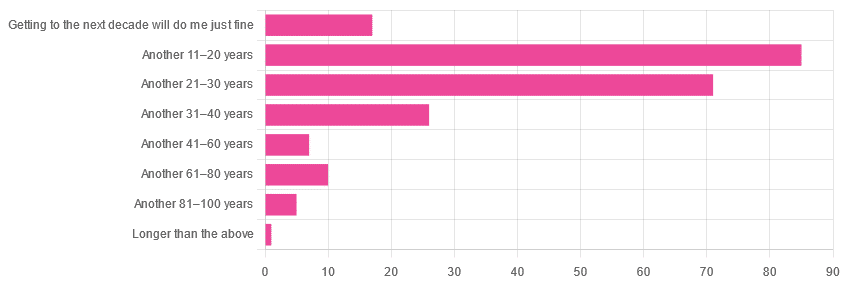DBT Made Simple – by Sheri van Dijk
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book offers very clear explanations of DBT. In fact, a more fitting title might have been “DBT made clear”, because it does it without oversimplification.
This is a way in which van Dijk’s work stands out from that of many writers on the subject! Many authors oversimplify, to the point that a reader may wonder “is that all it is?” when, in reality, there’s rather more to it.
This work is, therefore, refreshingly comprehensive, without sacrificing clarity.
Van Dijk also takes us through the four pillars of DBT:
- Mindfulness
- Distress tolerance
- Emotional regulation
- Interpersonal effectiveness
Each of these can help an individual alone; together, they produce a composite effect with a synergy that makes each more effective. Hence, pillars.
On the topic of “an individual”, you may be wondering “is this book for therapists or the general public?” and the answer is yes, yes it is.
That is to say: it’s written with the assumption that the reader wants to learn DBT in order to practice it as a therapist… and/but is written in such a fashion that it’s very easy to apply the skills to oneself, too. As it’s an introductory guide—a comprehensive one, but without assuming prior knowledge—it’s a perfect resource for anyone to get a good grounding in the subject.
Bottom line: if you’ve been hearing about DBT (possibly from us!) and wondering where you might start, this book is an excellent place to begin.
Click here to check out DBT Made Simple, and start making many parts of life easier!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
See what other 10almonds subscribers are asking!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Q: I would be interested in learning more about collagen and especially collagen supplements/powders and of course if needed, what is the best collagen product to take. What is collagen? Why do we need to supplement the collagen in our body? Thank you PS love the information I am receiving in the news letters. Keep it up
We’re glad you’re enjoying them! Your request prompted us to do our recent Research Review Monday main feature on collagen supplementation—we hope it helped, and if you’ve any more specific (or other) question, go ahead and let us know! We love questions and requests
Q: Great article about the health risks of salt to organs other than the heart! Is pink Himalayan sea salt, the pink kind, healthier?
Thank you! And, no, sorry. Any salt that is sodium chloride has the exact same effect because it’s chemically the same substance, even if impurities (however pretty) make it look different.
If you want a lower-sodium salt, we recommend the kind that says “low sodium” or “reduced sodium” or similar. Check the ingredients, it’ll probably be sodium chloride cut with potassium chloride. Potassium chloride is not only not a source of sodium, but also, it’s a source of potassium, which (unlike sodium) most of us could stand to get a little more of.
For your convenience: here’s an example on Amazon!
Bonus: you can get a reduced sodium version of pink Himalayan salt too!
Q: Can you let us know about more studies that have been done on statins? Are they really worth taking?
That is a great question! We imagine it might have been our recent book recommendation that prompted it? It’s quite a broad question though, so we’ll do that as a main feature in the near future!
Q: Is MSG healthier than salt in terms of sodium content or is it the same or worse?
Great question, and for that matter, MSG itself is a great topic for another day. But your actual question, we can readily answer here and now:
- Firstly, by “salt” we’re assuming from context that you mean sodium chloride.
- Both salt and MSG do contain sodium. However…
- MSG contains only about a third of the sodium that salt does, gram-for-gram.
- It’s still wise to be mindful of it, though. Same with sodium in other ingredients!
- Baking soda contains about twice as much sodium, gram for gram, as MSG.
Wondering why this happens?
Salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is equal parts sodium and chlorine, by atom count, but sodium’s atomic mass is lower than chlorine’s, so 100g of salt contains only 39.34g of sodium.
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO₃) is one part sodium for one part hydrogen, one part carbon, and three parts oxygen. Taking each of their diverse atomic masses into account, we see that 100g of baking soda contains 27.4g sodium.
MSG (monosodium glutamate, C₅H₈NO₄Na) is only one part sodium for 5 parts carbon, 8 parts hydrogen, 1 part nitrogen, and 4 parts oxygen… And all those other atoms put together weigh a lot (comparatively), so 100g of MSG contains only 12.28g sodium.
Q: Thanks for the info about dairy. As a vegan, I look forward to a future comment about milk alternatives
Thanks for bringing it up! What we research and write about is heavily driven by subscriber feedback, so notes like this really help us know there’s an audience for a given topic!
We’ll do a main feature on it, to do it justice. Watch out for Research Review Monday!
Share This Post
-
International Women’s Day (and what it can mean for you, really)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to not just #EmbraceEquity, but actually grow it, this International Women’s Day!
It’s International Women’s Day, and there’s a lot going on beyond the hashtagging! So, what’s happening, and how could you get involved in more than a “token” way in your workplace, business, or general life?
Well, that depends on your own environment and circumstances, but for example…
A feminist policy for productivity in the food sector?
We tend to think that in this modern world, we all have equal standing when it comes to productivity, food, and health. And yet…
❝If women do 70 per cent of the work in agriculture worldwide, but the land is mainly owned by men, then we don’t have equity yet. If in Germany, only one-tenth of female farmers manage the farm on which they work on, while they also manage the household, then there is no equity yet❞
~ Lea Leimann, Germany
What to do about it, though? It turns out there’s a worldwide organization dedicated to fixing this! It’s called Slow Food.
Their mission is to make food…
- GOOD: quality, flavorsome and healthy food
- CLEAN: production that does not harm the environment
- FAIR: accessible prices for consumers and fair conditions and pay for producers
…and yes, that explicitly includes feminism-attentive food policy:
Read all about it: Slow Food women forge change in the food system
Do you work in the food system?
If so, you can have an impact. Your knee-jerk reaction might be “I don’t”, but there are a LOT of steps from farm-to-table, so, are you sure?
Story time: me, I’m a writer (you’d never have guessed, right?) and wouldn’t immediately think of myself as working “in the food system”.
But! Not long back I (a woman) was contracted by a marketing agent (a woman) to write marketing materials for a small business (owned by a woman) selling pickles and chutneys across the Australian market, based on the recipes she learned from her mother, in India. The result?
I made an impact in the food chain the other side of the planet from me, without leaving my desk.
Furthermore, the way I went about my work empowered—at the very least—myself and the end client (the lady making and selling the pickles and chutneys).
Sometimes we can’t change the world by ourselves… but we don’t have to.
If we all just nudge things in the right direction, we’ll end up with a healthier, better-fed, more productive system for all!
Share This Post
-
How Likely Are You To Live To 100?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How much hope can we reasonably have of reaching 100?
Yesterday, we asked you: assuming a good Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL), how much longer do you hope to live?
We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- A little over 38% of respondents hope to live another 11–20 years
- A little over 31% hope to live another 31–40 years
- A little over 7% will be content to make it to the next decade
- One (1) respondent hopes to live longer than an additional 100 years
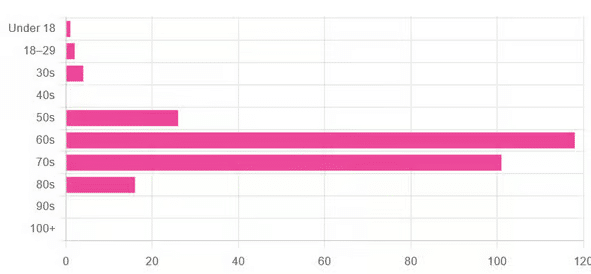
This is interesting when we put it against our graph of how old our subscribers are:
…because it corresponds inversely, right down to the gap/dent in the 40s. And—we may hypothesize—that one person under 18 who hopes to live to 120, perhaps.
This suggests that optimism remains more or less constant, with just a few wobbles that would probably be un-wobbled with a larger sample size.
In other words: most of our education-minded, health-conscious subscriber-base hope to make it to the age of 90-something, while for the most part feeling that 100+ is overly optimistic.
Writer’s anecdote: once upon a time, I was at a longevity conference in Brussels, and a speaker did a similar survey, but by show of hands. He started low by asking “put your hands up if you want to live at least a few more minutes”. I did so, with an urgency that made him laugh, and say “Don’t worry; I don’t have a gun hidden up here!”
Conjecture aside… What does the science say about our optimism?
First of all, a quick recap…
To not give you the same information twice, let’s note we did an “aging mythbusting” piece already covering:
- Aging is inevitable: True or False?
- Aging is, and always will be, unstoppable: True or False?
- We can slow aging: True or False?
- It’s too early to worry about… / It’s too late to do anything about… True or False?
- We can halt aging: True or False?
- We can reverse aging: True or False?
- But those aren’t really being younger, we’ll still die when our time is up: True or False?
You can read the answers to all of those here:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
Now, onwards…
It is unreasonable to expect to live past 100: True or False?
True or False, depending on your own circumstances.
First, external circumstances: the modal average person in Hong Kong is currently in their 50s and can expect to live into their late 80s, while the modal average person in Gaza is 14 and may not expect to make it to 15 right now.
To avoid extremes, let’s look at the US, where the modal average person is currently in their 30s and can expect to live into their 70s:
United States Mortality Database
Now, before that unduly worries our many readers already in their 70s…
Next, personal circumstances: not just your health, but your socioeconomic standing. And in the US, one of the biggest factors is the kind of health insurance one has:
SOA Research Institute | Life Expectancy Calculator 2021
You may note that the above source puts all groups into a life expectancy in the 80s—whereas the previous source gave 70s.
Why is this? It’s because the SOA, whose primary job is calculating life insurance risks, is working from a sample of people who have, or are applying for, life insurance. So it misses out many people who die younger without such.
New advances in medical technology are helping people to live longer: True or False?
True, assuming access to those. Our subscribers are mostly in North America, and have an economic position that affords good access to healthcare. But beware…
On the one hand:
The number of people who live past the age of 100 has been on the rise for decades
On the other hand:
The average life expectancy in the U.S. has been on the decline for three consecutive years
COVID is, of course, largely to blame for that, though:
❝The decline of 1.8 years in life expectancy was primarily due to increases in mortality from COVID-19 (61.2% of the negative contribution).
The decline in life expectancy would have been even greater if not for the offsetting effects of decreases in mortality due to cancer (43.1%)❞
Source: National Vital Statistics Reports
The US stats are applicable to Canada, the UK, and Australia: True or False?
False: it’s not quite so universal. Differences in healthcare systems will account for a lot, but there are other factors too:
- Life expectancy in Canada fell for the 3rd year in a row. What’s happening?
- UK life expectancy lagging behind rest of G7 except the US
- Australians are living longer but what does it take to reach 100 years old?
Here’s an interesting (UK-based) tool that calculates not just your life expectancy, but also gives the odds of living to various ages (e.g. this writer was given odds of living to 87, 96, 100).
Check yours here:
Office of National Statistics | Life Expectancy Calculator
To finish on a cheery note…
Data from Italian centenarians suggests a “mortality plateau”:
❝The risk of dying leveled off in people 105 and older, the team reports online today in Science.
That means a 106-year-old has the same probability of living to 107 as a 111-year-old does of living to 112.
Furthermore, when the researchers broke down the data by the subjects’ year of birth, they noticed that over time, more people appear to be reaching age 105.❞
Pop-sci source: Once you hit this age, aging appears to stop
Actual paper: The plateau of human mortality: demography of longevity pioneers
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
One Critical Mistake That Costs Seniors Their Mobility
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Will Harlow, the over-50s specialist physio, advises what to do instead:
Nose over toes
Often considered the most important test of mobility in later life (or in general, but later life is when it tends to decline) is the ability to get up off the floor without using your arms.
Many seniors, meanwhile, struggle to get out of a chair without using their arms.
Now, sitting in chairs in the first place is not good for the health, but that’s another matter and beyond the scope of today’s article.
If, perchance, you struggle to get up from a chair (especially if it’s low/deep, like many armchairs are) without using your hands, then here’s the way to do it:
- While practicing, cross your arms in front of you, so that you cannot use them.
- Shuffle yourself towards the front of the chair. No, don’t use your arms for this either, do a little butt-walk instead, to get you to the front edge of the chair.
- Lean forwards to position your nose over your toes (hence the mnemonic: “nose over toes”; memorize that!), as this will put your center of gravity where it needs to be.
- Now, push with your feet to rise up and forwards; slowly is better than quickly (quickly may be easier, but slowly will improve your strength and balance).
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Butter vs Plant Oils: What The Latest Evidence Shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve done some relevant head-to-head comparisons before in our “This or That” section:
- Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Sesame Oil vs Almond Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Sunflower Oil vs Canola Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Margarine vs Butter – Which is Healthier
- Butter vs Ghee – Which is Healthier?
We also did a deeper-dive into butter vs margarine:
Butter vs Margarine – Mythbusting Edition ← this one clears up a lot of misinformation about both butter and margarine
As well as: Saturated Fats: What’s The Truth? Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
So, we’re not coming into this one today unawares, and/but it’s an interesting comparison we haven’t directly written about before: butter vs plant oils in general
The Study
It was a JAMA Internal Medicine cohort study, which followed 221,054 adults (average age 56 at the start of the study, with a standard deviation of 7 years from that age) for up to 33 years.
Why “up to”? Because not everybody survived the study.
Specifically, 50,932 deaths were recorded, including 12,241 from cancer and 11,240 from cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Participants were categorized into quartiles based on butter or plant-based oil intake, and…
- The highest quartile (i.e. the 25% of people who consumed the most) butter intake linked to a 15% higher total mortality.
- The highest quartile (i.e. the 25% of people who consumed the most) plant-based oil intake linked to a 16% lower total mortality.
But, if those are the opposite ends of the spectrum, what about smaller differences?
Every 10g/day increase in consumption of plant-based oils yielded…
- 11% lower cancer mortality.
- 6% lower CVD mortality.
Meanwhile, 10g/day increase in butter consumption yielded…
- 12% higher cancer mortality.
- 17% higher CVD mortality.
These benefits must have a cap (after all, one cannot just drink liters of olive oil per day for for a 3400% decrease in mortality), but that cap was not ascertained, because there was no group drinking liters of plant oils per day, not even for science.
However, in the realm of small changes, substituting even 10g/intake of total butter with an equivalent amount of plant-based oils yielded 17% lower total mortality.
You can read the study in full, here: Butter and Plant-Based Oils Intake and Mortality
“So, what about the surely great difference between seed oils and olive oil?”
Compared the the vast gaping statistical chasm that lay between the results of butter and the results of plant oils, which plant oil one chooses doesn’t make a huge difference, iff one isn’t consuming a large amount—the important thing was skipping butter in favor of a plant oil of some kind.
Note also that, for example, deep-frying a starchy food like potatoes will cause the resultant fries (or such), even if not visibly oily, to now have about 10–15% of their original weight in water, replaced with oil. So, 100g (about 3oz) of fries may have around 10-15g oil. Obviously, this does depend on the cut and other factors, but that’s a ballpark figure.
Here’s a lengthier discussion about seed oils than we have room for today:
If you’re worried about inflammation, stop stressing about seed oils and focus on the basics ← in other words, yes it counts, but there are other things that count a lot more, such that if you’re paying attention to the other things, the fact that you sprayed your wok with a little canola oil before stir-frying those vegetables isn’t going to make a meaningful difference.
An as for olive oil? It’s a famously healthy oil, and certainly a candidate for the top spot along with avocado oil*:
All About Olive Oil ← we talk lipids, polyphenols, virginity, and more!
*…and it’s worth noting that these two oils’ (excellent) lipids profiles are very similar, meaning that the main factor between them is that olive oil usually retains vitamins that avocado oil doesn’t.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Ant Oil Just “Snake Oil”?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Tested Out “Ant Egg Oil”
Did you know?! There’s a special protein found only in the eggs of a particular species of ant found in Turkey, that can painlessly and permanently stop (not just slow!) hair regrowth in places you’d rather not have hair.
Neither did we, and when we heard about it, we did our usual research, and discovered a startling secret.
…there probably isn’t.
We decided to dig deeper, and the plot (unlike the hair in question) thickens:
We could not find any science for or against (or even generally about) the use of ant egg oil to prevent hair regrowth. Not a peep. What we did find though was a cosmetic chemist who did an analysis of the oil as sold, and found its main ingredient appears to be furan-2-carbaldehyde, or Furfural, to its friends.
Surprise! There’s also no science that we could find about the effect of Furfural (we love the name, though! Fur for all!) on hair, except that it’s bad for rodents (and their hair) if they eat a lot of it. So please don’t eat it. Especially if you’re a mouse.
And yet, many ostensibly real reviews out in the wild claim it works wonders. So, we took the investigative reporting approach and tried it ourselves.
That’s right, a plucky member of our team tried it, and she reports:
❝ At first glance, it seems like olive oil. There’s something else though, adding a darker colour and a slight bitterness to the smell.
After waxing, I applied a little every few days. When the hair eventually regrew (and it did), it grew back thinner, and removing the new hairs was a strangely easy experience, like pulling hairs out of soft soap instead of out of skin. It didn’t hurt at all, either.
I had more of the oil, so I kept going with the treatment, and twelve weeks later there are very few hairs regrowing at all; probably there will be none left soon. Whatever’s in this, be it from ant eggs or wheat bran or something else entirely, it worked for me!❞
So in short: it remains a mystery for now! If you try it, let us know how it went for you.
Here’s the “interesting” website that sells it, though you may find it for less on eBay or similar. (Note, we aren’t earning any commissions from these links. We just wanted to make it easier for you to dive deeper).
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: