The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
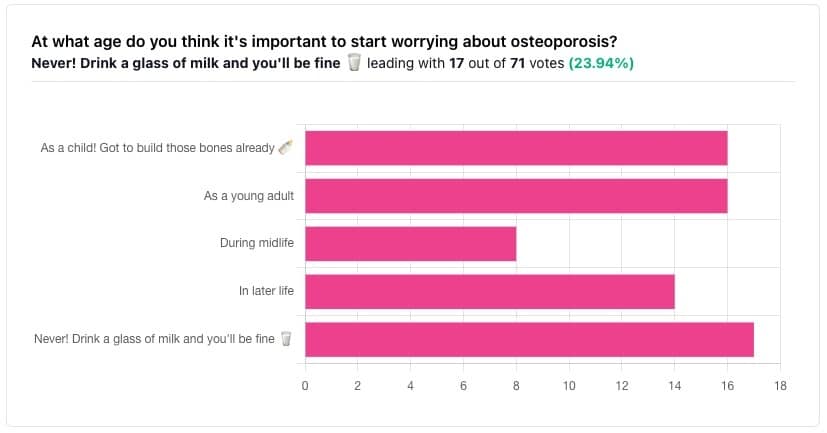
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
The Bare-bones Truth About Osteoporosis
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
At first glance it may seem shocking that a majority of respondents to a poll in a health-focused newsletter think it’ll never be an issue worth worrying about, but in fact this is partly a statistical quirk, because the vote of the strongest “early prevention” crowd was divided between “as a child” and “as a young adult”.
This poll also gave you the option to add a comment with your vote. Many subscribers chose to do so, explaining your choices… But, interestingly, not one single person who voted for “never” had any additional thoughts to add.
We loved reading your replies, by the way, and wish we had room to include them here, because they were very interesting and thought-provoking.
Let’s get to the myths and facts:
Top myth: “you will never need to worry about it; drink a glass of milk and you’ll be fine!”
The body is constantly repairing itself. Its ability to do that declines with age. Until about 35 on average, we can replace bone mineral as quickly as it is lost. After that, we lose it by up to 1% per year, and that rate climbs after 50, and climbs even more steeply for those who go through (untreated) menopause.
Losing 1% per year might not seem like a lot, but if you want to live to 100, there are some unfortunate implications!
About that menopause, by the way… Because declining estrogen levels late in life contribute significantly to osteoporosis, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be of value to many for the sake of bone health, never mind the more obvious and commonly-sought benefits.
On the topic of that glass of milk…
- Milk is a great source of calcium, which is useless to the body if you don’t also have good levels of vitamin D and magnesium.
- People’s vitamin D levels tend to directly correlate to the level of sun where they live, if supplementation isn’t undertaken.
- Plant-based milks are usually fortified with vitamin D (and calcium), by the way.
- Most people are deficient in magnesium, because green leafy things don’t form as big a part of most people’s diets as they should.
See also: An update on magnesium and bone health
Next most common myth: “bone health is all about calcium”
We spoke a little above about the importance of vitamin D and magnesium for being able to properly use that. But potassium is also critical:
Read more: The effects of potassium on bone health
While we’re on the topic…
People think of collagen as being for skin health. And it is important for that, but collagen’s benefits (and the negative effects of its absence) go much deeper, to include bone health. We’ve written about this before, so rather than take more space today, we’ll just drop the link:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Want to really maximize your bone health?
You might want to check out this well-sourced LiveStrong article:
Bone Health: Best and Worst Foods
(Teaser: leafy greens are in 2nd place, topped by sardines at #1—where do you think milk ranks?)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to pecans, we picked the pistachios.
Why?
Firstly, the macronutrients: pistachios have twice as much protein and fiber. Pecans have more fat, though in both of these nuts the fats are healthy.
The category of vitamins is an easy win for pistachios, with a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, and E. Especially the 8x vitamin A, 7x vitamin B6, 4x vitamin C, and 2x vitamin E, and as the percentages are good too, these aren’t small differences. Pecans, meanwhile, boast only a little more vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid, the one whose name means “it’s everywhere”, because that’s how easy it is to get it).
In terms of minerals, pistachios have more calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while pecans have more manganese and zinc. So, a fair win for pistachios on this one.
Adding up the three different kinds of win for pistachios means that *drumroll* pistachios win overall, and it’s not close.
As ever, do enjoy both though, because diversity is healthy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Grain Brain – by Dr. David Perlmutter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re a regular 10almonds reader, you probably know that refined flour, and processed food in general, is not great for the health. So, what does this book offer more?
Dr. Perlmutter sets out the case against (as the subtitle suggests) wheat, carbs, and sugar. Yes, including wholegrain wheat, and including starchy vegetables such as potatoes and parsnips. Fruit does also come under scrutiny, a clear distinction is made between whole fruits and juices. In the latter case, the lack of fiber (along with the more readily absorbable liquid state) allows for those sugars to zip straight into our blood.
The book includes lots of stats and facts, and many study citations, along with infographics and clear explanations.
If the book has a weakness, it’s when it forgets to clarify something that was obvious to the author. For example, when he talks about our ancestors’ diets being 75% fat and 5% carbs, he neglects to mention that this is 75% by calorie count, not by mass or volume. This makes a huge difference! It’s the difference between a fat-guzzling engine, and someone who eats mostly fruit and oily nuts but also some very high-fat meat/organs.
The book’s strengths, on the other hand, are found in its explanation, backed by good science, of what wheat, along with excessive carbohydrates (especially sugar) can do to our body, including (and most focusedly, hence the title) our brain, leading the way to not just obvious metabolic disorders like diabetes, but also inflammatory diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Bottom line: you don’t have to completely revamp your diet if it’s working for you, but data is data, and this book has lots, making it well-worth a read.
Click here to check out Grain Brain, and learn about how to avoid inflaming yours!
Share This Post
-
Avocado, Coconut & Lime Crumble Pots
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one’s a refreshing snack or dessert, whose ingredients come together to make a very good essential fatty acid supplement. Coconut is a good source of MCTs, avocados are rich in omega 3, 6, and 9, while chia seeds are a great ALA omega 3 food, topping up the healthy balance.
You will need
- flesh of 2 large ripe avocados
- grated zest and juice of 2 limes
- 3 tbsp coconut oil
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 2 tsp honey (omit if you prefer a less sweet dish)
- 1 tsp desiccated coconut
- 4 low-sugar oat biscuits
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the avocado, lime juice, coconut oil, honey, and half the desiccated coconut, in a food processor.
2) Scoop the mixture into 4 ramekins (or equivalent-sized glasses), making sure to leave a ½” gap at the top. Refrigerate for at least 2–4 hours (longer is fine if you’re not ready to serve yet).
3) Assemble, by crumbling the oat biscuits and sprinkling on top of each serving, along with the other half of the desiccated coconut, the lime zest, and the chia seeds.
4) Serve immediately:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Blue Zones, Second Edition – by Dan Buettner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat beans & greens, take walks, have a purpose; you can probably list off the top of your head some of the “advices from Blue Zones”, so what makes this book stand out?
This is perhaps one of the most thoughtful investigations; the author (a National Geographic researcher) toured and researched all the Blue Zones, took many many notes (we get details), and asked a lot of questions that others skipped.
For example, a lot of books about the Blue Zones mention the importance of community—but they don’t go into much detail of what that looks like… And they certainly don’t tend to explain what we should do about it.
And that’s because community is often viewed as environmental in a way that we can’t control. If we want to take supplements, eat a certain way, exercise, etc, we can do all those things alone if we want. But if we want community? We’re reliant on other people—and that’s a taboo in the US, and US-influenced places.
So, one way this book excels is in describing how exactly people foster community in the Blue Zones (hint: the big picture—the form of the community—is different in each place, but the individual actions taken are similar), with particular attention to the roles actively taken on by the community elders.
In a similar vein, “reduce stress” is good, but what mindsets and mechanisms do they use that are still reproducible if we are not, for example, Okinawan farmers? Again, Buettner delivers in spades.
Bottom line: this is the Blue Zones book that digs deeper than others, and makes the advices much more applicable no matter where we live.
Click here to check out The Blue Zones, and build these 9 things into your life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Basil vs Oregano – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing basil to oregano, we picked the basil.
Why?
You may be thinking: these are just herbs; we don’t eat enough of these for the nutritional values to be relevant!
And to this we say: there’s nothing stopping you :p Herbs are full of flavor and goodness and there is really no reason to deny yourself. On this note, check out the sabzi khordan (traditional Levantine herb platter), linked below. You’ll start thinking about herbs in new ways, and you can thank us later!
Now, in terms of macros, nominally basil has more protein and oregano has more carbs and fiber, but the numbers are so close in each case that we’re going to call this category a tie.
When it comes to vitamins, things get more interesting: basil has more of vitamins B2, B3, B6, B9, K, and choline, while oregano has more of vitamins A, B1, B5, C, and E. This means a 6:5 win for basil, but note how the two herbs together give an impressive vitamin coverage. In other words, they complement each other nutritionally, not just culinarily!
In the category of minerals, basil has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium and zinc, while oregano has more selenium. Now, this is obviously a clear win for basil, but we’d like to highlight that both of these herbs are incredibly rich in minerals (i.e. oregano is a very good source of all those minerals we listed for basil, too!); it’s just that basil has even more of most of them.
When looking at any nutrient-dense food (which most herbs are), it’s worth looking at polyphenols. In this case, both are very abundant in polyphenols, and/but their respective numbers are close enough to be within each other’s margin of variation (i.e. exact numbers will depend on the individual plant’s life history), so this category is a tie.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall clear win for basil, but absolutely please do enjoy both unless you have a good reason not to—they complement each other so well, in nutrients as well as in flavor!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Cilantro vs Parsley – Which is Healthier?
- Holy Basil: What Does (And Doesn’t) It Do?
- Invigorating Sabzi Khordan (A Traditional Levantine Platter Of Herbs & Accompaniments)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Immunostimulant Superfood
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat These Greens!
Chlorella vulgaris, henceforth “chlorella”, is a simple green algae that has a lot of health benefits.
Note: most of the studies here are for Chlorella vulgaris specifically. However, some are for other species of the Chlorella genus, of which Chlorella vulgaris is by far the most common, hence the name (vulgaris = common). The relevant phytochemical properties appear to be the same regardless.
Superfood
While people generally take it as a supplement rather than a food item in any kind of bulk, it is more than 50% protein and contains all 9 essential amino acids.
As you might expect of a green superfood, it’s also full of many antioxidants, most of them carotenoids, and these pack a punch, for example against cancer:
It also has a lot of vitamins and minerals, and even omega-3.
Which latter also means it helps improve lipids and is thus particularly…
Heart healthy
❝Daily consumption of Chlorella supplements provided the potential of health benefits reducing serum lipid risk factors, mainly triglycerides and total cholesterol❞
Its heart-healthy benefits don’t stop at lipids though, and include blood pressure management, as in this study that found…
❝GABA-rich Chlorella significantly decreased high-normal blood pressure and borderline hypertension, and is a beneficial dietary supplement for prevention of the development of hypertension. ❞
About that GABA, if you’re curious about that, check out:
GABA Against Stress, Anxiety, & More
May remove heavy metals
We’re going with “may” for this one as we could only find animal studies so far (probably because most humans don’t have megadoses of heavy metals in them, which makes testing harder).
Here’s an example animal study, though:
Enhanced elimination of tissue methyl mercury in [Chlorella]-fed mice
Immunostimulant
This one’s clearer, for example in this 8-week study (with humans) that found…
❝Serum concentrations of interferon-γ (p<0.05) and interleukin-1β (p<0.001) significantly increased and that of interleukin-12 (p<0.1) tended to increase in the Chlorella group.
The increments of these cytokines after the intervention were significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than those in the placebo group. In addition, NK cell activities (%) were significantly increased in Chlorella group, but not in Placebo group.
The increments of NK cell activities (%) were also significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than the placebo group.
Additionally, changed levels of NK cell activity were positively correlated with those of serum interleukin-1β (r=0.280, p=0.047) and interferon-γ (r=0.271, p<0.005).❞
tl;dr = it boosts numerous different kinds of immune cells
PS, if you click though to the study, you may be momentarily alarmed by the first paragraph of the abstract that says “However, there were no direct evidences for the effect of Chlorella supplementation on immune/inflammation response in healthy humans“
this is from the “Background” section of the abstract, so what they are saying is “before we did this study, nobody had done this yet”.
So, be assured that the results are worthwhile and compelling.
Is it safe?
Based on the studies, it has a good safety profile. However, as it boosts the immune system, you may want to check with your doctor if you have an autoimmune disorder, and/or you are on immunosuppressants.
And in general, of course always check with your doctor/pharmacist if unsure about any potential drug interactions.
Want some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: