Healthy Mind In A Healthy Body
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The 8-minute piece of music “Weightless” by Marconi was created scientifically to lower the heart rate and relax the listener. How did they do it? You can read the British Academy of Sound Therapy’s explanation of the methodology here, but important results of the study were:
- “Weightless” was able to induce greater relaxation levels than a massage (increase of 6%).
- “Weightless” also induced an 11% increase in relaxation over all other relaxing music tracks in the study.
- “Weightless” was also subjectively rated as more relaxing than any other music by all the participants.
Try it for yourself!
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Isn’t that better? Whenever you’re ready, read on…
Today we’re going to share a technique for dealing with difficult emotions. The technique is used in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), and it’s called RAIN:
- Recognizing: ask yourself “what is it that I’m feeling?”, and put a name to it. It could be anger, despair, fear, frustration, anxiety, overwhelm etc.
- Accepting: “OK, so, I’m feeling ________”. There’s no point in denying it, or being defensive about it, these things won’t help you. For now, just accept it.
- Investigating: “Why am I feeling ________?” Maybe there is an obvious reason, maybe you need to dig for a reason—or dig deeper for the real reason. Most bad feelings are driven by some sort of fear or insecurity, so that can be a good avenue for examination. Important: your feelings may be rational or irrational. That’s fine. This is a time for investigating, not judging.
- Non-Identification: not making whatever it is you’re feeling into a part of you. Once you get too attached to “I am jealous”, “I am angry”, “I am sad” etc, it can be difficult to manage something that has become a part of your personality; you’ll defend your jealousy, anger, sadness etc rather than tackle it.
As a CBT tool, this is something you can do for yourself at any time. It won’t magically solve your problems, but it can stop you from spiralling into a state of crisis, and get you back on a more useful track.
As a DBT tool, to give this its full strength, ideally now you will communicate what you’re feeling, to somebody you trust, perhaps a partner or friend, for instance.
Humans are fundamentally social creatures, and we achieve our greatest strengths when we support each other—and that also means sometimes seeking and accepting support!
Do you have a good technique you’d like to share? Reply to this email and let us know!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Quinoa vs Couscous – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing quinoa to couscous, we picked the quinoa.
Why?
Firstly, quinoa is the least processed by far. Couscous, even if wholewheat, has by necessity been processed to make what is more or less the same general “stuff” as pasta. Now, the degree to which something has or has not been processed is a common indicator of healthiness, but not necessarily declarative. There are some processed foods that are healthy (e.g. many fermented products) and there are some unprocessed plant or animal products that can kill you (e.g. red meat’s health risks, or the wrong mushrooms). But in this case—quinoa vs couscous—it’s all borne out pretty much as expected.
For the purposes of the following comparisons, we’ll be looking at uncooked/dry weights.
In terms of macros, quinoa has a little more protein, slightly lower carbs, and several times the fiber. The amino acids making up quinoa’s protein are also much more varied.
In the category of vitamins, quinoa has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and B9, while couscous boasts a little more of vitamins B3 and B5. Given the respective margins of difference, as well as the total vitamins contained, this category is an easy win for quinoa.
When it comes to minerals, this one’s not even more clear. Quinoa has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. Couscous, meanwhile has more of just one mineral: sodium. So, maybe not one you want more of.
All in all, today’s is an easy pick: quinoa!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Carbohydrate Mythbusting: Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
- What’s The Real Deal With The Paleo Diet?
- Gluten Mythbusting: What’s The Truth? ← we didn’t mention it above, but couscous is by default gluten-free, and couscous, being made of wheat, is by default not gluten-free, which may be another reason for some to choose quinoa
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Inflammation Spectrum – by Dr. Will Cole
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Cole’s other book “Gut Feelings”, and now he’s back, this time to tackle inflammation.
The focus here is on understanding what things trigger inflammation in your body—personally yours, not someone else’s—by something close to the usual elimination process yes, but he offers a way of sliding into it gently instead of simply quitting all the things and gradually adding everything back in.
The next step he takes the reader through is eating not just to avoid triggering inflammation, but to actively combat it. From there, it should be possible for the reader to build an anti-inflammatory cookbook, that’s not only one’s own personal repertoire of cooking, but also specifically tailored to one’s own personal responses to different ingredients.
The style of this book is very pop-science, helpful, walking-the-reader-by-the-hand through the processes involved. Dr. Cole wants to make everything as easy as possible.
Bottom line: if your diet could use an anti-inflammatory revamp, this is a top-tier guidebook for doing just that.
Click here to check out The Inflammation Spectrum, find your food triggers and reset your system!
Share This Post
-
Yes, adults can develop food allergies. Here are 4 types you need to know about
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you didn’t have food allergies as a child, is it possible to develop them as an adult? The short answer is yes. But the reasons why are much more complicated.
Preschoolers are about four times more likely to have a food allergy than adults and are more likely to grow out of it as they get older.
It’s hard to get accurate figures on adult food allergy prevalence. The Australian National Allergy Council reports one in 50 adults have food allergies. But a US survey suggested as many as one in ten adults were allergic to at least one food, with some developing allergies in adulthood.
What is a food allergy
Food allergies are immune reactions involving immunoglobulin E (IgE) – an antibody that’s central to triggering allergic responses. These are known as “IgE-mediated food allergies”.
Food allergy symptoms that are not mediated by IgE are usually delayed reactions and called food intolerances or hypersensitivity.
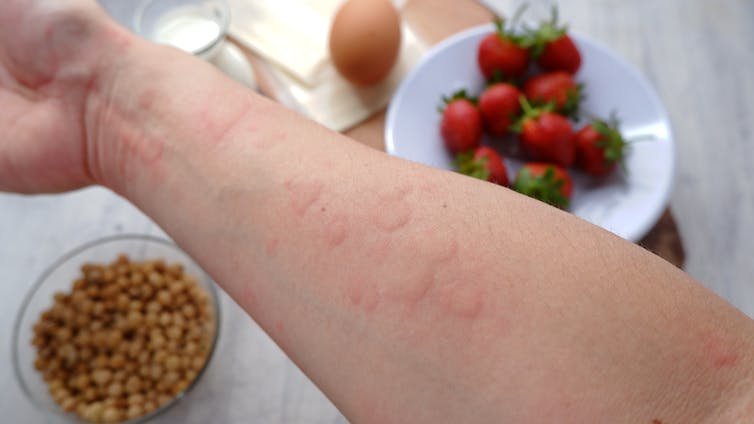
Food allergy symptoms can include hives, swelling, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, throat or chest tightening, trouble breathing, chest pain, rapid heart rate, dizziness, low blood pressure or anaphylaxis.
Symptoms include hives. wisely/Shutterstock IgE-mediated food allergies can be life threatening, so all adults need an action management plan developed in consultation with their medical team.
Here are four IgE-mediated food allergies that can occur in adults – from relatively common ones to rare allergies you’ve probably never heard of.
1. Single food allergies
The most common IgE-mediated food allergies in adults in a US survey were to:
- shellfish (2.9%)
- cow’s milk (1.9%)
- peanut (1.8%)
- tree nuts (1.2%)
- fin fish (0.9%) like barramundi, snapper, salmon, cod and perch.
In these adults, about 45% reported reacting to multiple foods.
This compares to most common childhood food allergies: cow’s milk, egg, peanut and soy.
Overall, adult food allergy prevalence appears to be increasing. Compared to older surveys published in 2003 and 2004, peanut allergy prevalence has increased about three-fold (from 0.6%), while tree nuts and fin fish roughly doubled (from 0.5% each), with shellfish similar (2.5%).
While new adult-onset food allergies are increasing, childhood-onset food allergies are also more likely to be retained into adulthood. Possible reasons for both include low vitamin D status, lack of immune system challenges due to being overly “clean”, heightened sensitisation due to allergen avoidance, and more frequent antibiotic use.
Some adults develop allergies to cow’s milk, while others retain their allergy from childhood. Sarah Swinton/Unsplash 2. Tick-meat allergy
Tick-meat allergy, also called α-Gal syndrome or mammalian meat allergy, is an allergic reaction to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose, or α-Gal for short.
Australian immunologists first reported links between α-Gal syndrome and tick bites in 2009, with cases also reported in the United States, Japan, Europe and South Africa. The US Centers for Disease Control estimates about 450,000 Americans could be affected.
The α-Gal contains a carbohydrate molecule that is bound to a protein molecule in mammals.
The IgE-mediated allergy is triggered after repeated bites from ticks or chigger mites that have bitten those mammals. When tick saliva crosses into your body through the bite, antibodies to α-Gal are produced.
When you subsequently eat foods that contain α-Gal, the allergy is triggered. These triggering foods include meat (lamb, beef, pork, rabbit, kangaroo), dairy products (yoghurt, cheese, ice-cream, cream), animal-origin gelatin added to gummy foods (jelly, lollies, marshmallow), prescription medications and over-the counter supplements containing gelatin (some antibiotics, vitamins and other supplements).
Tick-meat allergy reactions can be hard to recognise because they’re usually delayed, and they can be severe and include anaphylaxis. Allergy organisations produce management guidelines, so always discuss management with your doctor.
3. Fruit-pollen allergy
Fruit-pollen allergy, called pollen food allergy syndrome, is an IgE-mediated allergic reaction.
In susceptible adults, pollen in the air provokes the production of IgE antibodies to antigens in the pollen, but these antigens are similar to ones found in some fruits, vegetables and herbs. The problem is that eating those plants triggers an allergic reaction.
The most allergenic tree pollens are from birch, cypress, Japanese cedar, latex, grass, and ragweed. Their pollen can cross-react with fruit and vegetables, including kiwi, banana, mango, avocado, grapes, celery, carrot and potato, and some herbs such as caraway, coriander, fennel, pepper and paprika.
Fruit-pollen allergy is not common. Prevalence estimates are between 0.03% and 8% depending on the country, but it can be life-threatening. Reactions range from itching or tingling of lips, mouth, tongue and throat, called oral allergy syndrome, to mild hives, to anaphylaxis.
4. Food-dependent, exercise-induced food allergy
During heavy exercise, the stomach produces less acid than usual and gut permeability increases, meaning that small molecules in your gut are more likely to escape across the membrane into your blood. These include food molecules that trigger an IgE reaction.
If the person already has IgE antibodies to the foods eaten before exercise, then the risk of triggering food allergy reactions is increased. This allergy is called food-dependent exercise-induced allergy, with symptoms ranging from hives and swelling, to difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis.
This type of allergy is extremely rare. Ben O’Sullivan/Unsplash Common trigger foods include wheat, seafood, meat, poultry, egg, milk, nuts, grapes, celery and other foods, which could have been eaten many hours before exercising.
To complicate things even further, allergic reactions can occur at lower levels of trigger-food exposure, and be more severe if the person is simultaneously taking non-steroidal inflammatory medications like aspirin, drinking alcohol or is sleep-deprived.
Food-dependent exercise-induced allergy is extremely rare. Surveys have estimated prevalence as between one to 17 cases per 1,000 people worldwide with the highest prevalence between the teenage years to age 35. Those affected often have other allergic conditions such as hay fever, asthma, allergic conjunctivitis and dermatitis.
Allergies are a growing burden
The burden on physical health, psychological health and health costs due to food allergy is increasing. In the US, this financial burden was estimated as $24 billion per year.
Adult food allergy needs to be taken seriously and those with severe symptoms should wear a medical information bracelet or chain and carry an adrenaline auto-injector pen. Concerningly, surveys suggest only about one in four adults with food allergy have an adrenaline pen.
If you have an IgE-mediated food allergy, discuss your management plan with your doctor. You can also find more information at Allergy and Anaphylaxis Australia.
Clare Collins, Laureate Professor in Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Buckwheat vs Bulgur Wheat – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing buckwheat to bulgur, we picked the buckwheat.
Why?
First, some things to know up front:
- Bulgur wheat is a kind of cracked wheat product. As such, it contains wheat, and yes, gluten.
- Buckwheat is not a wheat, nor even a grass, but a flowering plant. Buckwheat is as related to wheat as a lionfish is to a lion. It does not contain gluten.
- Buckwheat can be purchased whole or hulled. We went with whole. If you go with hulled, the percentages of vitamins and minerals will be relatively higher, and/but this will be because you lost the fibrous husk, so they’ll be commensurately lower in fiber. If you were to go with hulled, we’d still pick it over bulgur wheat though, just for a different reason (as in that case, the vitamin and mineral contents would be more overwhelmingly in buckwheat’s favor, even though it’d have less fiber).
Ok, now that those things are covered…
Looking at the macronutrients, there’s not a lot between them, except that buckwheat has the much lower glycemic index (this is only the case if you got whole, not hulled—if you got hulled, the glycemic index would be about the same).
In terms of vitamins, buckwheat has more of vitamins B2, B5, B9, E, K, and choline, while bulgur wheat technically has more vitamin A, but the numbers are tiny; a cup of bulgur wheat will give you 0.12% of the RDA. So, an easy win (functionally: 5:0) for buckwheat.
When it comes to minerals, buckwheat has more copper, magnesium, potassium, and selenium, while bulgur wheat has more calcium and manganese. They’re equal on iron and phosphorus, making this a 4:2 win for buckwheat.
Adding up the categories makes this a clear win for buckwheat!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Mediterranean Diet Cookbook for Beginners – by Jessica Aledo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are a lot of Mediterranean Diet books on the market, and not all of them actually stick to the Mediterranean Diet. There’s a common mistake of thinking “Well, this dish is from the Mediterranean region, so…”, but that doesn’t make, for example, bacon-laden carbonara part of the Mediterranean Diet!
Jessica Aledo does better, and sticks unwaveringly to the Mediterranean Diet principles.
First, she gives a broad introduction, covering:
- The Mediterranean Diet pyramid
- Foods to eat on the Mediterranean Diet
- Foods to avoid on the Mediterranean Diet
- Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
Then, it’s straight into the recipes, of which there are 201 (as with many recipe books, the title is a little misleading about this).
They’re divided into sections, thus:
- Breakfasts
- Lunches
- Snacks
- Dinners
- Desserts
The recipes are clear and simple, one per double-page, with high quality color illustrations. They give ingredients/directions/nutrients. There’s no padding!
Helpfully, she does include a shopping list as an appendix, which is really useful!
Bottom line: if you’re looking to build your Mediterranean Diet repertoire, this book is an excellent choice.
Get your copy of The Mediterranean Diet Cookbook for Beginners from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Alzheimer’s Gut-Brain Connection—Caught On X-Ray!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about Alzheimer’s disease (a lot), and if you’re just joining us, then a great place to start is here:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
We’ve also written about gut health (a lot), and if you’re just joining us, then a great place to start is here:
Make Friends With Your Gut! (Here’s Why & How)
And as a hat trick, yes, we’ve also written (admittedly not as much) about the gut-brain connection; here’s a primer:
The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
Because of how gut microbes influence brain function, behavior, and cognition, scientists wondered whether one’s microbiome might play a role in Alzheimer’s development. Recently, scientists from Italy’s Institute of Nanotechnology, working with the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF), found some concrete answers:
How gut health affects Alzheimer’s
When the gut loses its healthy balance of bacteria, harmful bacteria (and fungi, like C. albicans, also popularly called by its first name, “Candida”) take the wheel. This problem (called “dysbiosis”) allows harmful microbes to produce toxic substances, leading to inflammation and weakening the protective barriers between the gut and brain.
In some cases, like the aforementioned C. albicans, they’ll even put roots through your gut wall (and interact with your nervous system, and they are a common reason for sugar and alcohol cravings—your CNS has literally been hacked by a fungal colony that wants sugar (including the sugar that occurs when alcohol is broken down—and that’s without considering the fact that alcohol also kills several of C. albicans competitors that rank amongst the “good bacteria”). Suffice it to say, the holes it puts in your gut wall aren’t great for the health either.
In any case, once the gut barrier is breached, it’s been hypothesized that harmful bacteria may even travel to the brain, triggering Alzheimer’s.
How the x-rays helped
To better understand gut changes in Alzheimer’s, scientists used a technique called nano- and micro- x-ray phase-contrast tomography (XPCT) at the aforementioned ESRF. That very fancy string of words refers to a commensurately powerful imaging method, which allows researchers to see detailed structures inside the gut without damaging tissue, or even adding contrast agents (like those unpleasant drinks that are sometimes required to be taken before soft-tissue x-rays).
The study examined gut samples from mice with Alzheimer’s (so yes, this does need to be repeated with humans, but in this case there’s no obvious reason why it shouldn’t be the same).
The scans revealed important changes in gut structures, including:
- The tiny finger-like villi and corresponding crypts in the gut lining
- Important cells* that help with digestion and protection
- Neurons involved in gut function
*e.g. Paneth cells, goblet cells, telocytes, and erythrocytes, all of whom would take more explanation than we have room for here, but suffice it to say they’re important to both digestion and correct mucus production (bearing in mind, mucus membranes are one of the main physical barriers to harmful bacteria—as humans, our conscious interactions with mucus are usually only the nuisance that occurs when we get a cold or something, but rest assured, mucus keeps us alive).
In short, all these findings suggest (we’d say “show”, but technically cause and effect have not been proven) gut health indeed plays a crucial role in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and pathology (i.e., how the disease begins and progresses, respectively).
Why it matters
To quote Dr. Alessia Cedola,
❝This technique represents a real breakthrough for the thorough analysis of the gut, and it could be pivotal in early detection and prognosis of the disease.
By gaining a deeper understanding of these processes, we hope to identify new therapeutic targets and develop innovative treatments for this devastating disease.❞
In short: the technology can be used as a super-early diagnostic tool, and ultimately, improve prevention (by encouraging people to focus on gut health) as well as, hopefully, leading to new treatments, too.
Want to see it?
Here’s the paper itself, where there are also abundant very clear images:
Are you on top of your gut health already?
If not, do refer back to that first link we dropped about gut health, up top!
If you are already sure you’re looking after your gut and want to do something else to avoid Alzheimer’s coming to call, you might want to consider:
How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer) ← your glymphatic system, something many people neglect, is the brain’s cleanup crew, and removes things like the beta-amyloid proteins that are implicated in Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. So, it’s worth knowing how to keep it in working order!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: