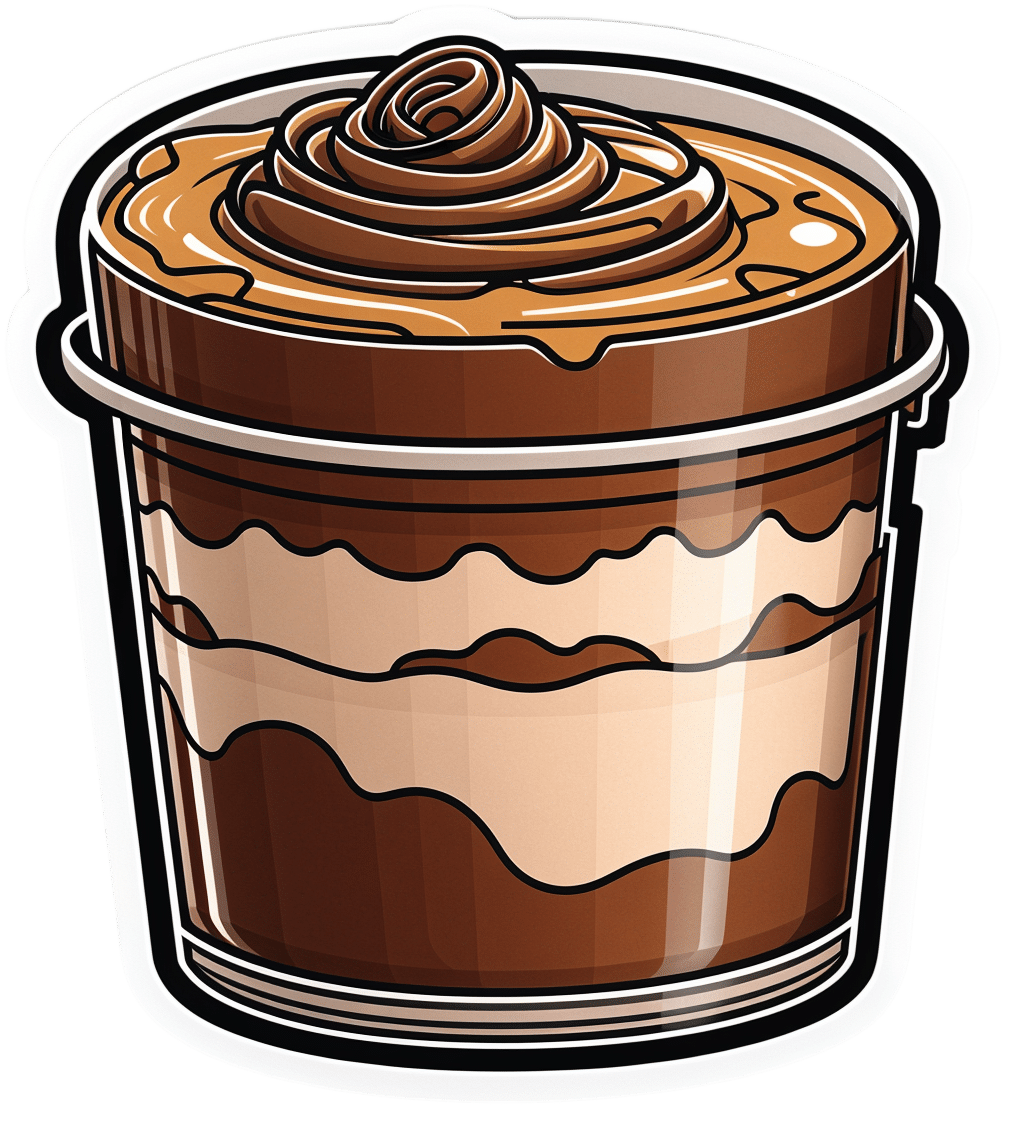
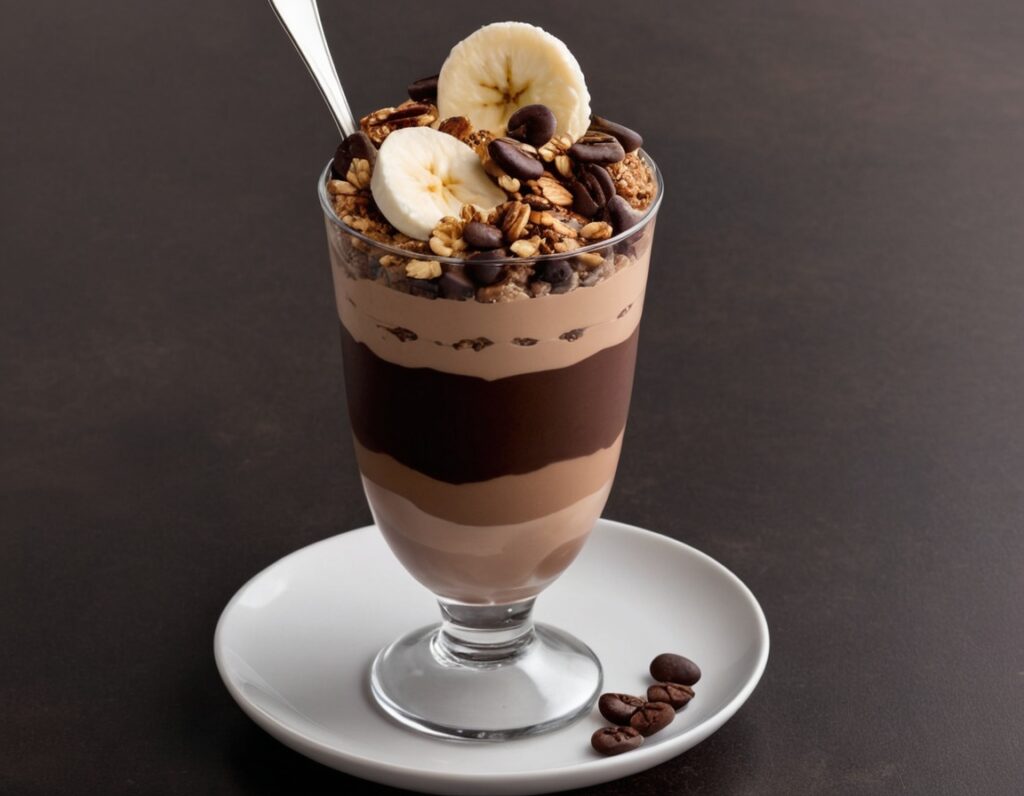
Loaded Mocha Chocolate Parfait
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Packed with nutrients, including a healthy dose of protein and fiber, these parfait pots can be a healthy dessert, snack, or even breakfast!
You will need (for 4 servings)
For the mocha cream:
- ½ cup almond milk
- ½ cup raw cashews
- ⅓ cup espresso
- 2 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
For the chocolate sauce:
- 4 tbsp coconut oil, melted
- 2 tbsp unsweetened cocoa powder
- 1 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
For the other layers:
- 1 banana, sliced
- 1 cup granola, no added sugar
Garnish (optional): 3 coffee beans per serving
Note about the maple syrup: since its viscosity is similar to the overall viscosity of the mocha cream and chocolate sauce, you can adjust this per your tastes, without affecting the composition of the dish much besides sweetness (and sugar content). If you don’t like sweetness, the maple syrup be reduced or even omitted entirely (your writer here is known for her enjoyment of very strong bitter flavors and rarely wants anything sweeter than a banana); if you prefer more sweetness than the recipe called for, that’s your choice too.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend all the mocha cream ingredients. If you have time, doing this in advance and keeping it in the fridge for a few hours (or even up to a week) will make the flavor richer. But if you don’t have time, that’s fine too.
2) Stir all the chocolate sauce ingredients together in a small bowl, and set it aside. This one should definitely not be refrigerated, or else the coconut oil will solidify and separate itself.
3) Gently swirl the the mocha cream and chocolate sauce together. You want a marble effect, not a full mixing. Omit this step if you want clearer layers.
4) Assemble in dessert glasses, alternating layers of banana, mocha chocolate marble mixture (or the two parts, if you didn’t swirl them together), and granola.
5) Add the coffee-bean garnish, if using, and serve!

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (Or Is It?)
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
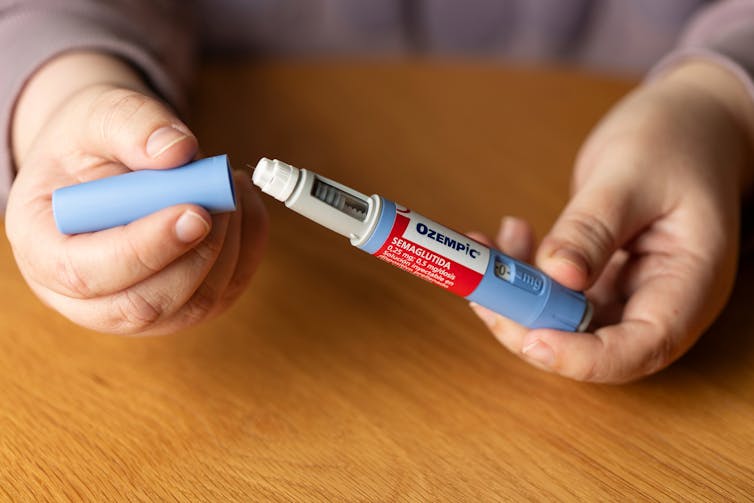
No, taking drugs like Ozempic isn’t ‘cheating’ at weight loss or the ‘easy way out’
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
Obesity medication that is effective has been a long time coming. Enter semaglutide (sold as Ozempic and Wegovy), which is helping people improve weight-related health, including lowering the risk of a having a heart attack or stroke, while also silencing “food noise”.
As demand for semaglutide increases, so are claims that taking it is “cheating” at weight loss or the “easy way out”.
We don’t tell people who need statin medication to treat high cholesterol or drugs to manage high blood pressure they’re cheating or taking the easy way out.
Nor should we shame people taking semaglutide. It’s a drug used to treat diabetes and obesity which needs to be taken long term and comes with risks and side effects, as well as benefits. When prescribed for obesity, it’s given alongside advice about diet and exercise.
How does it work?
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA). This means it makes your body’s own glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone, called GLP-1 for short, work better.
GLP-1 gets secreted by cells in your gut when it detects increased nutrient levels after eating. This stimulates insulin production, which lowers blood sugars.
GLP-1 also slows gastric emptying, which makes you feel full, and reduces hunger and feelings of reward after eating.
GLP-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) medications like Ozempic help the body’s own GLP-1 work better by mimicking and extending its action.
Some studies have found less GLP-1 gets released after meals in adults with obesity or type 2 diabetes mellitus compared to adults with normal glucose tolerance. So having less GLP-1 circulating in your blood means you don’t feel as full after eating and get hungry again sooner compared to people who produce more.
GLP-1 has a very short half-life of about two minutes. So GLP-1RA medications were designed to have a very long half-life of about seven days. That’s why semaglutide is given as a weekly injection.
What can users expect? What does the research say?
Higher doses of semaglutide are prescribed to treat obesity compared to type 2 diabetes management (up to 2.4mg versus 2.0mg weekly).
A large group of randomised controlled trials, called STEP trials, all tested weekly 2.4mg semaglutide injections versus different interventions or placebo drugs.
Trials lasting 1.3–2 years consistently found weekly 2.4 mg semaglutide injections led to 6–12% greater weight loss compared to placebo or alternative interventions. The average weight change depended on how long medication treatment lasted and length of follow-up.
Higher doses of semaglutide are prescribed for obesity than for type 2 diabetes. fcm82/Shutterstock Weight reduction due to semaglutide also leads to a reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure of about 4.8 mmHg and 2.5 mmHg respectively, a reduction in triglyceride levels (a type of blood fat) and improved physical function.
Another recent trial in adults with pre-existing heart disease and obesity, but without type 2 diabetes, found adults receiving weekly 2.4mg semaglutide injections had a 20% lower risk of specific cardiovascular events, including having a non-fatal heart attack, a stroke or dying from cardiovascular disease, after three years follow-up.
Who is eligible for semaglutide?
Australia’s regulator, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), has approved semaglutide, sold as Ozempic, for treating type 2 diabetes.
However, due to shortages, the TGA had advised doctors not to start new Ozempic prescriptions for “off-label use” such as obesity treatment and the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme doesn’t currently subsidise off-label use.
The TGA has approved Wegovy to treat obesity but it’s not currently available in Australia.
When it’s available, doctors will be able to prescribe semaglutide to treat obesity in conjunction with lifestyle interventions (including diet, physical activity and psychological support) in adults with obesity (a BMI of 30 or above) or those with a BMI of 27 or above who also have weight-related medical complications.
What else do you need to do during Ozempic treatment?
Checking details of the STEP trial intervention components, it’s clear participants invested a lot of time and effort. In addition to taking medication, people had brief lifestyle counselling sessions with dietitians or other health professionals every four weeks as a minimum in most trials.
Support sessions were designed to help people stick with consuming 2,000 kilojoules (500 calories) less daily compared to their energy needs, and performing 150 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, like brisk walking, dancing and gardening each week.
STEP trials varied in other components, with follow-up time periods varying from 68 to 104 weeks. The aim of these trials was to show the effect of adding the medication on top of other lifestyle counselling.
Trial participants also exercised for 150 minutes a week. Elena Nichizhenova/Shutterstock A review of obesity medication trials found people reported they needed less cognitive behaviour training to help them stick with the reduced energy intake. This is one aspect where drug treatment may make adherence a little easier. Not feeling as hungry and having environmental food cues “switched off” may mean less support is required for goal-setting, self-monitoring food intake and avoiding things that trigger eating.
But what are the side effects?
Semaglutide’s side-effects include nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, constipation, indigestion and abdominal pain.
In one study these led to discontinuation of medication in 6% of people, but interestingly also in 3% of people taking placebos.
More severe side-effects included gallbladder disease, acute pancreatitis, hypoglycaemia, acute kidney disease and injection site reactions.
To reduce risk or severity of side-effects, medication doses are increased very slowly over months. Once the full dose and response are achieved, research indicates you need to take it long term.
Given this long-term commitment, and associated high out-of-pocket cost of medication, when it comes to taking semaglutide to treat obesity, there is no way it can be considered “cheating”.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Clare Collins, Laureate Professor in Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Life After Death? (Your Life; A Loved One’s Death)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Show Must Go On
We’ve previously written about the topics of death and dying. It’s not cheery, but it is important to tackle.
Sooner is better than later, in the case of:
Preparations For Managing Your Own Mortality
And for those who are left behind, of course it is hardest of all:
What Grief Does To Your Body (And How To Manage It)
But what about what comes next? For those who are left behind, that is.
Life goes on
In cases when the death is that of a close loved one, the early days after death can seem like a surreal blur. How can the world go ticking on as normal when [loved one] is dead?
But incontrovertibly, it does, so we can only ask again: how?
And, we get to choose that, to a degree. The above-linked article about grief gives a “101” rundown, but it’s (by necessity, for space) a scant preparation for one of the biggest challenges in life that most of us will ever face.
For many people, processing grief involves a kind of “saying goodbye”. For others, it doesn’t, as in the following cases of grieving the loss of one’s child—something no parent should ever have to face, but it happens:
Dr. Ken Druck | The Love That Never Dies
(with warning, the above article is a little heavy)
In short: for those who choose not to “say goodbye” in the case of the death of a loved one, it’s more often not a case of cold neglect, but rather the opposite—a holding on. Not in the “denial” sense of holding on, but rather in the sense of “I am not letting go of this feeling of love, no matter how much it might hurt to hold onto; it’s all I have”.
What about widows, and love after death?
Note: we’ll use the feminine “widow” here as a) it’s the most common and b) most scientific literature focuses on widows, but there is no reason why most of the same things won’t also apply to widowers.
We say “most”, as society does tend to treat widows and widowers differently, having different expectations about a respectful mourning period, one’s comportment during same, and so on.
As an aside: most scientific literature also assumes heterosexuality, which is again statistically reasonable, and for the mostpart the main difference is any extra challenges presented by non-recognition of marriages, and/or homophobic in-laws. But otherwise, grief is grief, and as the saying goes, love is love.
One last specificity before we get into the meat of this: we are generally assuming marriages to be monogamous here. Polyamorous arrangements will likely sidestep most of these issues completely, but again, they’re not the norm.
Firstly, there’s a big difference between remarrying (or similar) after being widowed, and remarrying (or similar) after a divorce, and that largely lies in the difference of how they begin. A divorce is (however stressful it may often be) more often seen as a transition into a new period of freedom, whereas bereavement is almost always felt as a terrible loss.
The science, by the way, shows the stats for this; people are less likely to remarry, and slower to remarry if they do, in instances of bereavement rather than divorce, for example:
Timing of Remarriage Among Divorced and Widowed Parents
Love after death: the options
For widows, then, there seem to be multiple options:
- Hold on to the feelings for one’s deceased partner; never remarry
- Grieve, move on, find new love, relegating the old to history
- Try to balance the two (this is tricky but can be done*)
*Why is balancing the two tricky, and how can it be done?
It’s tricky because ultimately there are three people’s wishes at hand:
- The deceased (“they would want me to be happy” vs “I feel I would be betraying them”—which two feelings can also absolutely come together, by the way)
- Yourself (whether you actually want to get a new partner, or just remain single—this is your 100% your choice either way, and your decision should be made consciously)
- The new love (how comfortable are they with your continued feelings for your late love, really?)
And obviously only two of the above can be polled for opinions, and the latter one might say what they think we want to hear, only to secretly and/or later resent it.
One piece of solid advice for the happily married: talk with your partner now about how you each would feel about the other potentially remarrying in the event of your death. Do they have your pre-emptive blessing to do whatever, do you ask a respectable mourning period first (how long?), would the thought just plain make you jealous? Be honest, and bid your partner be honest too.
One piece of solid advice for everyone: make sure you, and your partner(s), as applicable, have a good emotional safety net, if you can. Close friends or family members that you genuinely completely trust to be there through thick and thin, to hold your/their hand through the emotional wreck that will likely follow.
Because, while depression and social loneliness are expected and looked out for, it’s emotional loneliness that actually hits the hardest, for most people:
Longitudinal Examination of Emotional Functioning in Older Adults After Spousal Bereavement
…which means that having even just one close friend or family member with whom one can be at one’s absolute worst, express emotions without censure, not have to put on the socially expected appearance of emotional stability… Having that one person (ideally more, but having at least one is critical) can make a huge difference.
But what if a person has nobody?
That’s definitely a hard place to be, but here’s a good starting point:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How a Friend’s Death Turned Colorado Teens Into Anti-Overdose Activists
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gavinn McKinney loved Nike shoes, fireworks, and sushi. He was studying Potawatomi, one of the languages of his Native American heritage. He loved holding his niece and smelling her baby smell. On his 15th birthday, the Durango, Colorado, teen spent a cold December afternoon chopping wood to help neighbors who couldn’t afford to heat their homes.
McKinney almost made it to his 16th birthday. He died of fentanyl poisoning at a friend’s house in December 2021. His friends say it was the first time he tried hard drugs. The memorial service was so packed people had to stand outside the funeral home.
Now, his peers are trying to cement their friend’s legacy in state law. They recently testified to state lawmakers in support of a bill they helped write to ensure students can carry naloxone with them at all times without fear of discipline or confiscation. School districts tend to have strict medication policies. Without special permission, Colorado students can’t even carry their own emergency medications, such as an inhaler, and they are not allowed to share them with others.
“We realized we could actually make a change if we put our hearts to it,” said Niko Peterson, a senior at Animas High School in Durango and one of McKinney’s friends who helped write the bill. “Being proactive versus being reactive is going to be the best possible solution.”
Individual school districts or counties in California, Maryland, and elsewhere have rules expressly allowing high school students to carry naloxone. But Jon Woodruff, managing attorney at the Legislative Analysis and Public Policy Association, said he wasn’t aware of any statewide law such as the one Colorado is considering. Woodruff’s Washington, D.C.-based organization researches and drafts legislation on substance use.
Naloxone is an opioid antagonist that can halt an overdose. Available over the counter as a nasal spray, it is considered the fire extinguisher of the opioid epidemic, for use in an emergency, but just one tool in a prevention strategy. (People often refer to it as “Narcan,” one of the more recognizable brand names, similar to how tissues, regardless of brand, are often called “Kleenex.”)
The Biden administration last year backed an ad campaign encouraging young people to carry the emergency medication.
Most states’ naloxone access laws protect do-gooders, including youth, from liability if they accidentally harm someone while administering naloxone. But without school policies explicitly allowing it, the students’ ability to bring naloxone to class falls into a gray area.
Ryan Christoff said that in September 2022 fellow staff at Centaurus High School in Lafayette, Colorado, where he worked and which one of his daughters attended at the time, confiscated naloxone from one of her classmates.
“She didn’t have anything on her other than the Narcan, and they took it away from her,” said Christoff, who had provided the confiscated Narcan to that student and many others after his daughter nearly died from fentanyl poisoning. “We should want every student to carry it.”
Boulder Valley School District spokesperson Randy Barber said the incident “was a one-off and we’ve done some work since to make sure nurses are aware.” The district now encourages everyone to consider carrying naloxone, he said.
Community’s Devastation Turns to Action
In Durango, McKinney’s death hit the community hard. McKinney’s friends and family said he didn’t do hard drugs. The substance he was hooked on was Tapatío hot sauce — he even brought some in his pocket to a Rockies game.
After McKinney died, people started getting tattoos of the phrase he was known for, which was emblazoned on his favorite sweatshirt: “Love is the cure.” Even a few of his teachers got them. But it was classmates, along with their friends at another high school in town, who turned his loss into a political movement.
“We’re making things happen on behalf of him,” Peterson said.
The mortality rate has spiked in recent years, with more than 1,500 other children and teens in the U.S. dying of fentanyl poisoning the same year as McKinney. Most youth who die of overdoses have no known history of taking opioids, and many of them likely thought they were taking prescription opioids like OxyContin or Percocet — not the fake prescription pills that increasingly carry a lethal dose of fentanyl.
“Most likely the largest group of teens that are dying are really teens that are experimenting, as opposed to teens that have a long-standing opioid use disorder,” said Joseph Friedman, a substance use researcher at UCLA who would like to see schools provide accurate drug education about counterfeit pills, such as with Stanford’s Safety First curriculum.
Allowing students to carry a low-risk, lifesaving drug with them is in many ways the minimum schools can do, he said.
“I would argue that what the schools should be doing is identifying high-risk teens and giving them the Narcan to take home with them and teaching them why it matters,” Friedman said.
Writing in The New England Journal of Medicine, Friedman identified Colorado as a hot spot for high school-aged adolescent overdose deaths, with a mortality rate more than double that of the nation from 2020 to 2022.
“Increasingly, fentanyl is being sold in pill form, and it’s happening to the largest degree in the West,” said Friedman. “I think that the teen overdose crisis is a direct result of that.”
If Colorado lawmakers approve the bill, “I think that’s a really important step,” said Ju Nyeong Park, an assistant professor of medicine at Brown University, who leads a research group focused on how to prevent overdoses. “I hope that the Colorado Legislature does and that other states follow as well.”
Park said comprehensive programs to test drugs for dangerous contaminants, better access to evidence-based treatment for adolescents who develop a substance use disorder, and promotion of harm reduction tools are also important. “For example, there is a national hotline called Never Use Alone that anyone can call anonymously to be supervised remotely in case of an emergency,” she said.
Taking Matters Into Their Own Hands
Many Colorado school districts are training staff how to administer naloxone and are stocking it on school grounds through a program that allows them to acquire it from the state at little to no cost. But it was clear to Peterson and other area high schoolers that having naloxone at school isn’t enough, especially in rural places.
“The teachers who are trained to use Narcan will not be at the parties where the students will be using the drugs,” he said.
And it isn’t enough to expect teens to keep it at home.
“It’s not going to be helpful if it’s in somebody’s house 20 minutes outside of town. It’s going to be helpful if it’s in their backpack always,” said Zoe Ramsey, another of McKinney’s friends and a senior at Animas High School.
“We were informed it was against the rules to carry naloxone, and especially to distribute it,” said Ilias “Leo” Stritikus, who graduated from Durango High School last year.
But students in the area, and their school administrators, were uncertain: Could students get in trouble for carrying the opioid antagonist in their backpacks, or if they distributed it to friends? And could a school or district be held liable if something went wrong?
He, along with Ramsey and Peterson, helped form the group Students Against Overdose. Together, they convinced Animas, which is a charter school, and the surrounding school district, to change policies. Now, with parental permission, and after going through training on how to administer it, students may carry naloxone on school grounds.
Durango School District 9-R spokesperson Karla Sluis said at least 45 students have completed the training.
School districts in other parts of the nation have also determined it’s important to clarify students’ ability to carry naloxone.
“We want to be a part of saving lives,” said Smita Malhotra, chief medical director for Los Angeles Unified School District in California.
Los Angeles County had one of the nation’s highest adolescent overdose death tallies of any U.S. county: From 2020 to 2022, 111 teens ages 14 to 18 died. One of them was a 15-year-old who died in a school bathroom of fentanyl poisoning. Malhotra’s district has since updated its policy on naloxone to permit students to carry and administer it.
“All students can carry naloxone in our school campuses without facing any discipline,” Malhotra said. She said the district is also doubling down on peer support and hosting educational sessions for families and students.
Montgomery County Public Schools in Maryland took a similar approach. School staff had to administer naloxone 18 times over the course of a school year, and five students died over the course of about one semester.
When the district held community forums on the issue, Patricia Kapunan, the district’s medical officer, said, “Students were very vocal about wanting access to naloxone. A student is very unlikely to carry something in their backpack which they think they might get in trouble for.”
So it, too, clarified its policy. While that was underway, local news reported that high school students found a teen passed out, with purple lips, in the bathroom of a McDonald’s down the street from their school, and used Narcan to revive them. It was during lunch on a school day.
“We can’t Narcan our way out of the opioid use crisis,” said Kapunan. “But it was critical to do it first. Just like knowing 911.”
Now, with the support of the district and county health department, students are training other students how to administer naloxone. Jackson Taylor, one of the student trainers, estimated they trained about 200 students over the course of three hours on a recent Saturday.
“It felt amazing, this footstep toward fixing the issue,” Taylor said.
Each trainee left with two doses of naloxone.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The 5 Love Languages Gone Wrong
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Levelling up the 5 love languages
The saying “happy wife; happy life” certainly goes regardless of gender, and if we’re partnered, it’s difficult to thrive in our individual lives if we’re not thriving as a couple. So, with the usual note that mental health is also just health, let’s take a look at getting beyond the basics of a well-known, often clumsily-applied model:
The 5 love languages
You’re probably familiar with “the 5 love languages”, as developed by Dr. Gary Chapman. If not, they are:
- Acts of Service
- Gift-Giving
- Physical Touch
- Quality Time
- Words of Affirmation
The idea is that we each weight these differently, and problems can arise when a couple are “speaking a different language”.
So, is this a basic compatibility test?
It doesn’t have to be!
We can, if we’re aware of each other’s primary love languages, make an effort to do a thing we wouldn’t necessarily do automatically, to ensure they’re loved the way they need to be.
But…
What a lot of people overlook is that we can also have different primary love languages for giving and for receiving. And, missing that can mean that even taking each other’s primarily love languages into account, efforts to make a partner feel loved, or to feel loved oneself, can miss 50% of the time.
For example, I (your writer here today, hi) could be asked my primary love language and respond without hesitation “Acts of Service!” because that’s my go-to for expressing love.
I’m the person who’ll run around bringing drinks, do all the housework, and without being indelicate, will tend towards giving in the bedroom. But…
A partner trying to act on that information to make me feel loved by giving Acts of Service would be doomed to catastrophic failure, because my knee-jerk reaction would be “No, here, let me do that for you!”
So it’s important for partners to ask each other…
- Not: “what’s your primary love language?” ❌
- But: “what’s your primary way of expressing love?” ✅
- And: “which love language makes you feel most loved?” ✅
For what it’s worth, I thrive on Words of Affirmation, so thanks again to everyone who leaves kind feedback on our articles! It lets me know I provided a good Act of Service
So far, so simple, right? You and your partner (or: other person! Because as we’ve just seen, these go for all kinds of dynamics, not just romantic partnerships) need to be aware of each other’s preferred love languages for giving and receiving.
But…
There’s another pitfall that many fall into, and that’s assuming that the other person has the same idea about what a given love language means, when there’s more to clarify.
For example:
- Acts of Service: is it more important that the service be useful, or that it took effort?
- Gift-Giving: is it better that a gift be more expensive, or more thoughtful and personal?
- Physical Touch: what counts here? If we’re shoulder-to-shoulder on the couch, is that physical touch or is something more active needed?
- Quality Time: does it count if we’re both doing our own thing but together in the same room, comfortable in silence together? Or does it need to be a more active and involved activity together? And is it quality time if we’re at a social event together, or does it need to be just us?
- Words of Affirmation: what, exactly, do we need to hear? For romantic partners, “I love you” can often be important, but is there something else we need to hear? Perhaps a “because…”, or perhaps a “so much that…”, or perhaps something else entirely? Does it no longer count if we have to put the words in our partner’s mouth, or is that just good two-way communication?
Bottom line:
There’s a lot more to this than a “What’s your love language?” click-through quiz, but with a little application and good communication, this model can really resolve a lot of would-be problems that can grow from feeling unappreciated or such. And, the same principles go just the same for friends and others as they do for romantic partners.
In short, it’s one of the keys to good interpersonal relationships in general—something critical for our overall well-being!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
6 Signs Of Stroke (One Month In Advance)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most people can recognise the signs of a stroke when it’s just happened, but knowing the signs that appear a month beforehand would be very useful. That’s what this video’s about!
The Warning Signs
- Persistently elevated blood pressure: one more reason to have an at-home testing kit and use it regularly! Or a smartwatch or similar that’ll do it for you. The reason this is relevant is because high blood pressure can lead to damaging blood vessels, causing a stroke.
- Excessive fatigue: of course, this one can have many possible causes, but one of them is a “transient ischemic attack” (TIA), which is essentially a micro-stroke, and can be a precursor to a more severe stroke. So, we’re not doing the Google MD thing here of saying “if this, then that”, but we are saying: paying attention to the overall patterns can be very useful. Rather than fretting unduly about a symptom in isolation, see how it fits into the big picture.
- Vision problems: especially if sudden-onset with no obvious alternative cause can be a sign of neural damage, and may indicate a stroke on the way.
- Speech problems: if there’s not an obvious alternative explanation (e.g. you’ve just finished your third martini, or was this the fourth?), then speech problems (e.g. slurred speech, trouble forming sentences, etc) are a very worrying indicator and should be treated as a medical emergency.
- Neurological problems: a bit of a catch-all category, but memory issues, loss of balance, nausea without an obvious alternative cause, are all things that should get checked out immediately just in case.
- Numbness or weakness in the extremities: especially if on one side of the body only, is often caused by the TIA we mentioned earlier. If it’s both sides, then peripheral neuropathy may be the culprit, but having a neurologist take a look at it is a good idea either way.
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Two Things You Can Do To Improve Stroke Survival Chances
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Each Monday, we’re going to be bringing you cutting-edge research reviews to not only make your health and productivity crazy simple, but also, constantly up-to-date.
But today, in this special edition, we want to lay out plain and simple how to see through a lot of the tricks used not just by popular news outlets, but even sometimes the research publications themselves.
That way, when we give you health-related science news, you won’t have to take our word for it, because you’ll be able to see whether the studies we cite really support the claims we make.
Of course, we’ll always give you the best, most honest information we have… But the point is that you shouldn’t have to trust us! So, buckle in for today’s special edition, and never have to blindly believe sci-hub (or Snopes!) again.
The above now-famous Tumblr post that became a meme is a popular and obvious example of how statistics can be misleading, either by error or by deliberate spin.
But what sort of mistakes and misrepresentations are we most likely to find in real research?
Spin Bias
Perhaps most common in popular media reporting of science, the Spin Bias hinges on the fact that most people perceive numbers in a very “fuzzy logic” sort of way. Do you?
Try this:
- A million seconds is 11.5 days
- A billion seconds is not weeks, but 13.2 months!
…just kidding, it’s actually nearly thirty-two years.
Did the months figure seem reasonable to you, though? If so, this is the same kind of “human brains don’t do large numbers” problem that occurs when looking at statistics.
Let’s have a look at reporting on statistically unlikely side effects for vaccines, as an example:
- “966 people in the US died after receiving this vaccine!” (So many! So risky!)
- “Fewer than 3 people per million died after receiving this vaccine!” (Hmm, I wonder if it is worth it?)
- “Half of unvaccinated people with this disease die of it” (Oh)
How to check for this: ask yourself “is what’s being described as very common really very common?”. To keep with the spiders theme, there are many (usually outright made-up) stats thrown around on social media about how near the nearest spider is at any given time. Apply this kind of thinking to medical conditions.. If something affects only 1% of the population (So few! What a tiny number!), how far would you have to go to find someone with that condition? The end of your street, perhaps?
Selection/Sampling Bias
Diabetes disproportionately affects black people, but diabetes research disproportionately focuses on white people with diabetes. There are many possible reasons for this, the most obvious being systemic/institutional racism. For example, advertisements for clinical trial volunteer opportunities might appear more frequently amongst a convenient, nearby, mostly-white student body. The selection bias, therefore, made the study much less reliable.
Alternatively: a researcher is conducting a study on depression, and advertises for research subjects. He struggles to get a large enough sample size, because depressed people are less likely to respond, but eventually gets enough. Little does he know, even the most depressed of his subjects are relatively happy and healthy compared with the silent majority of depressed people who didn’t respond.
See This And Many More Educational Cartoons At Sketchplanations.com!
How to check for this: Does the “method” section of the scientific article describe how they took pains to make sure their sample was representative of the relevant population, and how did they decide what the relevant population was?
Publication Bias
Scientific publications will tend to prioritise statistical significance. Which seems great, right? We want statistically significant studies… don’t we?
We do, but: usually, in science, we consider something “statistically significant” when it hits the magical marker of p=0.05 (in other words, the probability of getting that result is 1/20, and the results are reliably coming back on the right side of that marker).
However, this can result in the clinic stopping testing once p=0.05 is reached, because they want to have their paper published. (“Yay, we’ve reached out magical marker and now our paper will be published”)
So, you can think of publication bias as the tendency for researchers to publish ‘positive’ results.
If it weren’t for publication bias, we would have a lot more studies that say “we tested this, and here are our results, which didn’t help answer our question at all”—which would be bad for the publication, but good for science, because data is data.
To put it in non-numerical terms: this is the same misrepresentation as the technically true phrase “when I misplace something, it’s always in the last place I look for it”—obviously it is, because that’s when you stop looking.
There’s not a good way to check for this, but be sure to check out sample sizes and see that they’re reassuringly large.
Reporting/Detection/Survivorship Bias
There’s a famous example of the rise in “popularity” of left-handedness. Whilst Americans born in ~1910 had a bit under a 3.5% chance of being left handed, those born in ~1950 had a bit under a 12% change.
Why did left-handedness become so much more prevalent all of a sudden, and then plateau at 12%?
Simple, that’s when schools stopped forcing left-handed children to use their right hands instead.
In a similar fashion, countries have generally found that homosexuality became a lot more common once decriminalized. Of course the real incidence almost certainly did not change—it just became more visible to research.
So, these biases are caused when the method of data collection and/or measurement leads to a systematic error in results.
How to check for this: you’ll need to think this through logically, on a case by case basis. Is there a reason that we might not be seeing or hearing from a certain demographic?
And perhaps most common of all…
Confounding Bias
This is the bias that relates to the well-known idea “correlation ≠ causation”.
Everyone has heard the funny examples, such as “ice cream sales cause shark attacks” (in reality, both are more likely to happen in similar places and times; when many people are at the beach, for instance).
How can any research paper possibly screw this one up?
Often they don’t and it’s a case of Spin Bias (see above), but examples that are not so obviously wrong “by common sense” often fly under the radar:
“Horse-riding found to be the sport that most extends longevity”
Should we all take up horse-riding to increase our lifespans? Probably not; the reality is that people who can afford horses can probably afford better than average healthcare, and lead easier, less stressful lives overall. The fact that people with horses typically have wealthier lifestyles than those without, is the confounding variable here.
See This And Many More Educational Cartoons on XKCD.com!
In short, when you look at the scientific research papers cited in the articles you read (you do look at the studies, yes?), watch out for these biases that found their way into the research, and you’ll be able to draw your own conclusions, with well-informed confidence, about what the study actually tells us.
Science shouldn’t be gatekept, and definitely shouldn’t be abused, so the more people who know about these things, the better!
So…would one of your friends benefit from this knowledge? Forward it to them!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: