Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
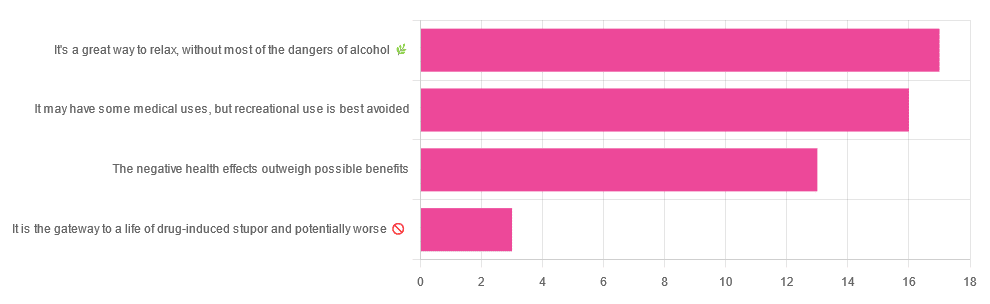
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Overcoming Gravity – by Steven Low
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a professional gymnast and coach with a background in the sciences, knows his stuff here. This is what it says on the tin: it’s rigorously systematic. It’s also the most science-based calisthenics book this reviewer has read to date.
If you just wanted to know how to do some exercises, then this book would be very much overkill, but if you want to be able to go from no knowledge to expert knowledge, then the nearly 600 pages of this weighty tome will do that for you.
This is a textbook, it’s a “the bible of…” style book, it’s the one that if you’re serious, will engage you thoroughly and enable you to craft the calisthenics-forged body you want, head to toe.
As if it weren’t already overdelivering, it also has plenty of information on injury avoidance (or injury/condition management if you have some existing injury or chronic condition), and building routines in a dynamic fashion that avoids becoming a grind, because it’s going from strength to strength while cycling through different body parts.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get serious about calisthenics, then this is the book for you.
Click here to check out Overcoming Gravity, and do just that!
Share This Post
-
Inverse Vaccines for Autoimmune Diseases
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inverse Vaccines for Autoimmune Diseases
This is Dr. Jeffrey Hubbell. He’s a molecular engineer, with a focus on immunotherapy, immune response, autoimmune diseases, and growth factor variants.
He’s held 88 patents, and was the recipient of the Society for Biomaterials’ Founders Award for his “long-term, landmark contributions to the discipline of biomaterials”, amongst other awards and honours that would make our article too long if we included them all.
And, his latest research has been about developing…
Inverse Vaccines
You may be thinking: “you mean diseases; he’s engineering diseases?”
And no, it’s not that. Here’s how it works:
Normally in the case of vaccine, it’s something to tell the body “hey, if you see something that looks like this, you should kill it on sight” and the body goes “ok, preparing countermeasures according to these specifications; thanks for the heads-up”
In the case of an inverse vaccine, it’s the inverse. It’s something to tell the body “hey, this thing you seem to think is a threat, it’s actually not, and you should leave it alone”.
Why this matters for people with autoimmune diseases
Normally, autoimmune diseases are treated in one or more of the following ways:
- Dampen the entire immune system (bad for immunity against actual diseases, obviously, and is part of why many immunocompromised people have suffered and died disproportionately from COVID, for example)
- Give up and find a workaround (a good example of this is Type 1 Diabetes, and just giving up on the pancreas not being constantly at war with itself, and living on exogenous insulin instead)
Neither of those are great.
What inverse vaccines do is offer a way to flag the attacked-in-error items as acceptable things to have in the body. Those might be things that are in our body by default, as in the case of many autoimmune diseases, or they may even be external items that should be allowed but aren’t, as in the case of gluten, in the context of Celiac disease.
The latest research is not yet accessible for free, alas, but you can read the abstract here:
Or if you prefer a more accessible pop-science approach, here’s a great explanatory article:
“Inverse vaccine” shows potential to treat multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases
Where can we get such inverse vaccines?
❝There are no clinically approved inverse vaccines yet, but we’re incredibly excited about moving this technology forward❞
~ Dr. Jeffrey Hubbell
But! Lest you be disappointed, you can get in line already, in the case of the Celiac disease inverse vaccine, if you’d like to be part of their clinical trial:
Click here to see if you are eligible to be part of their clinical trial
If you’re not up for that, or if your autoimmune disease is something else (most of the rest of their research is presently focusing on Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes), then:
- The phase 1 MS trial is currently active, estimated completion in summer 2024.
- They are in the process of submitting an investigational new drug (IND) application for Type 1 Diabetes
- This is the first step to starting clinical safety and efficacy trials
…so, watch this space!
Share This Post
-
Brown Rice vs Wild Rice – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing brown rice to wild rice, we picked the wild.
Why?
It’s close! But there are important distinctions.
First let’s clarify: despite the name and appearance, wild rice is botanically quite different from rice per se; it’s not the same species, it’s not even the same genus, though it is the same umbrella family. In other words, they’re about as closely related as humans and gorillas are to each other.
In terms of macros, wild rice has considerably more protein and a little more fiber, for slightly lower carbs.
Notably, however, wild rice’s carbs are a close-to-even mix of sucrose, fructose, and glucose, while brown rice’s carbs are 99% starch. Given the carb to fiber ratio, it’s worth noting that wild rice also has lower net carbs, and the lower glycemic index.
In the category of vitamins, wild rice leads with more of vitamins A, B2, B9, E, K, and choline. In contrast, brown rice has more of vitamins B1, B3, and B5. So, a moderate win for wild rice.
When it comes to minerals, brown rice finally gets a tally in its favor, even if only slightly: brown rice has more magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and selenium, while wild rice has more copper, potassium, and zinc. They’re equal in calcium and iron, by the way. Still, this category stands as a 4:3 win for brown rice.
Adding up the categories makes a modest win for wild rice, and additionally, if we had to consider one of these things more important than the others, it’d be wild rice being higher in fiber and protein and lower in total carbs and net carbs.
Still, enjoy either or both, per your preference!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Brown Rice Protein: Strengths & Weaknesses
- Rice vs Buckwheat – Which is Healthier? ← it’s worth noting, by the way, that buckwheat is so unrelated from wheat that it’s not even the same family of plants. They are about as closely related as a lion and a lionfish are to each other.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Your Science-Based Guide To Losing Fat & Toning Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This health coach researched the science and crunched the numbers so that you don’t have to:
Body by the numbers
Let’s get mathematical:
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) consists of:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): 70% of daily calorie burn (basic body functions, of which the brain is the single biggest calorie-burner)
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT): 15% (the normal movements that occur as you go about your daily life)
- Exercise Activity: 5% (actual workouts, often overestimated)
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): 10% (energy needed for digestion)
Basic BMR estimate:
- Women: body weight (kg) × 0.9 × 24
- Men: body weight (kg) × 24
But yours may differ, so if you have a fitness tracker or other gadget that estimates it for you, go with that!
Note: muscle burns calories just to maintain it, making muscle mass crucial to increasing one’s BMR.
And now some notes about running a caloric deficit:
- Safe caloric deficit: no more than 500 calories/day.
- Absolute minimum daily intake: 1,200 calories (women), 1,500 calories (men) (not sustainable long-term).
- Tracking calories is useful but not always accurate.
- Extreme calorie restriction slows metabolism and can lead to binge-eating.
- Your body will adjust to calorie deficits over time, making long-term drastic deficits ineffective.
Diet for fat loss & muscle gain:
- Protein Intake: 1.5–2g per pound of body weight.
- Aim for 30g of protein per meal (supports muscle & satiety).
- Protein has a higher thermic effect (20-30%) than carbs (5-10%) & fats (2-4%), meaning more calories are burned digesting protein.
- Fats are essential for hormone health & satiety (0.5–1g per kg of body weight).
- Carbs should be complex (whole grains, vegetables, fruits, etc.).
- Avoid excessive simple carbs (sugar, white bread, white pasta, etc) to maintain stable hunger signals.
- Hydration is key for appetite control & metabolism (often mistaken for hunger).
Exercise for fat loss & muscle gain:
- Resistance training (3-5x per week) is essential for toning & metabolism.
- Cardio is NOT necessary for fat loss but good for overall health.
- NEAT (non-exercise movement) burns significant calories (walking, taking stairs, fidgeting, etc.).
- “Hot girl walks” & daily movement can significantly aid weight loss.
- Women won’t get “bulky” from weight training unless they eat like a bodybuilder (i.e. several times the daily caloric requirement).
Some closing words in addition:
Poor sleep reduces fat loss by 50% and increases hunger. High stress levels lead to fat retention and cravings for unhealthy foods. Thus, managing stress & sleep is as important as diet & exercise for body transformation!
For more on all of this (plus the sources for the science), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Lose Weight (Healthily) ← our own main feature about such; we took a less numbers-based, more principles-based, approach. Both approaches work, so go with whichever suits your personal preference more!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are Supplements Worth Taking?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝There seems to be a lot of suggestions to take supplements for every thing, from your head to your toes. I know it’s up to the individual but what are the facts or stats to support taking them versus not?❞
Short answer:
- supplementary vitamins and minerals are probably neither needed nor beneficial for most (more on this later) people, with the exception of vitamin D which most people over a certain age need unless they are white and getting a lot of sun.
- other kinds of supplement can be very beneficial or useless, depending on what they are, of course, and also your own personal physiology.
With regard to vitamins and minerals, in most cases they should be covered by a healthy balanced diet, and the bioavailability is usually better from food anyway (bearing in mind, we say vitamin such-and-such, or name an elemental mineral, but there are usually multiple, often many, forms of each—and supplements will usually use whatever is cheapest to produce and most chemically stable).
However! It is also quite common for food to be grown in whatever way is cheapest and produces the greatest visible yield, rather than for micronutrient coverage.
This goes for most if not all plants, and it goes extra for animals (because of the greater costs and inefficiencies involved in rearing animals).
We wrote about this a while back in a mythbusting edition of 10almonds, covering:
- Food is less nutritious now than it used to be: True or False?
- Supplements aren’t absorbed properly and thus are a waste of money: True or False?
- We can get everything we need from our diet: True or False?
You can read the answers and explanations, and see the science that we presented, here:
Do We Need Supplements, And Do They Work?
You may be wondering: what was that about “most (more on this later) people”?
Sometimes someone will have a nutrient deficiency that can’t be easily remedied with diet. Often this occurs when their body:
- has trouble absorbing that nutrient, or
- does something inconvenient with it that makes a lot of it unusable when it gets it.
…which is why calcium, iron, vitamin B12, and vitamin D are quite common supplements to get prescribed by doctors after a certain age.
Still, it’s best to try getting things from one’s diet first all of all, of course.
Things we can’t (reasonably) get from food
This is another category entirely. There are many supplements that are convenient forms of things readily found in a lot of food, such as vitamins and minerals, or phytochemicals like quercetin, fisetin, and lycopene (to name just a few of very many).
Then there are things not readily found in food, or at least, not in food that’s readily available in supermarkets.
For example, if you go to your local supermarket and ask where the mimosa is, they’ll try to sell you a cocktail mix instead of the roots, bark, or leaves of a tropical tree. It is also unlikely they’ll stock lion’s mane mushroom, or reishi.
If perchance you do get the chance to acquire fresh lion’s mane mushroom, by the way, give it a try! It’s delicious shallow-fried in a little olive oil with black pepper and garlic.
In short, this last category, the things most of us can’t reasonably get from food without going far out of our way, are the kind of thing whereby supplements actually can be helpful.
And yet, still, not every supplement has evidence to support the claims made by its sellers, so it’s good to do your research beforehand. We do that on Mondays, with our “Research Review Monday” editions, of which you can find in our searchable research review archive ← we also review some drugs that can’t be classified as supplements, but mostly, it’s supplements.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleep: yes, you really do still need it!
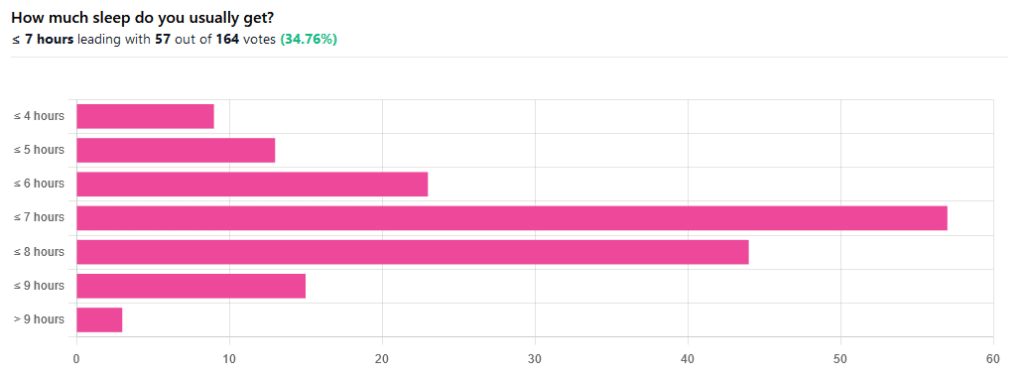
We asked you how much sleep you usually get, and got the above-pictured, below-described set of responses:
- A little of a third of all respondents selected the option “< 7 hours”
- However, because respondents also selected options such as < 6 hours, < 5 hours, and < 4 hours, so if we include those in the tally, the actual total percentage of respondents who reported getting under 7 hours, is actually more like 62%, or just under two thirds of all respondents.
- Nine respondents, which was about 5% of the total, reported usually getting under 4 hours sleep
- A little over quarter of respondents reported usually getting between 7 and 8 hours sleep
- Fifteen respondents, which was a little under 10% of the total, reported usually getting between 8 and 9 hours of sleep
- Three respondents, which was a little under 2% of the total, reported getting over 9 hours of sleep
- In terms of the classic “you should get 7–9 hours sleep”, approximately a third of respondents reported getting this amount.
You need to get 7–9 hours sleep: True or False?
True! Unless you have a (rare!) mutated ADRB1 gene, which reduces that.
The way to know whether you have this, without genomic testing to know for sure, is: do you regularly get under 6.5 hours sleep, and yet continue to go through life bright-eyed and bushy-tailed? If so, you probably have that gene. If you experience daytime fatigue, brain fog, and restlessness, you probably don’t.
About that mutated ADRB1 gene:
NIH | Gene identified in people who need little sleep
Quality of sleep matters as much as duration, and a lot of studies use the “RU-Sated” framework, which assesses six key dimensions of sleep that have been consistently associated with better health outcomes. These are:
- regularity / usual hours
- satisfaction with sleep
- alertness during waking hours
- timing of sleep
- efficiency of sleep
- duration of sleep
But, that doesn’t mean that you can skimp on the last one if the others are in order. In fact, getting a good 7 hours sleep can reduce your risk of getting a cold by three or four times (compared with six or fewer hours):
Behaviorally Assessed Sleep and Susceptibility to the Common Cold
^This study was about the common cold, but you may be aware there are more serious respiratory viruses freely available, and you don’t want those, either.
Napping is good for the health: True or False?
True or False, depending on how you’re doing it!
If you’re trying to do it to sleep less in total (per polyphasic sleep scheduling), then no, this will not work in any sustainable fashion and will be ruinous to the health. We did a Mythbusting Friday special on specifically this, a while back:
Could Just Two Hours Sleep Per Day Be Enough?
PS: you might remember Betteridge’s Law of Headlines
If you’re doing it as a energy-boosting supplement to a reasonable night’s sleep, napping can indeed be beneficial to the health, and can give benefits such as:
- Increased alertness
- Helps with learning
- Improved memory
- Boost to immunity
- Enhance athletic performance
However! There is still a right and a wrong way to go about it, and we wrote about this previously, for a Saturday Life Hacks edition of 10almonds:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
As we get older, we need less sleep: True or False
False, with one small caveat.
The small caveat: children and adolescents need 9–12 hours sleep because, uncredited as it goes, they are doing some seriously impressive bodybuilding, and that is exhausting to the body. So, an adult (with a normal lifestyle, who is not a bodybuilder) will tend to need less sleep than a child/adolescent.
But, the statement “As we get older, we need less sleep” is generally taken to mean “People in the 65+ age bracket need less sleep than younger adults”, and this popular myth is based on anecdotal observational evidence: older people tend to sleep less (as our survey above shows! For any who aren’t aware, our readership is heavily weighted towards the 60+ demographic), and still continue functioning, after all.
Just because we survive something with a degree of resilience doesn’t mean it’s good for us.
In fact, there can be serious health risks from not getting enough sleep in later years, for example:
Sleep deficiency promotes Alzheimer’s disease development and progression
Want to get better sleep?
What gets measured, gets done. Sleep tracking apps can be a really good tool for getting one’s sleep on a healthier track. We compared and contrasted some popular ones:
The Head-To-Head Of Google and Apple’s Top Apps For Getting Your Head Down
Take good care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: