Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Good Things Come In Small Packages
“Sprouting” grains and seeds—that is, allowing them to germinate and begin to grow—enhances their nutritional qualities, boosting their available vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and even antioxidants.
You may be thinking: surely whatever nutrients are in there, are in there already; how can it be increased?
Well, the grand sweeping miracle of life itself is beyond the scope of what we have room to cover today, but in few words: there are processes that allow plants to transform stuff into other stuff, and that is part of what is happening.
Additionally, in the cases of some nutrients, they were there already, but the sprouting process allows them to become more available to us. Think about the later example of how it’s easier to eat and digest a ripe fruit than an unripe one, and now scale that back to a seed and a sprouted seed.
A third way that sprouting benefits us is by reducing“antinutrients”, such as phytic acid.
Let’s drop a few examples of the “what”, before we press on to the “how”:
- Enhancement of attributes of cereals by germination and fermentation: a review
- Sprouting characteristics and associated changes in nutritional composition of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata)
- Phytic acid, in vitro protein digestibility, dietary fiber, and minerals of pulses as influenced by processing methods
- Effects of germination on the nutritional properties, phenolic profiles, and antioxidant activities of buckwheat
- Effect of several germination treatments on phosphatases activities and degradation of phytate in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) and azuki bean (Vigna angularis L.)
Sounds great! How do we do it?
First, take the seeds, grains, nuts, beans, etc that you’re going to sprout. Fine examples to try for a first sprouting session include:
- Grains: buckwheat, brown rice, quinoa
- Legumes: soy beans, black beans, kidney beans
- Greens: broccoli, mustard greens, radish
- Nuts/seeds: almonds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds
Note: whatever you use should be as unprocessed as possible to start with:
- On the one hand, you’d be surprised how often “life finds a way” when it comes to sprouting ridiculous choices
- On the other hand, it’s usually easier if you’re not trying to sprout blanched almonds, split lentils, rolled oats, or toasted hulled buckwheat.
Second, you will need clean water, a jar with a lid, muslin cloth or similar, and a rubber band.
Next, take an amount of the plants you’ll be sprouting. Let’s say beans of some kind. Try it with ¼ cup to start with; you can do bigger batches once you’re more confident of your setup and the process.
Rinse and soak them for at least 24 hours. Take care to add more water than it looks like you’ll need, because those beans are thirsty, and sprouting is thirsty work.
Drain, rinse, and put them in a clean glass jar, covering with just the muslin cloth in place of the lid, held in place by the rubber band. No extra water in it this time, and you’re going to be storing the jar upside down (with ventilation underneath, so for example on some sort of wire rack is ideal) in a dark moderately warm place (e.g. 80℉ / 25℃ is often ideal, but it doesn’t have to be exact, you have wiggle-room, and some things will enjoy a few degrees cooler or warmer than that)
Each day, rinse and replace until you see that they are sprouting. When they’re sprouting, they’re ready to eat!
Unless you want to grow a whole plant, in which case, go for it (we recommend looking for a gardening guide in that case).
But watch out!
That 80℉ / 25℃ temperature at which our sprouting seeds, beans, grains etc thrive? There are other things that thrive at that temperature too! Things like:
- E. coli
- Salmonella
- Listeria
…amongst others.
So, some things to keep you safe:
- If it looks or smells bad, throw it out
- If in doubt, throw it out
- Even if it looks perfect, blanch it (by boiling it in water for 30 seconds, before rinsing it in cold water to take it back to a colder temperature) before eating it or refrigerating it for later.
- When you come back to get it from the fridge, see once again points 1 and 2 above.
- Ideally you should enjoy sprouted things within 5 days.
Want to know more about sprouting?
You’ll love this book that we reviewed recently:
The Sprout Book – by Doug Evans
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Supergreen Superfood Salad Slaw
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to “eating the rainbow”, in principle green should be the easiest color to get in, unless we live in a serious food desert (or serious food poverty). In practice, however, a lot of meals could do with a dash more green. This “supergreen superfood salad slaw” is remarkably versatile, and can be enjoyed as a very worthy accompaniment to almost any main.
You will need
For the bits:
- ½ small green cabbage, finely diced
- 7 oz tenderstem broccoli, finely chopped
- 2 stalks celery, finely chopped (if allergic, simply omit)
- ½ cucumber, diced into small cubes
- 2 oz kale, finely shredded
- 4 green (spring) onions, thinly sliced
For the dressing:
- 1 cup cashews (if allergic, substitute 1 cup roasted chickpeas)
- ½ cup extra virgin olive oil
- 2 oz baby spinach
- 1 oz basil leaves
- 1 oz chives
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- Juice of two limes
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the ingredients from the “bits” category in a bowl large enough to accommodate them comfortably
2) Blend the ingredients from the “dressing” category in a blender until very smooth (the crux here is you do not want any stringy bits of spinach remaining)
3) Pour the dressing onto the bits, and mix well to combine. Refrigerate, ideally covered, until ready to serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Spinach vs Kale – Which is Healthier?
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
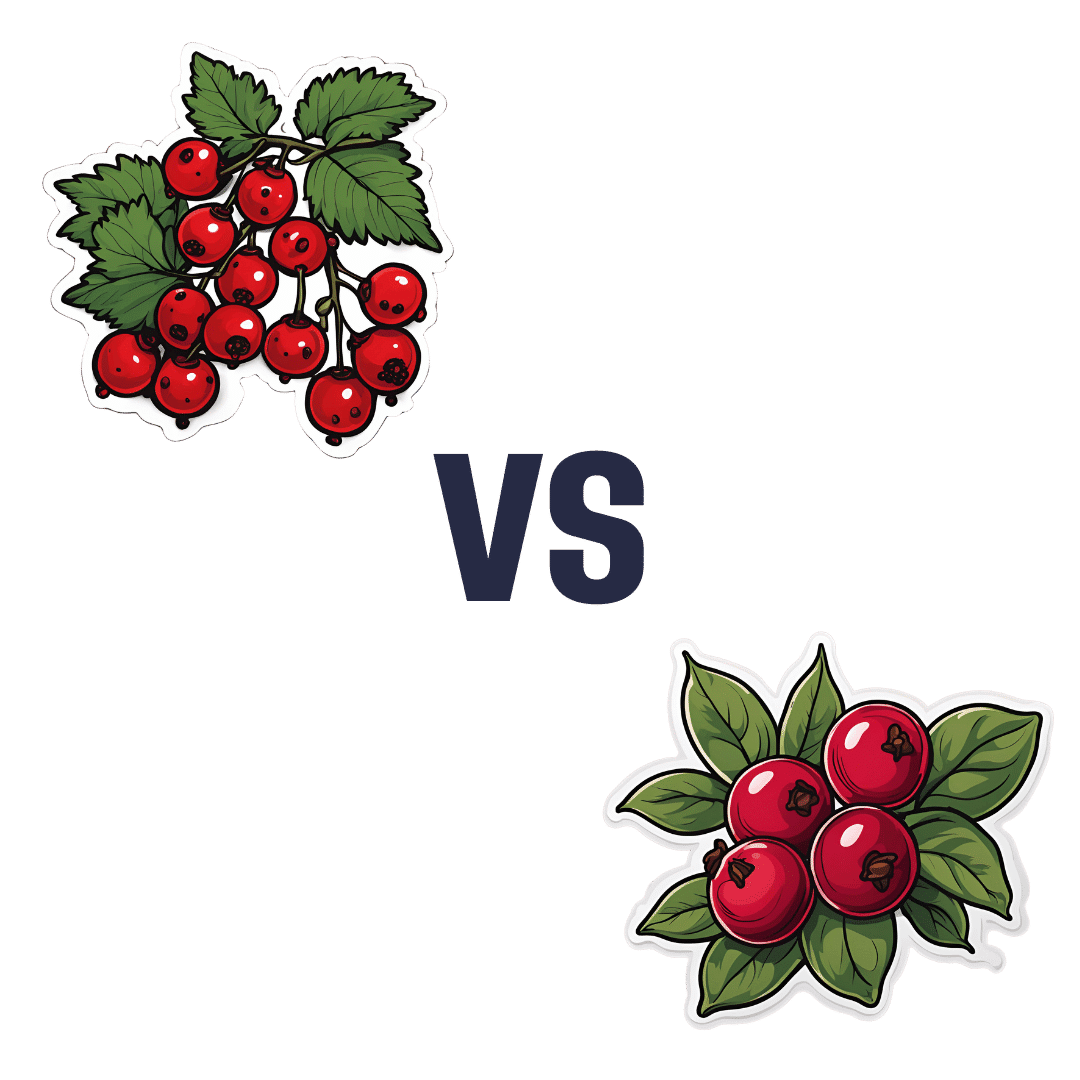
Redcurrants vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing redcurrants to cranberries, we picked the redcurrants.
Why?
First know: here we’re comparing raw redcurrants to raw cranberries, with no additives in either case. If you buy jelly made from either, or if you buy dried fruits but the ingredients list has a lot of added sugar and often some vegetable oil, then that’s going to be very different. But for now… Let’s look at just the fruits:
In terms of macros, redcurrants are higher in carbs, but also higher in fiber, and have the lower glycemic index as cranberries have nearly 2x the GI.
When it comes to vitamins, redcurrants have more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, B9, C, K, and choline, while cranberries have more of vitamins A, B5, and E. In other words, a clear win for redcurrants.
In the category of minerals, redcurrants sweep even more convincingly with a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, cranberries boast a little more manganese; they also have about 2x the sodium.
Both berries have generous amounts of assorted phytochemicals (flavonoids and others), and/but nothing to set one ahead of the other.
As per any berries that aren’t poisonous, both of these are fine choices for most people most of the time, but redcurrants win with room to spare in most categories.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Children with traumatic experiences have a higher risk of obesity – but this can be turned around
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Children with traumatic experiences in their early lives have a higher risk of obesity. But as our new research shows, this risk can be reduced through positive experiences.
Childhood traumatic experiences are alarmingly common. Our analysis of data from nearly 5,000 children in the Growing Up in New Zealand study revealed almost nine out of ten (87%) faced at least one significant source of trauma by the time they were eight years old. Multiple adverse experiences were also prevalent, with one in three children (32%) experiencing at least three traumatic events.
Childhood trauma includes a range of experiences such as physical and emotional abuse, peer bullying and exposure to domestic violence. It also includes parental substance abuse, mental illness, incarceration, separation or divorce and ethnic discrimination.
We found children from financially disadvantaged households and Māori and Pasifika had the highest prevalence of nearly all types of adverse experiences, as well as higher overall numbers of adversities.
The consequences of these experiences were far-reaching. Children who experienced at least one adverse event were twice as likely to be obese by age eight. The risk increased with the number of traumatic experiences. Children with four or more adverse experiences were nearly three times more likely to be obese.
Notably, certain traumatic experiences (including physical abuse and parental domestic violence) related more strongly to obesity than others. This highlights the strong connection between early-life adversity and physical health outcomes.
PickPik, CC BY-SA Connecting trauma to obesity
One potential explanation could be that the accumulation of early stress in children’s family, school and social environments is associated with greater psychological distress. This in turn makes children more likely to adopt unhealthy weight-related behaviours.
This includes consuming excessive high-calorie “comfort” foods such as fast food and sugary drinks, inadequate intake of nutritious foods, poor sleep, excessive screen time and physical inactivity. In our research, children who experienced adverse events were more likely to adopt these unhealthy behaviours. These, in turn, were associated with a higher risk of obesity.
Despite these challenges, our research also explored a promising area: the protective and mitigating effects of positive experiences.
We defined positive experiences as:
- parents in a committed relationship
- mothers interacting well with their children
- mothers involved in social groups
- children engaged in enriching experiences and activities such as visiting libraries or museums and participating in sports and community events
- children living in households with routines and rules, including those regulating bedtime, screen time and mealtimes
- children attending effective early childhood education.
The findings were encouraging. Children with more positive experiences were significantly less likely to be obese by age eight.
For example, those with five or six positive experiences were 60% less likely to be overweight or obese compared to children with zero or one positive experience. Even two positive experiences reduced the likelihood by 25%.
Positive childhood experiences such as playing sports or visiting libraries can lower the risk of obesity. Getty Images How positive experiences counteract trauma
Positive experiences can help mitigate the negative effects of childhood trauma. But a minimum of four positive experiences was required to significantly counteract the impact of adverse events.
While nearly half (48%) of the study participants had at least four positive experiences, a concerning proportion (more than one in ten children) reported zero or only one positive experience.
The implications are clear. Traditional weight-loss programmes focused solely on changing behaviours are not enough to tackle childhood obesity. To create lasting change, we must also address the social environments, life experiences and emotional scars of early trauma shaping children’s lives.
Fostering positive experiences is a vital part of this holistic approach. These experiences not only help protect children from the harmful effects of adversity but also promote their overall physical and mental wellbeing. This isn’t just about preventing obesity – it’s about giving children the foundation to thrive and reach their full potential.
Creating supportive environments for vulnerable children
Policymakers, schools and families all have a role to play. Community-based programmes, such as after-school activities, healthy relationship initiatives and mental health services should be prioritised to support vulnerable families.
Trauma-informed care is crucial, particularly for children from disadvantaged households who face higher levels of adversity and fewer positive experiences. Trauma-informed approaches are especially crucial for addressing the effects of domestic violence and other adverse childhood experiences.
Comprehensive strategies should prioritise both safety and emotional healing by equipping families with tools to create safe, nurturing environments and providing access to mental health services and community support initiatives.
At the family level, parents can establish stable routines, participate in social networks and engage children in enriching activities. Schools and early-childhood education providers also play a key role in fostering supportive environments that help children build resilience and recover from trauma.
Policymakers should invest in resources that promote positive experiences across communities, addressing inequalities that leave some children more vulnerable than others. By creating nurturing environments, we can counterbalance the impacts of trauma and help children lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
When positive experiences outweigh negative ones, children have a far greater chance of thriving – physically, emotionally and socially.
Ladan Hashemi, Senior Research Fellow in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Chorus or Cacophony? Cicada Song Hits Some Ears Harder Than Others
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ST. LOUIS — Shhhooo. Wee-uuu. Chick, chick, chick. That’s the sound of three different cicada species. For some people, those sounds are the song of the summer. Others wish the insects would turn it down. The cacophony can be especially irritating for people on the autism spectrum who have hearing sensitivity.
Warren Rickly, 14, lives in suburban south St. Louis County, Missouri. Warren, who has autism, was at the bus stop recently waiting for his younger brother when the sound of cicadas became too much to bear.
“He said it sounds like there’s always a train running next to him,” his mother, Jamie Reed, said.
Warren told her the noise hurt.
Starting this spring, trillions of the red-eyed insects crawled their way out of the ground across the Midwest and Southeast. It’s part of a rare simultaneous emergence of two broods — one that appears every 13 years, the other every 17.
The noisy insects can be stressful. People with autism can have a sensitivity to texture, brightness, and sound.
“I think the difference for individuals with autism is the level of intensity or how upsetting some of these sensory differences are,” said Rachel Follmer, a developmental and behavioral pediatrician at Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago.
“It can get to the extreme where it can cause physical discomfort,” she said.
When a large group of cicadas starts to sing, the chorus can be as loud as a motorcycle. Researchers at the University of Missouri-St. Louis this year crowdsourced cicada noise levels as high as 86 decibels, about as loud as a food blender.
That can be stressful, not melodic, Follmer said.
To help children cope, she suggests giving them a primer before they encounter a noisy situation. For cicadas, that could mean explaining what they are, that they don’t bite or sting, and that they’ll be here for just a short time.
“When something is uncomfortable, not having power in that situation can be very scary for a lot of individuals, whether you’re on the spectrum or not,” Follmer said.
Jamie Reed’s family has been using this and other strategies to help her son. Warren wears noise-canceling headphones, listens to music, and has been teaching himself about cicadas.
“For him, researching it and looking into it I think grounds him a little bit,” Reed said.
Fatima Husain is a professor and neuroscientist at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and studies how the brain processes sound. She said people with tinnitus may also struggle with cicada song.
Tinnitus, a ringing or other noise in the ears, is a person’s perception of sound without an external source.
“Some people say it sounds like buzzing, like wind blowing through trees, and ironically, quite a few people say it sounds like cicadas,” Husain said.
For most people with tinnitus the cicada’s song is harmless background noise, according to Husain, but for others the ringing can prevent easy conversation or sleep. Those with tinnitus are also more likely to have anxiety or depression. A loud persistent sound, like singing cicadas, can make someone’s tinnitus worse, Husain said.
It’s not always bad, though. The cicada’s song can also be a relief.
For some, tinnitus gets worse in a quiet environment. Husain said she’s seen reports this year of patients saying the cicadas’ song has been like soothing white noise.
“The sound is loud enough that in some ways it’s drowning their internal tinnitus,” Husain said.
As loud as the cicadas can be, they won’t necessarily damage anyone’s hearing, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hearing loss builds up over time from repeated exposure to loud sounds. Cicadas aren’t loud enough for long enough to do lasting damage, Husain said.
Everyday sources of noise come with a higher risk. Husain said constant exposure to loud highways, an airport, industrial sites, or household appliances like blenders and hair dryers can be a concern. And they can take a toll on someone’s emotional well-being.
“If you are being exposed to very loud sounds for a part of your school day or your working day, it may make you more stressed out; it may make you more angry about things,” she said.
Unlike the highway or an airport, cicadas won’t be around long. Most of the current brood will be gone in the next few weeks. Just in time for another noisy summer event: the Fourth of July.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
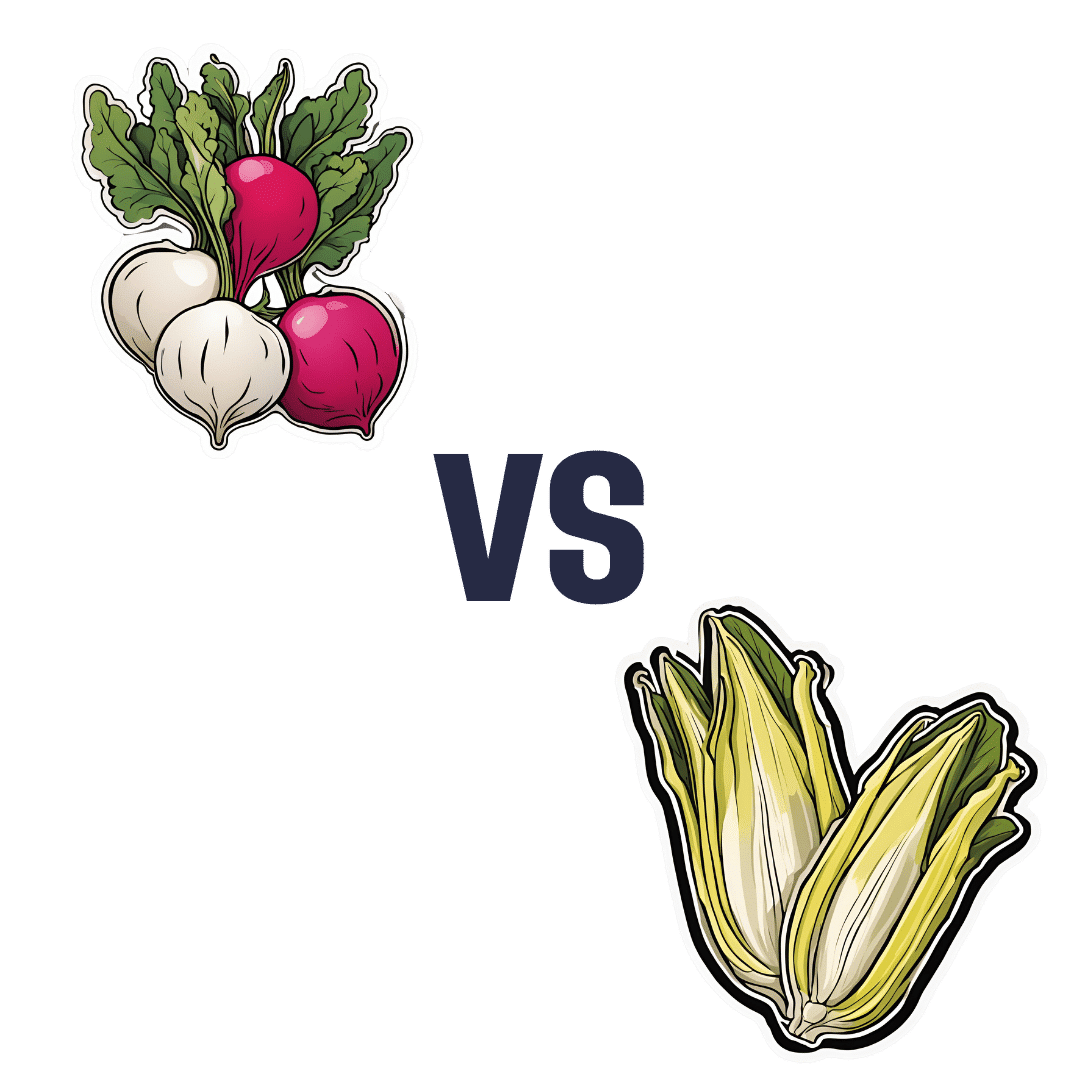
Radishes vs Endives – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing radishes to endives, we picked the endives.
Why?
These are both great, but there’s a clear winner here in every category!
In terms of macros, radishes have more carbs while endives have more fiber and protein.
In the category of vitamins, radishes have more of vitamins B6 and C, while endives have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B4, B5, B7, B9, E, K, and choline.
When it comes to minerals, things are not less one-sided: radishes have more selenium, while endives have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc.
You may be thinking: but what about radishes’ shiny red bit? Doesn’t that usually mean more of something important, like carotenoids or anthocyanins or something? And the answer is that the red pigment in radishes is so thinly-distributed on the exterior that it’s barely there and if we’re looking at values per 100g, it’s a tiny fraction of a tiny fraction.
In both cases, their bitter taste comes mostly from flavonols, of which mostly kaempferol, of which endives have about 20x what radishes have, on average.
All in all, an overwhelming win for endives.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
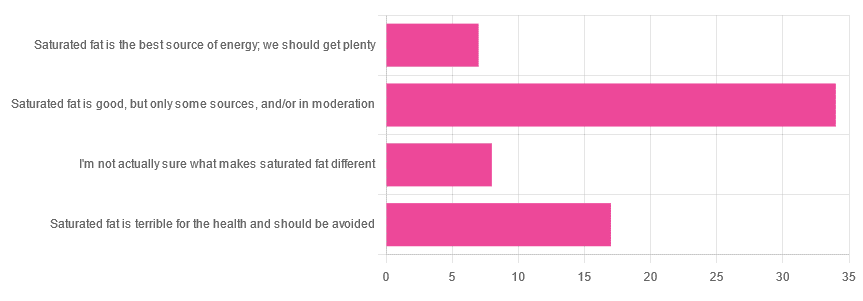
We asked you for your health-related opinion of saturated fat, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of results.
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
- This is an easy one to vote for, because of the “and/or in moderation” part, which tends to be a “safe bet” for most things.
- Next most popular was “Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided”
- About half as many recorded votes were for “I’m not actually sure what makes saturated fat different”, which is a very laudable option to click. Admitting when we don’t know things (and none of us know everything) is a very good first step to learning about them!
- Fewest recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty”.
So, what does the science say?
First, a bit of physics, chemistry, and biology
You may be wondering what, exactly, saturated fats are “saturated” with. That’s a fair question, so…
All fats have a molecular structure made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen, and thus have only single bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated fats have at least one double-bond between carbon atoms).
The observable effect this has on them, is that fats that are saturated with hydrogen are solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. Their different properties also make for different interactions inside the human body, including how likely or not they are to (for example) clog arteries.
See also: Could fat in your bloodstream cause blood clots?
Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty: True or False?
False, in any reasonable interpretation, anyway. That is to say, if your idea of “plenty” is under 13g (e.g: two tablespoons of butter, and no saturated fat from other sources, e.g. meat) per day, then yes, by all means feel free to eat plenty. More than that, though, and you might want to consider trimming it down a bit.
The American Heart Association has this to say:
❝When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fats, which are found in butter, cheese, red meat and other animal-based foods, and tropical oils.
Decades of sound science has proven it can raise your “bad” cholesterol and put you at higher risk for heart disease.❞
Source: The American Heart Association Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations on Saturated Fat
The British Heart Foundation has a similar statement:
❝Despite what you read in the media, our advice is clear: replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats and avoid trans fats. Saturated fat is the kind of fat found in butter, lard, ghee, fatty meats and cheese. This is linked to an increased risk of heart and circulatory disease❞
Source: British Heart Foundation: What does fat do and what is saturated fat?
As for the World Health Organization:
❝1. WHO strongly recommends that adults and children reduce saturated fatty acid intake to 10% of total energy intake
2. WHO suggests further reducing saturated fatty acid intake to less than 10% of total energy intake
3. WHO strongly recommends replacing saturated fatty acids in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids; monounsaturated fatty acids from plant sources; or carbohydrates from foods containing naturally occurring dietary fibre, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses.❞
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
Please note, organizations such as the AHA, the BHF, and the WHO are not trying to sell us anything, and just would like us to not die of heart disease, the world’s #1 killer.
As for “the best source of energy”…
We evolved to eat (much like our nearest primate cousins) a diet consisting mostly of fruits and other edible plants, with a small supplementary amount of animal-source protein and fats.
That’s not to say that because we evolved that way we have to eat that way—we are versatile omnivores. But for example, we are certainly not complete carnivores, and would quickly sicken and die if we tried to live on only meat and animal fat (we need more fiber, more carbohydrates, and many micronutrients that we usually get from plants)
The closest that humans tend to come to doing such is the ketogenic diet, which focuses on a high fat, low carbohydrate imbalance, to promote ketosis, in which the body burns fat for energy.
The ketogenic diet does work, and/but can cause a lot of health problems if a lot of care is not taken to avoid them.
See for example: 7 Keto Risks To Keep In Mind
Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided: True or False?
False, if we are talking about “completely”.
Firstly, it’s practically impossible to cut out all saturated fats, given that most dietary sources of fat are a mix of saturated, unsaturated (mono- and poly-), and trans fats (which are by far the worst, but beyond the scope of today’s main feature).
Secondly, a lot of research has been conducted and found insignificant or inconclusive results, in cases where saturated fat intake was already within acceptable levels (per the recommendations we mentioned earlier), and then cut down further.
Rather than fill up the newsletter with individual studies of this kind here’s a high-quality research review, looking at 19 meta-analyses, each of those meta-analyses having looked at many studies:
Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: a narrative review
Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation: True or False?
True! The moderation part is easy to guess, so let’s take a look at the “but only some sources”.
We were not able to find any convincing science to argue for health-based reasons to favor plant- or animal-sourced saturated fat. However…
Not all saturated fats are created equal (there are many kinds), and also many of the foods containing them have additional nutrients, or harmful compounds, that make a big difference to overall health, when compared gram-for-gram in terms of containing the same amount of saturated fat.
For example:
- Palm oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of palmitic acid, which raises LDL (“bad” cholesterol) without affecting HDL (“good” cholesterol), thus having an overall heart-harmful effect.
- Most animal fats contain a disproportionate amount of stearic acid, which has statistically insignificant effects on LDL and HDL levels, and thus is broadly considered “heart neutral” (in moderation!)
- Coconut oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of lauric acid, which raises total cholesterol, but mostly HDL without affecting LDL, thus having an overall heart-beneficial effect (in moderation!)
Do you know what’s in the food you eat?
Test your knowledge with the BHF’s saturated fat quiz!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”