The Sugar Alcohol That Reduces BMI!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inositol Does-It-Ol’!
First things first, a quick clarification up-front:
Myo-inositol or D-chiro-inositol?
We’re going to be talking about inositol today, which comes in numerous forms, but most importantly:
- Myo-inositol (myo-Ins)
- D-chiro-inositol (D-chiro-Ins)
These are both inositol, (a sugar alcohol!) and for our purposes today, the most relevant form is myo-inositol.
The studies we’ll look at today are either:
- just about myo-inositol, or
- about myo-inositol in the presence of d-chiro-inositol at a 40:1 ratio.
You have both in your body naturally; wherever supplementation is mentioned, it means supplementing with either:
- extra myo-inositol (because that’s the one the body more often needs more of), or
- both, at the 40:1 ratio that we mentioned above (because that’s one way to help balance an imbalanced ratio)
With that in mind…
Inositol against diabetes?
Inositol is known to:
- decrease insulin resistance
- increase insulin sensitivity
- have an important role in cell signaling
- have an important role in metabolism
The first two things there both mean that inositol is good against diabetes. It’s not “take this and you’re cured”, but:
- if you’re pre-diabetic it may help you avoid type 2 diabetes
- if you are diabetic (either type) it can help in the management of your diabetes.
It does this by allowing your body to make better use of insulin (regardless of whether that insulin is from your pancreas or from the pharmacy).
How does it do that? Research is still underway and there’s a lot we don’t know yet, but here’s one way, for example:
❝Evidence showed that inositol phosphates might enhance the browning of white adipocytes and directly improve insulin sensitivity through adipocytes❞
Read: Role of Inositols and Inositol Phosphates in Energy Metabolism
We mentioned its role in metabolism in a bullet-point above, and we didn’t just mean insulin sensitivity! There’s also…
Inositol for thyroid function?
The thyroid is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and it controls how quickly the body burns energy, makes proteins, and how sensitive the body should be to other hormones. So, it working correctly or not can have a big impact on everything from your mood to your weight to your energy levels.
How does inositol affect thyroid function?
- Inositol has an important role in thyroid function and dealing with autoimmune diseases.
- Inositol is essential to produce H2O2 (yes, really) required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- Depletion of inositol may lead to the development of some thyroid diseases, such as hypothyroidism.
- Inositol supplementation seems to help in the management of thyroid diseases.
Read: The Role of Inositol in Thyroid Physiology and in Subclinical Hypothyroidism Management
Inositol for PCOS?
A systematic review published in the Journal of Gynecological Endocrinology noted:
- Inositol can restore spontaneous ovarian activity (and consequently fertility) in most patients with PCOS.
- Myo-inositol is a safe and effective treatment to improve:
- ovarian function
- healthy metabolism
- healthy hormonal balance
While very comprehensive (which is why we included it here), that review’s a little old, so…
Check out this cutting edge (Jan 2023) study whose title says it all:
Inositol for fertility?
Just last year, Mendoza et al published that inositol supplementation, together with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, could be an optimal strategy to improve female fertility.
This built from Gambiole and Forte’s work, which laid out how inositol is a safe compound for many issues related to fertility and pregnancy. In particular, several clinical trials demonstrated that:
- inositol can have therapeutic effects in infertile women
- inositol can also be useful as a preventive treatment during pregnancy
- inositol could prevent the onset of neural tube defects
- inositol also reduces the occurrence of gestational diabetes
Due to the safety and efficiency of inositol, it can take the place of many drugs that are contraindicated in pregnancy. Basically: take this, and you’ll need fewer other drugs. Always a win!
Read: Myo-Inositol as a Key Supporter of Fertility and Physiological Gestation
Inositol For Weight Loss
We promised you “this alcohol sugar can reduce your BMI”, and we weren’t making it up!
Zarezadeh et al conducited a very extensive systematic review, and found:
- Oral inositol supplementation has positive effect on BMI reduction.
- Inositol in the form of myo-inositol had the strongest effect on BMI reduction.
- Participants with PCOS and/or who were overweight, experienced the most significant improvement of all.
Want some inositol?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here’s myo-inositol and d-chiro-inositol at a 40:1 ratio, available on Amazon!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tasty Versatile Rice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In the nearish future, we’re going to do some incredible rice dishes, but first we need to make sure we’re all on the same page about cooking rice, so here’s a simple recipe first, to get technique down and work in some essentials. We’ll be using wholegrain basmati rice, because it has a low glycemic index, lowest likelihood of heavy metal contamination (a problem for some kinds of rice), and it’s one of the easiest rices to cook well.
You will need
- 1 cup wholegrain basmati rice (it may also be called “brown basmati rice“; this is the same)
- 1 1/2 cups vegetable stock (ideally you have made this yourself from vegetable offcuts that you saved in the freezer, then it will be healthiest and lowest in sodium; failing that, low-sodium vegetable stock cubes can be purchased at most large supermarkets. and then made up at home with hot water)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp turmeric powder (this small quantity will not change the flavor, but it has important health benefits, and also makes the rice a pleasant golden color)
- 1 tsp garlic powder
- 1 tsp yeast extract (this gently improves the savory flavor and also adds vitamin B12)
- Optional small quantity of green herbs for garnish. Cilantro is good (unless you have the soap gene); parsley never fails.
This is the ingredients list for a super-basic rice that will go with anything rice will go with; another day we can talk more extensive mixes of herbs and spice blends for different kinds of dishes (and different health benefits!), but for now, let’s get going!
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Wash the rice thoroughly. We recommend using a made-for-purpose rice-washing bowl (like this one, for example), but failing that, simply rinse it thoroughly with cold water using a bowl and a sieve. You will probably need to rinse it 4–5 times, but with practice, it will only take a few seconds per rinse, and the water will be coming up clear.
2) Warm the pan. It doesn’t matter for the moment whether you’re using an electronic rice cooker, a stovetop pressure cooker, electronic pressure cooker, or just a sturdy pan with a heavy lid available, aside from that if it’s something non-stovetop, you now want it to be on low to warm up already.
3) Separately in a saucepan, bring your stock to a simmer
4) Put the tbsp of olive oil into the pan (even if you’re confident the rice won’t stick; this isn’t entirely about that) and turn up the heat (if it’s a very simple rice cooker, most at least have a warm/cook differentiation; if so, turn it to “cook”). You don’t want the oil to get to the point of smoking, so, to test the temperature as it heats, flick a single drop of water from your fingertip (you did wash your hands first, right? We haven’t been including that step, but please do wash your hands before doing kitchen things) into the pan. If it sizzles, the pan is hot enough now for the next step.
5) Put the rice into the pan. That’s right, with no extra liquid yet; we’re going to toast it for a moment. Stir it a little, for no more than a minute; keep it moving; don’t let it burn! If you try this several times and fail, it could be that you need a better pan. Treat yourself to one when you get the opportunity; until then, skip the toasting part if necessary.
6) Add the chia seeds and spices, followed by the stock, followed by the yeast extract. Why did we do the stock before the yeast extract? It’s because hot liquid will get all the yeast extract off the teaspoon 🙂
7) Put the lid on/down (per what kind of pan or rice cooker you are using), and turn up the heat (if it is a variable heat source) until a tiny bit of steam starts making its way out. When it does, turn it down to a simmer, and let the rice cook. Don’t stir it, don’t jiggle it; trust the process. If you stir or jiggle it, the rice will cook unevenly and, paradoxically, probably stick.
8) Do keep an eye on it, because when steam stops coming out, it is done, and needs taking off the heat immediately. If using an automatic rice cooker, you can be less attentive if you like, because it will monitor this for you.
Note: if you are using a simple pan with a non-fastening lid (any other kind of rice cooking setup is better), more steam will escape than the other methods, and it’s possible that it might run out of steam (literally) before the rice is finished. If the steam stops and you find the rice isn’t done, add a splash of water as necessary (the rice doesn’t need to be submerged, it just needs to have liquid; the steam is part of the cooking process), and make a note of how much you had to add (so that next time you can just add it at the start), and put it back on the heat until it is done.
9) Having taken it off the heat, let it sit for 5 minutes (with the lid still on) before doing any fluffing-up. Then you can fluff-up and serve, adding the garnish if you want one.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Teenage Brain – by Dr. Frances Jensen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We realize that we probably have more grandparents of teenagers than parents of teenagers here, but most of us have at least some teenage relative(s). Which makes this book interesting.
There are a lot of myths about the teenage brain, and a lot of popular assumptions that usually have some basis in fact but are often misleading.
Dr. Jensen gives us a strong foundational grounding in the neurophysiology of adolescence, from the obvious-but-often-unclear (such as the role of hormones) to less-known things like the teenage brain’s general lack of myelination. Not just “heightened neuroplasticity” but, if you imagine the brain as an electrical machine, then think of myelin as the insulation between the wires. Little wonder some wires may get crossed sometimes!
She also talks about such things as the teenage circadian rhythm’s innate differences, the impact of success and failure on the brain, and harder topics such as addiction—and the adolescent cortisol functions that can lead to teenagers needing to seek something to relax in the first place.
In criticism, we can only say that sometimes the author makes sweeping generalizations without acknowledging such, but that doesn’t detract from what she has to say on the topic of neurophysiology.
Bottom line: if there’s a teenager in your life whose behavior and/or moods are sometimes baffling to you, and whose mysteries you’d like to unravel, this is a great book.
Click here to check out the Teenage Brain, and better understand those around you!
Share This Post
-
Getting antivirals for COVID too often depends on where you live and how wealthy you are
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Medical experts recommend antivirals for people aged 70 and older who get COVID, and for other groups at risk of severe illness and hospitalisation from COVID.
But many older Australians have missed out on antivirals after getting sick with COVID. It is yet another way the health system is failing the most vulnerable.
CGN089/Shutterstock Who missed out?
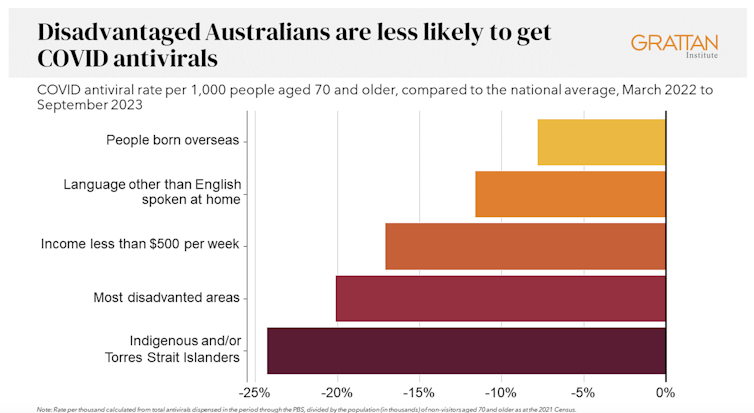
We analysed COVID antiviral uptake between March 2022 and September 2023. We found some groups were more likely to miss out on antivirals including Indigenous people, people from disadvantaged areas, and people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds.
Some of the differences will be due to different rates of infection. But across this 18-month period, many older Australians were infected at least once, and rates of infection were higher in some disadvantaged communities.
How stark are the differences?
Compared to the national average, Indigenous Australians were nearly 25% less likely to get antivirals, older people living in disadvantaged areas were 20% less likely to get them, and people with a culturally or linguistically diverse background were 13% less likely to get a script.
People in remote areas were 37% less likely to get antivirals than people living in major cities. People in outer regional areas were 25% less likely.
Dispensing rates by group. Grattan Institute Even within the same city, the differences are stark. In Sydney, people older than 70 in the affluent eastern suburbs (including Vaucluse, Point Piper and Bondi) were nearly twice as likely to have had an antiviral as those in Fairfield, in Sydney’s south-west.
Older people in leafy inner-eastern Melbourne (including Canterbury, Hawthorn and Kew) were 1.8 times more likely to have had an antiviral as those in Brimbank (which includes Sunshine) in the city’s west.
Why are people missing out?
COVID antivirals should be taken when symptoms first appear. While awareness of COVID antivirals is generally strong, people often don’t realise they would benefit from the medication. They wait until symptoms get worse and it is too late.
Frequent GP visits make a big difference. Our analysis found people 70 and older who see a GP more frequently were much more likely to be dispensed a COVID antiviral.
Regular visits give an opportunity for preventive care and patient education. For example, GPs can provide high-risk patients with “COVID treatment plans” as a reminder to get tested and seek treatment as soon as they are unwell.
Difficulty seeing a GP could help explain low antiviral use in rural areas. Compared to people in major cities, people in small rural towns have about 35% fewer GPs, see their GP about half as often, and are 30% more likely to report waiting too long for an appointment.
Just like for vaccination, a GP’s focus on antivirals probably matters, as does providing care that is accessible to people from different cultural backgrounds.
Care should go those who need it
Since the period we looked at, evidence has emerged that raises doubts about how effective antivirals are, particularly for people at lower risk of severe illness. That means getting vaccinated is more important than getting antivirals.
But all Australians who are eligible for antivirals should have the same chance of getting them.
These drugs have cost more than A$1.7 billion, with the vast majority of that money coming from the federal government. While dispensing rates have fallen, more than 30,000 packs of COVID antivirals were dispensed in August, costing about $35 million.
Such a huge investment shouldn’t be leaving so many people behind. Getting treatment shouldn’t depend on your income, cultural background or where you live. Instead, care should go to those who need it the most.
Getting antivirals shouldn’t depend on who your GP is. National Cancer Institute/Unsplash People born overseas have been 40% more likely to die from COVID than those born here. Indigenous Australians have been 60% more likely to die from COVID than non-Indigenous people. And the most disadvantaged people have been 2.8 times more likely to die from COVID than those in the wealthiest areas.
All those at-risk groups have been more likely to miss out on antivirals.
It’s not just a problem with antivirals. The same groups are also disproportionately missing out on COVID vaccination, compounding their risk of severe illness. The pattern is repeated for other important preventive health care, such as cancer screening.
A 3-step plan to meet patients’ needs
The federal government should do three things to close these gaps in preventive care.
First, the government should make Primary Health Networks (PHNs) responsible for reducing them. PHNs, the regional bodies responsible for improving primary care, should share data with GPs and step in to boost uptake in communities that are missing out.
Second, the government should extend its MyMedicare reforms. MyMedicare gives general practices flexible funding to care for patients who live in residential aged care or who visit hospital frequently. That approach should be expanded to all patients, with more funding for poorer and sicker patients. That will give GP clinics time to advise patients about preventive health, including COVID vaccines and antivirals, before they get sick.
Third, team-based pharmacist prescribing should be introduced. Then pharmacists could quickly dispense antivirals for patients if they have a prior agreement with the patient’s GP. It’s an approach that would also work for medications for chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease.
COVID antivirals, unlike vaccines, have been keeping up with new variants without the need for updates. If a new and more harmful variant emerges, or when a new pandemic hits, governments should have these systems in place to make sure everyone who needs treatment can get it fast.
In the meantime, fairer access to care will help close the big and persistent gaps in health between different groups of Australians.
Peter Breadon, Program Director, Health and Aged Care, Grattan Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Getting Things Done – by David Allen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our “to-do” lists are usually hopelessly tangled:
“To do thing x needs thing y doing first but that can only be done with information that I must get by doing thing z”, and so on.
Suddenly that two-minute task is looking like half an hour, which is making our overall to-do list look gargantuan. Tackling tiny parts of tasks seems useless; tackling large tasks seems overwhelming. What a headache!
Getting Things Done (“GTD”, to its friends) shows us how to gather all our to-dos, and then use the quickest ways to break down a task (in reality, often a mini-project) into its constituent parts and which things can be done next, and what order to do them in (or defer, or delegate, or ditch).
In a nutshell: The GTD system aims to make all your tasks comprehensible and manageable, for stress-free productivity. No need to strategize everything every time; you have a system now, and always know where to begin.
And by popular accounts, it delivers—many put this book in the “life-changing” category.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Xylitol vs Erythritol – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing xylitol to erythritol, we picked the xylitol.
Why?
They’re both sugar alcohols, which so far as the body is concerned are neither sugars nor alcohols in the way those words are commonly understood; it’s just a chemical term. The sugars aren’t processed as such by the body and are passed as dietary fiber, and nor is there any intoxicating effect as one might expect from an alcohol.
In terms of macronutrients, while technically they both have carbs, for all functional purposes they don’t and just have a little fiber.
In terms of micronutrients, they don’t have any.
The one thing that sets them apart is their respective safety profiles. Xylitol is prothrombotic and associated with major adverse cardiac events (CI=95, adjusted hazard ratio=1.57, range=1.12-2.21), while erythritol is also prothrombotic and more strongly associated with major adverse cardiac events (CI=95, adjusted hazard ratio=2.21, range=1.20-4.07).
So, xylitol is bad and erythritol is worse, which means the relatively “healthier” is xylitol. We don’t recommend either, though.
Studies for both:
- Xylitol is prothrombotic and associated with cardiovascular risk
- The artificial sweetener erythritol and cardiovascular event risk
Links for the specific products we compared, in case our assessment hasn’t put you off them:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- The WHO’s New View On Sugar-Free Sweeteners ← the WHO’s advice is “don’t”
- Stevia vs Acesulfame Potassium – Which is Healthier? ← stevia’s pretty much the healthiest artificial sweetener around, though, if you’re going to use one
- The Fascinating Truth About Aspartame, Cancer, & Neurotoxicity ← under the cold light of science, aspartame isn’t actually as bad as it was painted a few decades ago, mostly by a viral hoax letter. Per the WHO’s advice, it’s still good to avoid sweeteners in general, however.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Sugar The New Smoking?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Could you do a this or that of which. Is worse, smoking cigarettes or having a sweet tooth? Also, perhaps have us evaluate one part of newsletter at a time, rather than overall. I especially appreciate your book reviews and often find them through my library system.❞
We’re glad you enjoy the book reviews! We certainly enjoy reading many books to write about them for you.
As for the idea having readers evaluate one part of the newsletter at a time, rather than overall, there is a technical limitation that embedded polls are very large, data-wise, so if we were to do a poll for each section, the email would then get clipped by gmail and other email providers. However, you are always more than welcome to do as you’ve done, and include comments about what section(s) you took the most value from.
Now, onto your main question/request: as it doesn’t quite fit the usual format for our This vs That section, we’ve opted to do it as a main feature here 🙂
So, let’s get into it…
Not a zero-sum game
First, let’s be clear that for most people there is no pressing reason that this should be an either/or decision. There is nothing inherent to quitting either one that makes the other loom larger.
However, that said, if you’re (speaking generally here, and not making any presumptions about the asker) currently smoking regularly and partaking of a lot of added sugar, then you may be wondering which you should prioritize quitting first—as it is indeed generally recommended to only try to quit one thing at a time.
Indeed, we wrote previously, as a guideline for “what to do in one what order”:
Not sure where to start? We suggest this order of priorities, unless you have a major health condition that makes something else a higher priority:
- If you smoke, stop
- If you drink, reduce, or ideally stop
- Improve your diet
About that diet…
Worry less about what to exclude, and instead focus on adding more variety of fruit/veg.
See also: Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
That said, if you’re looking for things to cut, sugar is a top candidate (and red meat is in clear second place albeit some way below)
That’s truncated from a larger list, but those were the top items.
You can read the rest in full, here: The Best Few Interventions For The Best Health: These Top 5 Things Make The Biggest Difference
The flipside of this “you can quit both” reality is that the inverse is also true: much like how having one disease makes it more likely we will get another, unhealthy habits tend to come in clusters too, as each will weaken our resolve with regard to the others. Thus, there is a sort of “comorbidity of habits” that occurs.
The good news is: the same can be said for healthy habits, so they (just like unhealthy habits) can support each other, stack, and compound. This means that while it may seem harder to quit two bad habits than one, in actual fact, the more bad habits you quit, the more it’ll become easy to quit the others. And similarly, the more good habits you adopt, the more it’ll become easy to adopt others.
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
So, let’s keep that in mind, while we then look at the cases against smoking, and sugar:
The case against smoking
This is perhaps one of the easiest cases to make in the entirety of the health science world, and the only difficult part is knowing where to start, when there’s so much.
The World Health Organization leads with these key facts, on its tobacco fact sheet:
- Tobacco kills up to half of its users who don’t quit.
- Tobacco kills more than 8 million people each year, including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.
- Around 80% of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.
- In 2020, 22.3% of the world’s population used tobacco: 36.7% of men and 7.8% of women.
- To address the tobacco epidemic, WHO Member States adopted the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) in 2003. Currently 182 countries are Parties to this treaty.
- The WHO MPOWER measures are in line with the WHO FCTC and have been shown to save lives and reduce costs from averted healthcare expenditure.
Source: World Health Organization | Tobacco
Now, some of those are just interesting sociological considerations (well, they are of practical use to the WHO whose job it is to offer global health policy guidelines, but for us at 10almonds, with the more modest goal of helping individual people lead their best healthy lives, there’s not so much that we can do with the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control, for example), but for the individual smoker, the first two are really very serious, so let’s take a closer look:
❝Tobacco kills up to half of its users who don’t quit.❞
A bold claim, backed up by at least three very large, very compelling studies:
- Mortality in relation to smoking: 50 years’ observations on male British doctors
- Tobacco smoking and all-cause mortality in a large Australian cohort study: findings from a mature epidemic with current low smoking prevalence
- Global burden of disease due to smokeless tobacco consumption in adults: an updated analysis of data from 127 countries
❝Tobacco kills more than 8 million people each year, including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.❞
The WHO’s cited source for this was gatekept in a way we couldn’t access (and so probably most of our readers can’t either), but take a look at what the CDC has to say for the US alone (bearing in mind the US’s population of a little over 300,000,000, which is just 3.75% of the global population of a little over 8,000,000,000):
❝smoking causes more than 480,000 deaths [in the US] annually, with an estimated 41,000 deaths from secondhand smoke exposure, and it can reduce a person’s life expectancy by 10 years. Quitting smoking before the age of 40 reduces the risk of dying from smoking-related disease by about 90%❞
If we now remember that third bullet point, that said “Around 80% of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.”, then we can imagine the numbers are worse for many other countries, including large-population countries that have a lower median income than the US, such as India and Brazil.
Source for the CDC comment: Tobacco-Related Mortality
See also: AAMC | Smoking is still the leading cause of preventable death in the U.S.
We only have so much room here, but if that’s not enough…
More than 100 reasons to quit tobacco
The case against sugar
We reviewed an interesting book about this:
The Case Against Sugar – by Gary Taubes
But suffice it to say, added sugar is a big health problem; not in the same league as tobacco, but it’s big, because of how it messes with our metabolism (and when our metabolism goes wrong, everything else goes wrong):
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
The epidemiology of sugar consumption and related mortality is harder to give clear stats about than smoking, because there’s not a clear yes/no indicator, and cause and effect are harder to establish when the waters are so muddied by other factors. But for comparison, we’ll note that compared to the 480,000 deaths caused by tobacco in the US annually, the total death to diabetes (which is not necessarily “caused by sugar consumption”, but there’s at least an obvious link when it comes to type 2 diabetes and refined carbohydrates) was 101,209 deaths due to diabetes in 2022:
National Center for Health Statistics | Diabetes
Now, superficially, that looks like “ok, so smoking is just under 5x more deadly”, but it’s important to remember that almost everyone eats added sugar, whereas a minority of people smoke, and those are mortality per total US population figures, not mortality per user of the substance in question. So in fact, smoking is, proportionally to how many people smoke, many times more deadly than diabetes, which currently ranks 8th in the “top causes of death” list.
Note: we recognize that you did say “having a sweet tooth” rather than “consuming added sugar”, but it’s worth noting that artificial sweeteners are not a get-out-of-illness-free card either:
Let’s get back to sugar though, as while it’s a very different beast than tobacco, it is arguably addictive also, by multiple mechanisms of addiction:
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
That said, those mechanisms of addiction are not necessarily as strong as some others, so in the category of what’s easy or hard to quit, this is on the easier end of things—not that that means it’s easy, just, quitting many drugs is harder. In any case, it can be done:
When It’s More Than “Just” Cravings: Beat Food Addictions!
In summary
Neither are good for the health, but tobacco is orders of magnitude worse, and should be the priority to quit, unless your doctor(s) tell you otherwise because of your personal situation, and even then, try to get multiple opinions to be sure.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: