Perfectionism, And How To Make Yours Work For You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Harness The Power Of Your Perfectionism
A lot of people see perfectionism as a problem—and it can be that!
We can use perfectionism as a would-be shield against our fear of failure, by putting things off until we’re better prepared (repeat forever, or at least until the deadliniest deadline that ever deadlined), or do things but really struggle to draw a line under them and check them off as “done” because we keep tweaking and improving and improving… With diminishing returns (forever). So, that’s not helpful.
But, if we’re mindful, we can also leverage our perfectionism to our benefit.
Great! How?
First we need to be able to discern the ways in which perfectionism can be bad or good for us. Or as it’s called in psychology, ways in which our perfectionism can be maladaptive or adaptive.
- Maladaptive: describing a behavioral adaptation to our environment—specifically, a reactive behavioral adaptation that is unhealthy and really is not a solution to the problem at hand
- Adaptive: describing a behavioral adaptation to our environment—specifically, a responsive behavioral adaptation that is healthy and helps us to thrive
So in the case of perfectionism, one example for each might be:
- Maladaptive: never taking up that new hobby, because you’re just going to suck at it anyway, and what’s the point if you’re not going to excel? You’re a perfectionist, and you don’t settle for anything less than excellence.
- Adaptive: researching the new hobby, learning the basics, and recognizing that even if the results are not immediately perfect, the learning process can be… Yes, even with mistakes along the way, for they too are part of learning! You’re a perfectionist, and you’re going to be the best possible student of your new hobby.
Did you catch the key there?
When it comes to approaching things we do in life—either because we want to or because we must—there are two kinds of mindset: goal-oriented, and task-oriented.
Broadly speaking, each has their merits, and as a general topic, it’s beyond the scope of today’s main feature. Here we’re looking at it in the context of perfectionism, and in that frame, there’s a clear qualitative difference:
- The goal-oriented perfectionist will be frustrated to the point of torment, at not immediately attaining the goal. Everything short of that will be a means to an end, at best. Not fun.
- The task-oriented perfectionist will take joy in going about the task in the best way possible, and optimizing their process as they go. The journey itself will be rewarding and a tangible product of their consistent perfectionism.
The good news is: you get to choose! You’re not stuck in a box.
If you’re thinking “I’m a perfectionist and I’m generally a goal-oriented person”, that’s fine. You’re just going to need to reframe your goals.
- Instead of: my goal is to be fluent in Arabic
- …so you never speak it, because to err is human, all too human, and you’re a perfectionist, so you don’t want that!
- Let’s try: my goal is to study Arabic for at least 15 minutes per day, every day, without fail, covering at least some new material each time, no matter how small the increase
- …and then you go and throw yourself into conversation way out of your depth, make mistakes, and get corrections, because that’s how you learn, and you’re a perfectionist, so you want that!
This goes for any field of expertise, of course.
- If you want to play the violin solo in Carnegie Hall, you have to pick up your violin and practice each day.
- If you want to be a world-renowned pastry chef, you have to make a consistent habit of baking.
- If you want to write a bestselling book, you have to show up at your keyboard.
Be perfect all you want, but be the perfect student.
And as your skills grow, maybe you’ll upgrade that to also being the perfect practitioner, and perhaps later still, the perfect teacher.
But just remember:
Perfection comes not from the end goal (that would be backwards thinking!) but from the process (which includes mistakes; they’re an important part of learning; embrace them and grow!), so perfect that first.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
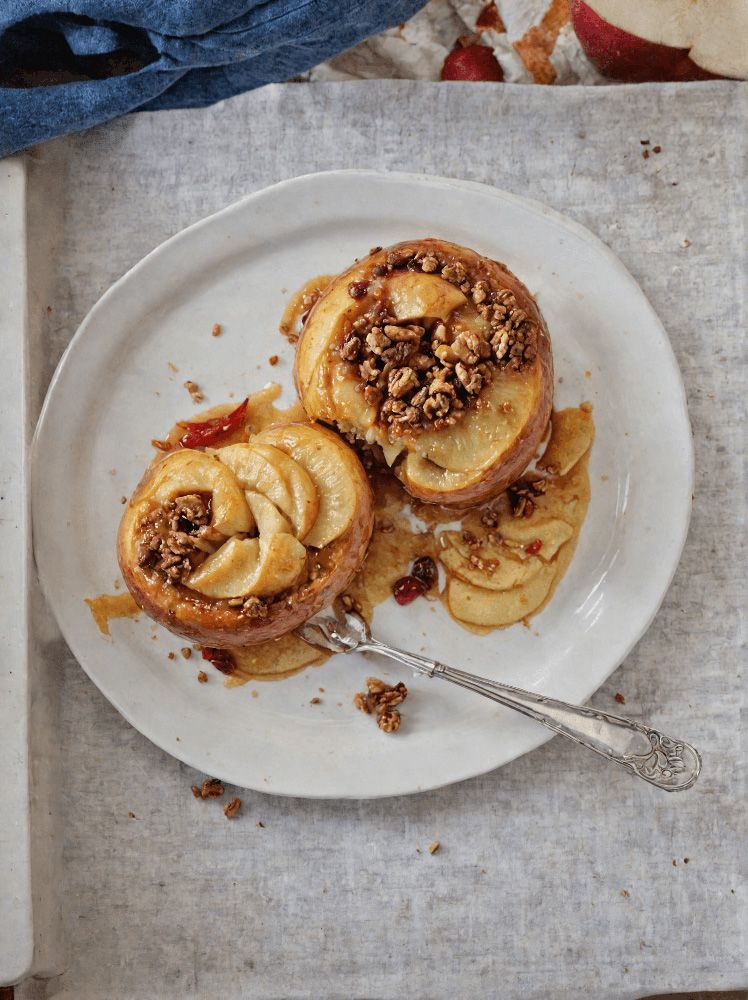
Superfood Baked Apples
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Superfoods, and super-tasty. This is a healthy twist on a classic; your blood sugars will thank you for choosing this tasty sweet delight. It’s also packed with nutrients!
You will need
- 2 large firm baking apples, cored but not peeled
- 1/2 cup chopped walnuts
- 3 tbsp goji berries, rehydrated (soak them in warm water for 10–15minutes and drain)
- 1 tbsp honey, or maple syrup, per your preference (this writer is also a fan of aged balsamic vinegar for its strong flavor and much milder sweetness. If you don’t like things to be too sweet, this is the option for you)
- 2 tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp ground ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 180℃ / 350℉ / gas mark 4
2) Mix the chopped walnuts with the goji berries and the honey (or whatever you used instead of the honey) as well as the sweet cinnamon and the ginger.
3) Place the apples in shallow baking dish, and use the mixture you just made to stuff their holes.
4) Add 1/2 cup water to the dish, around the apples. Cover gently with foil, and bake until soft.
Tip: check them every 20 minutes; they may be done in 40 or it may take 60; in honesty it depends on your oven. If unsure, cook them for longer at a lower temperature.
5) Serve warm.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose C’s
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- The Sugary Food That Lowers Blood Sugars
- Honey vs Maple Syrup – Which is Healthier?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons ← this is important, about why we chose the sweet cinnamon
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Older Men’s Connections Often Wither When They’re on Their Own
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At age 66, South Carolina physician Paul Rousseau decided to retire after tending for decades to the suffering of people who were seriously ill or dying. It was a difficult and emotionally fraught transition.
“I didn’t know what I was going to do, where I was going to go,” he told me, describing a period of crisis that began in 2017.
Seeking a change of venue, Rousseau moved to the mountains of North Carolina, the start of an extended period of wandering. Soon, a sense of emptiness enveloped him. He had no friends or hobbies — his work as a doctor had been all-consuming. Former colleagues didn’t get in touch, nor did he reach out.
His wife had passed away after a painful illness a decade earlier. Rousseau was estranged from one adult daughter and in only occasional contact with another. His isolation mounted as his three dogs, his most reliable companions, died.
Rousseau was completely alone — without friends, family, or a professional identity — and overcome by a sense of loss.
“I was a somewhat distinguished physician with a 60-page resume,” Rousseau, now 73, wrote in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society in May. “Now, I’m ‘no one,’ a retired, forgotten old man who dithers away the days.”
In some ways, older men living alone are disadvantaged compared with older women in similar circumstances. Research shows that men tend to have fewer friends than women and be less inclined to make new friends. Often, they’re reluctant to ask for help.
“Men have a harder time being connected and reaching out,” said Robert Waldinger, a psychiatrist who directs the Harvard Study of Adult Development, which has traced the arc of hundreds of men’s lives over a span of more than eight decades. The men in the study who fared the worst, Waldinger said, “didn’t have friendships and things they were interested in — and couldn’t find them.” He recommends that men invest in their “social fitness” in addition to their physical fitness to ensure they have satisfying social interactions.
Slightly more than 1 in every 5 men ages 65 to 74 live alone, according to 2022 Census Bureau data. That rises to nearly 1 in 4 for those 75 or older. Nearly 40% of these men are divorced, 31% are widowed, and 21% never married.
That’s a significant change from 2000, when only 1 in 6 older men lived by themselves. Longer life spans for men and rising divorce rates are contributing to the trend. It’s difficult to find information about this group — which is dwarfed by the number of women who live alone — because it hasn’t been studied in depth. But psychologists and psychiatrists say these older men can be quite vulnerable.
When men are widowed, their health and well-being tend to decline more than women’s.
“Older men have a tendency to ruminate, to get into our heads with worries and fears and to feel more lonely and isolated,” said Jed Diamond, 80, a therapist and the author of “Surviving Male Menopause” and “The Irritable Male Syndrome.”
Add in the decline of civic institutions where men used to congregate — think of the Elks or the Shriners — and older men’s reduced ability to participate in athletic activities, and the result is a lack of stimulation and the loss of a sense of belonging.
Depression can ensue, fueling excessive alcohol use, accidents, or, in the most extreme cases, suicide. Of all age groups in the United States, men over age 75 have the highest suicide rate, by far.
For this column, I spoke at length to several older men who live alone. All but two (who’d been divorced) were widowed. Their experiences don’t represent all men who live alone. But still, they’re revealing.
The first person I called was Art Koff, 88, of Chicago, a longtime marketing executive I’d known for several years. When I reached out in January, I learned that Koff’s wife, Norma, had died the year before, leaving him hobbled by grief. Uninterested in eating and beset by unremitting loneliness, Koff lost 45 pounds.
“I’ve had a long and wonderful life, and I have lots of family and lots of friends who are terrific,” Koff told me. But now, he said, “nothing is of interest to me any longer.”
“I’m not happy living this life,” he said.
Nine days later, I learned that Koff had died. His nephew, Alexander Koff, said he had passed out and was gone within a day. The death certificate cited “end stage protein calorie malnutrition” as the cause.
The transition from being coupled to being single can be profoundly disorienting for older men. Lodovico Balducci, 80, was married to his wife, Claudia, for 52 years before she died in October 2023. Balducci, a renowned physician known as the “patriarch of geriatric oncology,” wrote about his emotional reaction in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, likening Claudia’s death to an “amputation.”
“I find myself talking to her all the time, most of the time in my head,” Balducci told me in a phone conversation. When I asked him whom he confides in, he admitted, “Maybe I don’t have any close friends.”
Disoriented and disorganized since Claudia died, he said his “anxiety has exploded.”
We spoke in late February. Two weeks later, Balducci moved from Tampa to New Orleans, to be near his son and daughter-in-law and their two teenagers.
“I am planning to help as much as possible with my grandchildren,” he said. “Life has to go on.”
Verne Ostrander, a carpenter in the small town of Willits, California, about 140 miles north of San Francisco, was reflective when I spoke with him, also in late February. His second wife, Cindy Morninglight, died four years ago after a long battle with cancer.
“Here I am, almost 80 years old — alone,” Ostrander said. “Who would have guessed?”
When Ostrander isn’t painting watercolors, composing music, or playing guitar, “I fall into this lonely state, and I cry quite a bit,” he told me. “I don’t ignore those feelings. I let myself feel them. It’s like therapy.”
Ostrander has lived in Willits for nearly 50 years and belongs to a men’s group and a couples’ group that’s been meeting for 20 years. He’s in remarkably good health and in close touch with his three adult children, who live within easy driving distance.
“The hard part of living alone is missing Cindy,” he told me. “The good part is the freedom to do whatever I want. My goal is to live another 20 to 30 years and become a better artist and get to know my kids when they get older.”
The Rev. Johnny Walker, 76, lives in a low-income apartment building in a financially challenged neighborhood on Chicago’s West Side. Twice divorced, he’s been on his own for five years. He, too, has close family connections. At least one of his several children and grandchildren checks in on him every day.
Walker says he had a life-changing religious conversion in 1993. Since then, he has depended on his faith and his church for a sense of meaning and community.
“It’s not hard being alone,” Walker said when I asked whether he was lonely. “I accept Christ in my life, and he said that he would never leave us or forsake us. When I wake up in the morning, that’s a new blessing. I just thank God that he has brought me this far.”
Waldinger recommended that men “make an effort every day to be in touch with people. Find what you love — golf, gardening, birdwatching, pickleball, working on a political campaign — and pursue it,” he said. “Put yourself in a situation where you’re going to see the same people over and over again. Because that’s the most natural way conversations get struck up and friendships start to develop.”
Rousseau, the retired South Carolina doctor, said he doesn’t think about the future much. After feeling lost for several years, he moved across the country to Jackson, Wyoming, in the summer of 2023. He embraced solitude, choosing a remarkably isolated spot to live — a 150-square-foot cabin with no running water and no bathroom, surrounded by 25,000 undeveloped acres of public and privately owned land.
“Yes, I’m still lonely, but the nature and the beauty here totally changed me and focused me on what’s really important,” he told me, describing a feeling of redemption in his solitude.
Rousseau realizes that the death of his parents and a very close friend in his childhood left him with a sense of loss that he kept at bay for most of his life. Now, he said, rather than denying his vulnerability, he’s trying to live with it. “There’s only so long you can put off dealing with all the things you’re trying to escape from.”
It’s not the life he envisioned, but it’s one that fits him, Rousseau said. He stays busy with volunteer activities — cleaning tanks and running tours at Jackson’s fish hatchery, serving as a part-time park ranger, and maintaining trails in nearby national forests. Those activities put him in touch with other people, mostly strangers, only intermittently.
What will happen to him when this way of living is no longer possible?
“I wish I had an answer, but I don’t,” Rousseau said. “I don’t see my daughters taking care of me. As far as someone else, I don’t think there’s anyone else who’s going to help me.”
We’re eager to hear from readers about questions you’d like answered, problems you’ve been having with your care, and advice you need in dealing with the health care system. Visit http://kffhealthnews.org/columnists to submit your requests or tips.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Sunflower Seeds vs Sesame Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sunflower seeds to sesame seeds, we picked the sunflower.
Why?
In moderation, both are very healthy. We say “in moderation” because they’re both about 50% fat and such fats, while vital for life, are generally best enjoyed in small portions. Of that fat, sunflower has the slightly better fat profile; they’re both mostly poly- and monounsaturated fats, but sunflower has 10% saturated fat while sesame has 15%. Aside from fats, sunflower has slightly more protein and sesame has slightly more carbs. While sesame has slightly more fiber, because of the carb profile sunflower still has the lower glycemic index. All in all, a moderate win for sunflower in the macros category.
You may be wondering, with all that discussion of fats, what they’re like for omega-3, and sesame seeds have more omega-3, though sunflower seeds contain it too. Still, a point in sesame’s favor here.
When it comes to vitamins, sunflower has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, and choline, while sesame is not higher in any vitamins.
In the category of minerals, sunflower has more phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while sesame has more calcium, copper, iron, and zinc. This is nominally a marginal win for sesame, but it should be noted that sunflower is still very rich in copper, iron, and zinc too (but not calcium).
Adding up the categories makes for a moderate win for sunflower seeds, but as ever, enjoy both; diversity is best!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How the stress of playing chess can be fatal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The death of a chess player in the middle of a match at the world’s most prestigious competition may have shocked those who view the game as a relaxing pastime. Kurt Meier, 67, collapsed during his final match in the tournament and died in hospital later that day. But chess, like any other game or sport, can lead to an immense amount of stress, which can be bad for a competitor’s physical health too.
We tend to associate playing sport or games with good health and well-being. And there are a countless number of studies showing playing games has an association with feeling happier. While this argument is true for recreational players, the story can be different for the elite, where success and failure are won and lost by the finest margins and where winning can mean funding and a future, and losing can mean poverty and unemployment. If this is the case, can being successful at a sport or game actually be bad for you?
Competitive anxiety
Elite competition can be stressful because the outcome is so important to the competitors. We can measure stress using a whole range of physiological indicators such as heart rate and temperature, and responses such as changes in the intensity of our emotions.
Emotions provide a warning of threat. So if you feel that achieving your goal is going to be difficult, then expect to feel intense emotions. The leading candidate that signals we are experiencing stress is anxiety, characterised by thoughts of worry, fears of dread about performance, along with accompanying physiological responses such as increased heart rate and sweaty palms. If these symptoms are experienced regularly or chronically, then this is clearly detrimental to health.
This stress response is probably not restricted to elite athletes. Intense emotions are linked to trying to achieve important goals and while it isn’t the only situation where it occurs, it is just very noticeable in sport.
The causes of stress
It makes more sense to focus on what the causes of stress are rather than where we experience it. The principle is that the more important the goal is to achieve, then the greater the propensity for the situation to intensify emotions.
Emotions intensify also by the degree of uncertainty and competing, at whatever level of a sport, is uncertain when the opposition is trying its hardest to win the contest and also has a motivation to succeed. The key point is that almost all athletes at any level can suffer bouts of stress, partly due to high levels of motivation.
A stress response is also linked to how performance is judged and reported. Potentially stressful tasks tend to be ones where performance is public and feedback is immediate. In chess – as with most sporting contests – we see who the winner is and can start celebrating success or commiserating failure as soon as the game is over.
There are many tasks which have similar features. Giving a speech in public, taking an academic examination, or taking your driving test are all examples of tasks that can illicit stress. Stress is not restricted to formal tasks but can also include social tasks. Asking a potential partner for a date, hand in marriage, and meeting the in-laws for the first time can be equally stressful.
Winning a contest or going on a date relate to higher-order goals about how we see ourselves. If we define ourselves as “being a good player” or “being attractive or likeable” then contrasting information is likely to associate with unpleasant emotions. You will feel devastated if you are turned down when asking someone out on a date, for instance, and if this was repeated, it could lead to reduced self-esteem and depression.
The key message here is to recognise what your goals are and think about how important they are. If you want to achieve them with a passion and if the act of achieving them leads to intense and sometimes unwanted emotions, then it’s worth thinking about doing some work to manage these emotions.
Andrew Lane, Professor in Sport and Learning, University of Wolverhampton
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Yes, adults can develop food allergies. Here are 4 types you need to know about
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you didn’t have food allergies as a child, is it possible to develop them as an adult? The short answer is yes. But the reasons why are much more complicated.
Preschoolers are about four times more likely to have a food allergy than adults and are more likely to grow out of it as they get older.
It’s hard to get accurate figures on adult food allergy prevalence. The Australian National Allergy Council reports one in 50 adults have food allergies. But a US survey suggested as many as one in ten adults were allergic to at least one food, with some developing allergies in adulthood.
What is a food allergy
Food allergies are immune reactions involving immunoglobulin E (IgE) – an antibody that’s central to triggering allergic responses. These are known as “IgE-mediated food allergies”.
Food allergy symptoms that are not mediated by IgE are usually delayed reactions and called food intolerances or hypersensitivity.
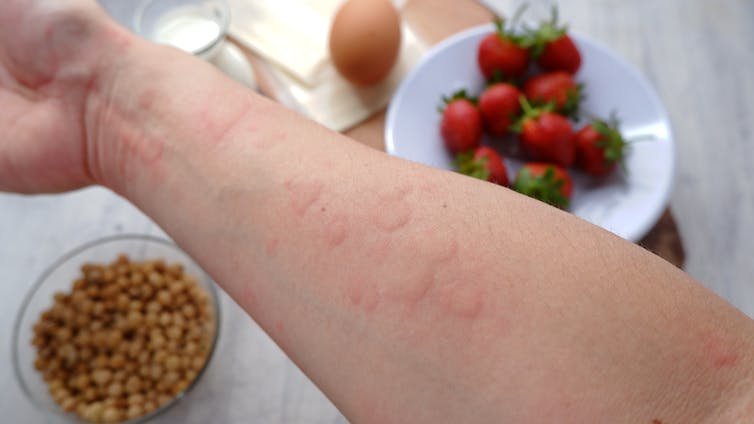
Food allergy symptoms can include hives, swelling, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, throat or chest tightening, trouble breathing, chest pain, rapid heart rate, dizziness, low blood pressure or anaphylaxis.
Symptoms include hives. wisely/Shutterstock IgE-mediated food allergies can be life threatening, so all adults need an action management plan developed in consultation with their medical team.
Here are four IgE-mediated food allergies that can occur in adults – from relatively common ones to rare allergies you’ve probably never heard of.
1. Single food allergies
The most common IgE-mediated food allergies in adults in a US survey were to:
- shellfish (2.9%)
- cow’s milk (1.9%)
- peanut (1.8%)
- tree nuts (1.2%)
- fin fish (0.9%) like barramundi, snapper, salmon, cod and perch.
In these adults, about 45% reported reacting to multiple foods.
This compares to most common childhood food allergies: cow’s milk, egg, peanut and soy.
Overall, adult food allergy prevalence appears to be increasing. Compared to older surveys published in 2003 and 2004, peanut allergy prevalence has increased about three-fold (from 0.6%), while tree nuts and fin fish roughly doubled (from 0.5% each), with shellfish similar (2.5%).
While new adult-onset food allergies are increasing, childhood-onset food allergies are also more likely to be retained into adulthood. Possible reasons for both include low vitamin D status, lack of immune system challenges due to being overly “clean”, heightened sensitisation due to allergen avoidance, and more frequent antibiotic use.
Some adults develop allergies to cow’s milk, while others retain their allergy from childhood. Sarah Swinton/Unsplash 2. Tick-meat allergy
Tick-meat allergy, also called α-Gal syndrome or mammalian meat allergy, is an allergic reaction to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose, or α-Gal for short.
Australian immunologists first reported links between α-Gal syndrome and tick bites in 2009, with cases also reported in the United States, Japan, Europe and South Africa. The US Centers for Disease Control estimates about 450,000 Americans could be affected.
The α-Gal contains a carbohydrate molecule that is bound to a protein molecule in mammals.
The IgE-mediated allergy is triggered after repeated bites from ticks or chigger mites that have bitten those mammals. When tick saliva crosses into your body through the bite, antibodies to α-Gal are produced.
When you subsequently eat foods that contain α-Gal, the allergy is triggered. These triggering foods include meat (lamb, beef, pork, rabbit, kangaroo), dairy products (yoghurt, cheese, ice-cream, cream), animal-origin gelatin added to gummy foods (jelly, lollies, marshmallow), prescription medications and over-the counter supplements containing gelatin (some antibiotics, vitamins and other supplements).
Tick-meat allergy reactions can be hard to recognise because they’re usually delayed, and they can be severe and include anaphylaxis. Allergy organisations produce management guidelines, so always discuss management with your doctor.
3. Fruit-pollen allergy
Fruit-pollen allergy, called pollen food allergy syndrome, is an IgE-mediated allergic reaction.
In susceptible adults, pollen in the air provokes the production of IgE antibodies to antigens in the pollen, but these antigens are similar to ones found in some fruits, vegetables and herbs. The problem is that eating those plants triggers an allergic reaction.
The most allergenic tree pollens are from birch, cypress, Japanese cedar, latex, grass, and ragweed. Their pollen can cross-react with fruit and vegetables, including kiwi, banana, mango, avocado, grapes, celery, carrot and potato, and some herbs such as caraway, coriander, fennel, pepper and paprika.
Fruit-pollen allergy is not common. Prevalence estimates are between 0.03% and 8% depending on the country, but it can be life-threatening. Reactions range from itching or tingling of lips, mouth, tongue and throat, called oral allergy syndrome, to mild hives, to anaphylaxis.
4. Food-dependent, exercise-induced food allergy
During heavy exercise, the stomach produces less acid than usual and gut permeability increases, meaning that small molecules in your gut are more likely to escape across the membrane into your blood. These include food molecules that trigger an IgE reaction.
If the person already has IgE antibodies to the foods eaten before exercise, then the risk of triggering food allergy reactions is increased. This allergy is called food-dependent exercise-induced allergy, with symptoms ranging from hives and swelling, to difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis.
This type of allergy is extremely rare. Ben O’Sullivan/Unsplash Common trigger foods include wheat, seafood, meat, poultry, egg, milk, nuts, grapes, celery and other foods, which could have been eaten many hours before exercising.
To complicate things even further, allergic reactions can occur at lower levels of trigger-food exposure, and be more severe if the person is simultaneously taking non-steroidal inflammatory medications like aspirin, drinking alcohol or is sleep-deprived.
Food-dependent exercise-induced allergy is extremely rare. Surveys have estimated prevalence as between one to 17 cases per 1,000 people worldwide with the highest prevalence between the teenage years to age 35. Those affected often have other allergic conditions such as hay fever, asthma, allergic conjunctivitis and dermatitis.
Allergies are a growing burden
The burden on physical health, psychological health and health costs due to food allergy is increasing. In the US, this financial burden was estimated as $24 billion per year.
Adult food allergy needs to be taken seriously and those with severe symptoms should wear a medical information bracelet or chain and carry an adrenaline auto-injector pen. Concerningly, surveys suggest only about one in four adults with food allergy have an adrenaline pen.
If you have an IgE-mediated food allergy, discuss your management plan with your doctor. You can also find more information at Allergy and Anaphylaxis Australia.
Clare Collins, Laureate Professor in Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do We Need Supplements, And Do They Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does our diet need a little help?
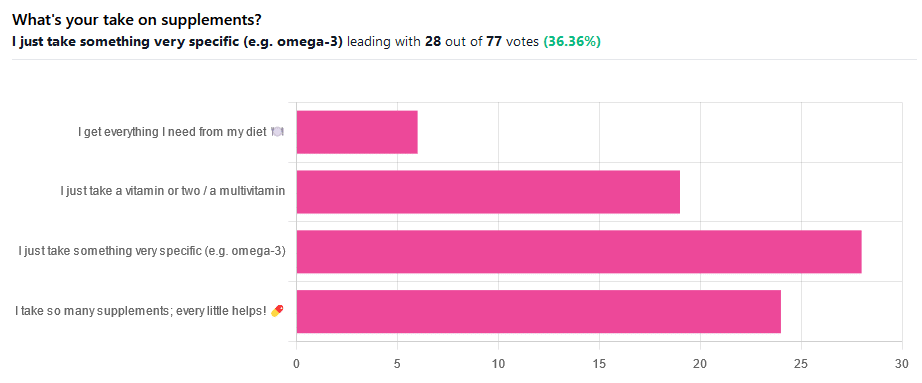
We asked you for your take on supplements, and got the above-illustrated, below-described set of results.
- The largest minority of respondents (a little over a third) voted for “I just take something very specific”
- The next most respondents voted for “I take so many supplements; every little helps!”
- Almost as many voted for “I just take a vitamin or two / a multivitamin”
- Fewest, about 8%, voted for “I get everything I need from my diet”
But what does the science say?
Food is less nutritious now than it used to be: True or False?
True or False depending on how you measure it.
An apple today and an apple from a hundred years ago are likely to contain the same amounts of micronutrients per apple, but a lower percentage of micronutrients per 100g of apple.
The reason for this is that apples (and many other food products; apples are just an arbitrary example) have been selectively bred (and in some cases, modified) for size, and because the soil mineral density has remained the same, the micronutrients per apple have not increased commensurate to the increase in carbohydrate weight and/or water weight. Thus, the resultant percentage will be lower, despite the quantity remaining the same.
We’re going to share some science on this, and/but would like to forewarn readers that the language of this paper is a bit biased, as it looks to “debunk” claims of nutritional values dropping while skimming over “yes, they really have dropped percentage-wise” in favor of “but look, the discrete mass values are still the same, so that’s just a mathematical illusion”.
The reality is, it’s no more a mathematical illusion than is the converse standpoint of saying the nutritional value is the same, despite the per-100g values dropping. After all, sometimes we eat an apple as-is; sometimes we buy a bag of frozen chopped fruit. That 500g bag of chopped fruit is going to contain less copper (for example) than one from decades past.
Here’s the paper, and you’ll see what we mean:
Supplements aren’t absorbed properly and thus are a waste of money: True or False?
True or False depending on the supplement (and your body, and the rest of your diet)
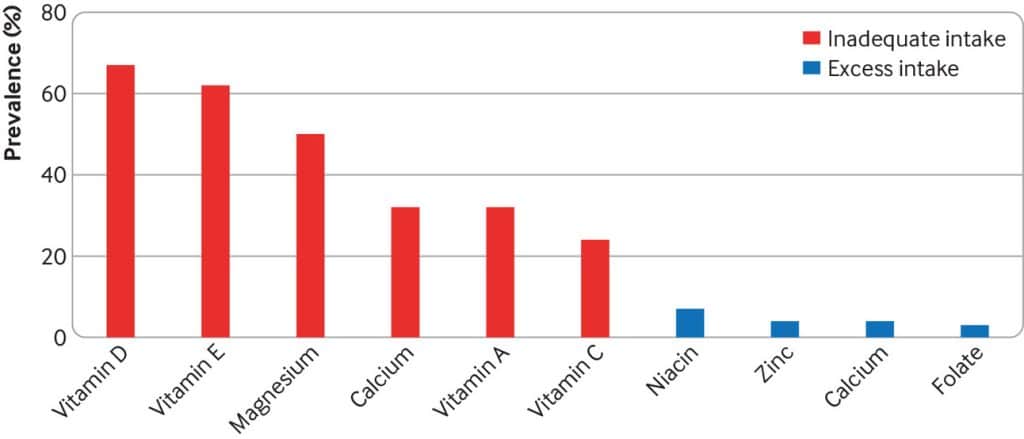
Many people are suffering from dietary deficiencies of vitamins and minerals, that could be easily correctable by supplementation:
However, as this study by Dr. Fang Fang Zhang shows, a lot of vitamin and mineral supplementation does not appear to have much of an effect on actual health outcomes, vis-à-vis specific diseases. She looks at:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Osteoporosis
Her key take-aways from this study were:
- Randomised trial evidence does not support use of vitamin, mineral, and fish oil supplements to reduce the risk of non-communicable diseases
- People using supplements tend to be older, female, and have higher education, income, and healthier lifestyles than people who do not use them
- Use of supplements appreciably reduces the prevalence of inadequate intake for most nutrients but also increases the prevalence of excess intake for some nutrients
- Further research is needed to assess the long term effects of supplements on the health of the general population and in individuals with specific nutritional needs, including those from low and middle income countries
Read her damning report: Health effects of vitamin and mineral supplements
On the other hand…
This is almost entirely about blanket vitamin-and-mineral supplementation. With regard to fish oil supplementation, many commercial fish oil supplements break down in the stomach rather than the intestines, and don’t get absorbed well. Additionally, many people take them in forms that aren’t pleasant, and thus result in low adherence (i.e., they nominally take them, but in fact they just sit on the kitchen counter for a year).
One thing we can conclude from this is that it’s good to check the science for any given supplement before taking it, and know what it will and won’t help for. Our “Monday Research Review” editions of 10almonds do this a lot, although we tend to focus on herbal supplements rather than vitamins and minerals.
We can get everything we need from our diet: True or False?
Contingently True (but here be caveats)
In principle, if we eat the recommended guideline amounts of various macro- and micro-nutrients, we will indeed get all that we are generally considered to need. Obviously.
However, this may come with:
- Make sure to get enough protein… Without too much meat, and also without too much carbohydrate, such as from most plant sources of protein
- Make sure to get enough carbohydrates… But only the right kinds, and not too much, nor at the wrong time, and without eating things in the wrong order
- Make sure to get enough healthy fats… Without too much of the unhealthy fats that often exist in the same foods
- Make sure to get the right amount of vitamins and minerals… We hope you have your calculators out to get the delicate balance of calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, and vitamin D right.
That last one’s a real pain, by the way. Too much or too little of one or another and the whole set start causing problems, and several of them interact with several others, and/or compete for resources, and/or are needed for the others to do their job.
And, that’s hard enough to balance when you’re taking supplements with the mg/µg amount written on them, never mind when you’re juggling cabbages and sardines.
On the topic of those sardines, don’t forget to carefully balance your omega-3, -6, and -9, and even within omega-3, balancing ALA, EPA, and DHA, and we hope you’re juggling those HDL and LDL levels too.
So, when it comes to getting everything we need from our diet, for most of us (who aren’t living in food deserts and/or experiencing food poverty, or having a medical condition that restricts our diet), the biggest task is not “getting enough”, it’s “getting enough of the right things without simultaneously overdoing it on the others”.
With supplements, it’s a lot easier to control what we’re putting in our bodies.
And of course, unless our diet includes things that usually can’t be bought in supermarkets, we’re not going to get the benefits of taking, as a supplement, such things as:
Etc.
So, there definitely are supplements with strong science-backed benefits, that probably can’t be found on your plate!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: