The Brain As A Work-In-Progress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
And The Brain Goes Marching On!
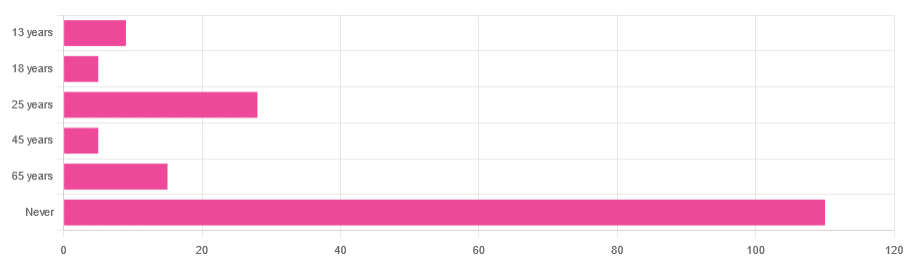
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you “when does the human brain stop developing?” and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 64% of people said “Never”
- About 16% of people said “25 years”
- About 9% of people said “65 years”
- About 5% of people said “13 years”
- About 3% of people said “18 years”
- About 3% of people said “45 years”
Some thoughts, before we get into the science:
An alternative wording for the original question was “when does the human brain finish developing”; the meaning is the same but the feeling is slightly different:
- “When does the human brain stop developing?” focuses attention on the idea of cessation, and will skew responses to later ages
- When does the human brain finish developing?” focuses on attention on a kind of “is it done yet?” and will skew responses to earlier ages
Ultimately, since we had to chose one word or another, we picked the shortest one, but it would have been interesting if we could have done an A/B test, and asked half one way, and half the other way!
Why we picked those ages
We picked those ages as poll options for reasons people might be drawn to them:
- 13 years: in English-speaking cultures, an important milestone of entering adolescence (note that the concept of a “teenager” is not precisely universal as most languages do not have “-teen” numbers in the same way; the concept of “adolescent” may thus be tied to other milestones)
- 18 years: age of legal majority in N. America and many other places
- 25 years: age popularly believed to be when the brain is finished developing, due to a study that we’ll talk about shortly (we guess that’s why there’s a spike in our results for this, too!)
- 45 years: age where many midlife hormonal changes occur, and many professionals are considered to have peaked in competence and start looking towards retirement
- 65 years: age considered “senior” in much of N. America and many other places, as well as the cut-off and/or starting point for a lot of medical research
Notice, therefore, how a lot of things are coming from places they really shouldn’t. For example, because there are many studies saying “n% of people over 65 get Alzheimer’s” or “n% of people over 65 get age-related cognitive decline”, etc, 65 becomes the age where we start expecting this—because of an arbitrary human choice of where to draw the cut-off for the study enrollment!
Similarly, we may look at common ages of legal majority, or retirement pensions, and assume “well it must be for a good reason”, and dear reader, those reasons are more often economically motivated than they are biologically reasoned.
So, what does the science say?
Our brains are never finished developing: True or False?
True! If we define “finished developing” as “we cease doing neurogenesis and neuroplasticity is no longer in effect”.
Glossary:
- Neurogenesis: the process of creating new brain cells
- Neuroplasticity: the process of the brain adapting to changes by essentially rebuilding itself to suit our perceived current needs
We say “perceived” because sometimes neuroplasticity can do very unhelpful things to us (e.g: psychological trauma, or even just bad habits), but on a biological level, it is always doing its best to serve our overall success as an organism.
For a long time it was thought that we don’t do neurogenesis at all as adults, but this was found to be untrue:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
Summary of conclusions of the above: we’re all growing new brain cells at every age, even if we be in our 80s and with Alzheimer’s disease, but there are things we can do to enhance our neurogenic potential along the way.
Neuroplasticity will always be somewhat enhanced by neurogenesis (after all, new neurons get given jobs to do), and we reviewed a great book about the marvels of neuroplasticity including in older age:
Our brains are still developing up to the age of 25: True or False?
True! And then it keeps on developing after that, too. Now this is abundantly obvious considering what we just talked about, but see what a difference the phrasing makes? Now it makes it sound like it stops at 25, which this statement doesn’t claim at all—it only speaks for the time up to that age.
A lot of the popular press about “the brain isn’t fully mature until the age of 25” stems from a 2006 study that found:
❝For instance, frontal gray matter volume peaks at about age 11.0 years in girls and 12.1 years in boys, whereas temporal gray matter volume peaks at about age at 16.7 years in girls and 16.2 years in boys. The dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex, important for controlling impulses, is among the latest brain regions to mature without reaching adult dimensions until the early 20s.❞
Source: Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Adolescent Brain
There are several things to note here:
- The above statement is talking about the physical size of the brain growing
- Nowhere does he say “and stops developing at 25”
However… The study only looked at brains up to the age of 25. After that, they stopped looking, because the study was about “the adolescent brain” so there has to be a cut-off somewhere, and that was the cut-off they chose.
This is the equivalent of saying “it didn’t stop raining until four o’clock” when the reality is that four o’clock is simply when you gave up on checking.
The study didn’t misrepresent this, by the way, but the popular press did!
Another 2012 study looked at various metrics of brain development, and found:
- Synapse overproduction into the teens
- Cortex pruning into the late 20s
- Prefrontal pruning into middle age at least (they stopped looking)
- Myelination beyond middle age (they stopped looking)
Source: Experience and the developing prefrontal cortex ← check out figure 1, and make sure you’re looking at the human data not the rat data
So how’s the most recent research looking?
Here’s a 2022 study that looked at 123,984 brain scans spanning the age range from mid-gestation to 100 postnatal years, and as you can see from its own figure 1… Most (if not all) brain-things keep growing for life, even though most slow down at some point, they don’t stop:
Brain charts for the human lifespan ← check out figure 1; don’t get too excited about the ventricular volume column as that is basically “brain that isn’t being a brain”. Do get excited about the rest, though!
Want to know how not to get caught out by science being misrepresented by the popular press? Check out:
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Finish What You Start – by Peter Hollins
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For some people, getting started is the problem. For others of us, getting started is the easy part! We just need a little help not dropping things we started.
There are summaries at the starts and ends of sections, and many “quick tips” to get you back on track.
As a taster: one of these is “temptation bundling“, combining unpleasant things with pleasant. A kind of “spoonful of sugar” approach.
Hollins also discusses hyperbolic discounting (the way we tend to value rewards according to how near they are, and procrastinate accordingly). He offers a tool to overcome this, too, the “10–10–10 rule“.
Also dealt with is “the preparation trap“, and how to know when you have enough information to press on.
For a lot of us, the places we’re most likely to drop a project is 20% in (initial enthusiasm wore off) or 80% in (“it’s nearly done; no need to worry about it”). Those are the times when the advices in this book can be particularly handy!
All in all, a great book for seeing a lot of things to completion.
Share This Post
-
5 Steps To Quit Sugar Easily
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sugar is one of the least healthy things that most people consume, yet because it’s so prevalent, it can also be tricky to avoid at first, and the cravings can also be a challenge. So, how to quit it?
Step by step
Dr. Mike Hansen recommends the following steps:
- Be aware: a lot of sugar consumption is without realizing it or thinking about it, because of how common it is for there to be added sugar in things we might purchase ready-made, even supposedly healthy things like yogurts, or easy-to-disregard things like condiments.
- Recognize sugar addiction: a controversial topic, but Dr. Hansen comes down squarely on the side of “yes, it’s an addiction”. He wants us to understand more about the mechanics of how this happens, and what it does to us.
- Reduce gradually: instead of going “cold turkey”, he recommends we avoid withdrawal symptoms by first cutting back on liquid sugars like sodas, juices, and syrups, before eliminating solid sugar-heavy things like candy, sugar cookies, etc, and finally the more insidious “why did they put sugar in this?” added-sugar products.
- Find healthy alternatives: simple like-for-like substitutions; whole fruits instead of juices/smoothies, for example. 10almonds tip: stuffing dates with an almond each makes it very much like eating chocolate, experientially!
- Manage cravings: Dr. Hansen recommends distraction, and focusing on upping other healthy habits such as hydration, exercise, and getting more vegetables.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Mythbusting The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
Take care!
Share This Post
-
These Top Few Things Make The Biggest Difference To Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Best Few Interventions For The Best Health
Writer’s note: I was going to do something completely different for today (so that can go out another week now), but when reflecting on my own “what should I focus on in the new year?” (in terms of my own personal health goals and such) it occured to me that I should look back on the year’s articles, to take our own advice myself, and see what most important things I should make sure to focus on.
In so doing for myself, it occured to me that you, our subscribers who like condensed information and simple interventions for big positive effects, might also find value in a similar once-over. And so, today’s main feature was born!
Sometimes at 10almonds we talk about “those five things that affect everything”. They are:
- Good diet
- Good exercise
- Good sleep
- Not drinking
- Not smoking
If we were to add a sixth in terms of things that make a huge difference, it would be “manage stress effectively” and a seventh, beyond the scope of our newsletter, would be “don’t be socioeconomically disadvantaged” (e.g. poor, and/or part of some disprivileged minority group).
But as for those five we listed, it still leaves the question: what are the few most effective things we can do to improve them? Where can we invest our time/energy/effort for greatest effect?
Good diet
Best current science consistently recommends the Mediterranean Diet:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For?
But it can be tweaked for specific desired health considerations:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
Other most-effective dietary tweaks that impact a lot of other areas of health include looking after your gut health and looking after your blood sugars:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
and
“Let Them Eat Cake”, She Said (10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars)
Good exercise
Most exercise is good, but two of the most beneficial things that are (for most people) easy to implement are walking, and High-Intensity Interval Training:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Good sleep
This means quality and quantity! We cannot skimp on either and expect good health:
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
and as for quality,
The Head-To-Head Of Google and Apple’s Top Apps For Getting Your Head Down
Not drinking
According to the World Health Organization, the only safe amount of alcohol is zero.
See also:
Can We Drink To Good Health? (e.g. Red Wine & Heart Health)
and
Not smoking
We haven’t done a main feature on this! It’s probably not really necessary, as it’s not very contentious to say “smoking is bad for everything”.
WHO | Tobacco kills up to half its users who don’t quit
However, as a side-note, while cannabis is generally recognised as not as harmful as tobacco-based products, it has some fairly major drawbacks too. For some people, the benefits (e.g. pain relief) may outweigh the risks, though:
Final thoughts
Not sure where to start? We suggest this order of priorities, unless you have a major health condition that makes something else a higher priority:
- If you smoke, stop
- If you drink, reduce, or ideally stop
- Improve your diet
About that diet…
- Worry less about what to exclude, and instead focus on adding more variety of fruit/veg
- See also: Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- That said, if you’re looking for things to cut, sugar is a top candidate (and red meat is in clear second place albeit some way below)
When it comes to exercise, get your 10,000 daily steps in (actually, science says 8,000 steps is fine), and consider adding HIIT per our above article, when you feel like adding that in. As for that about the steps:
When it comes to sleep, if you’re taking care of the above things, and set a regular early wake-up time that you do not deviate from, then this will probably take care of itself, if you don’t have a sleep-inconvenient lifestyle (e.g. shift work, just had a baby, etc) or a sleep disorder.
For further pointers, see: 10 Tips for Better Sleep: Starting In The Morning
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Survival of the Prettiest – by Dr. Nancy Etcoff
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Beauty is in the eye of the beholder, right? And what does it matter, in this modern world, especially if we are already in a happy stable partnership?
The science of it, as it turns out, is less poetic. Not only is evolutionary psychology still the foundation of our perception of human beauty (yes, even if we have zero possibility of further procreation personally), but also, its effects are far, far wider than partner selection.
From how nice people are to you, to how much they trust you, to how easily they will forgive a (real or perceived) misdeed, to what kind of medical care you get (or don’t), your looks shape your experiences.
In this very easy-reading work that nevertheless contains very many references, Dr. Etcoff explores the science of beauty. Not just what traits are attractive and why, but also, what they will do for (or against) us—in concrete terms, with numbers.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the subconscious biases held by yourself and others, this book is a top-tier primer.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wholesome Threesome Protein Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This soup has two protein– and fiber-rich pseudo-grains, one real wholegrain, and nutrient-dense cashews for yet even more protein, and all of the above are full of many great vitamins and minerals. All in all, a well-balanced and highly-nutritious light meal!
You will need
- ⅓ cup quinoa
- ⅓ cup green lentils
- ⅓ cup wholegrain rice
- 5 cups low-sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made this yourself from offcuts of vegetables, but failing that, low-sodium stock cubes can be bought in most large supermarkets)
- ¼ cup cashews
- 1 tbsp dried thyme
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Optional topping:
- ⅓ cup pine nuts
- ⅓ cup finely chopped fresh mint leaves
- 2 tbsp coconut oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Rinse the quinoa, lentils, and rice.
2) Boil 4 cups of the stock and add the grains and seasonings (MSG/salt, pepper, thyme); simmer for about 25 minutes.
3) Blend the cashews with the other cup of vegetable stock, until smooth. Add the cashew mixture to the soup, stirring it in, and allow to simmer for another 5 minutes.
4) Heat the coconut oil in a skillet and add the pine nuts, stirring until they are golden brown.
5) Serve the soup into bowls, adding the mint and pine nuts to each.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Give Us This Day Our Daily Dozen
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We often write about polyphenols here at 10almonds; sometimes mentioning that a certain food is good because it has them, or else occasionally an entire article about a particular polyphenol. But what about a birds-eye view of polyphenols as a whole?
Well, there are many, but we’ve picked 21 particularly beneficial for human health, and what foods contain them.
We’ll be working from this fantastic database, by the way:
❝Phenol-Explorer is the first comprehensive database on polyphenol content in foods. The database contains more than 35,000 content values for 500 different polyphenols in over 400 foods. These data are derived from the systematic collection of more than 60,000 original content values found in more than 1,300 scientific publications. Each of these publications has been critically evaluated before inclusion in the database. The whole data on the polyphenol composition of foods is available for download.❞
Source: Phenol-Explorer.EU | Database on polyphenol content in foods
We use this database at least several times per week while writing 10almonds; it’s a truly invaluable resource!
However, 500 is a lot, so here’s a rundown of 21 especially impactful ones; we’ve sorted them per the categories used in the explorer, and in some cases we’ve aggregated several very similar polyphenols typically found together in the same foods, into one item (so for example we just list “quercetin” instead of quercetin 3-O-rutinoside + quercetin 4′-O-glucoside + quercetin 3,4′-O-diglucoside, etc etc). We’ve also broadly grouped some particularly populous ones such as “anthocyanins”, “catechins”, and so forth.
Without further ado, here’s what you ideally want to be getting plenty of in your diet:
Flavonoids
- Quercetin
- Foods: onions, apples, berries, kale, broccoli, capers.
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, reduces allergy symptoms, supports heart and brain health, and may lower blood pressure.
- See also: Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
- Kaempferol
- Foods: spinach, kale, tea (green and black), capers, brussels sprouts.
- Benefits: antioxidant, may reduce the risk of cancer, supports cardiovascular health, and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
- Foods: green tea, matcha.
- Benefits: potent antioxidant, promotes weight loss, supports brain health, and may reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Anthocyanins
- Foods: blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, red cabbage, cherries.
- Benefits: improve brain health, support eye health, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Apigenin
- Foods: parsley, celery, chamomile tea.
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, reduces anxiety, and supports brain and immune system health.
- Luteolin
- Foods: peppers, thyme, celery, carrots.
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, supports brain health, and may help reduce the growth of cancer cells.
- Catechins (aside from EGCG)
- Foods: green tea, dark chocolate, apples
- Benefits: boosts metabolism, supports cardiovascular health, and reduces oxidative stress.
- Hesperidin
- Foods: oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits.
- Benefits: supports vascular health, reduces inflammation, and may help manage diabetes.
- Naringenin
- Foods: oranges, grapefruits, tomatoes.
- Benefits: antioxidant, supports liver health, and may improve cholesterol levels.
For more on epigallocatechin gallate and other catechins, see: Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
Phenolic Acids
- Chlorogenic acid
- Foods: coffee, artichokes, apples, pears.
- Benefits: supports weight management, improves blood sugar regulation, and reduces inflammation.
- See also: Green Coffee Bean Extract: Coffee Benefits Without The Coffee?
- Caffeic acid
- Foods: coffee, thyme, sage, basil.
- Benefits: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and supports skin health.
- See also: The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Ferulic acid
- Foods: whole grains, rice bran, oats, flaxseeds, spinach.
- Benefits: protects skin from UV damage, reduces inflammation, and supports cardiovascular health.
- Gallic acid
- Foods: green tea, berries, walnuts.
- Benefits: antioxidant, may reduce the risk of cancer, and supports brain health.
Stilbenes
- Resveratrol
- Foods: red currants, blueberries, peanuts.
- Benefits: anti-aging properties, supports heart health, and reduces inflammation.
- See also: Resveratrol & Healthy Aging ← and no, you can’t usefully get it from red wine; here’s why!
Lignans
- Secoisolariciresinol
- Foods: flaxseeds, sesame seeds, whole grains.
- Benefits: supports hormone balance, reduces the risk of hormone-related cancers, and promotes gut health.
- Matairesinol
- Foods: rye, oats, barley, sesame seeds.
- Benefits: hormonal support, antioxidant, and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
See also: Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc ← for maximum nutritional availability!
Tannins
- Ellagic acid
- Foods: pomegranates, raspberries, walnuts.
- Benefits: anti-cancer properties, supports skin health, and reduces inflammation.
- Proanthocyanidins
- Foods: cranberries, apples, grapes, dark chocolate.
- Benefits: supports urinary tract health, reduces inflammation, and improves blood vessel health.
See also: Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Curcuminoids
- Curcumin
- Foods: turmeric.
- Benefits: potent anti-inflammatory, supports joint health, and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- See also: Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Isoflavones
- Genistein
- Foods: soybeans, chickpeas.
- Benefits: supports bone health, reduces the risk of hormone-related cancers, and promotes heart health.
- Daidzein
- Foods: soybeans, legumes.
- Benefits: hormonal balance, supports bone health, and may help alleviate menopausal symptoms.
See also: What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
Well, that’s a lot of things to remember!
If you want to make it easier for yourself, you can simply make sure to get at least 30 different kinds of plant into your diet per week, and by doing so, statistically, you should cover most of these!
Read more: What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Alternatively, for a middle-ground approach of targetting 16 most polyphenol delivering foods, check out this super-dense arrangement:
Mediterranean Diet… In A Pill? ← it’s about plant extracts from 16 specific foods, and the polyphenols they deliver
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Quercetin