An Elegant Defense – by Matt Richtel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In a way, Richtel got the best and worst of the publication date lottery. This book, which he’d obviously been working on for however long, was published in March 2020. Yes, that March 2020. So, it obviously got a huge boost in sales that launced it to bestseller status, and/but it doesn’t actually discuss COVID at all.
What it does discuss, is—as one might expect—the immune system. Or really, the immune systems, plural, several systems working alongside each other. How we got to have such, how our immune functions work, where all the various immune cells come from and what part they play. What pathogens can do to fight and/or confuse (or even co-opt) our immune response, and what modern medicine can do to counteract the pathogens’ anti-countermeasure countermeasures. And how it can still go wrong.
The “Four Lives” promised in the subtitle are stories, and Richtel explains the immune system through specific people’s specific battles. In particular, a friend of his who had quite a remarkable battle against cancer, which was of course terrible for him, but illustrative for us.
The style of the book is very readably journalistic. The author is a Pulitzer-winning NYT journalist, and not normally a science writer. Here at 10almonds, “we like big bibliographies and we cannot lie”, and we didn’t get to enjoy that in this case. The book contained no bibliography (nor appropriate inline citations, nor equivalent footnotes). Maybe a future addition will include this.
Bottom line: there’s a lot of “science for the lay reader” here. While the lack of references is a big oversight, the book does give a very good overview of what both sides (immune response and pathogenic invasion) bring to the battle of your body.
Click here to check out Elegant Defense, and demystify immunology!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why You Can’t Deep Squat (And the Benefits You’re Missing)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Matt Hsu fought his own battle with chronic pain from the age of 16 in his feet, knees, hips, back, shoulders, elbows, forearms, wrists, hands, and head. Seeking answers, he’s spent a career in corrective exercise, posture alignment, structural integration, orthopedic exercise, sports medicine, and has more certifications than we care to list. In short, he knows his stuff.
Yes you can (with some work)
The deep squat, also called Asian squat, Slav squat, sitting squat, resting squat, primal squat, and various other names, is an important way of sitting that has implications for a lot of aspects of health.
Why it’s so important: it preserves the mobility of our hips, ankles, and everything in between, and maintaining especially the hip mobility makes a big difference not only to general health, but also to reducing the risk of injury. It also maintains lower body strength, making falls in older age less likely in the first place, and if falls do happen, makes injury less likely, and if injury does happen, makes the injury likely less severe.
An important misconception: there is a popular, but unfounded, belief that the ability or inability to do this is decided by genes—or if not outright decided, that at the very least Asians and Slavs have a genetic advantage. However, this is simply not true. Westerners and others can learn to do it just fine, and on the flipside, Asians and Slavs who grew up in the West may often struggle with it. The truth is, the deciding factor is lifestyle: if your culture involves sitting this way more often, you’ll be able to do it more comfortably and easily than if you’re just now trying it for the first time.
Factors that you can control: you can’t change where you grew up, but you can change how you sit down now. Achieving the squat requires repeated position practice, and the more frequently you do so (even if you just start with a few seconds and work your way up to longer periods), the better you’ll get at it. And, on the contrary, sitting in chairs weakens and shortens the muscles involved, so any time you spend sitting in chairs is working against you. There are many reasons it’s advisable to avoid sitting in chairs more than necessary, and this is one of them.
10almonds tip: a limiting factor for many people initially is ankle flexibility, which may result in one’s center of gravity being a bit far back, leading to a tendency to have to change something to avoid toppling over backwards. Rather than holding onto something immobile (e.g. furniture) in front of where you are sitting, consider simply holding an object in front of you in your hands. A book is a fine example; holding that in front of you (feel free to read the book) will shift your center of gravity forwards a bit, and will thus allow you to sit there a little longer, thus improving your strength and flexibility while you do, until you can do it without holding something in front of you. If you try with a book and you’re still prone to toppling backwards, try with something heavier, but do use the minimum weight necessary, because ultimately the counterbalance is just a crutch to get you to where you need to be.
For more visual advice on how to do it, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
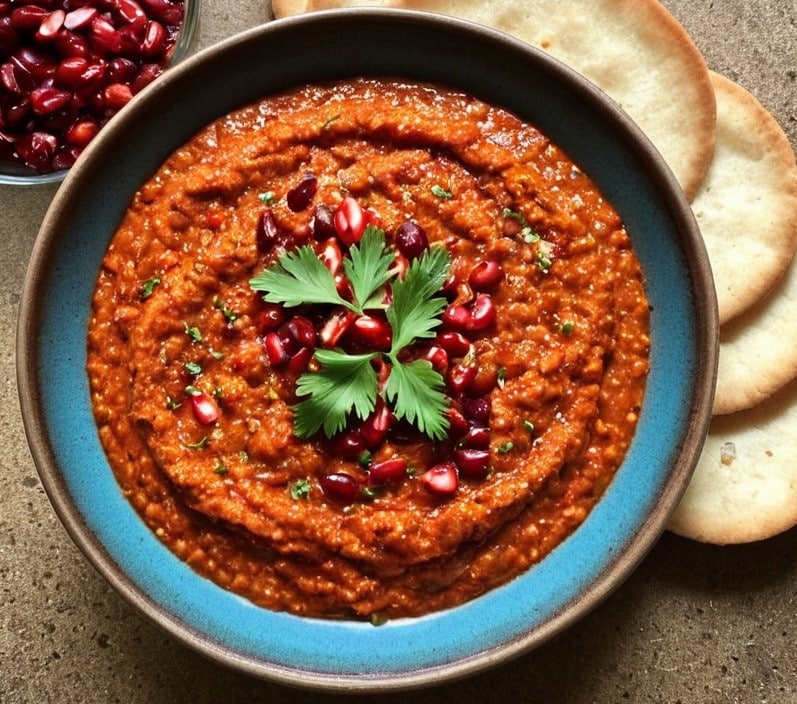
This is a Levantine dish, Syrian in origin (although Lebanese cuisine uses it plenty too) and popularly enjoyed all the way up to Turkey, down to Egypt, and across to Armenia. And today, perhaps rather further afield! It’s first and foremost a spicy dip/spread, though it can be lengthened into a sauce, and/or made more substantial by adding an extra protein. We’ll give you the basic recipe though, and let you see where it takes you! Healthwise, it’s very nutritionally dense, mostly thanks to the walnuts and red peppers, though spices and olive oil bring their healthy benefits too.
You will need
- ½ cup chopped walnuts (ideally: toasted)
- 3 red peppers, from a jar (jarred over fresh not only improves the consistency, but also makes it extra gut-healthy due to the fermentation bacteria present; if you must use fresh, roast them first)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp pomegranate molasses (you can omit if you don’t like sweetness, but this is traditional)
- 1 tbsp tomato purée
- 1 tbsp Aleppo pepper flakes (less, if you don’t like heat) (substitute another hot pepper if necessary)
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tsp ground smoked paprika
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Juice of 1 lemon
- Optional: handful of pomegranate seeds
- Optional: herb garnish, e.g. cilantro or parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add everything except the pomegranate seeds and herbs to a blender, and blend to a smooth consistency.
2) Add the pomegranate seeds and herbs, as a garnish.
3) Serve! Can be enjoyed as a dip (perhaps using our Homemade Healthy Flatbreads recipe), or as a spread, or used as a sauce poured over chickpeas or some other bulky protein, to make a more substantial dish.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Walnuts vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Red Bell Peppers vs Tomatoes – Which is Healthier?
- Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How to Fall Back Asleep After Waking Up in the Middle of the Night
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michael Bruce, the Sleep Doctor, addresses a common concern: waking up in the middle of the night and struggling to fall back asleep.
Understanding the Wake-Up
Firstly, why are we waking up during the night?
Waking up between 2 AM and 3 AM is said to be normal, and linked to your core body temperature. As your body core temperature drops, to trigger melatonin release, and then rises again, you get into a lighter stage of sleep. This lighter stage of sleep makes you more prone to waking up.
Note, there are also some medical conditions (such as sleep apnea) that can cause you to wake up during the night.
But, what can we do about it? Aside from constantly shifting sleeping position (Should I be sleeping on my back? On my left? Right?)
Avoid the Clock
The first step is to resist the urge to check the time. It’s easy to be tempted to have a look at the clock, however, doing so can increase anxiety, making it harder to fall back asleep. As Dr. Bruce says, sleep is like love—the less you chase it, the more it comes.
It may be useful to point your alarm clock (if you still have one of those) the opposite direction to your bed.
Embracing Non-Sleep Deep Rest (NSDR)
Whilst this may not help you fall back asleep, it’s worth pointing out that just lying quietly in the dark without moving still offers rejuvenation. This revujenating stage is called Non-Sleep Deep Rest (otherwise known as NSDR)
If you’re not familiar with NSDR, check out our overview of Andrew Huberman’s opinions on NSDR here.
So, you can reassure yourself that whilst you may not be asleep, you are still resting.
Keep Your Heart Rate Down
To fall back asleep, it’s best if your heart rate is below 60 bpm. So, Dr. Bruce advises avoiding void getting up unnecessarily, as moving around can elevate your heart rate.
On a similar vain, he introduces the 4-7-8 breathing technique, which is designed to lower your heart rate. The technique is simple:
- Breathe in for 4 seconds.
- Hold for 7 seconds.
- Exhale for 8 seconds.
Repeat this cycle gently to calm your body and mind.
As per any of our Video Breakdowns, we only try to capture the most important pieces of information in text; the rest can be garnered from the video itself:
Wishing you a thorough night’s rest!
Do you know any other good videos on sleep? Send them to us via email!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What To Do If Having A Stroke Alone?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Thank you for the video about what to do if you have a heart attack alone, what about what to do if you have a stroke alone?❞
(for anyone who missed that video, here it is)
That’s a good question, especially as stroke risk is rising in the industrialized world in general, and the US in particular.
However, let’s start with the caveat that if you are having a stroke, there’s a good chance you will forget what we are about to say, what with the immediate effects it has on the brain. That said…
The general advice when it comes to looking after someone else who is experiencing a stroke, is, “don’t”.
In other words, call emergency services, and don’t do anything else, e.g:
- don’t give them anything to eat or drink
- don’t give them any medications
- don’t let them go to sleep
- don’t let them talk you out of calling emergency services
- don’t let them drive themselves to hospital
- don’t drive them to hospital yourself either*
*This is for two reasons:
- an ambulance crew has skills and resources that you don’t, and can begin treatment en-route, and also,
- not all hospitals have appropriate resources to treat stroke, so the ambulance crew will know to drive to one that does, instead of driving to a random hospital and hoping for the best
So, flipping this for if it’s you having the stroke, and you’re cognizant enough to remember this:
- do call an ambulance; stay on the line and don’t do anything else unless instructed by the emergency services.
In order to do that, of course it’s important to recognize the symptoms; you probably know these but just in case, the mnemonic is “FAST”:
- Face: is there weakness on one side of their face?
- Arms: if they raise both arms, does one drift downwards?
- Speech: if they speak, is their speech slurred or otherwise unusual?
- Time: to call emergency services
It’s great to not get caught out by surprise, so you might also want to check out:
6 Signs Of Stroke (One Month In Advance)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Too Much Or Too Little Testosterone?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One Man’s Saw Palmetto Is Another Woman’s Serenoa Repens…
Today we’re going to look at saw palmetto. So, first:
What is it?
Saw palmetto is a type of palm native to the southeastern United States. Its scientific name is “Serenoa repens”, so if that name appears in studies we cite, it’s the same thing. By whichever name, it’s widely enjoyed as a herbal supplement.
Why do people take it?
Here’s where it gets interesting, because people take it for some completely opposite reasons…
Indeed, searching for it on the Internet will cause Google to suggest “…for men” and “…for women” as the top suggestions.
That’s because it works on testosterone, and testosterone can be a bit of a double-edged sword, so some people want to increase or decrease certain testosterone-related effects on their body.
And it works for both! Here be science:
- Testosterone (henceforth, “T”) is produced in the human body.
- Yes, all human bodies, to some extent.
- An enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase converts T in to DHT (dihydrogen testosterone)
- DHT is a much more potent androgen (masculinizing agent) than T alone, such that its effects are often unwanted, including:
- Enlarged prostate (if you have one)
- Hair loss (especially in men)
- New facial hair growth (usually unwanted by women)
- Women are more likely to get this due to PCOS and/or the menopause
To avoid those effects, you really want less of your T to be converted into DHT.
Saw palmetto is a 5α-reductase inhibitor, so if you take it, you’ll have less DHT, and you’ll consequently lose less hair, have fewer prostate problems, etc.
^The above study showed that saw palmetto extract performed comparably to finasteride. Finasteride is the world’s main go-to prescription drug for treating enlarged prostate and/or hair loss.
See also: Natural Hair Supplement: Friend or Foe? Saw Palmetto, a Systematic Review in Alopecia
Hair today… Growing tomorrow!
So, what was that about increasing T levels?
Men usually suffer declining T levels as they get older, with a marked drop around the age of 45. With lower T comes lower energy, lower mood, lower libido, erectile dysfunction, etc.
Guess what… It’s T that’s needed for those things, not DHT. So if you block the conversion of T to DHT, you’ll have higher blood serum T levels, higher energy, higher mood, higher libido, and all that.
(the above assumes you have testicles, without which, your T levels will certainly not increase)
Saw Palmetto Against Enlarged Prostate?
With higher DHT levels in mid-late life, prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperlasia) can become a problem for many men. The size of that problem ranges from urinary inconvenience (common, when the prostate presses against the bladder) to prostate cancer (less common, much more serious). Saw palmetto, like other 5α-reductase inhibitors such as finasteride, may be used to prevent or treat this.
Wondering how safe/reliable it is? We found a very high-quality fifteen-year longitudinal observational study of the use of saw palmetto, and it found:
❝The 15 years’ study results suggest that taking S. repens plant extract continuously at a daily dose of 320 mg is an effective and safe way to prevent the progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia.❞
Want a second opinion? We also found a 10-year study (by different researchers with different people taking it), which reached the same conclusion:
❝The results of study showed the absence of progression, both on subjective criteria (IPSS, and QoL scores), and objective criteria (prostate volume, the rate of urination, residual urine volume). Furthermore, patients had no undesirable effects directly related to the use of this drug.❞
- IPSS = International Prostate Symptom Score
- QoL = Quality of Life
❝But wait a minute; I, a man over the age of 45 with potentially declining T levels but a fabulous beard, remember that you said just a minute ago that saw palmetto is used by women to avoid having facial hair; I don’t want to lose mine!❞
You won’t. Once your facial hair follicles were fully developed and activated during puberty, they’ll carry on doing what they do for life. That’s no longer regulated by hormones once they’re up and running.
The use of saw palmetto can only be used to limit facial hair if caught early—so it’s more useful at the onset of menopause, for those who have (or will have) such, or else upon the arrival of PCOS symptoms or hirsuitism from some other cause.
Take The Test!
Do you have a prostate, and would like to know your IPSS score, and what that means for your prostate health?
(takes 1 minute, no need to pee or go probing for anything)
Bottom Line on Saw Palmetto
- It blocks the conversion of T into DHT
- It will increase blood serum T levels, thus boosting mood, energy, libido, etc in men (who typically have more T, but whose T levels decline with age)
- It will decrease DHT levels, thus limiting hair loss (especially in men) and later-life new facial hair growth (especially in women).
- It can be used to prevent or treat prostate enlargement
- Bonus: it’s a potent antioxidant and thus reduces general inflammation (in everyone)
Want To Try Saw Palmetto?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience…
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Testosterone (henceforth, “T”) is produced in the human body.
-
Is Sugar The New Smoking?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Could you do a this or that of which. Is worse, smoking cigarettes or having a sweet tooth? Also, perhaps have us evaluate one part of newsletter at a time, rather than overall. I especially appreciate your book reviews and often find them through my library system.❞
We’re glad you enjoy the book reviews! We certainly enjoy reading many books to write about them for you.
As for the idea having readers evaluate one part of the newsletter at a time, rather than overall, there is a technical limitation that embedded polls are very large, data-wise, so if we were to do a poll for each section, the email would then get clipped by gmail and other email providers. However, you are always more than welcome to do as you’ve done, and include comments about what section(s) you took the most value from.
Now, onto your main question/request: as it doesn’t quite fit the usual format for our This vs That section, we’ve opted to do it as a main feature here 🙂
So, let’s get into it…
Not a zero-sum game
First, let’s be clear that for most people there is no pressing reason that this should be an either/or decision. There is nothing inherent to quitting either one that makes the other loom larger.
However, that said, if you’re (speaking generally here, and not making any presumptions about the asker) currently smoking regularly and partaking of a lot of added sugar, then you may be wondering which you should prioritize quitting first—as it is indeed generally recommended to only try to quit one thing at a time.
Indeed, we wrote previously, as a guideline for “what to do in one what order”:
Not sure where to start? We suggest this order of priorities, unless you have a major health condition that makes something else a higher priority:
- If you smoke, stop
- If you drink, reduce, or ideally stop
- Improve your diet
About that diet…
Worry less about what to exclude, and instead focus on adding more variety of fruit/veg.
See also: Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
That said, if you’re looking for things to cut, sugar is a top candidate (and red meat is in clear second place albeit some way below)
That’s truncated from a larger list, but those were the top items.
You can read the rest in full, here: The Best Few Interventions For The Best Health: These Top 5 Things Make The Biggest Difference
The flipside of this “you can quit both” reality is that the inverse is also true: much like how having one disease makes it more likely we will get another, unhealthy habits tend to come in clusters too, as each will weaken our resolve with regard to the others. Thus, there is a sort of “comorbidity of habits” that occurs.
The good news is: the same can be said for healthy habits, so they (just like unhealthy habits) can support each other, stack, and compound. This means that while it may seem harder to quit two bad habits than one, in actual fact, the more bad habits you quit, the more it’ll become easy to quit the others. And similarly, the more good habits you adopt, the more it’ll become easy to adopt others.
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
So, let’s keep that in mind, while we then look at the cases against smoking, and sugar:
The case against smoking
This is perhaps one of the easiest cases to make in the entirety of the health science world, and the only difficult part is knowing where to start, when there’s so much.
The World Health Organization leads with these key facts, on its tobacco fact sheet:
- Tobacco kills up to half of its users who don’t quit.
- Tobacco kills more than 8 million people each year, including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.
- Around 80% of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.
- In 2020, 22.3% of the world’s population used tobacco: 36.7% of men and 7.8% of women.
- To address the tobacco epidemic, WHO Member States adopted the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) in 2003. Currently 182 countries are Parties to this treaty.
- The WHO MPOWER measures are in line with the WHO FCTC and have been shown to save lives and reduce costs from averted healthcare expenditure.
Source: World Health Organization | Tobacco
Now, some of those are just interesting sociological considerations (well, they are of practical use to the WHO whose job it is to offer global health policy guidelines, but for us at 10almonds, with the more modest goal of helping individual people lead their best healthy lives, there’s not so much that we can do with the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control, for example), but for the individual smoker, the first two are really very serious, so let’s take a closer look:
❝Tobacco kills up to half of its users who don’t quit.❞
A bold claim, backed up by at least three very large, very compelling studies:
- Mortality in relation to smoking: 50 years’ observations on male British doctors
- Tobacco smoking and all-cause mortality in a large Australian cohort study: findings from a mature epidemic with current low smoking prevalence
- Global burden of disease due to smokeless tobacco consumption in adults: an updated analysis of data from 127 countries
❝Tobacco kills more than 8 million people each year, including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.❞
The WHO’s cited source for this was gatekept in a way we couldn’t access (and so probably most of our readers can’t either), but take a look at what the CDC has to say for the US alone (bearing in mind the US’s population of a little over 300,000,000, which is just 3.75% of the global population of a little over 8,000,000,000):
❝smoking causes more than 480,000 deaths [in the US] annually, with an estimated 41,000 deaths from secondhand smoke exposure, and it can reduce a person’s life expectancy by 10 years. Quitting smoking before the age of 40 reduces the risk of dying from smoking-related disease by about 90%❞
If we now remember that third bullet point, that said “Around 80% of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.”, then we can imagine the numbers are worse for many other countries, including large-population countries that have a lower median income than the US, such as India and Brazil.
Source for the CDC comment: Tobacco-Related Mortality
See also: AAMC | Smoking is still the leading cause of preventable death in the U.S.
We only have so much room here, but if that’s not enough…
More than 100 reasons to quit tobacco
The case against sugar
We reviewed an interesting book about this:
The Case Against Sugar – by Gary Taubes
But suffice it to say, added sugar is a big health problem; not in the same league as tobacco, but it’s big, because of how it messes with our metabolism (and when our metabolism goes wrong, everything else goes wrong):
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
The epidemiology of sugar consumption and related mortality is harder to give clear stats about than smoking, because there’s not a clear yes/no indicator, and cause and effect are harder to establish when the waters are so muddied by other factors. But for comparison, we’ll note that compared to the 480,000 deaths caused by tobacco in the US annually, the total death to diabetes (which is not necessarily “caused by sugar consumption”, but there’s at least an obvious link when it comes to type 2 diabetes and refined carbohydrates) was 101,209 deaths due to diabetes in 2022:
National Center for Health Statistics | Diabetes
Now, superficially, that looks like “ok, so smoking is just under 5x more deadly”, but it’s important to remember that almost everyone eats added sugar, whereas a minority of people smoke, and those are mortality per total US population figures, not mortality per user of the substance in question. So in fact, smoking is, proportionally to how many people smoke, many times more deadly than diabetes, which currently ranks 8th in the “top causes of death” list.
Note: we recognize that you did say “having a sweet tooth” rather than “consuming added sugar”, but it’s worth noting that artificial sweeteners are not a get-out-of-illness-free card either:
Let’s get back to sugar though, as while it’s a very different beast than tobacco, it is arguably addictive also, by multiple mechanisms of addiction:
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
That said, those mechanisms of addiction are not necessarily as strong as some others, so in the category of what’s easy or hard to quit, this is on the easier end of things—not that that means it’s easy, just, quitting many drugs is harder. In any case, it can be done:
When It’s More Than “Just” Cravings: Beat Food Addictions!
In summary
Neither are good for the health, but tobacco is orders of magnitude worse, and should be the priority to quit, unless your doctor(s) tell you otherwise because of your personal situation, and even then, try to get multiple opinions to be sure.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: