How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
High-Intensity Interval Training, henceforth “HIIT”, is a well-researched and well-evidenced approach to exercise that gives powerful health benefits.
Specifically, health benefits that we don’t get from moderate exercise (as important as that is too) or endurance training.
Super-quick overview of the benefits first:
- Burns more calories than other forms of exercise
- Boosts your metabolic rate for hours afterwards
- …which means it actually works* for fat loss
- Reduces blood pressure (unless already healthy)
- Can promote muscle growth (depends on other factors)
*remember that most forms of exercise aren’t very good for fat loss, because our metabolism will slow afterwards to compensate. So HIIT flipping this one is quite a big deal.
What actually is it?
HIIT means exercise sessions in which one alternates between high intensity “maximum effort” bursts, and short recovery periods during which more moderate exercise is performed.
An example for runners could be switching between sprinting or jogging, changing mode each time one passes a street light.
❝A total of only two minutes of sprint interval exercise was sufficient to elicit similar responses as 30 minutes of continuous moderate intensity aerobic exercise❞
What did you mean about not wrecking your body? Is that… Likely?
Hopefully not, but it’s a barrier to some! We are not all twenty-something college athletes, after all, and our bodies aren’t always as durable as they used to be.
HIIT relies on intense exercise and short recovery periods, but what if our bodies are not accustomed to intense exercise, and need longer recovery periods? Can we still get the same benefits?
The trick is not to change the intensity or the recovery periods, but the exercise itself.
For HIIT to work the “intense” part has to be best-effort or approaching such. That part’s not negotiable. The recovery periods can be stretched a bit if you need to, but with the right tweaks, you ideally won’t have to do that.
Great! How?
First, note that you can do resistance interval training without impact. For example, if you crank up the resistance on an exercise bike or similar machine, you will be doing resistance training along with your cardio, and you’ll be doing it without the impact on your joints that you would if out pounding the pavement on foot.
(Running is fine if your body is used to it, but please don’t make HIIT your first running exercise in a decade)
Second, consider your environment. That exercise bike? You can get off it any time and you’re already at home (or perhaps your gym, with your car outside). Not so if you took up mountain biking or road racing.
Third, go for what is gentle in motion, even if it’s not resistance work per se. Swimming is a fabulous option for most people, and can absolutely be done with HIIT principles. Since vision is often obscured while swimming, counting strokes can be a good way to do HIIT. For example, ten strokes max effort, ten strokes normal, repeat. Do make sure you are aware of where the end of the pool is, though!
Fourth, make it fun! Ok, this one’s not about the safety quite so much, but it is about sustainability, and that’s critical for practical purposes too. You will only continue an exercise routine that you enjoy, after all.
- Could you curate a musical playlist that shifts tempo to cue your exercise mode intervals?
- Could you train with an exercise partner? Extra fun if this has a “relay race” feel to it, i.e. when one person completes a high intensity interval, the other person must now begin theirs.
Need some pointers getting started?
There are a lot of HIIT apps out there, so you can just search for that on your device of choice.
But!
We at 10almonds have recommended 7-Minute Workout before, which is available for iOS and for Android, and we stand by that as a great starting choice.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Detox: What’s Real, What’s Not, What’s Useful, What’s Dangerous?
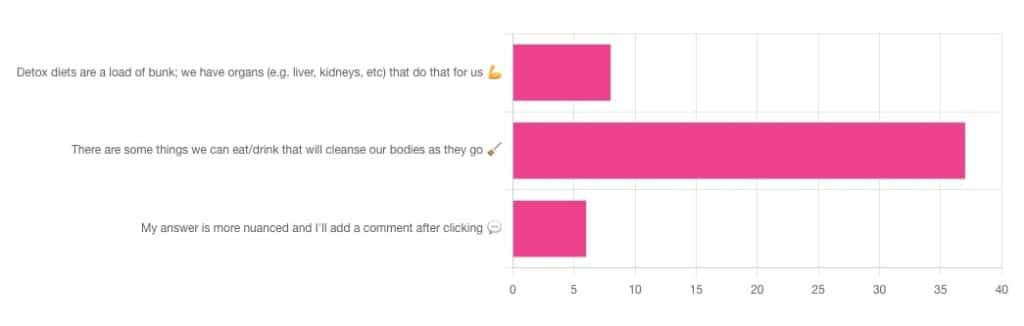
Out of the subscribers who engaged in the poll, it looks like we have a lot of confidence in at least some detox approaches being useful!
Celery juice is most people’s go-to, and indeed it was the only one to get mentioned in the comments added. So let’s take a look at that first…
Celery juice
Celery juice is enjoyed by many people, with many health benefits in mind, including to:
- reduce inflammation
- lower blood pressure
- heal the liver
- fight cancer
- reduce bloating
- support the digestive system
- increase energy
- support weight loss
- promote good mental health
An impressive list! With such an impressive list, we would hope for an impressive weight of evidence, so regular readers might be wondering why those bullet-pointed items aren’t all shiny hyperlinks to studies backing those claims. The reason is…
There aren’t any high-quality studies that back any of those claims.
We found one case study (so, a study with a sample size of one; not amazing) that observed a blood pressure change in an elderly man after drinking celery juice.
Rather than trawl up half of PubMed to show the lacklustre results in a way more befitting of Research Review Monday, though, here’s a nice compact article detailing the litany of disappointment that is science’s observations regards celery juice:
Why Are People Juicing Their Celery? – by Allison Webster, PhD, RD
A key take-away is: juicing destroys the fiber that is celery’s biggest benefit, and its phytochemicals are largely unproven to be of use.
If you enjoy celery, great! It (when not juiced) is a great source of fiber and water. If you juice it, it’s a great source of water.
Activated Charcoal
Unlike a lot of greenery—whose “cleansing” benefits mostly come from fiber and disappear when juiced—activated charcoal has a very different way of operating.
Activated charcoal is negatively charged on a molecular level*, and that—along with its porous nature—traps toxins. It really is a superpowered detox that actually works very well indeed.
But…
It works very well indeed. It will draw out toxins so well, that it’s commonly used to treat poisonings. “Wait”, we hear you say, “why was that a but”?
It doesn’t know what a toxin is. It just draws out all of the things. You took medicine recently? Not any more you didn’t. You didn’t even take that medication orally, you took it some other way? Activated charcoal does not care:
- The effect of activated charcoal on drug exposure following intravenous administration: A meta-analysis
- Activated charcoal for acute overdose: a reappraisal
Does this mean that activated charcoal can be used to “undo” a night of heavy drinking?
Sadly not. That’s one of the few things it just doesn’t work for. It won’t work for alcohol, salts, or metals:
The Use of Activated Charcoal to Treat Intoxications
*Fun chemistry mnemonic about ions:
Cations are pussitive
Anions (by process of elimination) are negative
Onions taste good in salad (remember also: Cole’s Law)
Bottom line on detox foods/drinks:
- Fiber is great; juicing removes fiber. Eat your greens (don’t drink them)!
- Activated charcoal is the heavy artillery of detoxing
- Sometimes it will remove things you didn’t want removed, though
- It also won’t help against alcohol, sadly
Share This Post
-
Health Nut: A Feel-Good Cookbook – by Jess Damuck
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is a classically trained chef (worked with Martha Stewart for a long time!), and while health is the focus here, it’s not the be-all-and-end-all, so there’s a lot of attention given to pleasure also. Which, after all, is not a zero-sum game—we can have both!
So, the title and subtitle together sum up the ethos of the book pretty well.
The recipes themselves are divided into categories by meal-type, snacks, desserts, etc. They’re varied enough to suit most moods and seasons, as well as being equally appropriate for cooking for one, or a family, or entertaining. Many (but not all) of the recipes are vegan, though where they’re not, the substitutions are mostly easy and obvious, or explained, or else alternative recipes are given (for example a vegan “tuna” recipe).
In terms of complexity, these are not very complex, yet include everything they need to to make things interesting. That said, the ingredients are also not obscure, and should be easy to find in any reasonably well-stocked supermarket.
One small downside is that many of the recipes are not illustrated, but the instructions are clear enough that this isn’t really a problem, in this reviewer’s opinion.
Bottom line: if you’d like to broaden your kitchen repertoire with plants-forward cooking from an accomplished chef, then this is a good book for that.
Click here to check out Health Nut, and enjoy the feel-good food!
Share This Post
-
Oral vaccines could provide relief for people who suffer regular UTIs. Here’s how they work
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In a recent TikTok video, Australian media personality Abbie Chatfield shared she was starting a vaccine to protect against urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Huge news for the UTI girlies. I am starting a UTI vaccine tonight for the first time.
Chatfield suffers from recurrent UTIs and has turned to the Uromune vaccine, an emerging option for those seeking relief beyond antibiotics.
But Uromune is not a traditional vaccine injected to your arm. So what is it and how does it work?
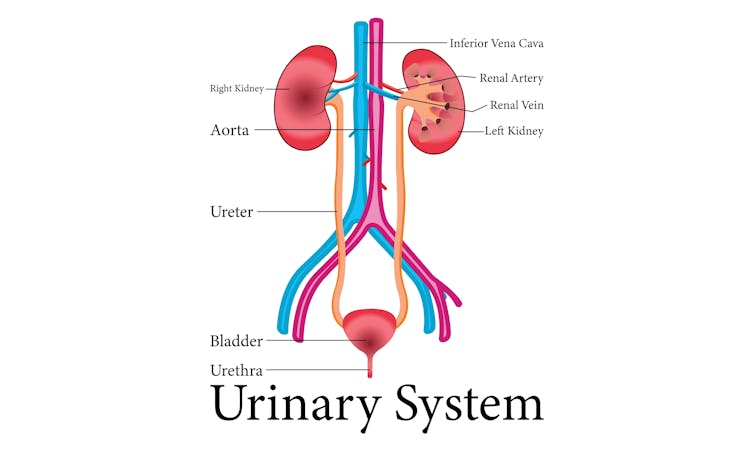
9nong/Shutterstock First, what are UTIs?
UTIs are caused by bacteria entering the urinary system. This system includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters (thin tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder), and the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the body).
The most common culprit is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria normally found in the intestines.
While most types of E. coli are harmless in the gut, it can cause infection if it enters the urinary tract. UTIs are particularly prevalent in women due to their shorter urethras, which make it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
Roughly 50% of women will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime, and up to half of those will have a recurrence within six months.
UTIs are caused by bacteria enterning the urinary system. oxo7051/Shutterstock The symptoms of a UTI typically include a burning sensation when you wee, frequent urges to go even when the bladder is empty, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back. If left untreated, a UTI can escalate into a kidney infection, which can require more intensive treatment.
While antibiotics are the go-to treatment for UTIs, the rise of antibiotic resistance and the fact many people experience frequent reinfections has sparked more interest in preventive options, including vaccines.
What is Uromune?
Uromune is a bit different to traditional vaccines that are injected into the muscle. It’s a sublingual spray, which means you spray it under your tongue. Uromune is generally used daily for three months.
It contains inactivated forms of four bacteria that are responsible for most UTIs, including E. coli. By introducing these bacteria in a controlled way, it helps your immune system learn to recognise and fight them off before they cause an infection. It can be classified as an immunotherapy.
A recent study involving 1,104 women found the Uromune vaccine was 91.7% effective at reducing recurrent UTIs after three months, with effectiveness dropping to 57.6% after 12 months.
These results suggest Uromune could provide significant (though time-limited) relief for women dealing with frequent UTIs, however peer-reviewed research remains limited.
Any side effects of Uromune are usually mild and may include dry mouth, slight stomach discomfort, and nausea. These side effects typically go away on their own and very few people stop treatment because of them. In rare cases, some people may experience an allergic reaction.
How can I access it?
In Australia, Uromune has not received full approval from the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), and so it’s not something you can just go and pick up from the pharmacy.
However, Uromune can be accessed via the TGA’s Special Access Scheme or the Authorised Prescriber pathway. This means a GP or specialist can apply for approval to prescribe Uromune for patients with recurrent UTIs. Once the patient has a form from their doctor documenting this approval, they can order the vaccine directly from the manufacturer.
Antibiotics are the go-to treatment for UTIs – but scientists are looking at options to prevent them in the first place. Photoroyalty/Shutterstock Uromune is not covered under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, meaning patients must cover the full cost out-of-pocket. The cost of a treatment program is around A$320.
Uromune is similarly available through special access programs in places like the United Kingdom and Europe.
Other options in the pipeline
In addition to Uromune, scientists are exploring other promising UTI vaccines.
Uro-Vaxom is an established immunomodulator, a substance that helps regulate or modify the immune system’s response to bacteria. It’s derived from E. coli proteins and has shown success in reducing UTI recurrences in several studies. Uro-Vaxom is typically prescribed as a daily oral capsule taken for 90 days.
FimCH, another vaccine in development, targets something called the adhesin protein that helps E. coli attach to urinary tract cells. FimCH is typically administered through an injection and early clinical trials have shown promising results.
Meanwhile, StroVac, which is already approved in Germany, contains inactivated strains of bacteria such as E. coli and provides protection for up to 12 months, requiring a booster dose after that. This injection works by stimulating the immune system in the bladder, offering temporary protection against recurrent infections.
These vaccines show promise, but challenges like achieving long-term immunity remain. Research is ongoing to improve these options.
No magic bullet, but there’s reason for optimism
While vaccines such as Uromune may not be an accessible or perfect solution for everyone, they offer real hope for people tired of recurring UTIs and endless rounds of antibiotics.
Although the road to long-term relief might still be a bit bumpy, it’s exciting to see innovative treatments like these giving people more options to take control of their health.
Iris Lim, Assistant Professor in Biomedical Science, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Black Cohosh vs The Menopause
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Black Cohosh, By Any Other Name…
Black cohosh is a flowering plant whose extracts are popularly used to relieve menopausal (and postmenopausal) symptoms.
Note on terms: we’ll use “black cohosh” in this article, but if you see the botanical names in studies, the reason it sometimes appears as Actaea racemosa and sometimes as Cimicfuga racemosa, is because it got changed and changed back on account of some disagreements between botanists. It’s the same plant, in any case!
Read: Reclassification of Actaea to include Cimicifuga and Souliea (Ranunculaceae)
Does it work?
In few words: it works for physical symptoms, but not emotional ones, based on this large (n=2,310) meta-analysis of studies:
❝Black cohosh extracts were associated with significant improvements in overall menopausal symptoms (Hedges’ g = 0.575, 95% CI = 0.283 to 0.867, P < 0.001), as well as in hot flashes (Hedges’ g = 0.315, 95% CIs = 0.107 to 0.524, P = 0.003), and somatic symptoms (Hedges’ g = 0.418, 95% CI = 0.165 to 0.670, P = 0.001), compared with placebo.
However, black cohosh did not significantly improve anxiety (Hedges’ g = 0.194, 95% CI = -0.296 to 0.684, P = 0.438) or depressive symptoms (Hedges’ g = 0.406, 95% CI = -0.121 to 0.932, P = 0.131)❞
~ Dr. Ryochi Sadahiro et al., 2023
Source: Black cohosh extracts in women with menopausal symptoms: an updated pairwise meta-analysis
Here’s an even larger (n=43,759) one that found similarly, and also noted on safety:
❝Treatment with iCR/iCR+HP was well tolerated with few minor adverse events, with a frequency comparable to placebo. The clinical data did not reveal any evidence of hepatotoxicity.
Hormone levels remained unchanged and estrogen-sensitive tissues (e.g. breast, endometrium) were unaffected by iCR treatment.
As benefits clearly outweigh risks, iCR/iCR+HP should be recommended as an evidence-based treatment option for natural climacteric symptoms.
With its good safety profile in general and at estrogen-sensitive organs, iCR as a non-hormonal herbal therapy can also be used in patients with hormone-dependent diseases who suffer from iatrogenic climacteric symptoms.❞
~ Dr. Castelo-Branco et al., 2020
(iCR = isopropanolic Cimicifuga racemosa)
So, is this estrogenic or not?
This is the question many scientists were asking, about 20 or so years ago. There are many papers from around 2000–2005, but here’s a good one that’s quite representative:
❝These new data dispute the estrogenic theory and demonstrate that extracts of black cohosh do not bind to the estrogen receptor in vitro, up-regulate estrogen-dependent genes, or stimulate the growth of estrogen-dependent tumors❞
Source: Is Black Cohosh Estrogenic?
(the abstract is a little vague, but if you click on the PDF icon, you can read the full paper, which is a lot clearer and more detailed)
The short answer: no, black cohosh is not estrogenic
Is it safe?
As ever, check with your doctor as everyone’s situation can vary, but broadly speaking, yes, it has a very good safety profile—including for breast cancer patients, at that. See for example:
- Black cohosh efficacy and safety for menopausal symptoms: the Spanish Menopause Society statement
- Black cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa): safety and efficacy for cancer patients
- The safety of black cohosh (Actaea racemosa, Cimicifuga racemosa)
Where can I get some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Antihistamines’ Generation Gap
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are You Ready For Allergy Season?
For those of us in the Northern Hemisphere, fall will be upon us soon, and we have a few weeks to be ready for it. A common seasonal ailment is of course seasonal allergies—it’s not serious for most of us, but it can be very annoying, and can disrupt a lot of our normal activities.
Suddenly, a thing that notionally does us no real harm, is making driving dangerous, cooking take three times as long, sex laughable if not off-the-table (so to speak), and the lightest tasks exhausting.
So, what to do about it?
Antihistamines: first generation
Ye olde antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine are probably not what to do about it.
They are small molecules that cross the blood-brain barrier and affect histamine receptors in the central nervous system. This will generally get the job done, but there’s a fair bit of neurological friendly-fire going on, and while they will produce drowsiness, the sleep will usually be of poor quality. They also tax the liver rather.
If you are using them and not experiencing unwanted side effects, then don’t let us stop you, but do be aware of the risks.
See also: Long-term use of diphenhydramine ← this is the active ingredient in Benadryl in the US and Canada, but safety regulations in many other countries mean that Benadryl has different, safer active ingredients elsewhere.
Antihistamines: later generations
We’re going to aggregate 2nd gen, 3rd gen, and 4th gen antihistamines here, because otherwise we’ll be writing a history article and we don’t have room for that. But suffice it to say, later generations of antihistamines do not come with the same problems.
Instead of going in all-guns-blazing to the CNS like first-gens, they are more specific in their receptor-targetting, resulting in negligible collateral damage:
Special shout-out to cetirizine and loratadine, which are the drugs behind half the brand names you’ll see on pharmacy shelves around most of the world these days (including many in the US and Canada).
Note that these two are very often discussed in the same sentence, sit next to each other on the shelf, and often have identical price and near-identical packaging. Their effectiveness (usually: moderate) and side effects (usually: low) are similar and comparable, but they are genuinely different drugs that just happen to do more or less the same thing.
This is relevant because if one of them isn’t working for you (and/or is creating an unwanted side effect), you might want to try the other one.
Another honorable mention goes to fexofenadine, for which pretty much all the same as the above goes, though it gets talked about less (and when it does get mentioned, it’s usually by its most popular brand name, Allegra).
Finally, one that’s a little different and also deserving of a special mention is azelastine. It was recently (ish, 2021) moved from being prescription-only to being non-prescription (OTC), and it’s a nasal spray.
It can cause drowsiness, but it’s considered safe and effective for most people. Its main benefit is not really the difference in drug, so much as the difference in the route of administration (nasal rather than oral). Because the drug is in liquid spray form, it can be absorbed through the mucus lining of the nose and get straight to work on blocking the symptoms—in contrast, oral antihistamines usually have to go into your stomach and take their chances there (we say “usually”, because there are some sublingual antihistamines that dissolve under the tongue, but they are less common.)
Better than antihistamines?
Writer’s note: at this point, I was given to wonder: “wait, what was I squirting up my nose last time anyway?”—because, dear readers, at the time I got it I just bought one of every different drug on the shelf, desperate to find something that worked. What worked for me, like magic, when nothing else had, was beclometasone dipropionate, which a) smelled delightfully of flowers, which might just be the brand I got, b) needs replacing now because I got it in March 2023 and it expired July 2024, and c) is not an antihistamine at all.
But, that brings us to the final chapter for today: systemic corticosteroids
They’re not ok for everyone (check with your doctor if unsure), and definitely should not be taken if immunocompromised and/or currently suffering from an infection (including colds, flu, COVID, etc) unless your doctor tells you otherwise (and even then, honestly, double-check).
But! They can work like magic when other things don’t. Unlike antihistamines, which only block the symptoms, systemic corticosteroids tackle the underlying inflammation, which can stop the whole thing in its tracks.
Here’s how they measure up against antihistamines:
❝The results of this systematic review, together with data on safety and cost effectiveness, support the use of intranasal corticosteroids over oral antihistamines as first line treatment for allergic rhinitis.❞
~ Dr. Robert Puy et al.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Link Between Introversion & Sensory Processing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about how to beat loneliness and isolation, and how that’s important for all of us, including those of us on the less social end of the scale.
However, while we all need at least the option of social contact in order to be at our best, there’s a large portion of the population who also need to be able to retreat to somewhere quiet to recover from too much social goings-on.
Clinically speaking, this sometimes gets called introversion, or at least a negative score for extroversion on the “Big Five Inventory”, the only personality-typing system that actually gets used in science. Today we’re going to be focusing on a term that typically gets applied to those generally considered introverts:
The “highly sensitive person”
This makes it sound like a very rare snowflake condition, when in fact the diagnostic criteria yield a population bell curve of 30:40:30, whereupon 30% are in the band of “high sensitivity”, 40% “normal sensitivity” and the remaining 30% “low sensitivity”.
You may note that “high” and “low” together outnumber “normal”, but statistics is like that. It is interesting to note, though, that this statistical spread renders it not a disorder, so much as simply a description.
You can read more about it here:
Sensory-processing sensitivity and its relation to introversion and emotionality
What it means in practical terms
Such a person will generally seek solitude more frequently during the day than others will, and it’s not because of misanthropy (at least, statistically speaking it’s not; can’t speak for individuals!), but rather, it’s about needing downtime after what has felt like too much sensory processing resulting:
If this need for solitude is not met (sometimes it’s simply not practicable), then it can lead to overwhelm.
Sidenote about overwhelm: pick your battles! No, pick fewer than that. Put some back. That’s still too many 😜
Back to seriousness: if you’re the sort of person to walk into a room and immediately do the Sherlock Holmes thing of noticing everything about everyone, who is doing what, what has changed about the room since last time you were there, etc… Then that’s great; it’s a sign of a sharp mind, but it’s also a lot of information to process and you’re probably going to need a little decompression afterwards:
This is the biological equivalent of needing to let an overworked computer or phone cool down after excessive high-intensity use of its CPU.
The same goes if you’re the sort of person who goes into “performance mode” when in company, is “the life and soul of the party” etc, and/or perhaps “the elegant hostess”, but needs to then collapse afterwards because it’s more of a role you play than your natural inclination.
Take care of your battery
To continue the technological metaphor from earlier, if you repeatedly overuse a device without allowing it cooldown periods, it will break down (and if it’s a certain generation of iPhone, it might explode).
Similarly, if you repeatedly overuse your own highly sensitive senses (such as being often in social environment where there’s a lot going on) without allowing yourself adequate cooldown periods, you will break down (or indeed, explode: not literally, but some people are prone to emotional outbursts after bottling things up).
None of this is good for the health, not in the short term and not in the long term, either:
With that in mind, take care to take care of yourself, meeting your actual needs instead of just those that get socially assumed.
Want to take the test?
Here’s a two-minute test (results available immediately right there on-screen; no need to give your email or anything) 😎
Want to know more?
We reviewed this book about playing to one’s strengths in the context of sensitivity, a while back, and highly recommend it:
Sensitive – by Jenn Granneman and Andre Sólo
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: