Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sea salt to MSG, we picked the MSG.
Why?
Surprise! Or maybe not? The results of the poll for this one should be interesting, and will help us know whether we need to keep mentioning in every second recipe that MSG is a healthier alternative to salt.
First of all, two things:
- Don’t be fooled by their respective names, and/or with such, an appeal to naturalism. For example, hydroxybenzoic acids are a major group of beneficial phenolic compounds, whereas hemlock is a wildflower that grows in this writer’s garden and will kill you if you eat it. Actually hydroxybenzoic acids also grow here (on the apple tree), but that’s not the point. The point is: worry less about names, and more about evidence!
- Don’t be fooled by the packaging. A lot of products go for “greenwashing” of one kind or another. You’re not eating the packaging (hopefully), so don’t be swayed by a graphic designer’s implementation of a marketing team’s aesthetic choices.
If naturalism is for some reason very important to you though, do bear in mind that glutamates occur generously in many common foodstuffs (tomatoes are a fine, healthy example) and eating tomato in the presence of salt will have the same biochemical effect as eating MSG, because it’s the same chemicals.
Since there are bad rumors about MSG’s safety, especially in the US where there is often a strong distrust of anything associated with China (actually MSG was first isolated in Japan, more than 100 years ago, by Japanese biochemist Dr. Kikunae Ikeda, but that gets drowned out by the “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome” fear in the US), know that this has resulted in MSG being one of the most-studied food additives in the last 40 years or so, with many teams of scientists trying to determine its risks and not finding any (aside from the same that could be said of any substance; anything in sufficient excess will kill you, including water or oxygen).
Well, that’s all been about safety, but what makes it healthier than sea salt?
Simply, it has about ⅓ of the sodium content, that’s all. So, if you are laboring all day in a field under the hot summer sun, then probably the sea salt will be healthier, to replenish more of the sodium you lost through sweat. But for most people most of the time, having less sodium rather than more is the healthier option.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
- MSG vs. Salt: Sodium Comparison ← here be chemistry
- More Salt, Not Less? ← No
- Pink Himalayan Salt: Health Facts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nicotine Benefits (That We Don’t Recommend)!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Does nicotine have any benefits at all? I know it’s incredibly addictive but if you exclude the addiction, does it do anything?❞
Good news: yes, nicotine is a stimulant and can be considered a performance enhancer, for example:
❝Compared with the placebo group, the nicotine group exhibited enhanced motor reaction times, grooved pegboard test (GPT) results on cognitive function, and baseball-hitting performance, and small effect sizes were noted (d = 0.47, 0.46 and 0.41, respectively).❞
Read in full: Acute Effects of Nicotine on Physiological Responses and Sport Performance in Healthy Baseball Players
However, another study found that its use as a cognitive enhancer was only of benefit when there was already a cognitive impairment:
❝Studies of the effects of nicotinic systems and/or nicotinic receptor stimulation in pathological disease states such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and schizophrenia show the potential for therapeutic utility of nicotinic drugs.
In contrast to studies in pathological states, studies of nicotine in normal-non-smokers tend to show deleterious effects.
This contradiction can be resolved by consideration of cognitive and biological baseline dependency differences between study populations in terms of the relationship of optimal cognitive performance to nicotinic receptor activity.
Although normal individuals are unlikely to show cognitive benefits after nicotinic stimulation except under extreme task conditions, individuals with a variety of disease states can benefit from nicotinic drugs❞
Read in full: Effects of nicotinic stimulation on cognitive performance
Bad news: its addictive qualities wipe out those benefits due to tolerance and thus normalization in short order. So you may get those benefits briefly, but then you’re addicted and also lose the benefits, as well as also ruining your health—making it a lose/lose/lose situation quite quickly.
As an aside, while nicotine is poisonous per se, in the quantities taken by most users, the nicotine itself is not usually what kills. It’s mostly the other stuff that comes with it (smoking is by far and away the worst of all; vaping is relatively less bad, but that’s not a strong statement in this case) that causes problems.
See also: Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
However, this is still not an argument for, say, getting nicotine gum and thinking “no harmful effects” because then you’ll be get a brief performance boost yes before it runs out and being addicted to it and now being in a position whereby if you stop, your performance will be lower than before you started (since you now got used to it, and it became your new normal), before eventually recovering:
In summary
We recommend against using nicotine in the first place, and for those who are addicted, we recommend quitting immediately if not contraindicated (check with your doctor if unsure; there are some situations where it is inadvisable to take away something your body is dependent on, until you correct some other thing first).
For more on quitting in general, see:
Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Take Your Mental Health As Seriously As General Health!
Sometimes, health and productivity means excelling—sometimes, it means avoiding illness and unproductivity. Both are essential, and today we’re going to tackle some ground-up stuff. If you don’t need it right now, great; we suggest to read it for when and if you do. But how likely is it that you will?
- One in four of us are affected by serious mental health issues in any given year.
- One in five of us have suicidal thoughts at some point in our lifetime.
- One in six of us are affected to at least some extent by the most commonly-reported mental health issues, anxiety and depression, in any given week.
…and that’s just what’s reported, of course. These stats are from a UK-based source but can be considered indicative generally. Jokes aside, the UK is not a special case and is not measurably worse for people’s mental health than, say, the US or Canada.
While this is not an inherently cheery topic, we think it’s an important one.
Depression, which we’re going to focus on today, is very very much a killer to both health and productivity, after all.
One of the most commonly-used measures of depression is known by the snappy name of “PHQ9”. It stands for “Patient Health Questionnaire Nine”, and you can take it anonymously online for free (without signing up for anything; it’s right there on the page already):
Take The PHQ9 Test Here! (under 2 minutes, immediate results)
There’s a chance you took that test and your score was, well, depressing. There’s also a chance you’re doing just peachy, or maybe somewhere in between. PHQ9 scores can fluctuate over time (because they focus on the past two weeks, and also rely on self-reports in the moment), so you might want to bookmark it to test again periodically. It can be interesting to track over time.
In the event that you’re struggling (or: in case one day you find yourself struggling, or want to be able to support a loved one who is struggling), some top tips that are useful:
Accept that it’s a medical condition like any other
Which means some important things:
- You/they are not lazy or otherwise being a bad person by being depressed
- You/they will probably get better at some point, especially if help is available
- You/they cannot, however, “just snap out of it”; illness doesn’t work that way
- Medication might help (it also might not)
Do what you can, how you can, when you can
Everyone knows the advice to exercise as a remedy for depression, and indeed, exercise helps many. Unfortunately, it’s not always that easy.
Did you ever see the 80s kids’ movie “The Neverending Story”? There’s a scene in which the young hero Atreyu must traverse the “Swamp of Sadness”, and while he has a magical talisman that protects him, his beloved horse Artax is not so lucky; he slows down, and eventually stops still, sinking slowly into the swamp. Atreyu pulls at him and begs him to keep going, but—despite being many times bigger and stronger than Atreyu, the horse just sinks into the swamp, literally drowning in despair.
See the scene: The Neverending Story movie clip – Artax and the Swamp of Sadness (1984)
Wow, they really don’t make kids’ movies like they used to, do they?
But, depression is very much like that, and advice “exercise to feel less depressed!” falls short of actually being helpful, when one is too depressed to do it.
If you’re in the position of supporting someone who’s depressed, the best tool in your toolbox will be not “here’s why you should do this” (they don’t care; not because they’re an uncaring person by nature, but because they are physiologically impeded from caring about themself at this time), but rather:
“please do this with me”
The reason this has a better chance of working is because the depressed person will in all likelihood be unable to care enough to raise and/or maintain an objection, and while they can’t remember why they should care about themself, they’re more likely to remember that they should care about you, and so will go with your want/need more easily than with their own. It’s not a magic bullet, but it’s worth a shot.
What if I’m the depressed person, though?
Honestly, the same, if there’s someone around you that you do care about; do what you can to look after you, for them, if that means you can find some extra motivation.
But I’m all alone… what now?
Firstly, you don’t have to be alone. There are free services that you can access, for example:
- US: https://nami.org/help
- Canada: https://www.wellnesstogether.ca/en-CA
- UK: https://www.samaritans.org/
…which varyingly offer advice, free phone services, webchats, and the like.
But also, there are ways you can look after yourself a little bit; do the things you’d advise someone else to do, even if you’re sure they won’t work:
- Take a little walk around the block
- Put the lights on when you’re not sleeping
- For that matter, get out of bed when you’re not sleeping. Literally lie on the floor if necessary, but change your location.
- Change your bedding, or at least your clothes
- If changing the bedding is too much, change just the pillowcase
- If changing your clothes is too much, change just one item of clothing
- Drink some water; it won’t magically cure you, but you’ll be in slightly better order
- On the topic of water, splash some on your face, if showering/bathing is too much right now
- Do something creative (that’s not self-harm). You may scoff at the notion of “art therapy” helping, but this is a way to get at least some of the lights on in areas of your brain that are a little dark right now. Worst case scenario is it’ll be a distraction from your problems, so give it a try.
- Find a connection to community—whatever that means to you—even if you don’t feel you can join it right now. Discover that there are people out there who would welcome you if you were able to go join them. Maybe one day you will!
- Hiding from the world? That’s probably not healthy, but while you’re hiding, take the time to read those books (write those books, if you’re so inclined), learn that new language, take up chess, take up baking, whatever. If you can find something that means anything to you, go with that for now, ride that wave. Motivation’s hard to come by during depression and you might let many things slide; you might as well get something out of this period if you can.
If you’re not depressed right now but you know you’re predisposed to such / can slip that way?
Write yourself instructions now. Copy the above list if you like.
Most of all: have a “things to do when I don’t feel like doing anything” list.
If you only take one piece of advice from today’s newsletter, let that one be it!
Share This Post
-
The Oh She Glows Cookbook – by Angela Liddon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s get the criticism out of the way first: notwithstanding the subtitle promising over 100 recipes, there are about 80-odd here, if we discount recipes that are no-brainer things like smoothies, sides such as for example “roasted garlic”, or meta-ingredients such as oat flour (instructions: blend the oats and you get oat flour).
The other criticism is more subjective: if you are like this reviewer, you will want to add more seasonings than recommended to most of the recipes. But that’s easy enough to do.
As for the rest: this is a very healthy cookbook, and quite wide-ranging and versatile, with recipes that are homely, with a lot of emphasis on comfort foods (but still, healthy), though certainly some are perfectly worthy of entertaining too.
A nice bonus of this book is that it offers a lot of available substitutions (much like we do at 10almonds), and also ways of turning the recipe into something else entirely with just a small change. This trait more than makes up for the slight swindle in terms of number of recipes, since some of the recipes have bonus recipes snuck in.
Bottom line: if you’d like to broaden your plant-based cooking range, this book is a fine option for expanding your repertoire.
Click here to check out The Oh She Glows Cookbook, and indeed glow!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Water Water Everywhere, But Which Is Best To Drink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Well Well Well…
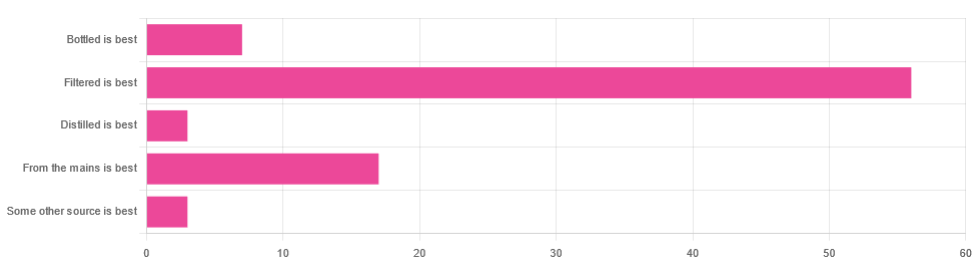
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on drinking water—with the understanding that this may vary from place to place. We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 65% said “Filtered is best”
- About 20% said “From the mains is best”
- About 8% said “Bottled is best”
- About 3% said “Distilled is best”
- About 3% said “Some other source is best”
Of those who said “some other source is best”, one clarified that their preferred source was well water.
So what does the science say?
Fluoridated water is bad for you: True or False?
False, assuming a normal level of consumption. Rather than take up more space today though, we’ll link to what we previously wrote on this topic:
You may be wondering: but what if my level of consumption is higher than normal?
Let’s quickly look at some stats:
- The maximum permitted safety level varies from place to place, but is (for example) 2mg/l in the US, 1.5mg/l in Canada & the UK.
- The minimum recommended amount also varies from place to place, but is (for example) 0.7mg/l in Canada and the US, and 1mg/l in the UK.
It doesn’t take grabbing a calculator to realize that if you drink twice as much water as someone else, then depending on where you are, water fluoridated to the minimum may give you more than the recommended maximum.
However… Those safety margins are set so much lower than the actual toxicity levels of fluoride, that it doesn’t make a difference.
For example: your writer here takes a medication that has the side effect of causing dryness of the mouth, and consequently she drinks at least 3l of water per day in a climate that could not be described as hot (except perhaps for about 2 weeks of the year). She weighs 72kg (that’s about 158 pounds), and the toxicity of fluoride (for ill symptoms, not death) is 0.2mg/kg. So, she’d need 14.4mg of fluoride, which even if the water fluoridation here were 2mg/l (it’s not; it’s lower here, but let’s go with the highest figure to make a point), would require drinking more than 7l of water faster than the body can process it.
For more about the numbers, check out:
Acute Fluoride Poisoning from a Public Water System
Bottled water is the best: True or False?
False, if we consider “best” to be “healthiest”, which in turn we consider to be “most nutrients, with highest safety”.
Bottled water generally does have higher levels of minerals than most local mains supply water does. That’s good!
But you know what else is generally has? Microplastics and nanoplastics. That’s bad!
We don’t like to be alarmist in tone; it’s not what we’re about here, but the stats on bottled water are simply not good; see:
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
You may be wondering: “but what about bottled water that comes in glass bottles?”
Indeed, water that comes in glass bottles can be expected to have lower levels of plastic than water that comes in plastic bottles, for obvious reasons.
However, we invite you to consider how likely you believe it to be that the water wasn’t stored in plastic while being processed, shipped and stored, before being portioned into its final store-ready glass bottles for end-consumer use.
Distilled water is the best: True or False?
False, generally, with caveats:
Distilled water is surely the safest water anywhere, because you know that you’ve removed any nasties.
However, it’s also devoid of nutrients, because you also removed any minerals it contained. Indeed, if you use a still, you’ll be accustomed to the build-up of these minerals (generally simplified and referenced as “limescale”, but it’s a whole collection of minerals).
Furthermore, that loss of nutrients can be more than just a “something good is missing”, because having removed certain ions, that water could now potentially strip minerals from your teeth. In practice, however, you’d probably have to swill it excessively to cause this damage.
Nevertheless, if you have the misfortune of living somewhere like Flint, Michigan, then a water still may be a fair necessity of life. In other places, it can simply be useful to have in case of emergency, of course.
Here’s an example product on Amazon if you’d like to invest in a water still for such cases.
PS: distilled water is also tasteless, and is generally considered bad, tastewise, for making tea and coffee. So we really don’t recommend distilling your water unless you have a good reason to do so.
Filtered water is the best: True or False?
True for most people in most places.
Let’s put it this way: it can’t logically be worse than whatever source of water you put into it…
Provided you change the filter regularly, of course.
Otherwise, after overusing a filter, at best it won’t be working, and at worst it’ll be adding in bacteria that have multiplied in the filter over however long you left it there.
You may be wondering: can water filters remove microplastics, and can they remove minerals?
The answer in both cases is: sometimes.
- For microplastics it depends on the filter size and the microplastic size (see our previous article for details on that).
- For minerals, it depends on the filter type. Check out:
The H2O Chronicles | 5 Water Filters That Remove Minerals
One other thing to think about: while most water filtration jugs are made of PFAS-free BPA-free plastics for obvious reasons, for greater peace of mind, you might consider investing in a glass filtration jug, like this one ← this is just one example product on Amazon; by all means shop around and find one you like
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sunflower Corn Burger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burgers are rarely a health food, but in this case, everything in the patty is healthy, and it’s packed with protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
You will need
- 1 can chickpeas
- ¾ cup frozen corn
- ½ cup chopped fresh parsley
- ⅓ cup sunflower seeds
- ⅓ cup cornichon pickles
- ⅓ cup wholegrain bread crumbs (gluten-free, if desired/required)
- ¼ bulb garlic (or more if you want a stronger flavor)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for frying
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (or 1 tsp yeast extract)
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp red pepper flakes
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp Dijon mustard
- To serve: 4 burger buns; these are not usually healthy, so making your own is best, but if you don’t have the means/time, then getting similarly shaped wholegrain bread buns works just fine.
- Optional: your preferred burger toppings, e.g. greenery, red onion, tomato slices, avocado, jalapeños, whatever does it for you
Note: there is no need to add salt; there is enough already in the pickles.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine all the ingredients except the buns (and any optional toppings) in a food processor, pulsing a few times for a coarse texture (not a purée).
2) Shape the mixture into 4 burger patties, and let them chill in the fridge for at least 30 minutes.
3) Heat a skillet over a medium-high heat with some olive oil, and fry the burgers on both sides until they develop a nice golden crust; this will probably take about 4 minutes per side.
4) Assemble in the buns with any toppings you want, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier? ← pumpkin seeds have more micronutrients; sunflower seeds have more healthy fats; feel free to use either or both in this recipe
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is TikTok right? Are there health benefits to eating sea moss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sea moss is the latest “superfood” wellness influencers are swearing by. They claim sea moss products – usually in gel form – have multiple health benefits. These include supporting brain and immune function, or protecting against viruses and other microbes.
But do these health claims stack up? Let’s take a look.
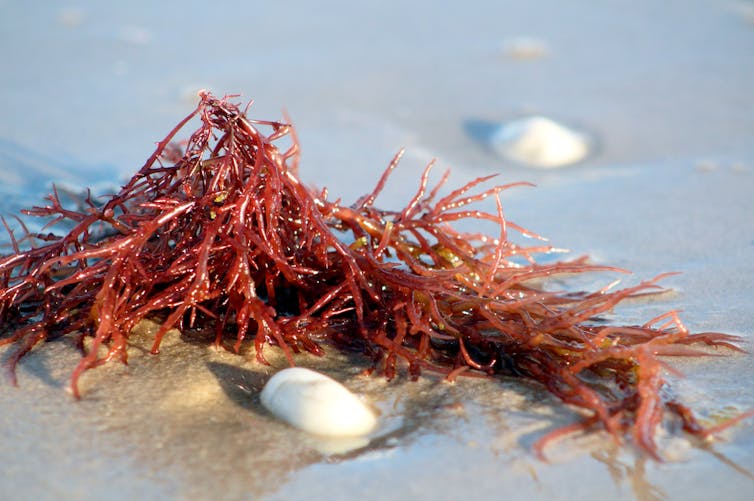
Plataresca/Shutterstock What is sea moss?
Sea moss is produced using a kind of seaweed – particularly red algae – that grow in various locations all around the world. Three main species are used in sea moss products:
- Chondrus crispus (known as Irish moss or carrageenan moss)
- Eucheuma cottonii (sea moss or seabird’s nest)
- Gracilaria (Irish moss or ogonori).
Some products also contain the brown algae Fucus vesiculosus (commonly known as bladderwrack, black tang, rockweed, sea grapes, bladder fucus, sea oak, cut weed, dyers fucus, red fucus or rock wrack).
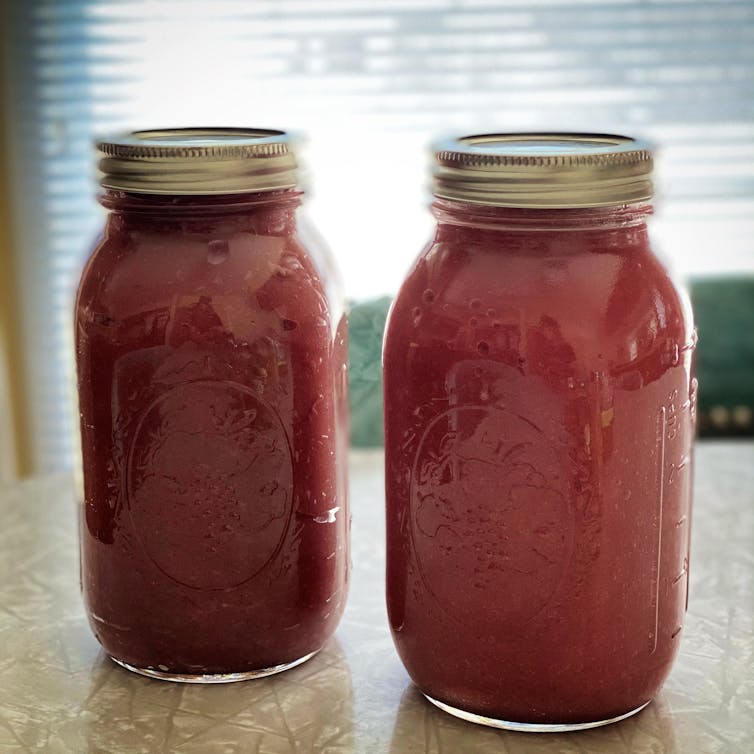
Most sea moss products are sold as a gel that can be added to recipes, used in smoothies, frozen into ice cubes or eaten on its own. The products also come in capsule form or can be purchased “raw” and used to make your own gels at home.
Several kinds of red algae are used in commercially-available sea moss products. Nancy Ann Bowe/Shutterstock What’s the evidence?
Sea moss products claim a host of potential health benefits, from supporting immunity, to promoting skin health and enhancing mood and focus, among many others.
But is there any evidence supporting these claims?
Recent studies have reviewed the biological properties of the main sea moss species (Chondrus crispus, Eucheuma cottonii, Gracilaria and Fucus vesiculosus).
They suggest these species may have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic and probiotic properties.
However, the vast majority of research relating to Chondrus crispus, Gracilaria and Fucus vesiculosus – and all of the research on Eucheuma cottonii – comes from studies done in test tubes or using cell and animal models. We should not assume the health effects seen would be the same in humans.
In cell and animal studies, researchers usually administer algae in a laboratory and use specific extracts rich in bioactive compounds rather than commercially available sea moss products.
They also use very different – often relatively larger – amounts compared to what someone would typically consume when they eat sea moss products.
This means the existing studies can’t tell us about the human body’s processes when eating and digesting sea moss.
Sea moss may have similar effects in humans. But so far there is very little evidence people who consume sea moss will experience any of the claimed health benefits.
Nutritional value
Eating sea moss does not replace the need for a balanced diet, including a variety of fruits and vegetables.
Chondrus crispus, Eucheuma cottonii and Gracilaria, like many seaweeds, are rich sources of nutrients such as fatty acids, amino acids, vitamin C and minerals. These nutrients are also likely to be present in sea moss, although some may be lost during the preparation of the product (for example, soaking may reduce vitamin C content), and those that remain could be present in relatively low quantities.
There are claims that sea moss may be harmful for people with thyroid problems. This relates to the relationship between thyroid function and iodine. The algae used to make sea moss are notable sources of iodine and excess iodine intake can contribute to thyroid problems, particularly for people with pre-existing conditions. That is why these products often carry disclaimers related to iodine sensitivity or thyroid health.
Is it worth it?
So you may be wondering if it’s worth trying sea moss. Here are a few things to consider before you decide whether to start scooping sea moss into your smoothies.
A 375mL jar costs around $A25–$30 and lasts about seven to ten days, if you follow the recommended serving suggestion of two tablespoons per day. This makes it a relatively expensive source of nutrients.
Sea moss is commonly sold as a gel that can be eaten on a kitchen bench. April Sims/Shutterstock Sea moss is often hyped for containing 92 different minerals. While there may be 92 minerals present, the amount of minerals in the algae will vary depending on growing location and conditions.
The efficiency with which minerals from algae can be absorbed and used by the body also varies for different minerals. For example, sodium is absorbed well, while only about 50% of iodine is absorbed.
But sea moss has also been shown to contain lead, mercury and other heavy metals – as well as radioactive elements (such as radon) that can be harmful to humans. Seaweeds are known for their ability to accumulate minerals from their environment, regardless of whether these are beneficial or harmful for human nutrition. Remember, more doesn’t always mean better.
What else am I eating?
While you won’t get a full nutritional breakdown on the jar, it is always wise to check what other ingredients you may be eating. Sea moss products can contain a range of other ingredients, such as lime, monk fruit powder, spirulina and ginger, among many others.
These ingredients differ between brands and products, so be aware of your needs and always check.
Despite their health claims, most sea moss products also carry disclaimers indicating that the products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
If you have concerns about your health, always speak to a health professional for accurate and personalised medical advice.
Margaret Murray, Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: