The Five Key Traits Of Healthy Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Five Keys Of Aging Healthily

This is Dr. Daniel Levitin. He’s a neuroscientist, and his research focuses on aging, the brain, health, productivity, and creativity. Also music, and he himself is an accomplished musician also, but we’re not going to be focusing on that today.
We’re going to be looking at the traits that, according to science, promote healthy longevity in old age. In other words, the things that increase our healthspan, from the perspective of a cognitive scientist.
What does he say we should do?
Dr. Levitin offers us what he calls the “COACH” traits:
- Curiosity
- Openness
- Associations
- Conscientiousness
- Healthy practices
By “associations”, he means relationships. However, that would have made the acronym “CORCH”, and decisions had to be made.
Curiosity
Leonardo da Vinci had a list of seven traits he considered most important.
We’ll not go into those today (he is not our featured expert of the day!), but we will say that he agreed with Dr. Levitin on what goes at the top of the list: curiosity.
- Without curiosity, we will tend not to learn things, and learning things is key to keeping good cognitive function in old age
- Without curiosity, we will tend not to form hypotheses about how/why things are the way they are, so we will not exercise imagination, creativity, problem-solving, and other key functions of our brain
- Without curiosity, we will tend not to seek out new experiences, and consequently, our stimuli will be limited—and thus, so will our brains
Openness
Being curious about taking up ballroom dancing will do little for you, if you are not also open to actually trying it. But, openness is not just a tag-on to curiosity; it deserves its spot in its own right too.
Sometimes, ideas and opportunities come to us unbidden, and we have to be able to be open to those too. This doesn’t mean being naïve, but it does mean having at least a position of open-minded skepticism.
Basically, Dr. Levitin is asking us to be the opposite of the pejorative stereotype of “an old person stuck in their ways”.
Associations
People are complex, and so they bring complexities to our lives. Hopefully, positively stimulating ones. Without them to challenge us (again, hopefully in a positive way), we can get very stuck in a narrow field of experience.
And of course, having at least a few good friends has numerous benefits to health. There’s been a lot of research on this; 5 appears to be optimal.
- More than that, and the depth tends to tail off, and/or stresses ensue from juggling too many relationships
- Fewer than that, and we might be only a calendar clash away from loneliness
Friends provide social stimulation and mutual support; they’re good for our mental health and even our physiological immunity (counterintuitively, by means of shared germs).
And, a strong secure romantic relationship is something that has been found time and again to extend healthy life.
Note: by popular statistics, this benefit is conferred upon men partnered with women, men partnered with men, women partnered with women, but not women partnered with men.
There may be a causative factor that’s beyond the scope of this article which is about cognitive science, not feminism, but there could also be a mathematical explanation for this apparent odd-one-out:
Since women tend to live longer than men (who are also often older than their female partners), women who live the longest are often not in a relationship—precisely because they are widows. So these long-lived widows will tend to skew the stats, through no fault of their husbands.
On the flipside of this, for a woman to predecease her (statistically older and shorter-lived) husband will often require that she die quite early (perhaps due to accident or illness unrelated to age), which will again skew the stats to “women married to men die younger”, without anything nefarious going on.
Conscientiousness
People who score highly in the character trait “conscientiousness” will tend to live longer. The impact is so great, that a child’s scores will tend to dictate who dies in their 60s or their 80s, for example.
What does conscientiousness mean? It’s a broad character trait that’s scored in psychometric tests, so it can be things that have a direct impact on health, such as brushing one’s teeth, or things that are merely correlated, such as checking one’s work for typos (this writer does her best!).
In short, if you are the sort of person who attends to the paperwork for your taxes on time, you are probably also the sort of person who remembers to get your flu vaccination and cancer screening.
Healthy practices
This means “the usual things”, such as:
- Healthy diet (Mediterranean Diet consistently scores up top)
- Good exercise (especially the tendency to keep moving in general)
- Good sleep (7–9 hours, no compromises)
- Not drinking (or at least only very moderate consumption, but the only safe amount is zero)
- Not smoking (just don’t; there is no wiggle room on this one)
Want to learn more?
You can check out his book, which we reviewed all so recently, and you can also enjoy this video, in which he talks about matters concerning healthy aging from a neuroscientist’s perspective, ranging from heart health and neurodegeneration, to the myth of failing memory, to music and lifespan and more:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Anti-Inflammatory Brownies
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Brownies are usually full of sugar, butter, and flour. These ones aren’t! Instead, they’re full of fiber (good against inflammation), healthy fats, and anti-inflammatory polyphenols:
You will need
- 1 can chickpeas (keep half the chickpea water, also called aquafaba, as we’ll be using it)
- 4 oz of your favorite nut butter (substitute with tahini if you’re allergic to nuts)
- 3 oz rolled oats
- 2 oz dark chocolate chips (or if you want the best quality: dark chocolate, chopped into very small pieces)
- 3 tbsp of your preferred plant milk (this is an anti-inflammatory recipe and unfermented dairy is inflammatory)
- 2 tbsp cocoa powder (pure cacao is best)
- 1 tbsp glycine (if unavailable, use 2 tbsp maple syrup, and skip the aquafaba)
- 2 tsp vanilla extract
- ½ tsp baking powder
- ¼ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃, and line a 7″ cake tin with baking paper.
2) Blend the oats in a food processor, until you have oat flour.
3) Add all the remaining ingredients except the dark chocolate chips, and process until the mixture resembles cookie dough.
3) Transfer to a bowl, and fold in the dark chocolate chips, distributing evenly.
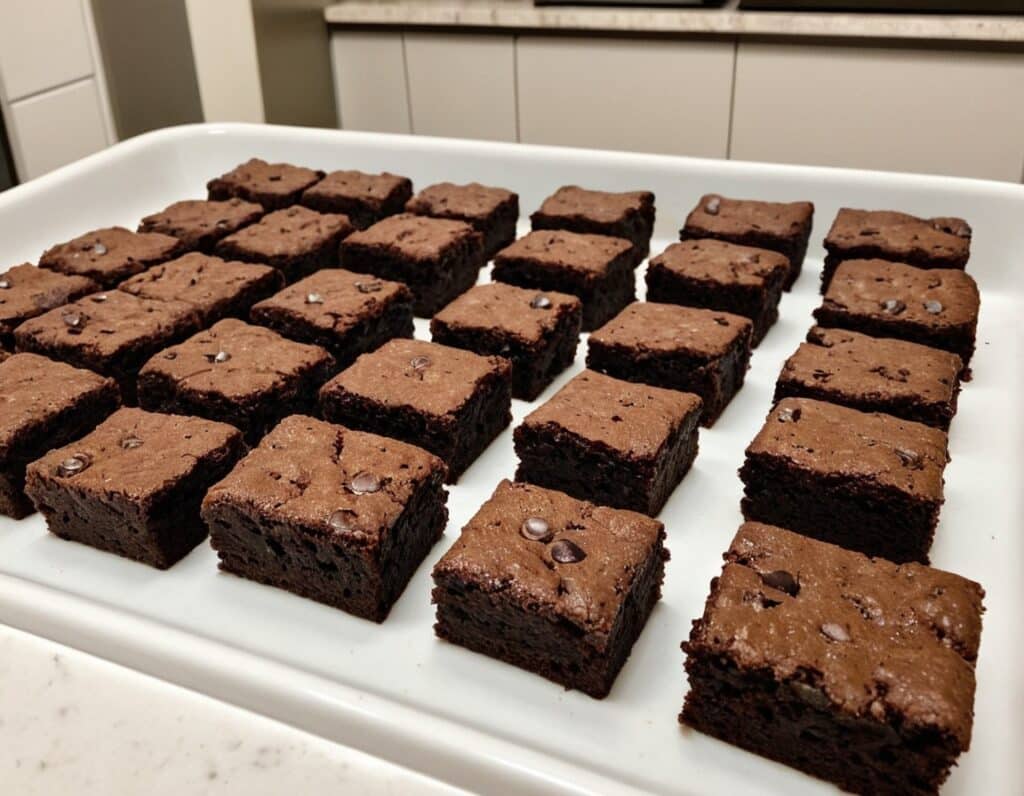
4) Add the mixture to the cake tin, and smooth the surface down so that it’s flat and even. Bake for about 25 minutes, and let them cool in the tin for at least 10 minutes, but longer is better, as they will firm up while they cool. Cut into cubes when ready to serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Keep Inflammation At Bay
- The Sweet Truth About Glycine
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Tell Yourself a Better Lie – by Marissa Peer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As humans, we generally lie to ourselves constantly. Or perhaps we really believe some of the things we tell ourselves, even if they’re not objectively necessarily true:
- I’ll always be poor
- I’m destined to be alone
- I don’t deserve good things
- Etc.
Superficially, it’s easy to flip those, and choose to tell oneself the opposite. But it feels hollow and fake, doesn’t it? That’s where Marissa Peer comes in.
Our stories that we tell ourselves don’t start where we are—they’re generally informed by things we learned along the way. Sometimes good lessons, sometimes bad ones. Sometimes things that were absolutely wrong and/or counterproductive.
Peer invites the reader to ask “What if…”, unravel how the unhelpful lessons got wired into our brains in the first place, and then set about untangling them.
“Tell yourself a better lie” does not mean self-deceit. It means that we’re the authors of our own stories, so we might as well make them work for us. Many things in life are genuinely fixed; others are open to interpretation.
Sorting one from the other, and then treating them correctly in a way that’s helpful to us? That’s how we can stop hurting ourselves, and instead bring our own stories around to uplift and fortify us.
Get Your Copy of “Tell Yourself A Better Lie” on Amazon Today!
Share This Post
-
Glutathione: More Than An Antioxidant
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Glutathione’s Benefits: The Usual And The Unique
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that does all the things we might reasonably expect an antioxidant to do, plus some beneficial quirks of its own.
We do make glutathione in our bodies, but we can also get it from our diet, and of course, we can also supplement it.
What foods is it in?
It’s in a lot of foods, but some top examples include:
- turmeric
- avocado
- asparagus
- almonds
- cruciferous vegetables
- watermelon
- garlic
For a fuller list and discussion, see:
What does it do?
Let’s start with the obvious; as with most things that are antioxidant, it is also anti-inflammatory. Increasing or decreasing glutathione levels is associated with decreased or increased inflammation, respectively. For example:
It being anti-inflammatory also means it can be beneficial in calming autoimmune disorders:
Glutathione: a key player in autoimmunity
And to complete the triad of “those three things that generally go together”, yes, this means it also has anticancer potential, but watch out!
❝Although in healthy cells [glutathione] is crucial for the removal and detoxification of carcinogens, elevated [glutathione] levels in tumor cells are associated with tumor progression and increased resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs❞
~ Dr. Miroslava Cuperlovic-Culf et al.
Read in full: Role of Glutathione in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapies
So in other words, when it comes to cancer risk management, glutathione is a great preventative, but the opposite of a cure.
What were those “beneficial quirks of its own”?
They are mainly twofold, and the first is that it improves insulin sensitivity. There are many studies showing this, but here’s a recent one from earlier this year:
The Role of Glutathione and Its Precursors in Type 2 Diabetes
The other main “beneficial quirk of its own” is that it helps prevent and/or reverse non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, as in this study from last year:
Because of glutathione’s presence in nuts, fruits, and vegetables, this makes it a great thing to work in tandem with a dietary approach to preventing/reversing NAFLD, by the way:
Anything else?
It’s being investigated as a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease symptoms, but the science is young for this one, so there is no definitive recommendation yet in this case. If you’re interested in that, though, do check out the current state of the science at:
Potential use of glutathione as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease
Is it safe?
While there is no 100% blanket statement of safety that can ever be made about anything (even water can kill people, and oxygen ultimately kills everyone that something else doesn’t get first), glutathione has one of the safest general safety profiles possible, with the exception we noted earlier (if you have cancer, it is probably better to skip this one unless an oncologist or similar advises you otherwise).
As ever, do speak with your doctor/pharmacist to be sure in any case, though!
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Are Fruit & Vegetable Extract Supplements Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At 10almonds we are always extolling the virtues of fruits and vegetables, but how much do those benefits still exist when we’re looking at a fruit and vegetable extract supplement?
We examined one aspect of this previously, here;
Mediterranean Diet… In A Pill?
This looked at getting the anti-inflammatory benefits of the Mediterranean diet, in supplement form, by providing extracts of 16 key plant extracts—which also provides an excellent shopping list, by the way, if you just want to skip the supplements and buy those plants; if nine top scientists (anti-aging specialists, neurobiologists, pharmacologists, and at least one professor of applied statistics) came to the conclusion that to get the absolute most bang-for-buck possible, those are the plants to get the phytochemicals from, then we’re not going to ignore that!
And yes, the short answer was “it does very significantly improve anti-inflammatory markers”, by the way.
But when it comes to benefits from polyphenols, anti-inflammatory powers are very much “low-hanging fruit”, so to speak. It’s the “fork found in kitchen” level of shocking revelation. It’s what polyphenols are best at (tied with antioxidant powers, which directly mediate their anti-inflammatory powers).
So, what about something more challenging, like brain benefits?
Underrated Brain Boosters
A European research team (Dr. Begoña Cerdá et al.) looked at the effects of polyphenol-rich nutraceuticals (plant extracts) on cognitive function and neuroprotection biomarkers.
It was a randomized, crossover, double-blind, sex-stratified, placebo-controlled clinical trial that had people take the supplement or a placebo for 16 weeks, have a 4-week washout phase (to minimize leftover effects contaminating the data) and then switching groups (still blinded to the placebo control) for 16 weeks.
They tested cognitive function and neuroprotection biomarkers in various ways before and after each of the testing phases (so, four testing sessions in total per person: before and after the supplement + before and after the placebo).
The results:
❝The results suggested that participants who consumed the polyphenol-rich nutraceutical demonstrated significant improvements in cognitive performance compared to the placebo group.
The Stroop Test scores indicated enhanced attention and inhibitory control, while RIST results suggested improvements in logical reasoning and memory. The Trail Making Test also revealed increased cognitive flexibility, highlighting the supplement’s potential to boost overall mental agility.
Furthermore, the ELISA results showed a notable increase in BDNF and CREB levels among participants who took the active supplement. BDNF is a protein that is essential for neuronal growth and survival, and its levels were significantly elevated, reinforcing its role in synaptic plasticity and long-term memory formation.
Additionally, CREB, a transcription factor involved in learning processes, also showed increased levels, supporting its function in cognitive enhancement.
Importantly, the correlation between improved test scores and higher biomarker levels suggested that polyphenols may directly influence brain function rather than merely offering general health benefits.
While the study focused on healthy adults, the findings also raised questions about whether similar interventions could benefit populations at risk for cognitive decline, including older adults and individuals with neurodegenerative conditions.❞
Key to abbreviations:
- RIST = Reynolds Intellectual Screening Test
- ELISA = Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assays
- BDNF = Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
- CREB = cAMP-Response Element Binding Protein
- cAMP = Cyclic Adenosine MonoPhosphate
Source: Daily fruit and vegetable extracts may boost brain power ← we quoted a pop-sci article for the above summary, for easier readability while still having the critical conclusions in one place
For those who do want to dive into the actual data and a lot more detail about the study methodology (which is well worth reading if you have the time, as it’s very good), here is the actual study:
If nothing else, be aware that the usual benchmark for statistical significance is p < 0.05, whereas the results in this study ranged from p < 0.01 to p < 0.001, in other words, ranging from 5x more significant than is required to be called “significant”, to 50x more significant than is required to be called “significant”.
In fewer words: impressively significant
In lay terms: the scientists are about as sure as scientists ever get about anything, that this supplement produces significant results
What was the supplement they tested?
Good news! It was…
- a commercially available supplement (JuicePlus), which is convenient, because it means we (and you, dear reader) can get it if we so choose
- not paid for by JuicePlus or anyone associated with them (indeed, the funding declaration on the study is “This research received no external funding”), so not subject to any conflict of interest that might introduce bias into the study
As for why they chose that one:
❝A unique aspect of the polyphenol-rich nutraceutical evaluated in this study lies in its composition, which integrates a blend of fruit, vegetable, and berry juice powders.
This product, Juice Plus+ Premium®, contains over 119 distinct polyphenolic compounds, including flavanols, anthocyanins, and flavones, as demonstrated in prior compositional analyses.
Compared to other polyphenol-based interventions, this nutraceutical stands out due to its comprehensive formulation, combining a wide range of bioactive compounds with complementary antioxidant and neuroprotective effects.
These characteristics ensure a more diverse interaction with neurobiological pathways, including those related to oxidative stress mitigation, synaptic plasticity, and cognitive function❞
Source: Ibid. (it’s in the introduction)
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but for your convenience, here’s where to get JuicePlus supplements Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Two-Second Advantage – by Vivek Ranadive and Kevin Maney
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The titular “two-second advantage” can in some cases be literal (imagine you got a two-second head-start in a boxing match!), in other cases can refer to being just a little ahead of things in a way that can confer a great advantage, often cumulatively—as anyone who’s played Monopoly can certainly attest.
Vivek Ranadivé and Kevin Maney give us lots of examples from business, sports, politics, economics, and more, in a way that seeks to cultivate a habit of asking the right questions in order to anticipate the future and not just be ahead of the competition—some areas of life don’t have competition for most people, like health, for example—but to generally have things “in hand”.
When it comes to personal finances, health, personal projects, and the like, those tiny initial advantages that lead to incremental further improvements, can be the difference between continually (and frantically) playing catch-up, or making the jump past breaking even to going from strength to strength.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Peripheral neuropathy (and what can be done about it)
Peripheral neuropathy is nerve damage, usually of the extremities. It can be caused by such things as:
- Diabetes
- Alcoholism
- Infection
- Injury
The manifestations can be different:
- In the case of diabetes, it’s also called diabetic neuropathy, and almost always affects the feet first.
- In the case of alcoholism, it is more generalized, but tends towards affecting the extremities first.
- In the case of infection, a lot depends on the nature of the infection and the body’s response.
- In the case of injury, it’ll naturally be the injured part, or a little “downstream” of the injured part.
- This could be the case of a single traumatic injury (e.g. hand got trapped in a slammed door)
This could be the case of a repetitive injury (carpal tunnel syndrome is a kind of peripheral neuropathy, and is usually caused by consistent misalignment of the carpal tunnel, the aperture through which a bundle of nerves make their way from the forearm to the hand)
Prevention is better than cure
If you already have peripheral neuropathy, don’t worry, we’ll get to that. But, if you can, prevention is better than cure. This means:
- Diabetes: if you can, avoid. This may seem like no-brainer advice, but it’s often something people don’t think about until hitting a pre-diabetic stage. Obviously, if you are Type 1 Diabetic, you don’t have this luxury. But in any case, whatever your current status, take care of your blood sugars as best you can, so that your blood can take care of you (and your nerves) in turn. You might want to check out our previous main feature about this:
- Alcoholism: obviously avoid, if you can. You might like this previous edition of 10almonds addressing this:
- Infection: this is so varied that one-liner advice is really just “try to look after your immune health”.
- We’ll do a main feature on this soon!
- Injury: obviously, try to be careful. But that goes for the more insidious version too! For example, if you spend a lot of time at your computer, consider an ergonomic mouse and keyboard.
- There are many kinds available, so read reviews, but here’s an example product on Amazon
Writer’s note: as you might guess, I spend a lot of time at my computer, and a lot of that time, writing. I additionally spend a lot of time reading. I also have assorted old injuries from my more exciting life long ago. Because of this, it’s been an investment in my health to have:
A standing desk
A vertical ergonomic mouse
An ergonomic split keyboard
A Kindle*
*Far lighter and more ergonomic than paper books. Don’t get me wrong, I’m writing to you from a room that also contains about a thousand paper books and I dearly love those too, but more often than not, I read on my e-reader for comfort and ease.
If you already have peripheral neuropathy
Most advice popular on the Internet is just about pain management, but what if we want to treat the cause rather than the symptom?
Let’s look at the things commonly suggested: try ice, try heat, try acupuncture, try spicy rubs (from brand names like Tiger Balm, to home-made chilli ointments), try meditation, try a warm bath, try massage.
And, all of these are good options; do you see what they have in common?
It’s about blood flow. And that’s why they can help even in the case of peripheral neuropathy that’s not painful (it can also manifest as numbness, and/or tingling sensations).
By getting the blood flowing nicely through the affected body part, the blood can nourish the nerves and help them function correctly. This is, in effect, the opposite of what the causes of peripheral neuropathy do.
But also don’t forget: rest
- Put your feet up (literally! But we’re talking horizontal here, not elevated past the height of your heart)
- Rest that weary wrist that has carpal tunnel syndrome (again, resting it flat, so your hand position is aligned with your forearm, so the nerves between are not kinked)
- Use a brace if necessary to help the affected part stay aligned correctly
- You can get made-for-purpose wrist and ankle braces—you can also get versions that are made for administering hot/cold therapy, too. That’s just an example product linked that we can recommend; by all means read reviews and choose for yourself, though. Try them and see what helps.
One more top tip
We did a feature not long back on lion’s mane mushroom, and it’s single most well-established, well-researched, well-evidenced, completely uncontested benefit is that it aids peripheral neurogenesis, that is to say, the regrowth and healing of the peripheral nervous system.
So you might want to check that out:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: