Staying Strong: Tips To Prevent Muscle Loss With Age
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Andrea Furlan, specialist in physical medicine and rehabilitation with 30 years of experience, has advice:
Fighting sarcopenia
Sarcopenia is so common as to be considered “natural”, but “natural” does not mean “obligatory” and it certainly doesn’t mean “healthy”. As for how to fight it?
You may be thinking “let us guess, is it eat protein and do resistance exercises? And yes it is, but that’s only part of it…
Firstly, she recommends remembering why you are doing this, or because understanding is key to compliance (i.e. your perfect diet and exercise program will mean nothing if you don’t actually do it, and you won’t do it enough to make it a habit, let alone keep it up, if the reasons aren’t clear in your mind).
Sarcopenia comes with an increased risk of falls, reduced physical capacity in general, resultant disability, social isolation, and depression. Of course, this is not a one-to-one equation; you will not necessarily become depressed the moment your muscle mass is below a certain percentage, but statistically speaking, the road to ruin is laid out clearly.
Secondly, she recommends being on the lookout for it. If you check your body composition regularly with a gadget, that’s great and laudable; if you don’t, then a) consider getting one (here’s an example product on Amazon), and b) watch out for decreased muscle strength, fatigue, reduced stamina, noticeable body shape changes with muscle loss and (likely) fat gain.
Thirdly, she recommends more than just regular resistance training and good protein intake. Yes, she recommends those things too, but also getting enough water (can’t rebuild the body without it), avoiding a sedentary lifestyle (sitting leads to atrophy of many supporting and stabilizing muscles, you know, the kind of muscles that don’t look flashy but stop you falling down), and getting good sleep—vital for all kinds of body maintenance, and muscle maintenance is no exception (there’s a reason bodybuilders sleep 9–12 hours daily when in a gaining phase; you don’t need to do that, but don’t skimp on your 7–9 hours, yes, really, even you, yes, at any age).
Lastly, she recommends continuing to learn about the topic, as otherwise it’s easy to go off-track.
For more information on all of the above and more, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
- Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
- Resistance Beyond Weights
- HIIT, But Make It HIRT ← this is about high-intensity resistance training (HIRT); confusing the muscles like one confuses the heart in HIIT, which thus yields improved results
- Sleep: Yes, You Really Do Still Need It
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Kiwi Fruit vs Pineapple – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi fruit to pineapple, we picked the kiwi.
Why?
In terms of macros, they’re mostly quite comparable, being fruits made of mostly water, and a similar carb count (slightly different proportions of sugar types, but nothing that throws out the end result, and the GI is low for both). Technically kiwi has twice the protein, but they are fruits and “twice the protein” means “0.5g difference per 100g”. Aside from that, and more meaningfully, kiwi also has twice the fiber.
When it comes to vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins A, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while pineapple has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6. This would be a marginal (6:5) win for kiwi, but kiwi’s margins of difference are greater per vitamin, including 72x more vitamin E (with a cupful giving 29% of the RDA, vs a cupful of pineapple giving 0.4% of the RDA) and 57x more vitamin K (with a cupful giving a day’s RDA, vs a cupful of pineapple giving a little under 2% of the RDA). So, this is a fair win for kiwi.
In the category of minerals, things are clear: kiwi has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while pineapple has more manganese. An overwhelming win for kiwi.
Looking at their respective anti-inflammatory powers, pineapple has its special bromelain enzymes, which is a point in its favour, but when it comes to actual polyphenols, the two fruits are quite balanced, with kiwi’s flavonoids vs pineapple’s lignans.
Adding up the sections, it’s a clear win for kiwi—but pineapple is a very respectable fruit too (especially because of its bromelain content), so do enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Procrastination, and how to pay off the to-do list debt
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Procrastination, and how pay off the to-do list debt
Sometimes we procrastinate because we feel overwhelmed by the mountain of things we are supposed to be doing. If you look at your to-do list and it shows 60 overdue items, it’s little wonder if you want to bury your head in the sand!
“What difference does it make if I do one of these things now; I will still have 59 which feels as bad as having 60”
So, treat it like you might a financial debt, and make a repayment plan. Now, instead of 60 overdue items today, you have 1/day for the next 60 days, or 2/day for the next 30 days, or 3/day for the next 20 days, etc. Obviously, you may need to work out whether some are greater temporal priorities and if so, bump those to the top of the list. But don’t sweat the minutiae; your list doesn’t have to be perfectly ordered, just broadly have more urgent things to the top and less urgent things to the bottom.
Note: this repayment plan means having set repayment dates.
Up front, sit down and assign each item a specific calendar date on which you will do that thing.
This is not a deadline! It is your schedule. You’ll not try to do it sooner, and you won’t postpone it for later. You will just do that item on that date.
A productivity app like ToDoist can help with this, but paper is fine too.
What’s important here, psychologically, is that each day you’re looking not at 60 things and doing the top item; you’re just looking at today’s item (only!) and doing it.
Debt Reduction/Cancellation
Much like you might manage a financial debt, you can also look to see if any of your debts could be reduced or cancelled.
We wrote previously about the “Getting Things Done” system. It’s a very good system if you want to do that; if not, no worries, but you might at least want to borrow this one idea….
Sort your items into:
Do / Defer / Delegate / Ditch
- Do: if it can be done in under 2 minutes, do it now.
- Defer: defer the item to a specific calendar date (per the repayment plan idea we just talked about)
- Delegate: could this item be done by someone else? Get it off your plate if you reasonably can.
- Ditch: sometimes, it’s ok to realize “you know what, this isn’t that important to me anymore” and scratch it from the list.
As a last resort, consider declaring bankruptcy
Towards the end of the dot-com boom, there was a fellow who unintentionally got his 5 minutes of viral fame for “declaring email bankruptcy”.
Basically, he publicly declared that his email backlog had got so far out of hand that he would now not reply to emails from before the declaration.
He pledged to keep on top of new emails only from that point onwards; a fresh start.
We can’t comment on whether he then did, but if you need a fresh start, that can be one way to get it!
In closing…
Procrastination is not usually a matter of laziness, it’s usually a matter of overwhelm. Hopefully the above approach will help reframe things, and make things more manageable.
Sometimes procrastination is a matter of perfectionism, and not starting on tasks because we worry we won’t do them well enough, and so we get stuck in a pseudo-preparation rut. If that’s the case, our previous main feature on perfectionism may help:
Share This Post
-
What Grief Does To Your Body (And How To Manage It)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Grief Does To The Body (And How To Manage It)
In life, we will almost all lose loved ones and suffer bereavement. For most people, this starts with grandparents, eventually moves to parents, and then people our own generation; partners, siblings, close friends. And of course, sometimes and perhaps most devastatingly, we can lose people younger than ourselves.
For something that almost everyone suffers, there is often very little in the way of preparation given beforehand, and afterwards, a condolences card is nice but can’t do a lot for our mental health.
And with mental health, our physical health can go too, if we very understandably neglect it at such a time.
So, how to survive devastating loss, and come out the other side, hopefully thriving? It seems like a tall order indeed.
First, the foundations:
You’re probably familiar with the stages of grief. In their most commonly-presented form, they are:
- Denial
- Anger
- Bargaining
- Depression
- Acceptance
You’ve probably also heard/read that we won’t always go through them in order, and also that grief is deeply personal and proceeds on its own timescale.
It is generally considered healthy to go through them.
What do they look like?
Naturally this can vary a lot from person to person, but examples in the case of bereavement could be:
- Denial: “This surely has not really happened; I’ll carry on as though it hasn’t”
- Anger: “Why didn’t I do xyz differently while I had the chance?!”
- Bargaining: “I will do such-and-such in their honor, and this will be a way of expressing the love I wish I could give them in a way they could receive”
- Depression: “What is the point of me without them? The sooner I join them, the better.”
- Acceptance: “I was so lucky that we had the time together that we did, and enriched each other’s lives while we could”
We can speedrun these or we can get stuck on one for years. We can bounce back and forth. We can think we’re at acceptance, and then a previous stage will hit us like a tonne of bricks.
What if we don’t?
Assuming that our lost loved one was indeed a loved one (as opposed to someone we are merely societally expected to mourn), then failing to process that grief will tend to have a big impact on our life—and health. These health problems can include:
As you can see, three out of five of those can result in death. The other two aren’t great either. So why isn’t this taken more seriously as a matter of health?
Death is, ironically, considered something we “just have to live with”.
But how?
Coping strategies
You’ll note that most of the stages of grief are not enjoyable per se. For this reason, it’s common to try to avoid them—hence denial usually being first.
But, that is like not getting a lump checked out because you don’t want a cancer diagnosis. The emotional reasoning is understandable, but it’s ultimately self-destructive.
First, have a plan. If a death is foreseen, you can even work out this plan together.
But even if that time has now passed, it’s “better late than never” to make a plan for looking after yourself, e.g:
- How you will try to get enough sleep (tricky, but sincerely try)
- How you will remember to eat (and ideally, healthily)
- How you will still get exercise (a walk in the park is fine; see some greenery and get some sunlight)
- How you will avoid self-destructive urges (from indirect, e.g. drinking, to direct, e.g. suicidality)
- How you will keep up with the other things important in your life (work, friends, family)
- How you will actively work to process your grief (e.g. journaling, or perhaps grief counselling)
Some previous articles of ours that may help:
- How To Keep On Keeping On ← this is about looking after general health when motivation is low
- The Mental Health First-Aid You’ll Hopefully Never Need ← this is about managing depression
- How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To) ← this is about managing suicidality
- Life After Death? (Your Life; A Loved One’s Death) ← this is about bereavement and romance
If it works, it works
If we are all unique, then any relationship between any two people is uniqueness squared. Little wonder, then, that our grief may be unique too. And it can be complicated further:
- Sometimes we had a complicated relationship with someone
- Sometimes the circumstances of their death were complicated
There is, for that matter, such a thing as “complicated grief”:
Read more: Complicated grief and prolonged grief disorder (Medical News Today)
We also previously reviewed a book on “ambiguous loss”, exploring grieving when we cannot grieve in the normal way because someone is gone and/but/maybe not gone.
For example, if someone is in a long-term coma from which they may never recover, or if they are missing-presumed-dead. Those kinds of situations are complicated too.
Unusual circumstances may call for unusual coping strategies, so how can we discern what is healthy and what isn’t?
The litmus test is: is it enabling you to continue going about your life in a way that allows you to fulfil your internal personal aspirations and external social responsibilities? If so, it’s probably healthy.
Look after yourself. And if you can, tell your loved ones you love them today.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
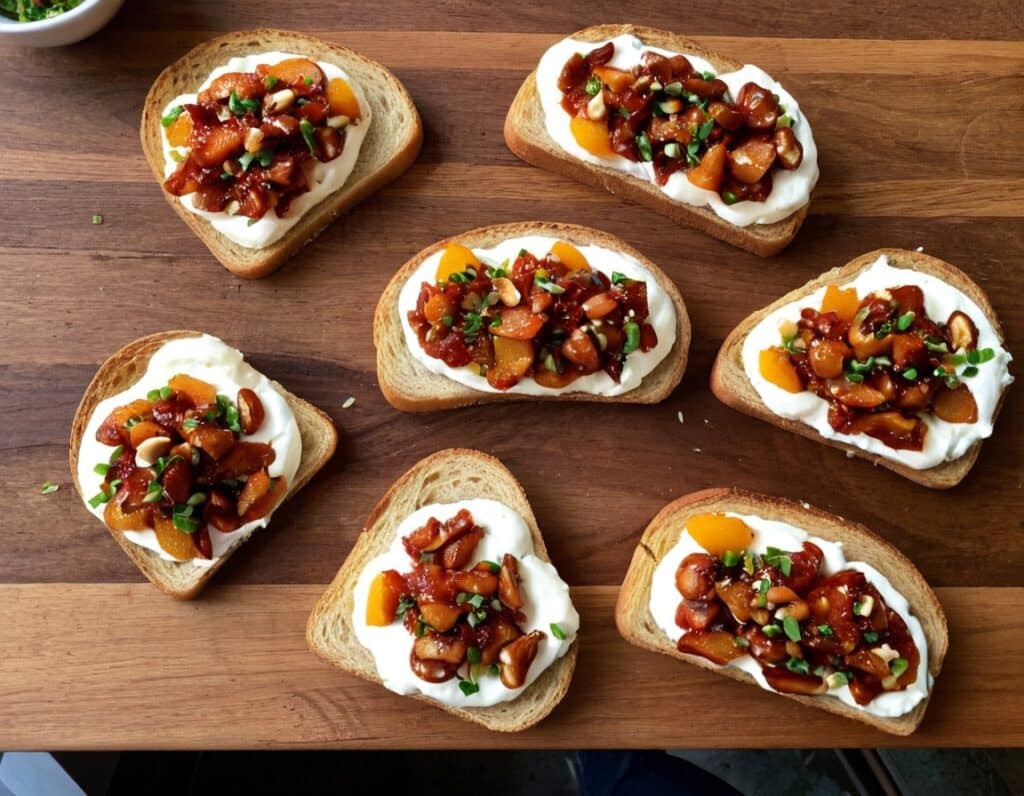
Chili Chestnut, Sweet Apricot, & Whipped Feta Toasts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a delightful breakfast or light lunch option, full of gut-healthy ingredients and a fair list of healthy polyphenols too.
You will need
- ½ baguette, sliced into ½” slices; if making your own, feel free to use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe. If buying shop-bought, a sourdough baguette will likely be the healthiest option, and tasty too.
- 4 oz feta cheese; if you are vegan, a plant-based version will work in culinary terms, but will have a different (less gut-healthy) nutritional profile, as plant-based cheeses generally use a lot of coconut oil and potato starch, and are not actually fermented.
- 1 tbsp yogurt; your preference what kind; live-cultured with minimal additives is of course best—and this time, plant-based is also just as good, healthwise, since they are fermented and contain more or less the same beneficial bacteria, and have a good macro profile too.
- 4 oz precooked chestnuts, finely chopped
- 6 dried apricots, finely chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated
- 2 tsp harissa paste
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- Optional garnish: finely chopped chives
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the feta and yogurt in a small, high-speed blender and process into a smooth purée. If it isn’t working, add 1 tbsp kettle-hot water and try again.
2) Heat the oil in a skillet over a medium heat; add the garlic and when it starts to turn golden, add the chestnuts and harissa, as well as the black pepper and MSG/salt. Stir for about 2 minutes, and then stir in the apricots and take it off the heat.
3) Toast the baguette slices under the grill. If you’re feeling bold about the multitasking, you can start this while still doing the previous step, for optimal timing. If not, simply doing it in the order presented is fine.
4) Assemble: spread the whipped feta over the toast; add the apricot-chestnut mixture, followed by the finely chopped chives if using, and serve immediately:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Nobody Likes Surgery, But Here’s How To Make It Much Less Bad
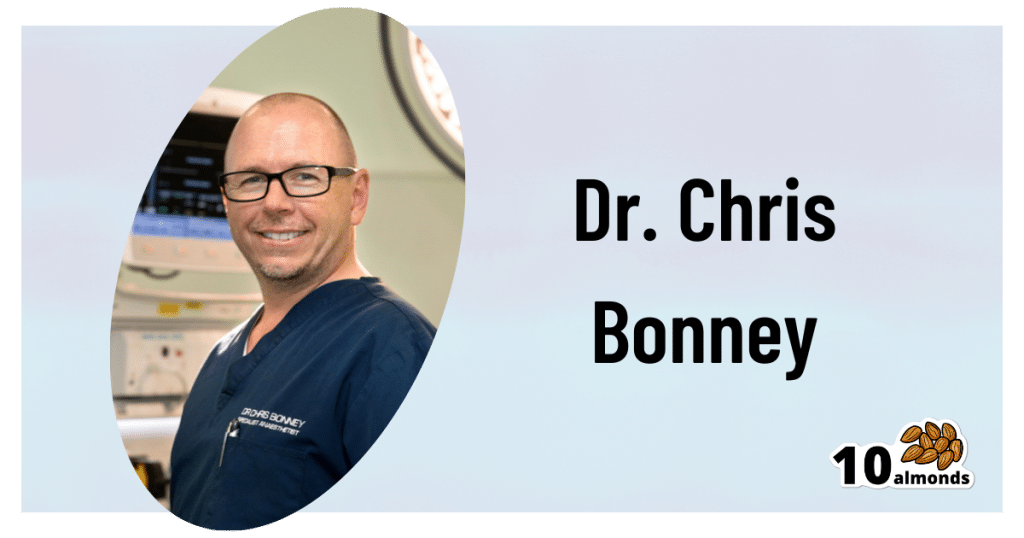
This is Dr. Chris Bonney. He’s an anesthesiologist. If you have a surgery, he wants you to go in feeling calm, and make a quick recovery afterwards, with minimal suffering in between.
Being a patient in a hospital is a bit like being a passenger in an airplane:
- Almost nobody enjoys the thing itself, but we very much want to get to the other side of the experience.
- We have limited freedoms and comforts, and small things can make a big difference between misery and tolerability.
- There are professionals present to look after us, but they are busy and have a lot of other people to tend to too.
So why is it that there are so many resources available full of “tips for travelers” and so few “tips for hospital patients”?
Especially given the relative risks of each, and likelihood, or even near-certainty of coming to at least some harm… One would think “tips for patients” would be more in demand!
Tips for surgery patients, from an insider expert
First, he advises us: empower yourself.
Empowering yourself in this context means:
- Relax—doctors really want you to feel better, quickly. They’re on your side.
- Research—knowledge is power, so research the procedure (and its risks!). Dr. Bonney, himself an anesthesiologist, particularly recommends you learn what specific anesthetic will be used (there are many, and they’re all a bit different!), and what effects (and/or after-effects) that may have.
- Reframe—you’re not just a patient; you’re a customer/client. Many people suffer from MDeity syndrome, and view doctors as authority figures, rather than what they are: service providers.
- Request—if something would make you feel better, ask for it. If it’s information, they will be not only obliged, but also enthusiastic, to give it. If it’s something else, they’ll oblige if they can, and the worst case scenario is something won’t be possible, but you won’t know if you don’t ask.
Next up, help them to help you
There are various ways you can be a useful member of your own care team:
- Go into surgery as healthy as you can. If there’s ever a time to get a little fitter, eat a little healthier, prioritize good quality sleep more, the time approaching your surgery is the time to do this.
- This will help to minimize complications and maximize recovery.
- Take with you any meds you’re taking, or at least have an up-to-date list of what you’re taking. Dr. Bonney has very many times had patients tell him such things as “Well, let me see. I have two little pink ones and a little white one…” and when asked what they’re for they tell him “I have no idea, you’d need to ask my doctor”.
- Help them to help you; have your meds with you, or at least a comprehensive list (including: medication name, dosage, frequency, any special instructions)
- Don’t stop taking your meds unless told to do so. Many people have heard that one should stop taking meds before a surgery, and sometimes that’s true, but often it isn’t. Keep taking them, unless told otherwise.
- If unsure, ask your surgical team in advance (not your own doctor, who will not be as familiar with what will or won’t interfere with a surgery).
Do any preparatory organization well in advance
Consider the following:
- What do you need to take with you? Medications, clothes, toiletries, phone charger, entertainment, headphones, paperwork, cash for the vending machine?
- Will the surgeons need to shave anywhere, and if so, might you prefer doing some other form of depilation (e.g. waxing etc) yourself in advance?
- Is your list of medications ready?
- Who will take you to the hospital and who will bring you back?
- Who will stay with you for the first 24 hours after you’re sent home?
- Is someone available to look after your kids/pets/plants etc?
Be aware of how you do (and don’t) need to fast before surgery
The American Society of Anesthesiologists gives the following fasting guidelines:
- Non-food liquids: fast for at least 2 hours before surgery
- Food liquids or light snacks: fast for at least 6 hours before surgery
- Fried foods, fatty foods, meat: fast for at least 8 hours before surgery
(see the above link for more details)
Dr. Bonney notes that many times he’s had patients who’ve had the worst thirst, or caffeine headache, because of abstaining unnecessarily for the day of the surgery.
Unless told otherwise by your surgical team, you can have black coffee/tea up until two hours before your surgery, and you can and should have water up until two hours before surgery.
Hydration is good for you and you will feel the difference!
Want to know more?
Dr. Bonney has his own website and blog, where he offers lots of advice, including for specific conditions and specific surgeries, with advice for before/during/after your hospital stay.
He also has a book with many more tips like those we shared today:
Calm For Surgery: Supertips For A Smooth Recovery
Take good care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No, you don’t need the ‘Barbie drug’ to tan, whatever TikTok says. Here’s why melanotan-II is so risky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
TikTok and Instagram influencers have been peddling the “Barbie drug” to help you tan.
But melanotan-II, as it’s called officially, is a solution that’s too good to be true. Just like tanning, this unapproved drug has a dark side.
Doctors, researchers and Australia’s drug regulator have been warning about its side effects – from nausea and vomiting to brain swelling and erection problems.
There are also safer ways of getting the tanned look, if that’s what you’re after.
AtlasStudio/Shutterstock What is melanotan-II?
No, it’s not a typo. Melanotan-II is very different from melatonin, which is a hormonal supplement used for insomnia and jet lag.
Melanotan-II is a synthetic version of the naturally ocurring hormone α-melanocyte stimulating hormone. This means the drug mimics the body’s hormone that stimulates production of the pigment melanin. This is what promotes skin darkening or tanning, even in people with little melanin.
Although the drug is promoted as a way of getting a “sunless tan”, it is usually promoted for use with UV exposure, to enhance the effect of UV and kickstart the tanning process.
Melanotan-II is related to, but different from, melanotan-I (afamelanotide), an approved drug used to treat the skin condition erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Melanotan-II is not registered for use with Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). It is illegal to advertise it to the public or to provide it without a prescription.
However, social media has been driving unlicensed melanotan-II sales, a study published last year confirms.
There are many black market suppliers of melanotan-II injections, tablets and creams. More recently, nasal sprays have become more popular.
What are the risks?
Just like any drug, melanotan-II comes with the risk of side effects, many of which we’ve known about for more than a decade. These include changes in the size and pigmentation of moles, rapid appearance of new moles, flushing to the face, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, chest pain and brain swelling.
It can also cause rhabdomyolysis, a dangerous syndrome where muscle breaks down and releases proteins into the bloodstream that damage the kidneys.
For men, the drug can cause priapism – a painful erection that does not go away and can damage the penis, requiring emergency treatment.
Its use has been linked with melanoma developing from existing moles either during or shortly after using the drug. This is thought to be due to stimulating pigment cells and causing the proliferation of abnormal cells.
Despite reports of melanoma, according to a study of social media posts the drug is often marketed as protecting against skin cancer. In fact, there’s no evidence to show it does this.
Social media posts about melanotan-II rarely mention health risks.
There are no studies on long-term safety of melanotan-II use.
Then there’s the issue of the drug not held to the high safety standards as TGA-approved products. This could result in variability in dose, undeclared ingredients and potential microbial contamination.
Thinking about melanotan-II? The drug can cause a long-lasting painful erection needing urgent medical care. Eugenio Marongiu/Shutterstock The TGA has previously warned consumers to steer clear of the drug due to its “serious side effects that can be very damaging to your health”.
According to an ABC article published earlier this week, the TGA is cracking down on the illegal promotion of the drug on various websites. However, we know banned sellers can pop back up under a different name.
TikTok has banned the hashtags #tanningnasalspray, #melanotan and #melanotan2, but these products continue to be promoted with more generic hashtags, such as #tanning.
Part of a wider trend
Australia has some of the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. The “slip, slop, slap” campaign is a public health success story, with increased awareness of sun safety, a cultural shift and a decline in melanoma in young people.
However, the image of a bronzed beach body remains a beauty standard, especially among some young people.
Disturbingly, tan lines are trending on TikTok as a sought after summer accessory and the hashtag #sunburnttanlines has millions of views. We’ve also seen a backlash against sunscreen among some young people, again promoted on TikTok.
The Cancer Council is so concerned about the trend towards normalising tanning it has launched the campaign End the Trend.
You have other options
There are options beyond spraying an illegal, unregulated product up your nose, or risking unprotected sun exposure: fake tan.
Fake tan tends to be much safer than melanotan-II and there’s more long-term safety data. It also comes with potential side effects, albeit rare ones, including breathing issues (with spray products) and skin inflammation in some people.
Better still, you can embrace your natural skin tone.
Rose Cairns, Senior Lecturer in Pharmacy, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: