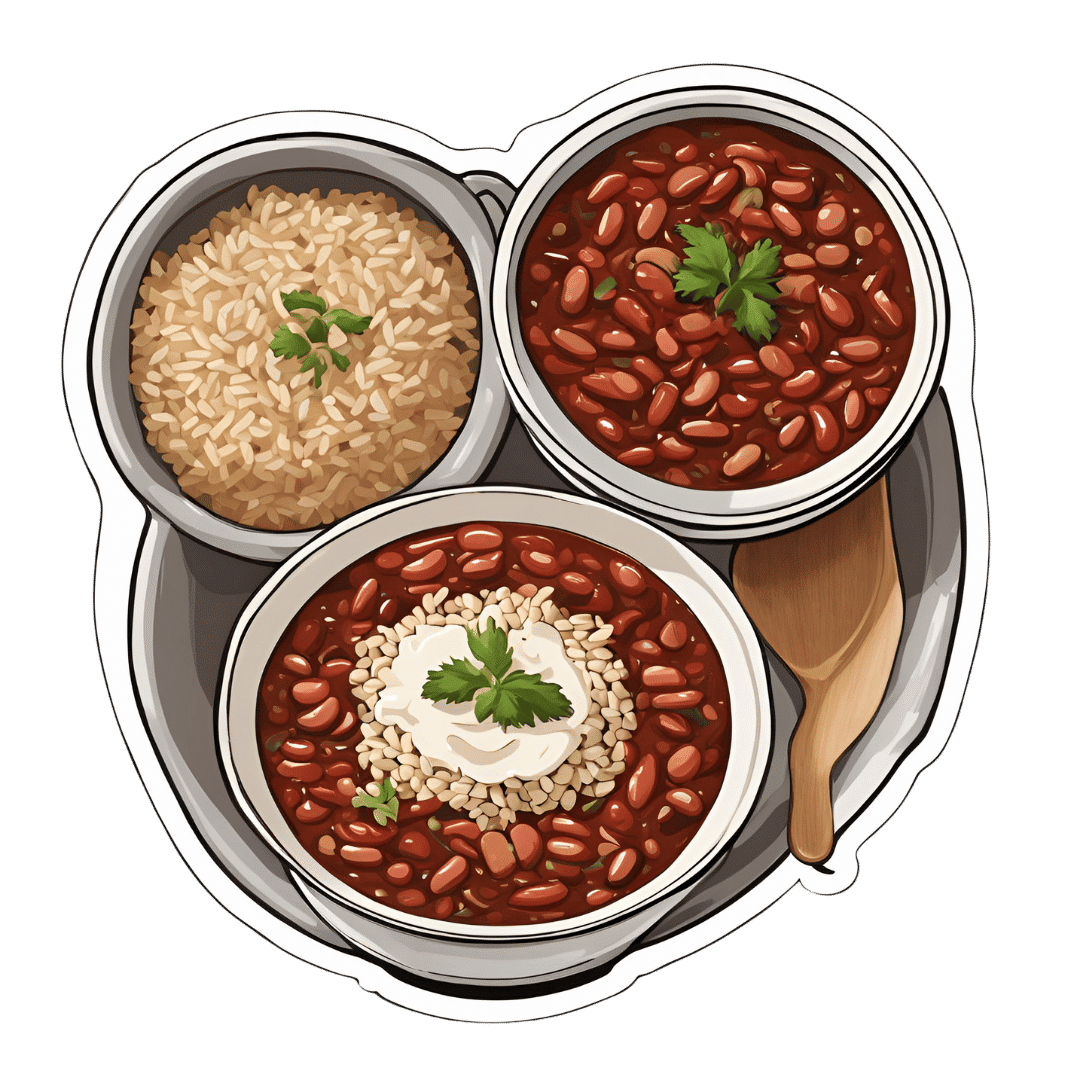
Three-Bean Chili & Cashew Cream
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A hearty classic with a twist! Delicious and filling and full of protein, fiber, and powerful phytonutrients (including heavy-hitters ergothioneine and lycopene), this recipe is also quite flexible, so you can always add in extra seasonal vegetables if you like (to get you started: cherry tomatoes in summer and sweet potato in fall are fine options)!
You will need
- 1 cup low-sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made it yourself from vegetable offcuts you kept in the freezer for this purpose, but if not, you should be able to find low-sodium stock cubes)
- 1 can kidney beans, drained and rinsed
- 1 can black beans, drained and rinsed
- 1 can chickpeas, drained and rinsed
- 2 cans chopped tomatoes
- 1 onion, finely chopped
- 1 carrot, diced
- 2 celery sticks, chopped
- 4 oz mushrooms, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp tomato purée
- 1 red chili pepper, finely chopped (multiply per your heat preferences)
- 1 tbsp ground paprika
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 2 tsp fresh rosemary (or 1 tbsp dried)
- 2 tsp fresh thyme (or 1 tbsp dried)
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
For the cashew cream:
- 6 oz cashews, soaked in kettle-hot water for at least 15 minutes
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp lemon juice
To serve:
- Handful of chopped parsley
- Your carbohydrates of choice; we recommend our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe, and/or our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some olive oil in a skillet and fry the onion for about 5 minutes, stirring as necessary.
2) Add the garlic and chili and cook for a further 1 minute.
3) Add the celery, carrot, and mushrooms and continue cooking for 1–2 minutes.
4) Add everything else from the main section, taking care to stir well to distribute the seasonings evenly. Reduce the heat and allow to simmer for around 20 minutes, stirring occasionally.
5) While you are waiting, drain the cashews, and add them to a high-speed blender with ½ cup (fresh) cold water, as well as the nutritional yeast and lemon juice. Blend on full power until smooth; this may take about 3 minutes, so we recommend doing it in 30-second bursts to avoid overheating the motor. You’ll also probably need to scrape it down the sides at least once. You can add a little more water if you want the cream to be thinner than it is appearing, but go slowly if you do.
6) Serve with rice, adding a dollop of the cream and garnishing with parsley, with bread on the side if you like.
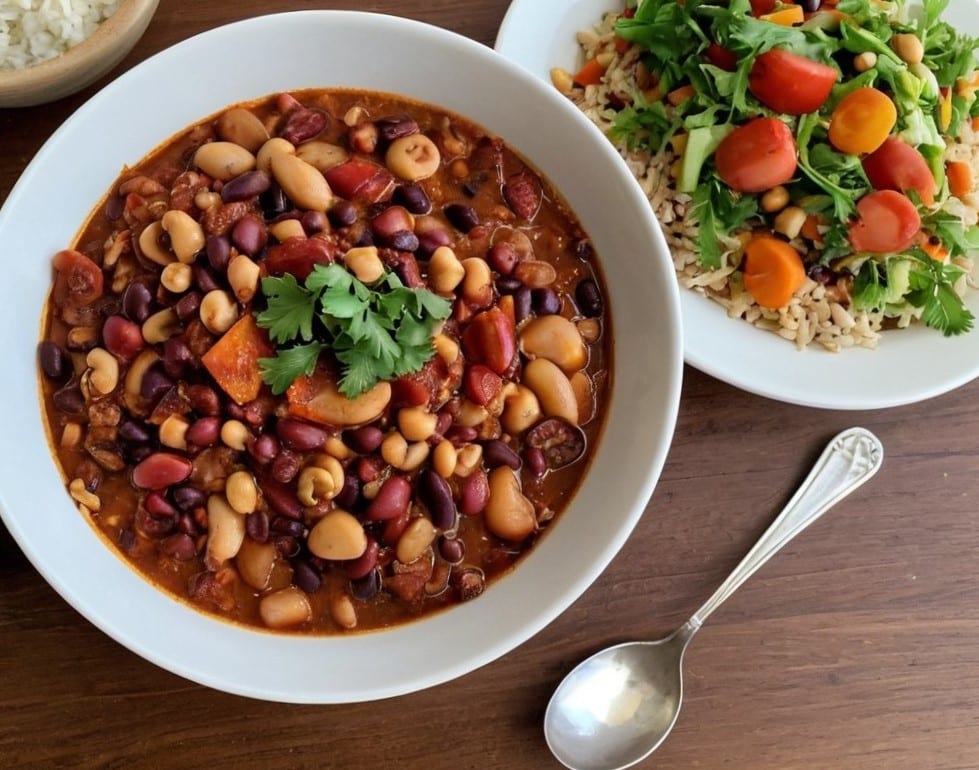

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- Kidney Beans or Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
- “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mythbusting Moldy Food
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most Food Should Not Be Fuzzy
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your policy when it comes to mold on food (aside from intentional mold, e.g. blue cheese etc), and the responses were interesting:
- About 49% said “throw the whole thing away no matter what it is; it is dangerous”
- About 24% said “cut the mold off and eat the rest of whatever it is”
- The remainder were divided equally between “eat it all; keep the immune system on its toes” and “cut the mold off bread, but moldy animal products are dangerous”
So what does the science say?
Some molds are safe to eat: True or False?
True! We don’t think this is contentious so we’ll not spend much time on it, but just for the sake of being methodical: foods that are supposed to have mold on, including many kinds of cheese and even some kinds of cured meat (salami is an example; that powdery coating is mold).
We could give a big list of safe and unsafe molds, but that would be a list of names and let’s face it, they don’t introduce themselves by name.
However! The litmus test of “is it safe to eat” is:
Did you acquire it with this mold already in place and exactly as expected and advertised?
- If so, it is safe to eat (unless you have an allergy or such)
- If not, it is almost certainly not safe to eat
(more on why, later)
The “sniff test” is a good way to tell if moldy food is bad: True or False?
False. Very false. Because of how the sense of smell works.
You may feel like smell is a way of knowing about something at a distance, but the only way you can smell something is if particles of it are physically connecting with your olfactory receptors inside you. Yes, that has unfortunate implications about bathroom smells, but for now, let’s keep our attention in the kitchen.
If you sniff a moldy item of food, you will now have its mold spores inside your respiratory system. You absolutely do not want them there.
If we cut off the mold, the rest is safe to eat: True or False?
True or False, depending on what it is:
- Hard vegetables (e.g carrots, cabbage), and hard cheeses (e.g. Gruyère, Gouda) – cut off with an inch margin, and it should be safe
- Soft vegetables (e.g. tomatoes, and any vegetables that were hard but are now soft after cooking) – discard entirely; it is unsafe
- Anything else – discard entirely; it is unsafe
The reason for this is because in the case of the hard products mentioned, the mycelium roots of the mold cannot penetrate far.
In the case of the soft products mentioned, the surface mold is “the tip of the iceberg”, and the mycelium roots, which you will not usually be able to see, will penetrate the rest of it.
“Anything else” seems like quite a sweeping statement, but fruits, soft cheeses, yogurt, liquids, jams and jellies, cooked grains and pasta, meats, and yes, bread, are all things where the roots can penetrate deeply and easily. Regardless of you only being able to see a small amount, the whole thing is probably moldy.
The USDA has a handy downloadable factsheet:
Molds On Food: Are They Dangerous?
Eating a little mold is good for the immune system: True or False?
False, generally. There are of course countless types of mold, but not only are many of them pathogenic (mycotoxins), but also, a food that has mold will usually also have pathogenic bacteria along with the mold.
See for example: Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food
Food poisoning will never make you healthier.
But penicillin is safe to eat: True or False?
False, and also penicillin is not the mold on your bread (or other foods).
Penicillin, an antibiotic* molecule, is produced by some species of Penicillium sp., a mold. There are hundreds of known species of Penicillium sp., and most of them are toxic, usually in multiple ways. Take for example:
Penicillium roqueforti PR toxin gene cluster characterization
*it is also not healthy to consume antibiotics unless it is seriously necessary. Antibiotics will wipe out most of your gut’s “good bacteria”, leaving you vulnerable. People have died from C. diff infections for this reason. So obviously, if you really need to take antibiotics, take them as directed, but if not, don’t.
See also: Four Ways Antibiotics Can Kill You
One last thing…
It may be that someone reading this is thinking “I’ve eaten plenty of mold, and I’m fine”. Or perhaps someone you tell about this will say that.
But there are two reasons this logic is flawed:
- Survivorship bias (like people who smoke and live to 102; we just didn’t hear from the 99.9% of people who smoke and die early)
- Being unaware of illness is not being absent of illness. Anyone who’s had an alarming diagnosis of something that started a while ago will know this, of course. It’s also possible to be “low-level ill” often and get used to it as a baseline for health. It doesn’t mean it’s not harmful for you.
Stay safe!
Share This Post
-
Almonds vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almonds to walnuts, we picked the almonds.
Why?
It wasn’t just our almond bias, but it was close!
In terms of macros, the main important differences are:
- Almonds are higher in protein
- Walnuts are higher in fats (they are healthy fats)
So far, so even.
In terms of vitamins, both are rich in many vitamins; mostly the same ones. However, walnuts have more of most of the B vitamins (except for B2 and B3, where almonds win easily), and almonds have more vitamin E by several orders of magnitude.
So far, so balanced.
Almonds have slightly more choline.
Almonds have a better mineral profile, with more of most minerals that they both contain, and especially, a lot more calcium.
Both nuts have [sometimes slightly different, but] comparable benefits against diabetes, cancer, neurodegeneration, and other diseases.
In summary
This one’s close. After balancing out the various “almonds have this but walnuts have that” equal-but-different benefits, we’re going to say almonds take first place by virtue of the better mineral profile, and more choline.
But: enjoy both!
Learn more
You might like this previous article of ours:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How extreme heat can affect you—and how you can protect yourself
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Because of climate change, last summer was the hottest in the Northern Hemisphere in 2,000 years—and this summer is expected to be even hotter. The record may continue to be broken: Extreme heat is expected to become even more frequent.
The scorching heat has led to an increase in heat-related deaths in the United States, according to the Department of Health and Human Services, with approximately 2,300 deaths in the summer of 2023. Extreme heat, defined as a period of two to three days with high heat and humidity with temperatures above 90 degrees Fahrenheit, can have serious health consequences, including symptoms like headache, dizziness, loss of consciousness, nausea, and confusion.
As we face more extreme heat, you may be wondering how you can protect yourself and your loved ones. Read on to learn about heat-related illness, who’s most at risk, and more.
What happens when our bodies are exposed to extreme heat?
As our body temperature rises, our bodies attempt to cool down by opening up more blood vessels near the skin to begin sweating. The evaporation of our sweat regulates our body temperature, but it also leads to losing fluids and minerals.
When it’s too humid, sweating alone doesn’t do the trick. The heart must work harder to bring blood around the body. It starts beating faster, which can cause light-headedness, nausea, and headache.
This process can affect our health in different ways, including increasing our risk of hospitalization for heart disease, worsening asthma, and injuring kidneys due to dehydration. It can also result in heat-related illness. Below are some effects of heat on our bodies:
- Heat cramps: Occur when a person loses salt through sweating, which causes painful cramps. Symptoms begin as painful spasms after heavy sweating, usually in the legs or the stomach. Heat cramps can lead to heat exhaustion or heat stroke.
- Heat exhaustion: This occurs when the body loses an excessive amount of water and salt, usually during intense physical activity. Symptoms include irritability, heavy sweating, and weakness, including muscle cramps. Heat exhaustion can lead to heat stroke.
- Heat stroke: This is the most severe heat-related illness. It happens when the body can’t cool down and reaches a temperature of 106 Fahrenheit or higher within 10 to 15 minutes. If the person doesn’t receive emergency treatment, it can cause permanent disability or death. Symptoms include confusion, loss of consciousness, and seizures.
What should I do if someone experiences a heat-related illness?
If you or someone you’re with begins to show signs of heat illness, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends the following:
- Heat cramps: Stop all physical activity, drink water or a sports drink, move to a cool place, and wait for cramps to go away before resuming activity. If the cramps last more than an hour, you’re on a low-sodium diet, or you have heart problems, get medical help.
- Heat exhaustion: Move the person to a cool place, loosen their clothes, use a cool bath or cloths to try to lower their body temperature, and give them a sip of water. If the person throws up, or if their symptoms last longer than an hour or worsen, get medical help.
- Heat stroke: Call 911 immediately. Then, move the person to a cooler place, use cool cloths or a cool bath to help lower their temperature, and don’t give them anything to drink.
Read more about heat-related illness and what to do in each case.
Who’s more vulnerable to extreme heat?
While everyone can be affected by extreme heat, some people are more at risk, including people of color.
A 2023 KFF report outlined that because of historical residential segregation in the U.S. (known as “redlining”), people of color are more likely to live in areas that experience higher temperatures from rooftops, asphalt, and sidewalks that retain the sun’s heat (known as the “urban heat island effect”). Additionally, communities of color are more likely to live in areas with fewer trees, which act as a canopy and provide shade, making the heat worse and more direct.
Children under 5, adults 65 or over, and pregnant people are also more vulnerable to extreme heat. If you have a chronic health condition like diabetes, heart problems, or a mental health condition, you’re also at higher risk. (Some psychiatric medications, like antidepressants, can also make people more susceptible to heat).
Lastly, anyone exposed to the sun and extreme heat for long periods is also at higher risk. This includes athletes, people who work outdoors, and unhoused people.
What can I do to prevent heat-related illness during a heat wave?
During a heat wave, follow these tips to stay cool and protect yourself from heat-related illness:
- Never leave your pets or children inside a car.
- Wear loose, light-colored clothing (dark colors absorb more heat).
- Find shade if you’re outside.
- If you don’t have air conditioning in your home, go to a place where you can cool down, such as a local library, community center, local pool or splash pad, or mall. Check to see if your city has designated cooling centers. (Cities like New York have a list of places.)
- Wear a hat.
- Drink (non-alcoholic) fluids often to stay hydrated—and if you have pets, give them water frequently as well.
- Check on your family members or older neighbors who may be more sensitive to extreme heat.
- Avoid using your stove or oven too often or during the hottest parts of the day.
- Cover your windows with shades to keep the heat out.
What are some resources to prevent heat-related illness?
If you need financial assistance to cool down your home, such as to purchase an air conditioner, apply to the federal government’s Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program.
Before you head outside during a heat wave, use the CDC’s HeatRisk tool: Enter your zip code to find the current heat risk in your area and get tips on what to do to stay safe with each risk level.
During a heat wave, also look for a cooling center in your state using the National Center for Healthy Housing’s list.
Check out the National Weather Service’s for more tips and resources.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
5 Steps To Beat Overwhelm
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dealing With Overwhelm
Whether we live a hectic life in general, or we usually casually take each day as it comes but sometimes several days gang up on us at once, everyone gets overwhelmed sometimes.
Today we’re going to look at how to deal with it healthily.
Step 1: Start anywhere
It’s easy to get stuck in “analysis paralysis” and not know how to tackle an unexpected large problem. An (unhealthy) alternative is to try to tackle everything at once, and end up doing nothing very well.
Even the most expert juggler will not successfully juggle 10 random things thrown unexpectedly at them.
So instead, just pick any part of the the mountain of to-dos, and start.
If you do want a little more finesse though, check out:
Procrastination, And How To Pay Off The To-Do List Debt
Step 2: Accept what you’re capable of
This one works both ways. It means being aware of your limitations yes, but also, of your actual abilities:
- Is the task ahead of you really beyond what you are capable of?
- Could you do it right now without hesitation if a loved one’s life depended on it?
- Could you do it, but there’s a price to pay (e.g. you can do it but it’ll wipe you out in some other life area)?
Work out what’s possible and acceptable to you, and make a decision. And remember, it could be that someone else could do it, but everyone has taken the “if you want something doing, give it to someone busy” approach. It’s flattering that people have such confidence in our competence, but it is also necessary to say “no” sometimes, or at least enlisting help.
Step 3: Listen to your body
…like a leader listening to an advisory council. Your perception of tiredness, pain, weakness, and all your emotions are simply messengers. Listen to the message! And then say “thank you for the information”, and proceed accordingly.
Sometimes that will be in the way the messengers seem to be hoping for!
Sometimes, however, maybe we (blessed with a weighty brain and not entirely a slave to our limbic system) know better, and know when it’s right to push through instead.
Similarly, that voice in your head? You get to decide where it goes and doesn’t. On which note…
Step 4: Be responsive, not reactive
We wrote previously on the difference between these:
A Bone To Pick… Up And Then Put Back Where We Found It
Measured responses will always be better than knee-jerk reactions, unless it is literally a case of a split-second making a difference. 99% of our problems in life are not so; usually the problem will still be there unchanged after a moment’s mindful consideration, so invest in that moment.
You’ve probably heard the saying “give me six hours to chop down a tree, and I’ll spend the first four sharpening the axe”. In this case, that can be your mind. Here’s a good starting point:
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
And if your mental state is already worse than that, mind racing with threats (real or perceived) and doom-laden scenarios, here’s how to get out of that negative spiral first, so that you can apply the rest of this:
Do remember to turn it on again afterwards, though
Step 5: Transcend discomfort
This is partly a callback to step 3, but it’s now coming from a place of a clear ready mind, so the territory should be looking quite different now. Nevertheless, it’s entirely possible that your clear view shows discomfort ahead.
You’re going to make a conscious decision whether or not to proceed through the discomfort (and if you’re not, then now’s the time to start calmly and measuredly looking at alternative plans; delegating, ditching, etc).
If you are going to proceed through discomfort, then it can help to frame the discomfort as simply a neutral part of the path to getting where you want. Maybe you’re going to be going way out of your comfort zone in order to deal with something, and if that’s the case, make your peace with it now, in advance.
“Certainly it hurts” / “Well, what’s the trick then?” / “The trick, William Potter, is not minding that it hurts”
(lines from a famous scene from the 1962 movie Lawrence of Arabia)
It’s ok to say to yourself (if it’s what you decide is the right thing to do) “Yep, this experience is going to suck terribly, but I’m going to do it anyway”.
See also (this being about Radical Acceptance):
What’s The Worst That Could Happen?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Gentler Hair Health Options
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hair, Gently
We have previously talked about the medicinal options for combatting the thinning hair that comes with age especially for men, but also for a lot of women. You can read about those medicinal options here:
Hair-Loss Remedies, By Science
We also did a whole supplement spotlight research review for saw palmetto! You can read about how that might help you keep your hair present and correct, here:
One Man’s Saw Palmetto Is Another Woman’s Serenoa Repens
Today we’re going to talk options that are less “heavy guns”, and/but still very useful.
Supplementation
First, the obvious. Taking vitamins and minerals, especially biotin, can help a lot. This writer takes 10,000µg (that’s micrograms, not milligrams!) biotin gummies, similar to this example product on Amazon (except mine also has other vitamins and minerals in, but the exact product doesn’t seem to be available on Amazon).
When thinking “what vitamins and minerals help hair?”, honestly, it’s most of them. So, focus on the ones that count for the most (usually: biotin and zinc), and then cover your bases for the rest with good diet and additional supplementation if you wish.
Caffeine (topical)
It may feel silly, giving one’s hair a stimulant, but topical caffeine application really does work to stimulate hair growth. And not “just a little help”, either:
❝Specifically, 0.2% topical caffeine-based solutions are typically safe with very minimal adverse effects for long-term treatment of AGA, and they are not inferior to topical 5% minoxidil therapy❞
(AGA = Androgenic Alopecia)
Argan oil
As with coconut oil, argan oil is great on hair. It won’t do a thing to improve hair growth or decrease hair shedding, but it will help you hair stay moisturized and thus reduce breakage—thus, may not be relevant for everyone, but for those of us with hair long enough to brush, it’s important.
Bonus: get an argan oil based hair serum that also contains keratin (the protein used to make hair), as this helps strengthen the hair too.
Here’s an example product on Amazon
Silk pillowcases
Or a silk hair bonnet to sleep in! They both do the same thing, which is prevent damaging the hair in one’s sleep by reducing the friction that it may have when moving/turning against the pillow in one’s sleep.
- Pros of the bonnet: if you have lots of hair and a partner in bed with you, your hair need not be in their face, and you also won’t get it caught under you or them.
- Pros of the pillowcase: you don’t have to wear a bonnet
Both are also used widely by people without hair loss issues, but with easily damaged and/or tangled hair—Black people especially with 3C or tighter curls in particular often benefit from this. Other people whose hair is curly and/or gray also stand to gain a lot.
Here are Amazon example products of a silk pillowcase (it’s expensive, but worth it) and a silk bonnet, respectively
Want to read more?
You might like this article:
From straight to curly, thick to thin: here’s how hormones and chemotherapy can change your hair
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Black Olives vs Green Olives – Which is Healthier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing black olives to green olives, we picked the black olives.
Why?
First know this: they are the same plant, just at different stages of ripening (green olives are, as you might expect, less ripe).
Next: the nutritional values of both, from macros down to the phytochemicals, are mostly very similar, but there are a few things that stand out:
• Black olives usually have more calories per serving, average about 25% more. But these are from healthy fats, so unless you’re on a calorie-restricted diet, this is probably not a consideration.
• Green olives are almost always “cured” for longer, which results in a much higher sodium content often around 200% that of black olives. Black olives are often not “cured” at all.Hence, we chose the black olives!
You may be wondering: do green olives have anything going for them that black olives don’t?
And the answer has a clue in the taste: green olives generally have a stronger, more bitter/pungent taste. And remember what we said about things that have a stronger, more bitter/pungent taste:
Tasty Polyphenols: Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
That’s right, green olives are a little higher in polyphenols than black olives.
But! If you want to enjoy the polyphenol content of green olives without the sodium content, the best way to do that is not olives, but olive oil—which is usually made from green olives.
For more about olive oil, check out:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: