Clean – by Dr. James Hamblin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our skin is our largest organ, and it’s easy to forget that, and how much it does for us. All things considered, it’s good to take good care of it! But what if we sometimes take too much “care” of it?
Dr. James Hamblin, a medical doctor-turned-writer, has explored this a lot both personally and in research. Through such, he has come to the conclusion there’s definitely a “sweet spot” of personal hygiene:
- Too little, and the Bubonic plague sweeps through Europe, or other plagues sweep through other places when European invaders came.
- Too much, and we strip our skin of one of its greatest qualities: the ability to protect us.
Dr. Hamblin asks (and answers) such questions as:
- What is good hygiene, and what is neurotically doing ourselves multiple levels of harm because advertising companies shamed us into doing so?
- Is it good or bad to use a series of products, each to undo the problem caused by the previous?
- What the difference between a 5-step skincare routine, and a series of gratuitous iatrogenic damage?
- Which products clean us most helpfully, and which clean us most harmfully?
- How often should we bathe/shower, really?
If the book has a weak point, it’s that it’s written mostly with his body in mind. That makes a difference when it comes to hairwashing, for example. He’s a white guy with short hair. If you’re black and/or have long hair, for example, your haircare needs will be quite different. Similarly, many women engage in shaving/depilation in places that most men don’t, and the consequences of that choice (and implications for any extra washing needs/harms) aren’t covered.
Bottom line: notwithstanding the aforementioned blind-spots, this book will help readers reduce the amount of harm we are doing to our bodies with our washing routines, without sacrificing actual hygiene.
Click here to check out Clean and help your skin to help you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How I Cured My Silent Reflux – by Don Daniels
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Acid reflux, in its various forms (not all of which include heartburn as a symptom!), affects around 1 in 8 people. Often it takes the form of coughing or excess mucus after eating, and it can trigger ostensibly random sweats, for example.
Don Daniels does an excellent job of demystifying the various kinds of acid reflux, explaining clearly and simply the mechanics of what is going on for each of them and why.
Further, he talks about the medications that can make things worse (and how and why), and supplements that can make it better (and supplements that can make it worse, too!), and a multiphase plan (diet on, meds weaned off, supplements on, supplements weaned off when asymptomatic, diet adjust to a new normal) to get free from acid reflux.
The writing style is simple, clear, and jargon-free, while referencing plenty of scientific literature, often quoting from it and providing sources, much like we often do at 10almonds. There are 50+ such references in all, for a 105-page book.
So, do also note that yes, it’s quite a short book for the price, but the content is of value and wouldn’t have benefitted from padding of the kind that many authors do just to make the book longer.
Bottom line: if you have, or suspect you may have, an acid reflux condition of any kind, then this book can guide you through fixing that.
Click here to check out How I Cured My Silent Reflux, and put up with it no longer!
Share This Post
-
The Other Circadian Rhythms
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about how circadian rhythm pertains not just to when it is ideal for us to sleep or be awake, but also at what times it is best to eat, exercise, and so forth:
The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
Most people just know about the light consideration, per for example:
- How light can shift your mood and mental health, and
- How light tells you when to sleep, focus and poo
When your body parts clock on and off at the wrong time…
Now, new research has brought attention to how these things and more are governed by different physiological clocks within our bodies—and what this means for our health. In other words, if you are doing the various things at different times than you “should”, you will be training the different parts of your body (each with their independent clocks) to be on a different schedule, and so the different parts of your body will out of temporal sync with each other.
To put this in jet-lag terms: if your brain is in New York, while your heart is in Istanbul (not Constantinople) and your gut is in Tokyo, then this arrangement is not good for the health.
As for how it is not good for your health (i.e. the consequences) there’s still research to be done on some of the longer-term implications, but in the short term, one of the biggest effects is on our mood—most notably, increasing depression scores significantly.
And even more importantly, this is in the real world. That is to say, until quite recently, most data we had from studies on the circadian rhythm was from sleep clinic laboratories, which is great for RCTs but will always have as a limitation that someone sleeping in a lab is going to have some differences than someone sleeping in their own bed at home.
As the researchers said:
❝A critical step to addressing this is the noninvasive collection of physiological time-series data outside laboratory settings in large populations. Digital tools offer promise in this endeavor. Here, using wearable data, we first quantify the degrees of circadian disruption, both between different internal rhythms and between each internal rhythm and the sleep-wake cycle. Our analysis, based on over 50,000 days of data from over 800 first-year training physicians, reveals bidirectional links between digital markers of circadian disruption and mood both before and after they began shift work, while accounting for confounders such as demographic and geographic variables. We further validate this by finding clinically relevant changes in the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire score.❞
Read in full: The real-world association between digital markers of circadian disruption and mental health risks
That questionnaire by the way sounds like an arbitrary thing they just made up, but the PHQ-9 (as it is known to its friends) is in fact the current intentional gold standard for measuring depression; we share it at the top of our article about depression, here:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need ← the test takes 2 minutes and you get immediate results
Want to know more?
For more about getting one’s entire self back into temporal sync (hey, wasn’t that the plot of a Star Trek episode?), sleep specialist Dr. Michael Breus wrote this excellent book that we reviewed a little while back:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Insights into Osteoporosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I would like to see some articles on osteoporosis❞
You might enjoy this mythbusting main feature we did a few weeks ago!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Top Micronutrient Deficiency In High Blood Pressure
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
High blood pressure is often considered a matter of too much sodium, but there’s another micronutrient that’s critical, and a lot of people have too little of it:
The Other Special K
Potassium helps regulate blood pressure by doing the opposite of what sodium does: high sodium intake increases blood volume and pressure by retaining fluid, while potassium promotes sodium excretion through urine, reducing fluid retention and lowering blood pressure.
Clinical studies (which you can find beneath the video, if you click through to YouTube) have shown that increasing potassium intake can reduce systolic blood pressure by an average of 3.49 units, with even greater reductions (up to 7 units) at higher potassium intakes of 3,500–4,700 mg/day.
Potassium-rich foods include most fruit*, leafy greens, broccoli, lentils, and beans.
*because of some popular mentions in TV shows, people get hung up on bananas being a good source of potassium. Which they are, but they’re not even in the top 10 of fruits for potassium. Here’s a non-exhaustive list of fruits that have more potassium than bananas, portion for portion:
- Honeydew melon
- Papaya
- Mango
- Prunes
- Figs
- Dates
- Nectarine
- Cantaloupe melon
- Kiwi
- Orange
These foods also provide fiber, which aids in weight management and further lowers risks for cardiovascular disease. Increasing fiber intake by just 14g a day has been shown not only to reduce calorie consumption and promote weight loss, but also (more importantly) lower blood pressure, cholesterol, and overall health risks.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure ← this is about fiber; while potassium is the most common micronutrient deficiency in people with high blood pressure, fiber is the most common macronutrient deficiency, and arguably the most critical in this regard.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eggs: Nutritional Powerhouse or Heart-Health Timebomb?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
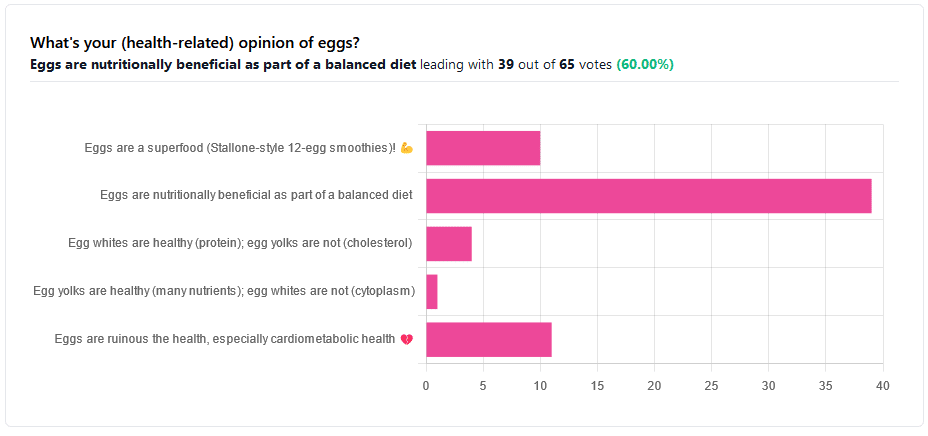
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on eggs. We specified that, for the sake of simplicity, let’s say that they are from happy healthy backyard hens who enjoy a good diet.
Apparently this one wasn’t as controversial as it might have been! We (for myth-busting purposes) try to pick something polarizing and sometimes even contentious for our Friday editions, and pick apart what science lies underneath public perceptions.
However, more than half (in fact, 60%) of the subscribers who voted in the poll voted for “Eggs are nutritionally beneficial as part of a balanced diet”, which very moderate statement is indeed pretty much the global scientific consensus.
Still, we’ve a main feature to write, so let’s look at the science, and what the other 40% had in mind:
Eggs are ruinous to health, especially cardiometabolic health: True or False?
False, per best current science, anyway!
Scientific consensus has changed over the years. We learned about cholesterol, then we learned about different types of cholesterol, and now we’ve even learned about in some instances even elevated levels of “bad” cholesterol aren’t necessarily a cause of cardiometabolic disorders so much as a symptom—especially in women.
Not to derail this main feature about eggs (rather than just cholesterol), but for those who missed it, this is actually really interesting: basically, research (pertaining to the use of statins) has found that in women, higher LDL levels aren’t anywhere near the same kind of risk factor as they are for men, and thus may mean that statins (whose main job is reducing LDL) may be much less helpful for women than for men, and more likely to cause unwanted serious side effects in women.
Check out our previous main feature about this: Statins: His & Hers?
But, for back on topic, several large studies (totalling 177,000 people in long-term studies in 50 countries) found:
❝Results from the three cohorts and from the updated meta-analysis show that moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) is not associated with cardiovascular disease risk overall, and is associated with potentially lower cardiovascular disease risk in Asian populations.❞
Egg whites are healthy (protein); egg yolks are not (cholesterol): True or False?
True and False, respectively. That is to say, egg whites are healthy (protein), and egg yolks are also healthy (many nutrients).
We talked a bit already about cholesterol, so we’ll not rehash that here. As to the rest:
Eggs are one of the most nutritionally dense foods around. After all, they have everything required to allow a cluster of cells to become a whole baby chick. That’s a lot of body-building!
They’re even more nutritionally heavy-hitters if you get omega-3 enriched eggs, which means the hens were fed extra omega-3, usually in the form of flax seeds.
Also, free-range is better healthwise than others. Do bear in mind that unless they really are from your backyard, or a neighbor’s, chances are that the reality is not what the advertising depicts, though. There are industry minimum standards to be able to advertise as “free-range”, and those standards are a) quite low b) often ignored, because an occasional fine is cheaper than maintaining good conditions.
So if you can look after your own hens, or get them from somewhere that you can see for yourself how they are looked after, so much the better!
Check out the differences side-by-side, though:
Pastured vs Omega-3 vs “Conventional” Eggs: What’s the Difference?
Stallone-style 12-egg smoothies are healthy: True or False?
False, at least if taken with any regularity. One can indeed have too much of a good thing.
So, what’s the “right amount” to eat?
It may vary depending on individual factors (including age and ethnicity), but a good average, according to science, is to keep it to 3 eggs or fewer per day. There are a lot of studies, but we only have so much room here, so we’ll pick one. Its findings are representative of (and in keeping with) the many other studies we looked at, so this seems uncontroversial scientifically:
❝Intake of 1 egg/d was sufficient to increase HDL function and large-LDL particle concentration; however, intake of 2-3 eggs/d supported greater improvements in HDL function as well as increased plasma carotenoids. Overall, intake of ≤3 eggs/d favored a less atherogenic LDL particle profile, improved HDL function, and increased plasma antioxidants in young, healthy adults.❞
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Be 7.5x More Likely To Develop Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what is it?
Many more people have chronic fatigue, which is the symptom of being exhausted all the time, than have chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) which is the illness of myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME).
This is because fatigue can be a symptom of many, many other conditions, and can be heavily influenced by lifestyle factors too.
A lot of the advice for dealing with chronic fatigue is often the same in both cases, but some will be different, because for example:
- If your fatigue is from some other condition, that condition probably impacts what lifestyle factors you are (and are not) able to change, too
- If your fatigue is from lifestyle factors, that hopefully means you can change those and enjoy less fatigue…
- But if it’s not from lifestyle factors, as in ME/CFS, then advice to “exercise more” etc is not going to help so much.
There are ways to know the difference though:
Check out: Do You Have Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
The chronic disease pipeline
While it had been strongly suspected that COVID infection could lead to CFS, with long COVID having chronic fatigue as one of its characteristic symptoms, a research team led by Dr. Suzanne Vernon has now established the nature of the relationship.
It was a large (n=13,224) longitudinal observational cohort study of people with no pre-existing ME/CFS, grouped according to their COVID infection status:
- acute infected, enrolled within 30 days of infection or enrolled as uninfected who became infected (n=4,515)
- post-acute infected, enrolled greater than 30 days after infection (n=7,270)
- uninfected (n=1,439).
(to be clear, that last means “never infected”, or else they would be in group 2)
Note: people who had COVID and were hospitalized for it were excluded from the study, so this risk is the risk represented by even just more “moderate” infections.
What they found:
❝The proportion of all RECOVER-Adult participants that met criteria for ME/CFS following SARS-CoV-2 infection was 4.5% (531 of 11,785) compared to 0.6% (9 of 1439) in uninfected participants.❞
There are then different numbers if we look per 100 person-years, as the study also did—in which case, we get a re-modelled increase in risk of 5x instead of 7.5x, but a) that’s still not good b) the “here-and-now” figures of 4.5% vs 0.6% are also relevant.
Read in full: Incidence and Prevalence of Post-COVID-19 Myalgic Encephalomyelitis: A Report from the Observational RECOVER-Adult Study
The killer nobody wants to talk about anymore
Of course, as we all know the pandemic is over, because politicians declared it so, which is very reassuring.
Nevertheless, COVID is currently the still 4th leading cause of death in the US, placing it higher than stroke, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and others.
See also: Emergency or Not, Covid Is Still Killing People. Here’s What Doctors Advise to Stay Safe
So, while it’s very good to take care of our hearts, brains, blood sugars, and so forth, let’s at the very least continue to keep on top of our vaccinations, avoid enclosed crowded spaces where possible, etc.
And for extra boosts to one’s chances: Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
What if I do get (or already have) long COVID and/or ME/CFS?
Well, that is definitely going to suck, but there are still some things that can be done.
Here’s a big one: How To Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue ← this will not, of course, cure you, but it’s a way of getting maximum nutrition for minimum effort, given that for someone with chronic fatigue, effort is a very finite resource that must be used sparingly
Finally, here are some further resources:
Support For Long COVID & Chronic Fatigue
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: