Spiced Fruit & Nut Chutney
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
‘Tis the season to make the chutney that will then be aged chutney when you want it later! And unlike supermarket varieties with their ingredients list that goes “Sugar, spirit vinegar, inverted glucose-fructose syrup,” this one has an array of health-giving fruits and nuts (just omit the nuts if you or someone you may want to give this to has an allergy), and really nothing bad in here at all. And of course, tasty healthful spices!
You will need
- 2 red onions, chopped
- 1½ cups dried apricots, chopped
- 1½ cups dried figs, chopped
- 1 cup raisins
- ½ cup apple cider vinegar
- ½ cup slivered almonds
- ½ lime, chopped and deseeded
- ¼ bulb garlic, chopped
- 1 hot pepper, chopped (your choice what kind; omit if you don’t like heat at all; multiply if you want more heat)
- 2 tablespoons honey or maple syrup (omit for a less sweet chutney; there is sweetness in the dried fruits already, after all)
- 1 tbsp freshly grated ginger
- 2 tsp sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp nutmeg
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ teaspoon allspice
- ½ MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a heavy-based pan that will be large enough for all ingredients to go into eventually. Fry the onions on a gentle heat for around 15 minutes. We don’t need to caramelize them yet (this will happen with time), but we do want them soft and sweet already.
2) Add the ginger, garlic, and chili, and stir in well.
3) When the onions start to brown, add the fruit and stir well to mix thoroughly.
4) Add the honey or maple syrup (if using), and the vinegar; add the remaining spices/seasonings, so everything is in there now except the almonds.
5) Cook gently for another 30 minutes while stirring. At some point it’ll become thick and sticky; add a little water as necessary. You don’t want to drown it, but you do want it to stay moist. It’ll probably take only a few tablespoons of added water in total, but add them one at a time and stir in before judging whether more is needed. By the end of the 30 minutes, it should be more solid, to the point it can stand up by itself.
6) Add the almonds, stir to combine, and leave to cool. Put it in jars until you need it (or perhaps give it as gifts).
Alternative method: if you don’t want to be standing at a stove stirring for about an hour in total, you can use a slow cooker / crock pot instead. Put the same ingredients in the same order, but don’t stir them, just leave them in layers (this is because of the pattern of heat distribution; it’ll be hotter at the bottom, so the things that need to be more cooked should be there, and the design means they won’t burn) for about two hours, then stir well to mix thoroughly, and leave it for another hour or two, before turning it off to let it cool. Put it in jars until you need it (or perhaps give it as gifts).
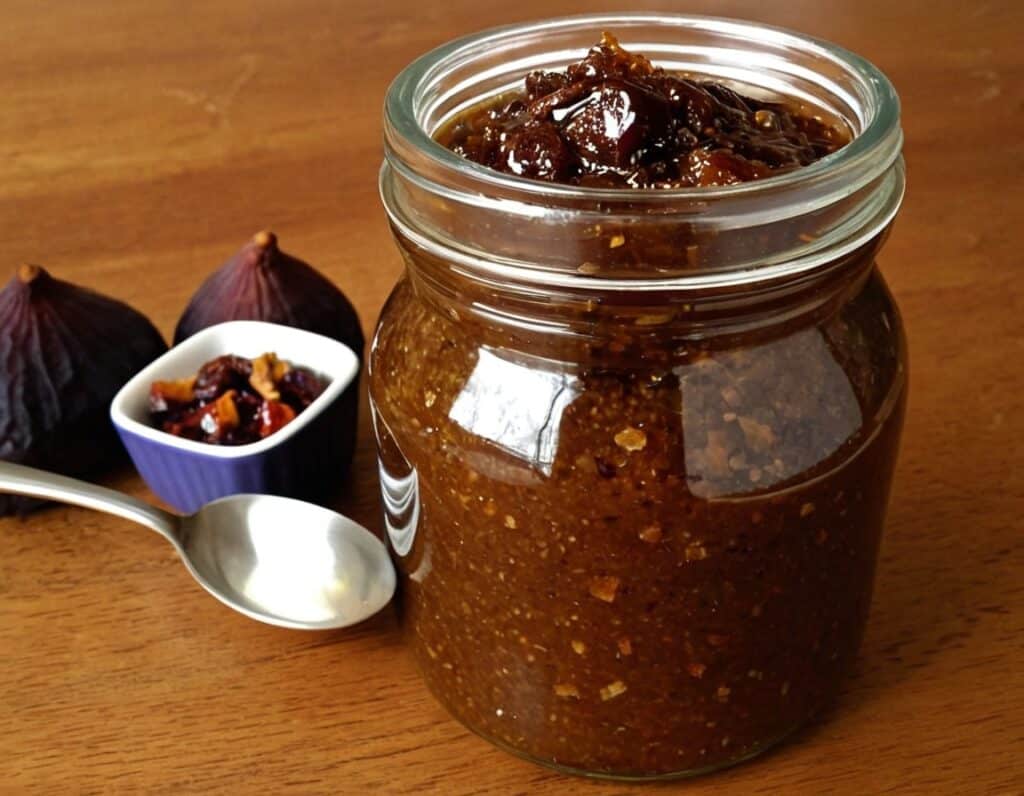

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← figs and apricots appear here
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Almonds vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier? ← almonds won, but walnuts were close and would also work in this recipe
- Pistachios vs Almonds – Which is Healthier? ← almonds won, but pistachios were close and would also work in this recipe
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored 4/5 today!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What causes the itch in mozzie bites? And why do some people get such a bad reaction?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you one of these people who loathes spending time outdoors at dusk as the weather warms and mosquitoes start biting?
Female mosquitoes need blood to develop their eggs. Even though they take a tiny amount of our blood, they can leave us with itchy red lumps that can last days. And sometimes something worse.
So why does our body react and itch after being bitten by a mosquito? And why are some people more affected than others?
Arthur Poulin/Unsplash What happens when a mosquito bites?
Mosquitoes are attracted to warm blooded animals, including us. They’re attracted to the carbon dioxide we exhale, our body temperatures and, most importantly, the smell of our skin.
The chemical cocktail of odours from bacteria and sweat on our skin sends out a signal to hungry mosquitoes.
Some people’s skin smells more appealing to mosquitoes, and they’re more likely to be bitten than others.
Once the mosquito has made its way to your skin, things get a little gross.
The mosquito pierces your skin with their “proboscis”, their feeding mouth part. But the proboscis isn’t a single, straight, needle-like tube. There are multiple tubes, some designed for sucking and some for spitting.
Once their mouth parts have been inserted into your skin, the mosquito will inject some saliva. This contains a mix of chemicals that gets the blood flowing better.
There has even been a suggestion that future medicines could be inspired by the anti-blood clotting properties of mosquito saliva.
A common pest mosquito around the world, Culex quinquefasciatus. Cameron Webb (NSW Health Pathology), CC BY It’s not the stabbing of our skin by the mosquito’s mouth parts that hurts, it’s the mozzie spit our bodies don’t like.
Are some people allergic to mosquito spit?
Once a mosquito has injected their saliva into our skin, a variety of reactions can follow. For the lucky few, nothing much happens at all.
For most people, and irrespective of the type of mosquito biting, there is some kind of reaction. Typically there is redness and swelling of the skin that appears within a few hours, but often more quickly, after just a few minutes.
Occasionally, the reaction can cause pain or discomfort. Then comes the itchiness.
Some people do suffer severe reactions to mosquito bites. It’s a condition often referred to as “skeeter syndrome” and is an allergic reaction caused by the protein in the mosquito’s saliva. This can cause large areas of swelling, blistering and fever.
The chemistry of mosquito spit hasn’t really been well studied. But it has been shown that, for those who do suffer allergic reactions to their bites, the reactions may differ depending on the type of mosquito biting.
We all probably get more tolerant of mosquito bites as we get older. Young children are certainly more likely to suffer more following mosquito bites. But as we get older, the reactions are less severe and may pass quickly without too much notice.
How best to treat the bites?
Research into treating bites has yet to provide a single easy solution.
There are many myths and home remedies about what works. But there is little scientific evidence supporting their use.
The best way to treat mosquito bites is by applying a cold pack to reduce swelling and to keep the skin clean to avoid any secondary infections. Antiseptic creams and lotions may also help.
There is some evidence that heat may alleviate some of the discomfort.
It’s particularly tough to keep young children from scratching at the bite and breaking the skin. This can form a nasty scab that may end up being worse than the bite itself.
Applying an anti-itch cream may help. If the reactions are severe, antihistamine medications may be required.
To save the scratching, stop the bites
Of course, it’s better not to be bitten by mosquitoes in the first place. Topical insect repellents are a safe, effective and affordable way to reduce mosquito bites.
Covering up with loose fitted long sleeved shirts, long pants and covered shoes also provides a physical barrier.
Mosquito coils and other devices can also assist, but should not be entirely relied on to stop bites.
There’s another important reason to avoid mosquito bites: millions of people around the world suffer from mosquito-borne diseases. More than half a million people die from malaria each year.
In Australia, Ross River virus infects more than 5,000 people every year. And in recent years, there have been cases of serious illnesses caused by Japanese encephalitis and Murray Valley encephalitis viruses.
Cameron Webb, Clinical Associate Professor and Principal Hospital Scientist, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Make Your Negativity Work For You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s The Right Balance?
We’ve written before about positivity the pitfalls and perils of toxic positivity:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
…as well as the benefits that can be found from selectively opting out of complaining:
A Bone To Pick… Up And Then Put Back Where We Found It
So… What place, if any, does negativity usefully have in our lives?
Carrot and Stick
We tend to think of “carrot and stick” motivation being extrinsic, i.e. there is some authority figure offering is reward and/or punishment, in response to our reactions.
In those cases when it really is extrinsic, the “stick” can still work for most people, by the way! At least in the short term.
Because in the long term, people are more likely to rebel against a “stick” that they consider unjust, and/or enter a state of learned helplessness, per “I’ll never be good enough to satisfy this person” and give up trying to please them.
But what about when you have your own carrot and stick? What about when it comes to, for example, your own management of your own healthy practices?
Here it becomes a little different—and more effective. We’ll get to that, but first, bear with us for a touch more about extrinsic motivation, because here be science:
We will generally be swayed more easily by negative feelings than positive ones.
For example, a study was conducted as part of a blood donation drive, and:
- Group A was told that their donation could save a life
- Group B was told that their donation could prevent a death
The negative wording given to group B boosted donations severalfold:
Read the paper: Life or Death Decisions: Framing the Call for Help
We have, by the way, noticed a similar trend—when it comes to subject lines in our newsletters. We continually change things up to see if trends change (and also to avoid becoming boring), but as a rule, the response we get from subscribers is typically greater when a subject line is phrased negatively, e.g. “how to avoid this bad thing” rather than “how to have this good thing”.
How we can all apply this as individuals?
When we want to make a health change (or keep up a healthy practice we already have)…
- it’s good to note the benefits of that change/practice!
- it’s even better to note the negative consequences of not doing it
For example, if you want to overcome an addiction, you will do better for your self-reminders to be about the bad consequences of using, more than the good consequences of abstinence.
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
This goes even just for things like diet and exercise! Things like diet and exercise can seem much more low-stakes than substance abuse, but at the end of the day, they can add healthy years onto our lives, or take them off.
Because of this, it’s good to take time to remember, when you don’t feel like exercising or do feel like ordering that triple cheeseburger with fries, the bad outcomes that you are planning to avoid with good diet and exercise.
Imagine yourself going in for that quadruple bypass surgery, asking yourself whether the unhealthy lifestyle was worth it. Double down on the emotions; imagine your loved ones grieving your premature death.
Oof, that was hard-hitting
It was, but it’s effective—if you choose to do it. We’re not the boss of you! Either way, we’ll continue to send the same good health advice and tips and research and whatnot every day, with the same (usually!) cheery tone.
One last thing…
While it’s good to note the negative, in order to avoid the things that lead to it, it’s not so good to dwell on the negative.
So if you get caught in negative thought spirals or the like, it’s still good to get yourself out of those.
If you need a little help with that sometimes, check out these:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
21 Most Beneficial Polyphenols & What Foods Have Them
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We often write about polyphenols here at 10almonds; sometimes mentioning that a certain food is good because it has them, or else occasionally an entire article about a particular polyphenol. But what about a birds-eye view of polyphenols as a whole?
Well, there are many, but we’ve picked 21 particularly beneficial for human health, and what foods contain them.
We’ll be working from this fantastic database, by the way:
❝Phenol-Explorer is the first comprehensive database on polyphenol content in foods. The database contains more than 35,000 content values for 500 different polyphenols in over 400 foods. These data are derived from the systematic collection of more than 60,000 original content values found in more than 1,300 scientific publications. Each of these publications has been critically evaluated before inclusion in the database. The whole data on the polyphenol composition of foods is available for download.❞
Source: Phenol-Explorer.EU | Database on polyphenol content in foods
We use this database at least several times per week while writing 10almonds; it’s a truly invaluable resource!
However, 500 is a lot, so here’s a rundown of 21 especially impactful ones; we’ve sorted them per the categories used in the explorer, and in some cases we’ve aggregated several very similar polyphenols typically found together in the same foods, into one item (so for example we just list “quercetin” instead of quercetin 3-O-rutinoside + quercetin 4′-O-glucoside + quercetin 3,4′-O-diglucoside, etc etc). We’ve also broadly grouped some particularly populous ones such as “anthocyanins”, “catechins”, and so forth.
Without further ado, here’s what you ideally want to be getting plenty of in your diet:
Flavonoids
- Quercetin
- Foods: onions, apples, berries, kale, broccoli, capers.
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, reduces allergy symptoms, supports heart and brain health, and may lower blood pressure.
- See also: Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
- Kaempferol
- Foods: spinach, kale, tea (green and black), capers, brussels sprouts.
- Benefits: antioxidant, may reduce the risk of cancer, supports cardiovascular health, and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
- Foods: green tea, matcha.
- Benefits: potent antioxidant, promotes weight loss, supports brain health, and may reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Anthocyanins
- Foods: blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, red cabbage, cherries.
- Benefits: improve brain health, support eye health, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Apigenin
- Foods: parsley, celery, chamomile tea.
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, reduces anxiety, and supports brain and immune system health.
- Luteolin
- Foods: peppers, thyme, celery, carrots.
- Benefits: anti-inflammatory, supports brain health, and may help reduce the growth of cancer cells.
- Catechins (aside from EGCG)
- Foods: green tea, dark chocolate, apples
- Benefits: boosts metabolism, supports cardiovascular health, and reduces oxidative stress.
- Hesperidin
- Foods: oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits.
- Benefits: supports vascular health, reduces inflammation, and may help manage diabetes.
- Naringenin
- Foods: oranges, grapefruits, tomatoes.
- Benefits: antioxidant, supports liver health, and may improve cholesterol levels.
For more on epigallocatechin gallate and other catechins, see: Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
Phenolic Acids
- Chlorogenic acid
- Foods: coffee, artichokes, apples, pears.
- Benefits: supports weight management, improves blood sugar regulation, and reduces inflammation.
- See also: Green Coffee Bean Extract: Coffee Benefits Without The Coffee?
- Caffeic acid
- Foods: coffee, thyme, sage, basil.
- Benefits: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and supports skin health.
- See also: The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Ferulic acid
- Foods: whole grains, rice bran, oats, flaxseeds, spinach.
- Benefits: protects skin from UV damage, reduces inflammation, and supports cardiovascular health.
- Gallic acid
- Foods: green tea, berries, walnuts.
- Benefits: antioxidant, may reduce the risk of cancer, and supports brain health.
Stilbenes
- Resveratrol
- Foods: red currants, blueberries, peanuts.
- Benefits: anti-aging properties, supports heart health, and reduces inflammation.
- See also: Resveratrol & Healthy Aging ← and no, you can’t usefully get it from red wine; here’s why!
Lignans
- Secoisolariciresinol
- Foods: flaxseeds, sesame seeds, whole grains.
- Benefits: supports hormone balance, reduces the risk of hormone-related cancers, and promotes gut health.
- Matairesinol
- Foods: rye, oats, barley, sesame seeds.
- Benefits: hormonal support, antioxidant, and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
See also: Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc ← for maximum nutritional availability!
Tannins
- Ellagic acid
- Foods: pomegranates, raspberries, walnuts.
- Benefits: anti-cancer properties, supports skin health, and reduces inflammation.
- Proanthocyanidins
- Foods: cranberries, apples, grapes, dark chocolate.
- Benefits: supports urinary tract health, reduces inflammation, and improves blood vessel health.
See also: Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Curcuminoids
- Curcumin
- Foods: turmeric.
- Benefits: potent anti-inflammatory, supports joint health, and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- See also: Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Isoflavones
- Genistein
- Foods: soybeans, chickpeas.
- Benefits: supports bone health, reduces the risk of hormone-related cancers, and promotes heart health.
- Daidzein
- Foods: soybeans, legumes.
- Benefits: hormonal balance, supports bone health, and may help alleviate menopausal symptoms.
See also: What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
Well, that’s a lot of things to remember!
If you want to make it easier for yourself, you can simply make sure to get at least 30 different kinds of plant into your diet per week, and by doing so, statistically, you should cover most of these!
Read more: What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Alternatively, for a middle-ground approach of targetting 16 most polyphenol delivering foods, check out this super-dense arrangement:
Mediterranean Diet… In A Pill? ← it’s about plant extracts from 16 specific foods, and the polyphenols they deliver
Enjoy!
Share This Post
- Quercetin
Related Posts
-
Fennel vs Artichoke – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing fennel to artichoke, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Both are great! But artichoke wins on nutritional density.
In terms of macros, artichoke has more protein and more fiber, for only slightly more carbs.
Vitamins are another win for artichoke, boasting more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, and choline. Meanwhile, fennel has more of vitamins A, E, and K, which is also very respectable but does allow artichoke a 6:3 lead.
In the category of minerals, artichoke has a lot more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus, while fennel has a little more calcium, potassium, and selenium.
One other relevant factor is that fennel is a moderate appetite suppressant, which may be good or bad depending on your food-related goals.
All in all though, we say the artichoke wins by virtue of its greater abundance of nutrients!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? ← appropriately enough, with fennel hearts and artichoke hearts!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Common Hospital Blood Pressure Mistake (Don’t Let This Happen To You Or A Loved One)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a major issue in healthcare, Dr. Suneel Dhand tells us, pertaining to the overtreatment of hypertension in hospitals. Here’s how to watch out for it and know when to question it:
Under pressure
When patients, particularly from older generations, are admitted to the hospital, their blood pressure often fluctuates due to illness, dehydration, and other factors. Despite this, they are often continued on their usual blood pressure medications, which can lead to dangerously low blood pressure.
Why does this happen? The problem arises from rigid protocols that dictate stopping blood pressure medication only if systolic pressure is below a certain threshold, often 100. However, Dr. Dhand argues that 100 is already low*, and administering medication when blood pressure is close to this can cause it to drop dangerously lower
*10almonds note: low for an adult, anyway, and especially for an older adult. To be clear: it’s not a bad thing! That is the average systolic blood pressure of a healthy teenager and it’s usually the opposite of a problem if we have that when older (indeed, this very healthy writer’s blood pressure averages 100/70, and suffice it to say, it’s been a long time since I was a teenager). But it does mean that we definitely don’t want to take medications to artificially lower it from there.
Low blood pressure from overtreatment can lead to severe consequences, requiring emergency interventions to stabilize the patient.
Dr. Dhand’s advice for patients and families is:
- Ensure medication accuracy: make sure the medical team knows the correct blood pressure medications and dosages for you or your loved one.
- Monitor vital signs: actively check blood pressure readings, especially if they are in the low 100s or even 110s, and discuss any medication concerns with the medical team.
- Watch for symptoms of low blood pressure: be alert for symptoms like dizziness or weakness, which could indicate dangerously low blood pressure.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Natto vs Tempeh – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing nattō to tempeh, we picked the nattō.
Why?
Both are great, but in the battle of fermented soybeans vs fermented soybeans with extra steps, it turns out that the simplest option is the best, even if tempeh was a close runner-up:
In terms of macros, nattō has more carbs and fiber for the same protein and fat; we’ll call this category a tie or a marginal win for nattō.
In the category of vitamins, nattō has more of vitamins B1, C, E, K, and choline, while tempeh has more of vitamins B2, B3, B6, and B9. A clearer, yet still modest, win for nattō.
Minerals, however, are what really set them apart: nattō has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while tempeh has more phosphorus. An overwhelming win for nattō this time.
In short: enjoy either or both, but nattō is the more nutritionally dense option!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nattō is featured as part of the diet 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: