it. The in, the out, whether you breathe to your chest or abdomen, through your nose or mouth, don’t worry about doing it “right”, just notice what you are doing. Observe without judgement.
Notice your thoughts—no need to try to stop them. Notice noticing your thoughts, and again, observe without judgement. Notice your feelings; are you angry, hopeful, stressed, serene? There are no wrong answers here, and there’s nothing you should try to “correct”. Just observe. No judgement, only observe. Watch your thoughts, and watch your thoughts go.
Did you forget about your breathing while watching your thoughts? Don’t worry about that either if so, just notice that it happened. If you have any feelings about that, notice them too, and carry on observing.
We go through so much of our lives in “autopilot”, that it can be an amazing experience to sometimes just “be”—and be aware of being.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fatty Acids For The Eyes & Brain: The Good And The Bad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Good For The Eyes; Good For The Brain
We’ve written before about omega-3 fatty acids, covering the basics and some lesser-known things:
What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
…and while we discussed its well-established benefits against cognitive decline (which is to be expected, because omega-3 is good against inflammation, and a large part of age-related neurodegeneration is heavily related to neuroinflammation), there’s a part of the brain we didn’t talk about in that article: the eyes.
We did, however, talk in another article about supplements that benefit the eyes and [the rest of the] brain, and the important links between the two, to the point that an examination of the levels of lutein in the retina can inform clinicians about the levels of lutein in the brain as a whole, and strongly predict Alzheimer’s disease (because Alzheimer’s patients have significantly less lutein), here:
Now, let’s tie these two ideas together
In a recent (June 2024) meta-analysis of high-quality observational studies from the US and around the world, involving nearly a quarter of a million people over 40 (n=241,151), researchers found that a higher intake of omega-3 is significantly linked to a lower risk of macular degeneration.
To put it in numbers, the highest intake of omega-3s was associated with an 18% reduced risk of early stage macular degeneration.
They also looked at a breakdown of what kinds of omega-3, and found that taking a blend DHA and EPA worked best of all, although of people who only took one kind, DHA was the best “single type” option.
You can read the paper in full, here:
Association between fatty acid intake and age-related macular degeneration: a meta-analysis
A word about trans-fatty acids (TFAs)
It was another feature of the same study that, while looking at fatty acids in general, they also found that higher consumption of trans-fatty acids was associated with a higher risk of advanced age-related macular degeneration.
Specifically, the highest intake of TFAs was associated with a more than 2x increased risk.
There are two main dietary sources of trans-fatty acids:
- Processed foods that were made with TFAs; these have now been banned in a lot of places, but only quite recently, and the ban is on the processing, not the sale, so if you buy processed foods that contain ingredients that were processed before 2021 (not uncommon, given the long life of many processed foods), the chances of them having TFAs is higher.
- Most animal products. Most notably from mammals and their milk, so beef, pork, lamb, milk, cheese, and yes even yogurt. Poultry and fish technically do also contain TFAs in most cases, but the levels are much lower.
Back to the omega-3 fatty acids…
If you’re wondering where to get good quality omega-3, well, we listed some of the best dietary sources in our main omega-3 article (linked at the top of today’s).
However, if you want to supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon that’s high in DHA and EPA, following the science of what we shared today 😎
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Frozen/Thawed/Refrozen Meat: How Much Is Safety, And How Much Is Taste?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What You Can (And Can’t) Safely Do With Frozen Meat
Yesterday, we asked you:
❝You have meat in the freezer. How long is it really safe to keep it?❞
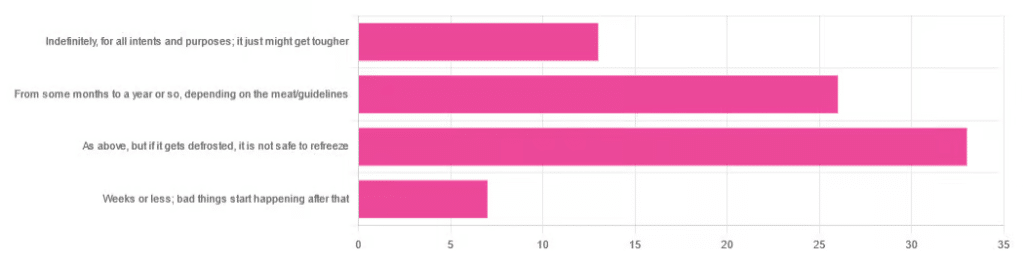
…and got a range of answers, mostly indicating to a) follow the instructions (a very safe general policy) and b) do not refreeze if thawed because that would be unsafe. Fewer respondents indicated that meat could be kept for much longer than guidelines say, or conversely, that it should only be kept for weeks or less.
So, what does the science say?
Meat can be kept indefinitely (for all intents and purposes) in a freezer; it just might get tougher: True or False?
False, assuming we are talking about a normal household electrical freezer that bottoms out at about -18℃ / 0℉.
Fun fact: cryobiologists cryopreserve tissue samples (so basically, meat) at -196℃ / -320℉, and down at those temperatures, the tissues will last a lot longer than you will (and, for all practical purposes: indefinitely). There are other complications with doing so (such as getting the sample through the glass transition point without cracking it during the vitrification process) but those are beyond the scope of this article.
If you remember back to your physics or perhaps chemistry classes at school, you’ll know that molecules move more quickly at higher temperatures, and more slowly at lower ones, only approaching true stillness as they near absolute zero (-273℃ / -459℉ / 0K ← we’re not saying it’s ok, although it is; rather, that is zero kelvin; no degree sign is used with kelvins)
That means that when food is frozen, the internal processes aren’t truly paused; it’s just slowed to a point of near imperceptibility.
So, all the way up at the relatively warm temperatures of a household freezer, a lot of processes are still going on.
What this means in practical terms: those guidelines saying “keep in the freezer for up to 4 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 9 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 12 months” etc are being honest with you.
More or less, anyway! They’ll usually underestimate a little to be on the safe side—but so should you.
Bad things start happening within weeks at most: True or False?
False, for all practical purposes. Again, assuming a normal and properly-working household freezer as described above.
(True, technically but misleadingly: the bad things never stopped; they just slowed down to a near imperceptible pace—again, as described above)
By “bad” here we should clarify we mean “dangerous”. One subscriber wrote:
❝Meat starts losing color and flavor after being in the freezer for too long. I keep meat in the freezer for about 2 months at the most❞
…and as a matter of taste, that’s fair enough!
It is unsafe to refreeze meat that has been thawed: True or False?
False! Assuming it has otherwise been kept chilled, just the same as for fresh meat.
Food poisoning comes from bacteria, and there is nothing about the meat previously having been frozen that will make it now have more bacteria.
That means, for example…
- if it was thawed (but chilled) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been chilled for that period of time (so probably: use it or freeze it, unless it’s been more than a few days)
- if it was thawed (and at room temperature) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been at room temperature for that period of time (so probably: throw it out, unless the period of time is very small indeed)
The USDA gives for 2 hours max at room temperature before considering it unsalvageable, by the way.
However! Whenever you freeze meat (or almost anything with cells, really), ice crystals will form in and between cells. How much ice crystallization occurs depends on several variables, with how much water there is present in the food is usually the biggest factor (remember that animal cells are—just like us—mostly water).
Those ice crystals will damage the cell walls, causing the food to lose structural integrity. When you thaw it out, the ice crystals will disappear but the damage will be left behind (this is what “freezer burn” is).
So if your food seems a little “squishy” after having been frozen and thawed, that’s why. It’s not rotten; it’s just been stabbed countless times on a microscopic level.
The more times you freeze and thaw and refreeze food, the more this will happen. Your food will degrade in structural integrity each time, but the safety of it won’t have changed meaningfully.
Want to know more?
Further reading:
You can thaw and refreeze meat: five food safety myths busted
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Healing Trauma – by Dr. Peter Levine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Levine’s better-selling book about trauma, Waking The Tiger, laid the foundations for this one, but the reason we’re skipping straight into Healing Trauma, is that while the former book is more about the ideas that led him to what he currently believes is the best approach to healing trauma, this book is the one that explains how to actually do it.
The core thesis is that trauma is a natural, transient response, and is not inherently pathological, but that it can become so if not allowed to do its thing.
This book outlines exercises, trademarked as “somatic experiencing”, which allow the body to go through the physiological processes it needs to, to facilitate healing. If you buy the physical book, there is also an audio CD, which this reviewer has not listened to and cannot comment on, but the exercises are clearly described in the book in any case.
The physical aspects of the exercises are similar to the principles of progressive relaxation, while the mental aspects of the exercises are about re-experiencing trauma in a safer fashion, in small doses.
Any kind of dealing with trauma is not going to be comfortable, so this book is not an enjoyable read.
As for how useful the exercises are, your mileage may vary. Like many books about trauma, the expectation is that once upon a time you were in a situation that was unsafe, and now you are safe. If that describes your trauma, you will get the most out of this. However, if your trauma is unrelated to your personal safety, or if it is about your personal safety but the threat still remains extant, then a lot of this may not help and may even make things worse.
In terms of discussing sexual trauma specifically, it was probably not a good choice to favorably quote Woody Allen, and little things like that may be quite jarring for a lot of readers.
Bottom line: if your trauma is PTSD of the kind “you faced an existential threat and now it is gone”, then chances are that this book can help you a lot. If your trauma is different, then your mileage may vary widely on this one.
Click here to check out Healing Trauma, if it seems right for you!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Spectrum of Hope – by Dr. Gayatri Devi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about Dr. Devi’s work (See: “Alzheimer’s: The Bad News And The Good“) but she has plenty more to say than we could fit in an article.
The book is written for patients, family/carers, and clinicians—without getting deep into the science, which it is assumed clinicians will know. the general style of the book is pop-science, and it’s more about addressing the misconceptions around Alzheimer’s, rather than focusing on neurological features such as beta amyloid plaques and tau proteins and the like.
Dr. Devi explains a lot about the experience of Alzheimer’s—what to expect, or rather, what to know about in advance. Because, as she explains, there are a lot of different manifestations of Alzheimer’s that are all lumped under the same umbrella.
This means that a person could have negligible memory but perfect language and reasoning skills, or the other way around, or some other combination of symptoms showing up or not.
Which means that any plan for managing one’s Alzheimer’s needs to be adaptable and personalized, which is something Dr. Devi talks us through, too.
Bottom line: if you are a loved one has Alzheimer’s, or you just like to be prepared, this is a great book to prepare anybody for just that.
Click here to check out The Spectrum of Hope, and hold onto that hope!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Knitting helps Tom Daley switch off. Its mental health benefits are not just for Olympians
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Olympian Tom Daley is the most decorated diver in Britain’s history. He is also an avid knitter. At the Paris 2024 Olympics Daley added a fifth medal to his collection – and caught the world’s attention knitting a bright blue “Paris 24” jumper while travelling to the games and in the stands.
At the Tokyo Olympics, where Daley was first spotted knitting, he explained its positive impact on his mental health.
It just turned into my mindfulness, my meditation, my calm and my way to escape the stresses of everyday life and, in particular, going to an Olympics.
The mental health benefits of knitting are well established. So why is someone famous like Daley knitting in public still so surprising?
Africa Voice/Shutterstock Knitting is gendered
Knitting is usually associated with women – especially older women – as a hobby done at home. In a large international survey of knitting, 99% of respondents identified as female.
But the history of yarn crafts and gender is more tangled. In Europe in the middle ages, knitting guilds were exclusive and reserved for men. They were part of a respected Europe-wide trade addressing a demand for knitted products that could not be satisfied by domestic workers alone.
The industrial revolution made the production of clothed goods cheaper and faster than hand-knitting. Knitting and other needle crafts became a leisure activity for women, done in the private sphere of the home.
World Wars I and II turned the spotlight back on knitting as a “patriotic duty”, but it was still largely taken up by women.
During COVID lockdowns, knitting saw another resurgence. But knitting still most often makes headlines when men – especially famous men like Daley or actor Ryan Gosling – do it.
Men who knit are often seen as subverting the stereotype it’s an activity for older women.
Knitting the stress away
Knitting can produce a sense of pride and accomplishment. But for an elite sportsperson like Daley – whose accomplishments already include four gold medals and one silver – its benefits lie elsewhere.
Olympics-level sport relies on perfect scores and world records. When it comes to knitting, many of the mental health benefits are associated with the process, rather than the end result.
Daley says knitting is the “one thing” that allows him to switch off completely, describing it as “my therapy”. https://www.youtube.com/embed/6wwXGOki–c?wmode=transparent&start=0
The Olympian says he could
knit for hours on end, honestly. There’s something that’s so satisfying to me about just having that rhythm and that little “click-clack” of the knitting needles. There is not a day that goes by where I don’t knit.
Knitting can create a “flow” state through rhythmic, repetitive movements of the yarn and needle. Flow offers us a balance between challenge, accessibility and a sense of control.
It’s been shown to have benefits relieving stress in high-pressure jobs beyond elite sport. Among surgeons, knitting has been found to improve wellbeing as well as manual dexterity, crucial to their role.
For other health professionals – including oncology nurses and mental health workers – knitting has helped to reduce “compassion fatigue” and burnout. Participants described the soothing noise of their knitting needles. They developed and strengthened team bonds through collective knitting practices. https://www.youtube.com/embed/dTTJjD_q2Ik?wmode=transparent&start=0 A Swiss psychiatrist says for those with trauma, knitting yarn can be like “knitting the two halves” of the brain “back together”.
Another study showed knitting in primary school may boost children’s executive function. That includes the ability to pay attention, remember relevant details and block out distractions.
As a regular creative practice, it has also been used in the treatment of grief, depression and subduing intrusive thoughts, as well countering chronic pain and cognitive decline.
Knitting is a community
The evidence for the benefits of knitting is often based on self-reporting. These studies tend to produce consistent results and involve large population samples.
This may point to another benefit of knitting: its social aspect.
Knitting and other yarn crafts can be done alone, and usually require simple materials. But they also provide a chance to socialise by bringing people together around a common interest, which can help reduce loneliness.
The free needle craft database and social network Ravelry contains more than one million patterns, contributed by users. “Yarn bombing” projects aim to engage the community and beautify public places by covering objects such as benches and stop signs with wool.
The interest in Daley’s knitting online videos have formed a community of their own.
In them he shows the process of making the jumper, not just the finished product. That includes where he “went wrong” and had to unwind his work.
His pride in the finished product – a little bit wonky, but “made with love” – can be a refreshing antidote to the flawless achievements often on display at the Olympics.
Michelle O’Shea, Senior Lecturer, School of Business, Western Sydney University and Gabrielle Weidemann, Associate Professor in Psychological Science, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Milk Thistle For The Brain, Bones, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Thistle Do Nicely”
Milk thistle is a popular supplement; it comes from the milk thistle plant (Silybum marianum), commonly just called thistles. There are other kinds of thistle too, but these are one of the most common.
So, what does it do?
Liver health
Milk thistle enjoys popular use to support liver health; the liver is a remarkably self-regenerative organ if given the chance, but sometimes it can use a helping hand.
See for example: How To Undo Liver Damage
As for milk thistle’s beneficence, it is very well established:
- Milk thistle in liver diseases: past, present, future
- Hepatoprotective effect of silymarin
- Silybum Marianum and Chronic Liver Disease: A Marriage of Many Years
Brain health
For this one the science is less well-established, as studies so far have been on non-human animals, or have been in vitro studies.
Nevertheless, the results so far are promising, and the mechanism of action seems to be a combination of reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, as well as suppressing amyloid β-protein (Aβ) fibril formation, in other words, reducing amyloid plaques.
General overview: A Mini Review on the Chemistry and Neuroprotective Effects of Silymarin
All about the plaques, but these are non-human animal studies:
- Mouse model: Silymarin attenuated the amyloid β plaque burden and improved behavioral abnormalities in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model
- Rat model: Silymarin effect on amyloid-β plaque accumulation and gene expression of APP in an Alzheimer’s disease rat model
Against diabetes
Milk thistle improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces fasting blood sugar levels and HbA1c levels. The research so far is mostly in type 2 diabetes, however (at least, so far as we could find). For example:
Studies we could find for T1D were very far from translatable to human usefulness, for example, “we poisoned these rats with streptozotocin then gave them megadoses of silymarin (10–15 times the dose usually recommended for humans) and found very small benefits to the lenses of their eyes” (source).
Against osteoporosis
In this case, milk thistle’s estrogenic effects may be of merit to those at risk of menopause-induced osteoporosis:
If you’d like a quick primer about such things as what antiosteoclastic activity is, here’s a quick recap:
Which Osteoporosis Medication, If Any, Is Right For You?
Is it safe?
It is “Generally Recognized As Safe”, and even when taken at high doses for long periods, side effects are very rare.
Contraindications include if you’re pregnant, nursing, or allergic.
Potential reasons for caution (but not necessarily contraindication) include if you’re diabetic (its blood-sugar lowering effects will decrease the risk of hyperglycemia while increasing the risk of hypoglycemia), or have a condition that could be exacerbated by its estrogenic effects—including if you are on HRT, because it’s an estrogen receptor agonist in some ways (for example those bone benefits we mentioned before) but an estrogen antagonist in others (for example, in the uterus, if you have one, or in nearby flat muscles, if you don’t).
As ever, speak with your doctor/pharmacist to be sure.
Want to try it?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: