Antioxidant Matcha Snack Bars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The antioxidants in this come not just from the matcha, but also the cacao nibs and chocolate, as well as lots of nutrients from the hazelnuts and cashews. If you’re allergic to nuts, we’ll give you substitutions that will change the nutritional profile (and flavor), but still work perfectly well and be healthy too.
You will need
For the base:
- ⅔ cup roasted hazelnuts (if allergic, substitute dessicated coconut)
- ⅔ cup chopped dates
For the main part:
- 1 cup raw cashews (if allergic, substitute raw coconut, chopped)
- ½ cup almond milk (or your preferred milk of any kind)
- ½ cup cacao nibs
- 2 tbsp lime juice
- 1 tbsp matcha powder
- 1 tbsp maple syrup (omit if you don’t care for sweetness)
For the topping (optional):
- 2oz dark chocolate, melted (and if you like, tempered—but this isn’t necessary; it’ll just make it glossier if you do)
- Spare cacao nibs, chopped nuts, or anything else you might want on there
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the base ingredients in a food processor until it has a coarse sticky texture, but isn’t yet a paste or dough.
2) Line a cake pan with baking paper and spread the base mix on the base; press it down to compact it a little and ensure it is flat. If there’s room, put this in the freezer while you do the next bit. If not, the fridge will suffice.
3) Blend the main part ingredients apart from the cacao nibs, until smooth. Stir in the cacao nibs with a spoon.
4) Spread the main part evenly over the base, and allow everything you’ve built (in this recipe, not in life in general) to chill in the fridge for at least 4 hours.
5) Cut it into blocks of the size and shape you want to eat them, and (if adding the optional topping) separate the blocks slightly from each other, before drizzling with the chocolate topping. Put it back in the fridge to cool this too; an hour should be sufficient.
6) Serve!

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
- Which Plant Milk?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Psychoactive Drugs Are Having a Moment. The FDA Will Soon Weigh In.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lori Tipton is among the growing number of people who say that MDMA, also known as ecstasy, saved their lives.
Raised in New Orleans by a mother with untreated bipolar disorder who later killed herself and two others, Tipton said she endured layers of trauma that eventually forced her to seek treatment for crippling anxiety and hypervigilance. For 10 years nothing helped, and she began to wonder if she was “unfixable.”
Then she answered an ad for a clinical trial for MDMA-assisted therapy to treat post-traumatic stress disorder. Tipton said the results were immediate, and she is convinced the drug could help a lot of people. But even as regulators weigh approval of the first MDMA-based treatment, she’s worried that it won’t reach those who need it most.
“The main thing that I’m always concerned about is just accessibility,” the 43-year-old nonprofit project manager said. “I don’t want to see this become just another expensive add-on therapy for people who can afford it when people are dying every day by their own hand because of PTSD.”
MDMA is part of a new wave of psychoactive drugs that show great potential for treating conditions such as severe depression and PTSD. Investors are piling into the nascent field, and a host of medications based on MDMA, LSD, psychedelic mushrooms, ketamine, the South American plant mixture ayahuasca, and the African plant ibogaine are now under development, and in some cases vying for approval by the Food and Drug Administration.
Proponents hope the efforts could yield the first major new therapies for mental illness since the introduction of modern antidepressants in the 1980s. But not all researchers are convinced that their benefits have been validated, or properly weighed against the risks. And they can be difficult to assess using traditional clinical trials.
The first MDMA-assisted assisted therapy appeared to be on track for FDA approval this August, but a recent report from an independent review committee challenged the integrity of the trial data from the drug’s maker, Lykos Therapeutics, a startup founded by a psychedelic research and advocacy group. The FDA will convene a panel of independent investigators on June 4 to determine whether to recommend the drug’s approval.
Proponents of the new therapies also worry that the FDA will impose treatment protocols, such as requiring multiple trained clinicians to monitor a patient for extended periods, that will render them far too expensive for most people.
Tipton’s MDMA-assisted therapy included three eight-hour medication sessions overseen by two therapists, each followed by an overnight stay at the facility and an integration session the following day.
“It does seem that some of these molecules can be administered safely,” said David Olson, director of the University of California-Davis Institute for Psychedelics and Neurotherapeutics. “I think the question is can they be administered safely at the scale needed to really make major improvements in mental health care.”
Breakthrough Therapies?
Psychedelics and other psychoactive substances, among the medicines with the oldest recorded use, have long been recognized for their potential therapeutic benefits. Modern research on them started in the mid-20th century, but clinical trial results didn’t live up to the claims of advocates, and they eventually got a bad name both from their use as party drugs and from rogue CIA experiments that involved dosing unsuspecting individuals.
The 1970 Controlled Substances Act made most psychoactive drugs illegal before any treatments were brought to market, and MDMA was classified as a Schedule 1 substance in 1985, which effectively ended any research. It wasn’t until 2000 that scientists at Johns Hopkins University were granted regulatory approval to study psilocybin anew.
Ketamine was in a different category, having been approved as an anesthetic in 1970. In the early 2000s, researchers discovered its antidepressant effects, and a ketamine-based therapy, Spravato, received FDA approval in 2019. Doctors can also prescribe generic ketamine off-label, and hundreds of clinics have sprung up across the nation. A clinical trial is underway to evaluate ketamine’s effectiveness in treating suicidal depression when used with other psychiatric medications.
Ketamine’s apparent effectiveness sparked renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of other psychoactive substances.
They fall into distinct categories: MDMA is an entactogen, also known as an empathogen, which induces a sense of connectedness and emotional communion, while LSD, psylocibin, and ibogaine are psychedelics, which create altered perceptual states. Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic, though it can produce hallucinations at the right dose.
Despite the drugs’ differences, Olson said they all create neuroplasticity and allow the brain to heal damaged neural circuits, which imaging shows can be shriveled up in patients with addiction, depression, and PTSD.
“All of these brain conditions are really disorders of neural circuits,” Olson said. “We’re basically looking for medicines that can regrow these neurons.”
Psychedelics are particularly good at doing this, he said, and hold promise for treating diseases including Alzheimer’s.
A number of psychoactive drugs have now received the FDA’s “breakthrough therapy” designation, which expedites development and review of drugs with the potential to treat serious conditions.
But standard clinical trials, in which one group of patients is given the drug and a control group is given a placebo, have proven problematic, for the simple reason that people have no trouble determining whether they’ve gotten the real thing.
The final clinical trial for Lykos’ MDMA treatment showed that 71% of participants no longer met the criteria for PTSD after 18 weeks of taking the drug versus 48% in the control group.
A March report by the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, an independent research group, questioned the company’s clinical trial results and challenged the objectivity of MDMA advocates who participated in the study as both patients and therapists. The institute also questioned the drug’s cost-effectiveness, which insurers factor into coverage decisions.
Lykos, a public benefit company, was formed in 2014 as an offshoot of the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies, a nonprofit that has invested more than $150 million into psychedelic research and advocacy.
The company said its researchers developed their studies in partnership with the FDA and used independent raters to ensure the reliability and validity of the results.
“We stand behind the design and results of our clinical trials,” a Lykos spokesperson said in an email.
There are other hazards too. Psychoactive substances can put patients in vulnerable states, making them potential victims for financial exploitation or other types of abuse. In Lykos’ second clinical trial, two therapists were found to have spooned, cuddled, blindfolded, and pinned down a female patient who was in distress.
The substances can also cause shallow breathing, heart issues, and hyperthermia.
To mitigate risks, the FDA can put restrictions on how drugs are administered.
“These are incredibly potent molecules and having them available in vending machines is probably a bad idea,” said Hayim Raclaw of Negev Capital, a venture capital fund focused on psychedelic drug development.
But if the protocols are too stringent, access is likely to be limited.
Rachel del Dosso, a trauma therapist in the greater Los Angeles area who offers ketamine-assisted therapy, said she’s been following the research on drugs like MDMA and psilocybin and is excited for their therapeutic potential but has reservations about the practicalities of treatment.
“As a therapist in clinical practice, I’ve been thinking through how could I make that accessible,” she said. “Because it would cost a lot for [patients] to have me with them for the whole thing.”
Del Dosso said a group therapy model, which is sometimes used in ketamine therapy, could help scale the adoption of other psychoactive treatments, too.
Artificial Intelligence and Analogs
Researchers expect plenty of new discoveries in the field. One of the companies Negev has invested in, Mindstate Design Labs, uses artificial intelligence to analyze “trip reports,” or self-reported drug experiences, to identify potentially therapeutic molecules. Mindstate has asked the FDA to green-light a clinical trial of the first molecule identified through this method, 5-MeO-MiPT, also known as moxy.
AlphaFold, an AI program developed by Google’s DeepMind, has identified thousands of potential psychedelic molecules.
There’s also a lot of work going into so-called analog compounds, which have the therapeutic effects of hallucinogens but without the hallucinations. The maker of a psilocybin analog announced in March that the FDA had granted it breakthrough therapy status.
“If you can harness the neuroplasticity-promoting properties of LSD while also creating an antipsychotic version of it, then that can be pretty powerful,” Olson said.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
The Food For Life Cookbook – by Dr. Tim Spector
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Spector’s “Food For Life”, and while that was more of an “explanatory science” book, this one takes that science (reiterating it more briefly this time, by way of introduction) and makes a cookbook of it.
The nutritional emphasis in these recipes is on two things: maximizing fiber, and maximizing plant diversity. The recipes are not all vegan or even vegetarian, but they are plant-centric, and if the reader is vegetarian/vegan, then substitutions are easy to make.
The recipes themselves are simple without being boring, and are easy to follow, with full-page photos to accompany them. The science parts are very clear, accessible, and pop-science in style.
Bottom line: if you’d like to incorporate more fiber and more plants into your diet without it being a burden, this book is great for that.
Click here to check out the Food For Life Cookbook, and get cooking for life!
Share This Post
-
I’ve recovered from a cold but I still have a hoarse voice. What should I do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cold, flu, COVID and RSV have been circulating across Australia this winter. Many of us have caught and recovered from one of these common upper respiratory tract infections.
But for some people their impact is ongoing. Even if your throat isn’t sore anymore, your voice may still be hoarse or croaky.
So what happens to the voice when we get a virus? And what happens after?
Here’s what you should know if your voice is still hoarse for days – or even weeks – after your other symptoms have resolved.
Why does my voice get croaky during a cold?
A healthy voice is normally clear and strong. It’s powered by the lungs, which push air past the vocal cords to make them vibrate. These vibrations are amplified in the throat and mouth, creating the voice we hear.
The vocal cords are two elastic muscles situated in your throat, around the level of your laryngeal prominence, or Adam’s apple. (Although everyone has one, it tends to be more pronounced in males.) The vocal cords are small and delicate – around the size of your fingernail. Any small change in their structure will affect how the voice sounds.
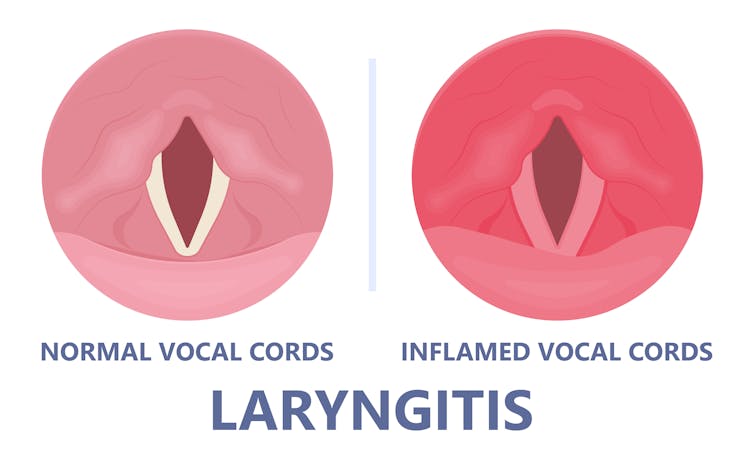
When the vocal cords become inflamed – known as laryngitis – your voice will sound different. Laryngitis is a common part of upper respiratory tract infections, but can also be caused through misuse.
Viruses such as the common cold can inflame the vocal cords. Pepermpron/Shutterstock Catching a virus triggers the body’s defence mechanisms. White blood cells are recruited to kill the virus and heal the tissues in the vocal cords. They become inflamed, but also stiffer. It’s harder for them to vibrate, so the voice comes out hoarse and croaky.
In some instances, you may find it hard to speak in a loud voice or have a reduced pitch range, meaning you can’t go as high or loud as normal. You may even “lose” your voice altogether.
Coughing can also make things worse. It is the body’s way of trying to clear the airways of irritation, including your own mucus dripping onto your throat (post-nasal drip). But coughing slams the vocal cords together with force.
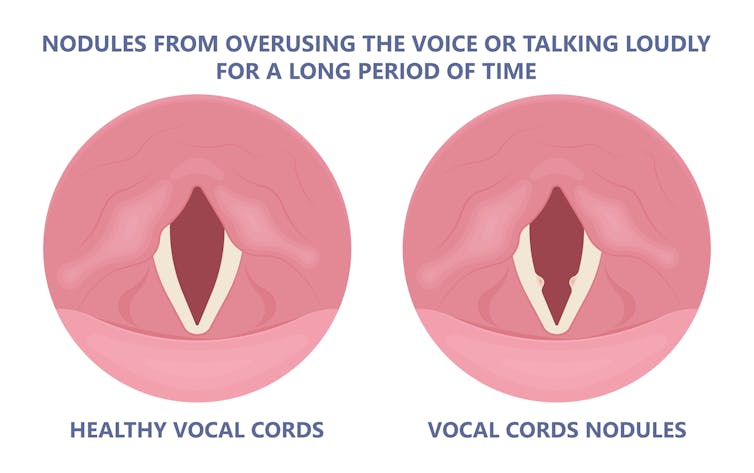
Chronic coughing can lead to persistent inflammation and even thicken the vocal cords. This thickening is the body trying to protect itself, similar to developing a callus when a pair of new shoes rubs.
Thickening on your vocal cords can lead to physical changes in the vocal cords – such as developing a growth or “nodule” – and further deterioration of your voice quality.
Coughing and exertion can cause inflamed vocal cords to thicken and develop nodules. Pepermpron/Shutterstock How can you care for your voice during infection?
People who use their voices a lot professionally – such as teachers, call centre workers and singers – are often desperate to resume their vocal activities. They are more at risk of forcing their voice before it’s ready.
The good news is most viral infections resolve themselves. Your voice is usually restored within five to ten days of recovering from a cold.
Occasionally, your pharmacist or doctor may prescribe cough suppressants to limit additional damage to the vocal cords (among other reasons) or mucolytics, which break down mucus. But the most effective treatments for viral upper respiratory tract infections are hydration and rest.
Drink plenty of water, avoid alcohol and exposure to cigarette smoke. Inhaling steam by making yourself a cup of hot water will also help clear blocked noses and hydrate your vocal cords.
Rest your voice by talking as little as possible. If you do need to talk, don’t whisper – this strains the muscles.
Instead, consider using “confidential voice”. This is a soft voice – not a whisper – that gently vibrates your vocal cords but puts less strain on your voice than normal speech. Think of the voice you use when communicating with someone close by.
During the first five to ten days of your infection, it is important not to push through. Exerting the voice by talking a lot or loudly will only exacerbate the situation. Once you’ve recovered from your cold, you can speak as you would normally.
What should you do if your voice is still hoarse after recovery?
If your voice hasn’t returned to normal after two to three weeks, you should seek medical attention from your doctor, who may refer you to an ear nose and throat specialist.
If you’ve developed a nodule, the specialist would likely refer you to a speech pathologist who will show you how to take care of your voice. Many nodules can be treated with voice therapy and don’t require surgery.
You may have also developed a habit of straining your vocal cords, if you forced yourself to speak or sing while they were inflamed. This can be a reason why some people continue to have a hoarse voice even when they’ve recovered from the cold.
In those cases, a speech pathologist may play a valuable role. They may teach you to exercises that make voicing more efficient. For example, lip trills (blowing raspberries) are a fun and easy way you can learn to relax the voice. This can help break the habit of straining your voice you may have developed during infection.
Yeptain Leung, Postdoctoral Research and Lecturer of Speech Pathology, School of Health Sciences, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cold Weather Health Risks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many Are Cold; Few Are Frozen
Many of those of us in the Northern Hemisphere are getting hit with a cold spell around now. How severe that may be depends on more precisely where we are, but it’s affecting a lot of people. So, with apologies to our readers in Australia, we’re going to do a special on that today.
Acute cold is, for most people, good for the health:
A Cold Shower A Day Keeps The Doctor Away?
Persistent cold, not so much. Let’s look at the risks, and what can be done about them…
Hypothermia
It kills. Don’t let it kill you or your loved ones.
And, this is really important: it doesn’t care whether you’re on a mountain or not.
In other words: a lot of people understand (correctly!) that hypothermia is a big risk to hikers, climbers, and the like. But if the heating goes out in your house and the temperature drops for long enough before the heating is fixed, you can get hypothermia there too just the same if you’re not careful.
How cold is too cold? It doesn’t even have to be sub-zero. According to the CDC, temperatures of 4℃ (40℉) can be low enough to cause hypothermia if other factors combine:
CDC | Prevent Hypothermia & Frostbite ← you can also see the list of symptoms to watch out for, there!
Skin health
Not generally an existential risk, but we may as well stay healthy as not!
Cold air often means dry air, so use a moisturizer with an oil base (if you don’t care for fancy beauty products, ordinary coconut oil is top-tier).
Bonus if you do it after a warming bath/shower!
Heart health
Cold has a vasconstricting effect; that is to say, it causes the body’s vasculature to shrink, increasing localized blood pressure. If it’s a cold shower as above, that can be very invigorating. If it’s a week of sub-zero temperatures, it can become a problem.
❝Shoveling a little snow off your sidewalk may not seem like hard work. However, […] combined with the fact that the exposure to cold air can constrict blood vessels throughout the body, you’re asking your heart to do a lot more work in conditions that are diminishing the heart’s ability to function at its best.❞
Source: Snow shoveling, cold temperatures combine for perfect storm of heart health hazards
If you have a heart condition, please do not shovel snow. Let someone else do it, or stay put.
And if you are normally able to exercise safely? Unless you’re sure your heart is in good order, exercising in the warmth, not the cold, seems to be the best bet.
See also: Heart Attack: His & Hers (Be Prepared!) ← can you remember which symptoms are for which sex? If not, now’s a good time to refresh that knowledge.
Immune health
We recently discussed how cold weather indirectly increases the risk of respiratory viral infection:
The Cold Truth About Respiratory Infections
So, now’s the time to be extra on-guard about that.
See also: Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Balance
Icy weather increases the risk of falling. If you think “having a fall” is something that happens to other/older people, please remember that there’s a first time for everything. Some tips:
- Walk across icy patches with small steps in a flat-footed fashion like a penguin.
- It may not be glamorous, but neither is going A-over-T and breaking (or even just spraining) things.
- Use a handrail if available, even if you don’t think you need to.
You can also check out our previous article about falling (avoiding falling, minimizing the damage of falling, etc):
Fall Special: Some Fall-Themed Advice
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Walk across icy patches with small steps in a flat-footed fashion like a penguin.
-
Bacopa Monnieri: A Well-Evidenced Cognitive Enhancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bacopa monnieri: a powerful nootropic
Bacopa monnieri is one of those “from traditional use” herbs that has made its way into science.
It’s been used for at least 1,400 years in Ayurvedic medicine, for cognitive enhancement, against anxiety, and some disease-specific treatments.
See: Pharmacological attributes of Bacopa monnieri extract: current updates and clinical manifestation
What are its claimed health benefits?
Bacopa monnieri is these days mostly sold and bought as a nootropic, and that’s what the science supports best.
Nootropic benefits claimed:
- Improves attention, learning, and memory
- Reduces depression, anxiety, and stress
- Reduces restlessness and impulsivity
Other benefits claimed:
- Antioxidant properties
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Anticancer properties
What does the science say?
Those last three, the antioxidant / anti-inflammatory / anticancer properties, when something has one of those qualities it often has all three, because there are overlapping systems at hand when it comes to oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular damage.
Bacopa monnieri is no exception to this “rule of thumb”, and/but studies to support these benefits have mostly been animal studies and/or in vitro studies (i.e., cell cultures in a petri dish in lab conditions).
For example:
- Inhibition of lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenase-2 enzymes by extracts isolated from Bacopa monnieri
- Assessing the anti-inflammatory effects of Bacopa-derived bioactive compounds using network pharmacology and in vitro studies
- The evolving roles of Bacopa monnieri as potential anticancer agent: a review
In the category of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the brain, sometimes results differ depending on the test population, for example:
- Neuroprotective effects of Bacopa monnieri in experimental model of dementia (it worked for rats)
- Use of Bacopa monnieri in the treatment of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review of randomized controlled trials (it didn’t work for humans)
Anything more promising than that?
Yes! The nootropic effects have been much better-studied in humans, and with much better results.
For example, in this 12-week study in healthy adults, taking 300mg/day significantly improved visual information processing, learning, and memory (tested against placebo):
The chronic effects of an extract of Bacopa monnieri on cognitive function in healthy human subjects
Another 12-week study showed older adults enjoyed the same cognitive enhancement benefits as their younger peers:
Children taking 225mg/day, meanwhile, saw a significant reduction in ADHD symptoms, such as restlessness and impulsivity:
And as for the mood benefits, 300mg/day significantly reduced anxiety and depression in elderly adults:
In summary
Bacopa monnieri, taken at 300mg/day (studies ranged from 225mg/day to 600mg/day, but 300mg is most common) has well-evidenced cognitive benefits, including:
- Improved attention, learning, and memory
- Reduced depression, anxiety, and stress
- Reduced restlessness and impulsivity
It may also have other benefits, including against oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer, but the research is thinner and/or not as conclusive for those.
Where to get it
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here is an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Building Psychological Resilience (Without Undue Hardship)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s The Worst That Could Happen?
When we talk about the five lifestyle factors that make the biggest difference to health, stress management would be a worthy addition as number six. We haven’t focused explicitly on that for a while, so let’s get ready to start the New Year on a good footing…
You’re not going to have a stress-free 2024
What a tender world that would be! Hopefully your stressors will be small and manageable, but rest assured, things will stress you.
And that’s key: “rest assured”. Know it now, prepare for it, and build resilience.
Sounds grim, doesn’t it? It doesn’t have to be, though.
When the forecast weather is cold and wet, you’re not afraid of it when you have a warm dry house. When the heating bill comes for that warm dry house, you’re not afraid of it when you have money to pay it. If you didn’t have the money and the warm dry house, the cold wet weather could be devastating to you.
The lesson here is: we can generally handle what we’re prepared for.
Negative visualization and the PNS
This is the opposite of what a lot of “think and grow rich”-style gurus would advise. And indeed, it’s not helpful to slide into anxious worrying.
If you do find yourself spiralling, here’s a tool for getting out of that spiral:
RAIN: an intervention for dealing with difficult emotions
For now, however, we’re going to practice Radical Acceptance.
First, some biology: you may be aware that your Central Nervous System (CNS) branches into the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) and the Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS).
The PNS is the part that cues our body to relax, and suppresses our fight/flight response. We’re going to activate it.
Activating the PNS is easy for most people in comfortable circumstances (e.g., you are not currently exposed to stressful stimuli). It may well be activated already, and if it’s not, a few deep breaths is usually all it takes.
If you’d like a quick and easy Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) technique, here you go:
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
Activating the PNS is hard for most people in difficult circumstances (e.g., you either are currently exposed to stressful stimuli, or you are in one of the emotional spirals we discussed earlier).
However, we can trick our bodies and brains by—when we are safe and unstressed—practicing imagining those stressful stimuli. Taking a moment to not just imagine it experientially, but immersively. This, in CBT and DBT, is the modern equivalent to the old samurai who simply accepted, before battle, that they were already dead—and thus went into battle with zero fear of death.
A less drastic example is the zen master who had a favorite teacup, and feared it would get broken. So he would tell himself “the cup is already broken”. One day, it actually broke, and he simply smiled ruefully and said “Of course”.
How this ties together: practice the mindfulness-based stress reduction we linked above, while imagining the things that do/would stress you the most.
Since it’s just imagination, this is a little easier than when the thing is actually happening. Practicing this way means that when and if the thing actually happens (an unfortunate diagnosis, a financial reversal, whatever it may be), our CNS is already well-trained to respond to stress with a dose of PNS-induced calm.
You can also leverage hormesis, a beneficial aspect of (in this case, optional and chosen by you) acute stress:
Dr. Elissa Epel | The Stress Prescription
Psychological resilience training
This (learned!) ability to respond to stress in an adaptive fashion (without maladaptive coping strategies such as unhelpful behavioral reactivity and/or substance use) is a key part of what in psychology is called resilience:
And yes, the CBT/DBT/MBSR methods we’ve been giving you are the evidence-based gold standard.
Only the best for 10almonds subscribers! 😎
❝That was helpful, but not cheery; can we finish the year on a cheerier note?❞
We can indeed:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: