The Sleep Solution – by Dr. Chris Winter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book’s blurb contains a bold claim:
❝If you want to fix your sleep problems, Internet tips and tricks aren’t going to do it for you. You need to really understand what’s going on with your sleep—both what your problems are and how to solve them.❞
So, how well does it deliver, on the strength of being a whole book rather than an Internet article?
Well, for sure we wouldn’t have the room to include all the information that Dr. Winter does, in one of our main feature articles here (we’d need to spread it out over several weeks, at least).
He examines very thoroughly what is going on with sleep, sleep disturbance, and sleep deprivation. What’s going on with the different phases of sleep (far more than your phone’s sleep app will), and how imbalances in these can cause problems.
While the usual sleep hygiene tips do get a mention, he broadly assumes we know that part already. Instead, he focuses on aligning as many components as possible of our rich and interesting circadian rhythm. Yes, even if that means clawing our way out of insomnia and/or a bad sleep schedule (or lack of coherent sleep schedule) first. He gives plenty of practical advice on how to do that.
Bottom line: if you’d like to more deeply understand sleep, what is or isn’t wrong with yours, and how you can fix it, this book is a great resource.
Click here to check out The Sleep Solution, and enjoy the benefits of better rest!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

The Five Key Traits Of Healthy Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Five Keys Of Aging Healthily

Image courtesy of Peter Prato. This is Dr. Daniel Levitin. He’s a neuroscientist, and his research focuses on aging, the brain, health, productivity, and creativity. Also music, and he himself is an accomplished musician also, but we’re not going to be focusing on that today.
We’re going to be looking at the traits that, according to science, promote healthy longevity in old age. In other words, the things that increase our healthspan, from the perspective of a cognitive scientist.
What does he say we should do?
Dr. Levitin offers us what he calls the “COACH” traits:
- Curiosity
- Openness
- Associations
- Conscientiousness
- Healthy practices
By “associations”, he means relationships. However, that would have made the acronym “CORCH”, and decisions had to be made.
Curiosity
Leonardo da Vinci had a list of seven traits he considered most important.
We’ll not go into those today (he is not our featured expert of the day!), but we will say that he agreed with Dr. Levitin on what goes at the top of the list: curiosity.
- Without curiosity, we will tend not to learn things, and learning things is key to keeping good cognitive function in old age
- Without curiosity, we will tend not to form hypotheses about how/why things are the way they are, so we will not exercise imagination, creativity, problem-solving, and other key functions of our brain
- Without curiosity, we will tend not to seek out new experiences, and consequently, our stimuli will be limited—and thus, so will our brains
Openness
Being curious about taking up ballroom dancing will do little for you, if you are not also open to actually trying it. But, openness is not just a tag-on to curiosity; it deserves its spot in its own right too.
Sometimes, ideas and opportunities come to us unbidden, and we have to be able to be open to those too. This doesn’t mean being naïve, but it does mean having at least a position of open-minded skepticism.
Basically, Dr. Levitin is asking us to be the opposite of the pejorative stereotype of “an old person stuck in their ways”.
Associations
People are complex, and so they bring complexities to our lives. Hopefully, positively stimulating ones. Without them to challenge us (again, hopefully in a positive way), we can get very stuck in a narrow field of experience.
And of course, having at least a few good friends has numerous benefits to health. There’s been a lot of research on this; 5 appears to be optimal.
- More than that, and the depth tends to tail off, and/or stresses ensue from juggling too many relationships
- Fewer than that, and we might be only a calendar clash away from loneliness
Friends provide social stimulation and mutual support; they’re good for our mental health and even our physiological immunity (counterintuitively, by means of shared germs).
And, a strong secure romantic relationship is something that has been found time and again to extend healthy life.
Note: by popular statistics, this benefit is conferred upon men partnered with women, men partnered with men, women partnered with women, but not women partnered with men.
There may be a causative factor that’s beyond the scope of this article which is about cognitive science, not feminism, but there could also be a mathematical explanation for this apparent odd-one-out:
Since women tend to live longer than men (who are also often older than their female partners), women who live the longest are often not in a relationship—precisely because they are widows. So these long-lived widows will tend to skew the stats, through no fault of their husbands.
On the flipside of this, for a woman to predecease her (statistically older and shorter-lived) husband will often require that she die quite early (perhaps due to accident or illness unrelated to age), which will again skew the stats to “women married to men die younger”, without anything nefarious going on.
Conscientiousness
People who score highly in the character trait “conscientiousness” will tend to live longer. The impact is so great, that a child’s scores will tend to dictate who dies in their 60s or their 80s, for example.
What does conscientiousness mean? It’s a broad character trait that’s scored in psychometric tests, so it can be things that have a direct impact on health, such as brushing one’s teeth, or things that are merely correlated, such as checking one’s work for typos (this writer does her best!).
In short, if you are the sort of person who attends to the paperwork for your taxes on time, you are probably also the sort of person who remembers to get your flu vaccination and cancer screening.
Healthy practices
This means “the usual things”, such as:
- Healthy diet (Mediterranean Diet consistently scores up top)
- Good exercise (especially the tendency to keep moving in general)
- Good sleep (7–9 hours, no compromises)
- Not drinking (or at least only very moderate consumption, but the only safe amount is zero)
- Not smoking (just don’t; there is no wiggle room on this one)
Want to learn more?
You can check out his book, which we reviewed all so recently, and you can also enjoy this video, in which he talks about matters concerning healthy aging from a neuroscientist’s perspective, ranging from heart health and neurodegeneration, to the myth of failing memory, to music and lifespan and more:
Share This Post

Can I Eat That? – by Jenefer Roberts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The answer to the question in the title is: you can eat pretty much anything, if you’re prepared for the consequences!
This book looks to give you the information to make your own decisions in that regard. There’s a large section on the science of glucose metabolism in the context of food (other aspects of glucose metabolism aren’t covered), so you will not simply be told “raw carrots are good; mashed potatoes are bad”, you’ll understand many factors that affect it, e.g:
- Macronutrient profiles of food and resultant base glycemic indices
- How the glycemic index changes if you cut something, crush it, mash it, juice it, etc
- How the glycemic index changes if you chill something, heat it, fry it, boil it, etc
- The many “this food works differently in the presence of this other food” factors
- How your relative level of insulin resistance affects things itself
…and much more.
The style is simple and explanatory, without deep science, but with good science and comprehensive advice.
There are also the promised recipes; they’re in an appendix at the back and aren’t the main meat of the book, though.
Bottom line: if you’ve ever found it confusing working out what works how in the mysterious world of diabetes nutrition, this book is a top tier demystifier.
Click here to check out Can I Eat That?, and gain confidence in your food choices!
Share This Post

Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does This Practice Really Hold A Candle To Evidence-Based Medicine?

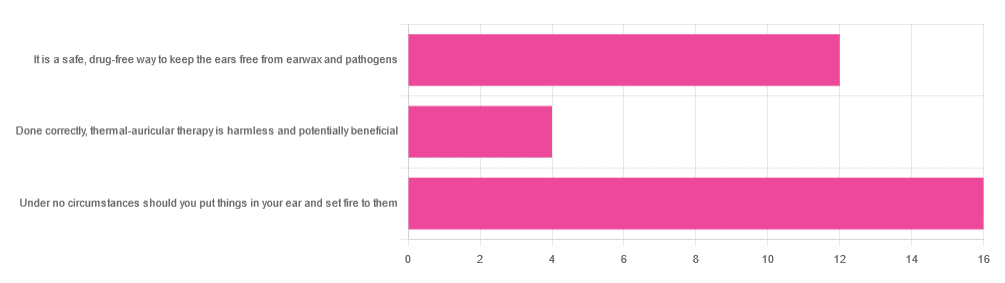
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion of ear candling, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- Exactly 50% said “Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them”
- About 38% said “It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens”
- About 13% said “Done correctly, thermal-auricular therapy is harmless and potentially beneficial”
This means that if we add the two positive-to-candling answers together, it’s a perfect 50:50 split between “do it” and “don’t do it”.
(Yes, 38%+13%=51%, but that’s because we round to the nearest integer in these reports, and more precisely it was 37.5% and 12.5%)
So, with the vote split, what does the science say?
First, a quick bit of background: nobody seems keen to admit to having invented this. One of the major manufacturers of ear candles refers to them as “Hopi” candles, which the actual Hopi tribe has spent a long time asking them not to do, as it is not and never has been used by the Hopi people. Other proposed origins offered by advocates of ear candling include Traditional Chinese Medicine (not used), Ancient Egypt (no evidence of such whatsoever), and Atlantis:
Quackwatch | Why Ear Candling Is Not A Good Idea
It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens: True or False?
False! In a lot of cases of alternative therapy claims, there’s an absence of evidence that doesn’t necessarily disprove the treatment. In this case, however, it’s not even an open matter; its claims have been actively disproven by experimentation:
- It doesn’t remove earwax; on the contrary, experimentation “showed no removal of cerumen from the external auditory canal. Candle wax was actually deposited in some“
- It doesn’t remove pathogens, and the proposed mechanism of action for removing pathogens, that of the “chimney effect”: the idea that the burning candle creates a vacuum that draws wax out of the ear along with debris and bacteria, simply does not work; on the contrary, “Tympanometric measurements in an ear canal model demonstrated that ear candles do not produce negative pressure”.
- It isn’t safe; on the contrary, “Ear candles have no benefit in the management of cerumen and may result in serious injury”
In a medium-sized survey (n=122), the following injuries were reported:
- 13 x burns
- 7 x occlusion of the ear canal
- 6 x temporary hearing loss
- 3 x otitis externa (this also called “swimmer’s ear”, and is an inflammation of the ear, accompanied by pain and swelling)
- 1 x tympanic membrane perforation
Indeed, authors of one paper concluded:
❝Ear candling appears to be popular and is heavily advertised with claims that could seem scientific to lay people. However, its claimed mechanism of action has not been verified, no positive clinical effect has been reliably recorded, and it is associated with considerable risk.
No evidence suggests that ear candling is an effective treatment for any condition. On this basis, we believe it can do more harm than good and we recommend that GPs discourage its use❞
Source: Canadian Family Physician | Ear Candling
Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them: True or False?
True! It’s generally considered good advice to not put objects in general in your ears.
Inserting flaming objects is a definite no-no. Please leave that for the Cirque du Soleil.
You may be thinking, “but I have done this and suffered no ill effects”, which seems reasonable, but is an example of survivorship bias in action—it doesn’t make the thing in question any safer, it just means you were one of the one of the ones who got away unscathed.
If you’re wondering what to do instead… Ear oils can help with the removal of earwax (if you don’t want to go get it sucked out at a clinic—the industry standard is to use a suction device, which actually does what ear candles claim to do). For information on safely getting rid of earwax, see our previous article:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts

The Easiest Way To Take Up Journaling
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dear Diary…
It’s well-established that journaling is generally good for mental health. It’s not a magical panacea, as evidenced by The Diaries of Franz Kafka for example (that man was not in good mental health). But for most of us, putting our thoughts and feelings down on paper (or the digital equivalent) is a good step for tidying our mind.
And as it can be said: mental health is also just health.
But…
What to write about?
It’s about self-expression (even if only you will read it), and…
❝Writing about traumatic, stressful or emotional events has been found to result in improvements in both physical and psychological health, in non-clinical and clinical populations.
In the expressive writing paradigm, participants are asked to write about such events for 15–20 minutes on 3–5 occasions.
Those who do so generally have significantly better physical and psychological outcomes compared with those who write about neutral topics.❞
Source: Emotional and physical health benefits of expressive writing
In other words, write about whatever moves you.
Working from prompts
If you read the advice above and thought “but I don’t know what moves me”, then fear not. It’s perfectly respectable to work from prompts, such as:
- What last made you cry?
- What last made you laugh?
- What was a recent meaningful moment with family?
- What is a serious mistake that you made and learned from?
- If you could be remembered for just one thing, what would you want it to be?
In fact, sometimes working from prompts has extra benefits, precisely because it challenges us to examine things we might not otherwise think about.
If a prompt asks “What tends to bring you most joy recently?” and the question stumps you, then a) you now are prompted to look at what you can change to find more joy b) you probably wouldn’t have thought of this question—most depressed people don’t, and if you cannot remember recent joy, then well, we’re not here to diagnose, but let’s just say that’s a symptom.
A quick aside: if you or a loved oneare prone to depressive episodes, here’s a good resource, by the way:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
And in the event of the mental health worst case scenario:
The six prompts we gave earlier are just ideas that came to this writer’s mind, but they’re (ok, some bias here) very good ones. If you’d like more though, here’s a good resource:
550+ Journal Prompts: The Ultimate List
The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly
While it’s not good to get stuck in ruminative negative thought spirals, it is good to have a safe outlet to express one’s negative thoughts/feelings:
Remember, your journal is (or ideally, should be) a place without censure. If you fear social consequences should your journal be read, then using an app with a good security policy and encryption options can be a good idea for journaling
Finch App is a good free option if it’s not too cutesy for your taste, because in terms of security:
- It can’t leak your data because your data never leaves your phone (unless you manually back up your data and then you choose to put it somewhere unsafe)
- It has an option to require passcode/biometrics etc to open the app
As a bonus, it also has very many optional journaling prompts, and also (optional) behavioral activation prompts, amongst more other offerings that we don’t have room to list here.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Who you are and where you live shouldn’t determine your ability to survive cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Canada, nearly everyone has a cancer story to share. It affects one in every two people, and despite improvements in cancer survivorship, one out of every four people affected by cancer still will die from it.
As a scientist dedicated to cancer care, I work directly with patients to reimagine a system that was never designed for them in the first place – a system in which your quality of care depends on social drivers like your appearance, your bank statements and your postal code.
We know that poverty, poor nutrition, housing instability and limited access to education and employment can contribute to both the development and progression of cancer. Quality nutrition and regular exercise reduce cancer risk but are contingent on affordable food options and the ability to stay active in safe, walkable neighbourhoods. Environmental hazards like air pollution and toxic waste elevate the risk of specific cancers, but are contingent on the built environment, laws safeguarding workers and the availability of affordable housing.
On a health-system level, we face implicit biases among care providers, a lack of health workforce competence in addressing the social determinants of health, and services that do not cater to the needs of marginalized individuals.
Indigenous peoples, racialized communities, those with low income and gender diverse individuals face the most discrimination in health care, resulting in inadequate experiences, missed diagnosis and avoidance of care. One patient living in subsidized housing told me, “You get treated like a piece of garbage – you come out and feel twice as bad.”
As Canadians, we benefit from a taxpayer funded health-care system that encompasses cancer care services. The average Canadian enjoys a life expectancy of more than 80 years and Canada boasts high cancer survival rates. While we have made incredible strides in cancer care, we must work together to ensure these benefits are equally shared amongst all people in Canada. We need to redesign systems of care so that they are:
- Anti-oppressive. We must begin by understanding and responding to historical and systemic racism that shapes cancer risk, access to care and quality of life for individuals facing marginalizing conditions. Without tackling the root causes, we will never be able to fully close the cancer care gap. This commitment involves undoing intergenerational trauma and harm through public policies that elevate the living and working conditions of all people.
- Patient-centric. We need to prioritize patient needs, preferences and values in all aspects of their health-care experience. This means tailoring treatments and services to individual patient needs. In policymaking, it involves creating policies that are informed by and responsive to the real-life experiences of patients. In research, it involves engaging patients in the research process and ensuring studies are relevant to and respectful of their unique perspectives and needs. This holistic approach ensures that patients’ perspectives are central to all aspects of health care.
- Socially just. We must strive for a society in which everyone has equal access to resources, opportunities and rights, and systemic inequalities and injustices are actively challenged and addressed. When redesigning the cancer care system, this involves proactive practices that create opportunities for all people, particularly those experiencing the most marginalization, to become involved in systemic health-care decision-making. A system that is responsive to the needs of the most marginalized will ultimately work better for all people.
Who you are, how you look, where you live and how much money you make should never be the difference between life and death. Let us commit to a future in which all people have the resources and support to prevent and treat cancer so that no one is left behind.
This article is republished from HealthyDebate under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Stop Trying To Lose Weight (And Do This Instead)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Lose weight” is a common goal of many people, and it’s especially a common goal handed down from medical authority figures, often as a manner of “kicking the can down the road” with regard to the doctor actually having to do some work. “Lose 20 pounds and then we’ll talk”, etc.
The thing is, it’s often not a very good or helpful goal… Even if it would be healthy for a given person to lose weight. Instead, biochemist Jessie Inchauspé argues, one should set a directly health-giving goal instead, and let any weight loss, if the body agrees it is appropriate, be a by-product of that
She recommends focusing on metabolic health, specifically, her own specialism is blood glucose maintenance. This is something that diabetics deal with (to one degree or another) every day, but it’s something whose importance should not be underestimated for non-diabetics too.
Keep our blood sugar levels healthy, she says, and a lot of the rest of good health will fall into place by itself—precisely because we’re not constantly sabotaging our body (first the pancreas and liver, then the rest of the body like dominoes).
To that end, she offers a multitude of “hacks” that really work.
Her magnum opus, “Glucose Revolution“, explains the science in great detail and does it very well! Not to be mistaken for her shorter, simpler, and entirely pragmatic “do this, then this”-style book, “The Glucose Goddess Method”, which is also great, but doesn’t go into the science more than absolutely necessary; it’s more for the “I’ll trust you; just tell me what I need to know” crowd.
In her own words:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Prefer text?
We’ve covered Inchauspé’s top 10 recommended hacks here:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: