Sleeping on Your Back after 50; Yay or Nay?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleeping Differently After 50
Sleeping is one of those things that, at any age, can be hard to master. Some of our most popular articles have been on getting better sleep, and effective sleep aids, and we’ve had a range of specific sleep-related questions, like whether air purifiers actually improve your sleep.
But perhaps there’s an underlying truth hidden in our opening sentence…is sleeping consistently difficult because the way we sleep should change according to our age?
Inspired by Brad and Mike’s video below (which was published to their 5 million+ subscribers!), there are 4 main elements to consider when sleeping on your back after you’ve hit the 50-year mark:
- Degenerative Disk Disease: As you age, your spine may start to show signs of wear and tear, which directly affects comfort while lying on your back.
- Sleep Apnea and Snoring: Sleep Apnea and snoring become more of an issue with age, and sleeping on your back can exacerbate these problems; when you sleep on your back, the soft tissues in your throat, as well as your tongue, “fall back” and partly obstruct your the airway.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal Stenosis–the often-age-related narrowing of your spinal canal–can put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine, which equally makes back-sleeping harder.
- GERD: The all-too-familiar gastroesophageal reflux disease can be more problematic when lying flat on your back, as doing so can allow easy access for stomach acid to move upwards.
Alternatives to Back Sleeping
Referencing the Mayo Clinic’s Sleep Facility’s director, Dr. Virend Somers, today’s video suggests a simple solution: sleeping on your side. The video goes into a bit more detail but, as you know, here at 10almonds we like to cut to the chase.
Modifications for Back Sleeping
If you’re a lifelong back-sleeping and cannot bear the idea of changing to your side, or your stomach, then there are a few modifications that you can make to ease any pain and discomfort.
Most solutions revolve around either leg wedges or pillow adjustments. For instance, if you’re suffering from back pain, try propping your knees up. Or if GERD is your worst enemy, a wedge pillow could help keep that acid down.
As can be expected, the video dives into more detail:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dates vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to banana, we picked the dates.
Why?
It was close, and bananas do have some strengths too! We pitted these two against each other as they’re both sweet fruits often used as a sweetening and consistency-altering ingredient in desserts and sweet snacks, so if you’re making a choice between them, here are the things to consider:
In terms of macros, dates have more than 3x the fiber, more than 2x the protein, and a little over 3x the carbs. You may be wondering how this adds up in terms of glycemic index: dates have the lower GI. So, we pick dates, here, for that reason and overall nutritional density too.
When it comes to vitamins, bananas have their moment, albeit barely: dates have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, and K, while bananas have more of vitamins A, B6, C, E, and choline, making for a marginal victory for bananas in this category.
Looking at minerals next, however, it’s quite a different story: dates have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while bananas are not higher in any mineral. No, not even potassium, for which they are famous—dates have nearly 2x more potassium than bananas.
Adding up these sections makes for a clear win for dates in general!
Enjoy either/both, but dates are the more nutritious snack/ingredient.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How To Avoid Self-Hatred & Learn To Love Oneself More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Alain de Botton gives a compassionate, but realistic, explanation in this video:
The enemy within
Or rather, the collaborator within. Because there’s usually first an enemy without—those who are critical of us, who consider that we are bad people in some fashion, and may indeed get quite colorful in their expressions of this.
Sometimes, their words will bounce straight off us; sometimes, their words will stick. So what’s the difference, and can we do anything about it?
The difference is: when their words stick, it’s usually because on some level we believe their words may be true. That doesn’t mean they necessarily are true!
They could be (and it would be a special kind of hubris to assume no detractor could ever find a valid criticism of us), but very often the reason we have that belief, or at least that fear/insecurity, is simply because it was taught to us at an early age, often by harsh words/actions of those around us; perhaps our parents, perhaps our schoolteachers, perhaps our classmates, and so forth.
The problem—and solution—is that we learn emotions much the same way that we learn language; only in part by reasoned thought, and rather for the most part, by immersion and repetition.
It can take a lot of conscious self-talk to undo the harm of decades of unconscious self-talk based on what was probably a few years of external criticisms when we were small and very impressionable… But, having missed the opportunity to start fixing this sooner, the next best time to do it is now.
We cannot, of course, simply do what a kind friend might do and expect any better results; if a kind friend tells us something nice that we do not believe is true, then however much they mean it, we’re not going to internalize it. So instead, we must simply chip away at those unhelpful longstanding counterproductive beliefs, and simply build up the habit of viewing ourselves in a kinder light.
For more on all this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Escape From The Clutches Of Shame
- To Err Is Human; To Forgive, Healthy
- How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Reduce Your Stroke Risk
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❝Each year in the U.S., over half a million people have a first stroke; however, up to 80% of strokes may be preventable.❞
~ American Stroke Association
Source: New guideline: Preventing a first stroke may be possible with screening, lifestyle changes
So, what should we do?
Some of the risk factors are unavoidable or not usefully avoidable, like genetic predispositions and old age, respectively (i.e. it is possible to avoid old age—by dying young, which is not a good approach).
Some of the risk factors are avoidable. Let’s look at the most obvious first:
You cannot drink to your good health
While overall, the World Health Organization has declared that “the only safe amount of alcohol is zero”, when it comes to stroke risk specifically, it seems that low consumption is not associated with stroke, while moderate to high consumption is associated with a commensurately increased risk of stroke:
Alcohol Intake as a Risk Factor for Acute Stroke
Note: there are some studies out there that say that a low to moderate consumption may decrease the risk compared to zero consumption. However, any such study that this writer has seen has had the methodological flaw of not addressing why those who do not drink alcohol, do not drink it. In many cases, someone who drinks no alcohol at all does so because either a) it would cause problems with some medication(s) they are taking, or b) they used to drink heavily, and quit. In either case, their reasons for not drinking alcohol may themselves be reasons for an increased stroke risk—not the lack of alcohol itself.
Smoke now = stroke later
This one is straightforward; smoking is bad for pretty much everything, and that includes stroke risk, as it’s bad for your heart and brain both, increasing stroke risk by 200–400%:
Smoking and stroke: the more you smoke the more you stroke
So, the advice here of course is: don’t smoke
Diet matters
The American Stroke Association’s guidelines recommend, just for a change, the Mediterranean Diet. This does not mean just whatever is eaten in the Mediterranean region though, and there are specifically foods that are included and excluded, and the ratios matter, so here’s a run-down of what the Mediterranean Diet does and doesn’t include:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← what isn’t it good for?!
You can outrun stroke
Or out-walk it; that’s fine too. Most important here is frequency of exercise, more than intensity. So basically, getting those 150 minutes moderate exercise per week as a minimum.
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less & Move More
Which is good, because it means we can get a lot of exercise in that doesn’t feel like “having to do” exercise, for example:
Do You Love To Go To The Gym? No? Enjoy These “No-Exercise Exercises”!
Your brain needs downtime too
Your brain (and your heart) both need you to get good regular sleep:
Sleep Disorders in Stroke: An Update on Management
We sometimes say that “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain” (because the heart feeds the brain, and also ultimately clears away detritus), and that’s true here too, so we might also want to prioritize sleep regularity over other factors, even over duration:
How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration ← this is about adverse cardiovascular events, including ischemic stroke
Keep on top of your blood pressure
High blood pressure is a very modifiable risk factor for stroke. Taking care of the above things will generally take care of this, especially the DASH variation of the Mediterranean diet:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
However, it’s still important to actually check your blood pressure regularly, because sometimes an unexpected extra factor can pop up for no obvious reason. As a bonus, you can do this improved version of the usual blood pressure test, still using just a blood pressure cuff:
Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
Consider GLP-1 receptor agonists (or…)
GLP-1 receptor agonists (like Ozempic et al.) seem to have cardioprotective and neuroprotective (thus: anti-stroke) activity independent of their weight loss benefits:
Of course, GLP-1 RAs aren’t everyone’s cup of tea, and they do have their downsides (including availability, cost, and the fact benefits reverse themselves if you stop taking them), so if you want a similar effect from a natural approach, there are some foods that work on the body’s incretin responses in the same way as GLP-1 RAs do:
5 Foods That Naturally Mimic The “Ozempic Effect”
Better to know sooner rather than too late
Rather than waiting until one half of our face is drooping to know that there was a stroke risk, here are things to watch out for to know about it before it’s too late:
6 Signs Of Stroke (One Month In Advance)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What is mitochondrial donation? And how might it help people have a healthy baby one day?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mitochondria are tiny structures in cells that convert the food we eat into the energy our cells need to function.
Mitochondrial disease (or mito for short) is a group of conditions that affect this ability to generate the energy organs require to work properly. There are many different forms of mito and depending on the form, it can disrupt one or more organs and can cause organ failure.
There is no cure for mito. But an IVF procedure called mitochondrial donation now offers hope to families affected by some forms of mito that they can have genetically related children free from mito.
After a law to allow mitochondrial donation in Australia was passed in 2022, scientists are now preparing for a clinical trial to see if mitochondrial donation is safe and works.
Jonathan Borba/Pexels What is mitochondrial disease?
There are two types of mitochondrial disease.
One is caused by faulty genes in the nuclear DNA, the DNA we inherit from both our parents and which makes us who we are.
The other is caused by faulty genes in the mitochondria’s own DNA. Mito caused by faulty mitochondrial DNA is passed down through the mother. But the risk of disease is unpredictable, so a mother who is only mildly affected can have a child who develops serious disease symptoms.
Mitochondrial disease is the most common inherited metabolic condition affecting one in 5,000 people.
Some people have mild symptoms that progress slowly, while others have severe symptoms that progress rapidly. Mito can affect any organ, but organs that need a lot of energy such as brain, muscle and heart are more often affected than other organs.
Mito that manifests in childhood often involves multiple organs, progresses rapidly, and has poor outcomes. Of all babies born each year in Australia, around 60 will develop life-threatening mitochondrial disease.
What is mitochondrial donation?
Mitochondrial donation is an experimental IVF-based technique that offers people who carry faulty mitochondrial DNA the potential to have genetically related children without passing on the faulty DNA.
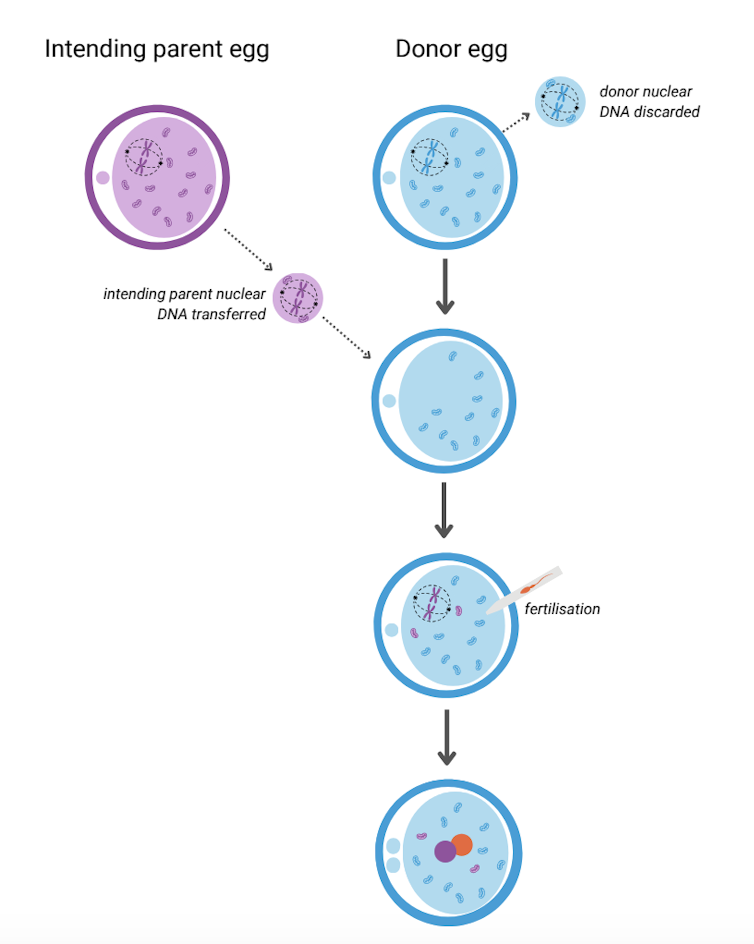
It involves removing the nuclear DNA from the egg of someone who carries faulty mitochondrial DNA and inserting it into a healthy egg donated by someone not affected by mito, which has had its nuclear DNA removed.
The donor egg (in blue) has had its nuclear DNA removed. Author provided The resulting egg has the nuclear DNA of the intending parent and functioning mitochondria from the donor. Sperm is then added and this allows the transmission of both intending parents’ nuclear DNA to the child.
A child born after mitochondrial donation will have genetic material from the three parties involved: nuclear DNA from the intending parents and mitochondrial DNA from the egg donor. As a result the child will likely have a reduced risk of mito, or no risk at all.
The procedure removes the faulty DNA to reduce the chance of it passing on to the baby. Josh Willink/Pexels This highly technical procedure requires specially trained scientists and sophisticated equipment. It also requires both the person with mito and the egg donor to have hormone injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. The eggs are then retrieved in an ultrasound-guided surgical procedure.
Mitochondrial donation has been pioneered in the United Kingdom where a handful of babies have been born as a result. To date there have been no reports about whether they are free of mito.
Maeve’s Law
After three years of public consultation The Mitochondrial Donation Law Reform (Maeve’s Law) Bill 2021 was passed in the Australian Senate in 2022, making mitochondrial donation legal in a research and clinical trial setting.
Maeve’s law stipulates strict conditions including that clinics need a special licence to perform mitochondrial donation.
To make sure mitochondrial donation works and is safe before it’s introduced into Australian clinical practice, the law also specifies that initial licences will be issued for pre-clinical and clinical trial research and training.
We’re expecting one such licence to be issued for the mitoHOPE (Healthy Outcomes Pilot and Evaluation) program, which we are part of, to perfect the technique and conduct a clinical trial to make sure mitochondrial donation is safe and effective.
Before starting the trial, a preclinical research and training program will ensure embryologists are trained in “real-life” clinical conditions and existing mitochondrial donation techniques are refined and improved. To do this, many human eggs are needed.
The need for donor eggs
One of the challenges with mitochondrial donation is sourcing eggs. For the preclinical research and training program, frozen eggs can be used, but for the clinical trial “fresh” eggs will be needed.
One possible source of frozen eggs is from people who have stored eggs they don’t intend to use.
A recent study looked at data on the outcomes of eggs stored at a Melbourne clinic from 2012 to 2021. Over the ten-year period, 1,132 eggs from 128 patients were discarded. No eggs were donated to research because the clinics where the eggs were stored did not conduct research requiring donor eggs.
However, research shows that among people with stored eggs, the number one choice for what to do with eggs they don’t need is to donate them to research.
This offers hope that, given the opportunity, those who have eggs stored that they don’t intend to use might be willing to donate them to mitochondrial donation preclinical research.
As for the “fresh” eggs needed in the future clinical trial, this will require individuals to volunteer to have their ovaries stimulated and eggs retrieved to give those people impacted by mito a chance to have a healthy baby. Egg donors may be people who are friends or relatives of those who enter the trial, or it might be people who don’t know someone affected by mito but would like to help them conceive.
At this stage, the aim is to begin enrolling participants in the clinical trial in the next 12 to 18 months. However this may change depending on when the required licences and ethics approvals are granted.
Karin Hammarberg, Senior Research Fellow, Global and Women’s Health, School of Public Health & Preventive Medicine, Monash University; Catherine Mills, Professor of Bioethics, Monash University; Mary Herbert, Professor, Anatomy & Developmental Biology, Monash University, and Molly Johnston, Research fellow, Monash Bioethics Centre, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
It’s Not Hysteria – by Dr. Karen Tan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, who this book is aimed at: in case it wasn’t clear, this book assumes you have, or at least have had, a uterus. If that’s not you, then well, it’ll still be an interesting read but it won’t be about your reproductive health.
Secondly, about that “reproductive health”: it’s mostly not actually about reproductive health literally, but rather, the health of one’s reproductive organs and the things that they affect—which is a lot more than the ability to reproduce!
Dr. Tang takes us on a (respectably in-depth) tour of the relevant anatomy, before moving on to physiology, before continuing to pathology (i.e. things that can go wrong, and often do), and finally various treatment options, including elective procedures, and the pros and cons thereof.
She also talks the reader through talking about things with gynecologists and other healthcare providers, and making sure concerns are not dismissed out-of-hand (something that happens a lot, of course).
The style throughout is quite detailed prose, but without being difficult at all to read, and (assuming one is interested in the topic) it’s very engaging.
Bottom line: if you would like to know more about uteri and everything that is (or commonly/unfortunately) can be attached to them, the effects they have on the rest of the body and health, and what can be done about things not being quite right, then this is a good book for that.
Click here to check out It’s Not Hysteria, and understand more of what’s going on down there!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pink Himalayan Salt: Health Facts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Q: Great article about the health risks of salt to organs other than the heart! Is pink Himalayan sea salt, the pink kind, healthier?
Thank you! And, no, sorry. Any salt that is sodium chloride has the exact same effect because it’s chemically the same substance, even if impurities (however pretty) make it look different.
If you want a lower-sodium salt, we recommend the kind that says “low sodium” or “reduced sodium” or similar. Check the ingredients, it’ll probably be sodium chloride cut with potassium chloride. Potassium chloride is not only not a source of sodium, but also, it’s a source of potassium, which (unlike sodium) most of us could stand to get a little more of.
For your convenience: here’s an example on Amazon!
Bonus: you can get a reduced sodium version of pink Himalayan salt too!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: