Kimchi Fried Rice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fried rice is not something that leaps to many people’s minds when one says “health food”. But it can be! Today’s recipe is great for many aspects of health, but especially the gut, because of its star ingredient, the kimchi—as well as the fiber in the rest of the dish, which is mostly a variety of vegetables, as well as the rice, which we are assuming you got wholegrain. An optional egg per person adds more healthy fats too!
You will need
- Avocado oil, for frying. We picked avocado oil for its healthy fats profile, neutral taste, and high smoke point (we’ll be working at very high temperatures today that might make olive oil or coconut oil smoke). We also recommend against seed oils (e.g. sunflower or canola) for health reasons.
- 1lb cooked and cooled rice—here’s our recipe for Tasty Versatile Rice if you don’t have leftovers you want to use
- 7oz kimchi, roughly chopped
- 4 spring onions, finely chopped
- 4oz white cabbage, finely shredded
- 3oz frozen peas, defrosted
- 1 bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 1 carrot, grated
- ½ red pepper, finely diced
- 2 tbsp chili oil (or 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil and 1 red chili, very finely chopped) ← don’t worry about the smoke point of this; it’s going to be for drizzling
- 1 tbsp dark soy sauce
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- Optional: 1 egg per person
- Note: we didn’t forget to include salt; there’s simply enough already in the dish because of the kimchi and soy sauce.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Lightly oil a wok (or similar) and crank up the heat as high as your stove can muster. Add the garlic and spring onions; keep them moving. When they’re turning golden, add the cabbage, carrot, and red pepper. Add them one by one, giving the wok a chance to get back to temperature each time before adding the next ingredient.
2) When the vegetables are beginning to caramelize (if the temperature is good, this should only be a couple of minutes at most), add the rice, as well as the kimchi, peas, soy sauce, and black pepper. Toss everything ensure it’s all well-combined and evenly cooked. When it’s done (probably only another minute or two), take it off the heat.
3) Optional: if you’re adding eggs, fry them now. Serve a bowl of kimchi-fried rice per person, adding 1 fried egg on top of each.
4) Drizzle the chili oil as a colorful, tasty garnish that’s full of healthful polyphenols too.
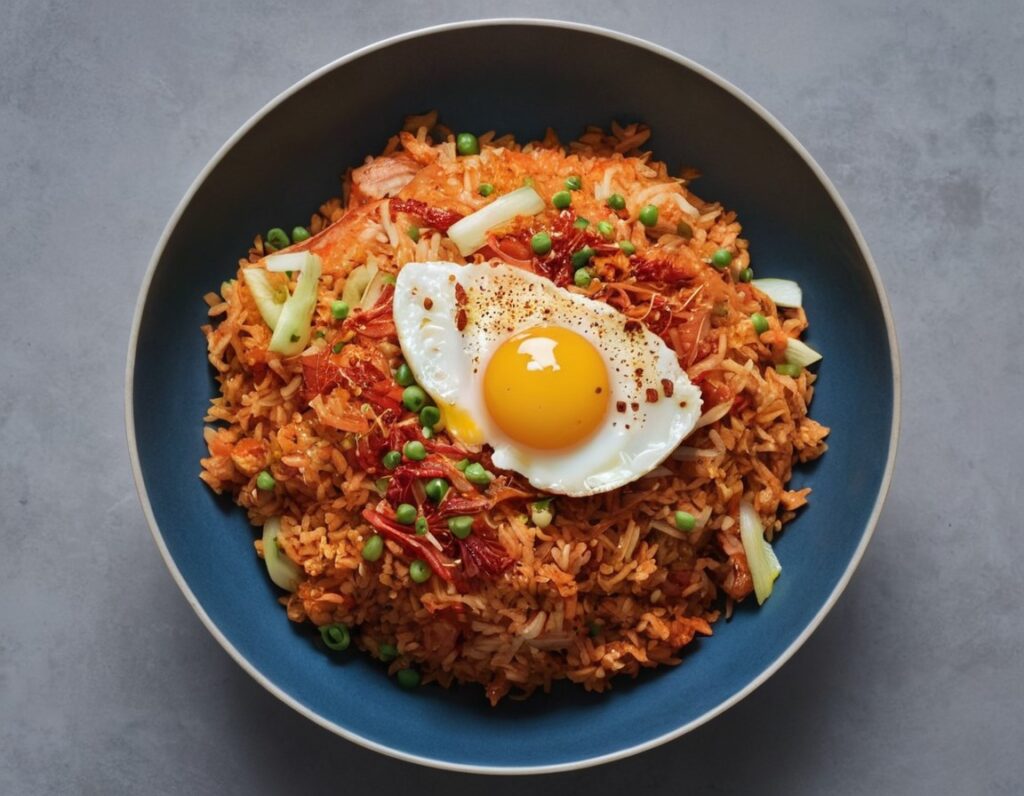

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Tasty Polyphenols ← this is about how foods that are pungent, bitter, spicy, etc tend to have the highest polyphenol contents
- Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
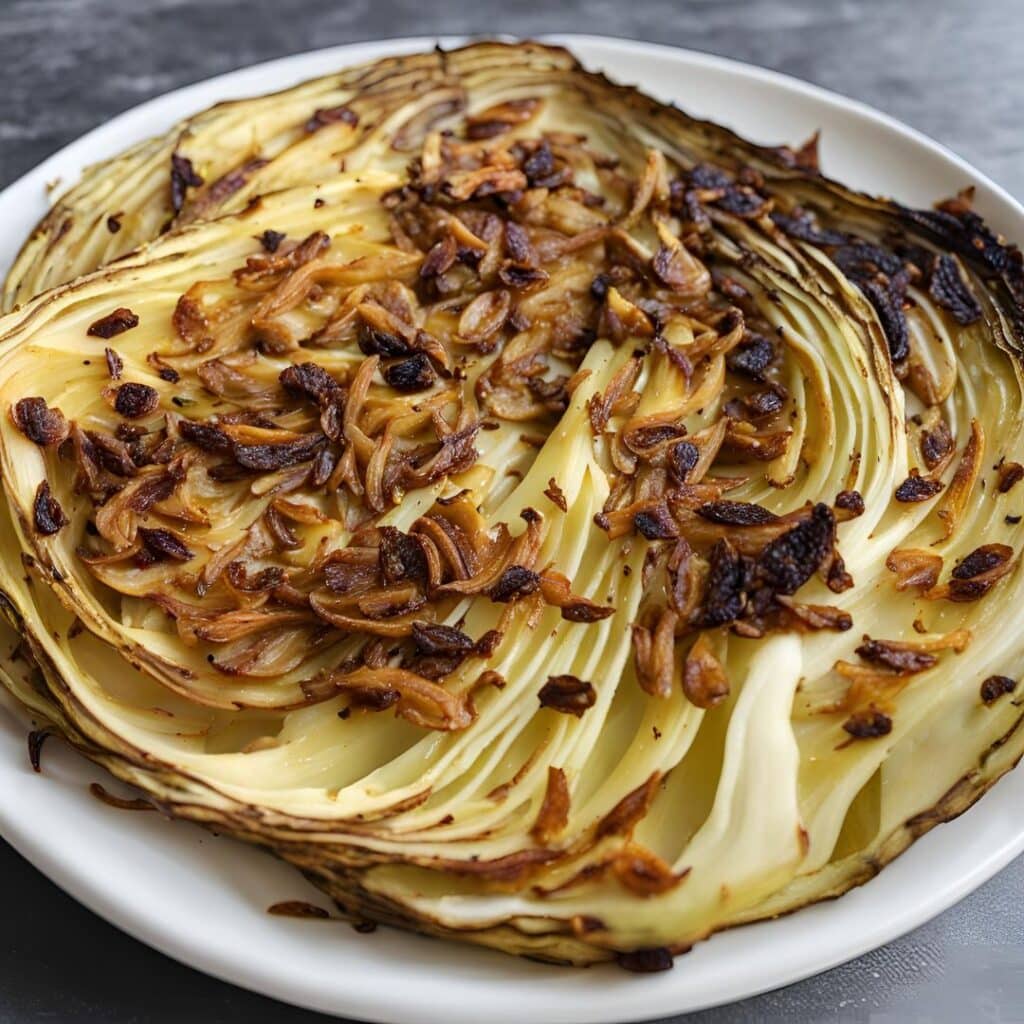
Caramelized Caraway Cabbage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cabbage is an underrated vegetable for its many nutrients and its culinary potential—here’s a great way to make it a delectable starter or respectable side.
You will need
- 1 medium white cabbage, sliced into 1″ thick slabs
- 1 tbsp extra-virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp caraway seeds
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp turmeric
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the non-cabbage ingredients in a small bowl, whisking to mix thoroughly—with a tiny whisk if you have one, but a fork will work if necessary.
3) Arrange the cabbage slices on a lined baking tray and brush the seasoning-and-oil mixture over both sides of each slice.
4) Roast for 20–25 minutes until the cabbage is tender and beginning to caramelize.
5) Serve warm.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Curcumin (Turmeric) is worth its weight in gold
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Anti-Aging Myths This Dermatologist Wants You To Stop Believing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dermatologist Dr. Sam Ellis lays all bare:
Bare-faced lies?
Obviously, we are hearing from a dermatologist here, so the focus is on skin aging specifically. We may well also not want to age our brain, joints, etc, but that’s not what this one is about.
So, without further ado, here are the myths she wants to bust:
- “Medical grade skincare”: the term “medical grade” is a marketing term and does not indicate superior efficacy or better ingredients.
- “Expensive skincare is more effective”: price does not always correlate with effectiveness; some high-end products justify their cost, but many do not.
- “More products = better results”: using too many products can reduce effectiveness and cause irritation; a simple routine with sunscreen and a retinoid is key.
- “Drink more water for better skin”: if you’re dehydrated, then yes, hydrate—but drinking excessive water does not improve skin appearance beyond normal hydration levels.
- “You don’t need anti-aging products until you see signs of aging”: starting skincare early, especially sun protection, helps maintain youthful skin longer.
- “Wrinkles are the first signs of aging”: hyperpigmentation and sagging are often more significant early indicators of aging than wrinkles.
- “Skincare is all you need for anti-aging”: by “skincare” here she means creams, lotions, tonics, etc, and recommends other treatments such as laser treatment and even Botox*.
- “Non-prescription retinoids are a waste of time”: over-the-counter retinoids like retinol and retinal can still be effective alternatives to prescription retinoids.
- “You must use retinoids every night”: retinoids are effective even when used a few times per week, depending on individual tolerance.
*We’re not convinced about the Botox; we’ll have to do a deep-dive research review one of these days!
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Retinoids: Retinol vs Retinal vs Retinoic Acid vs..?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
More Than One Way To Kill Pain
This is Dr. Deepak Ravindran (MD, FRCA. FFPMRCA, EDRA. FIPP, DMSMed). He has decades of experience and is a specialist in acute and chronic pain management, anesthesia, musculoskeletal medicine, and lifestyle medicine.
A quick catch-up, first:
We’ve written about chronic pain management before:
Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
As well as:
Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
Dr. Ravindran’s approach
Dr. Ravindran takes a “trauma-informed care” approach to his professional practice, and recommends the same for others.
In a nutshell, this means starting from a position of not “what’s wrong with you?”, but rather “what happened to you?”.
This seemingly subtle shift is important, because it means actually dealing with a person’s issues, instead of “take one of these and call my secretary next month”. Read more:
Pain itself can be something of a many-headed hydra. Dr. Ravindran’s approach is equally many-headed; specifically, he has a 7-point plan:
Medications
Dr. Ravindran sees painkillers (and a collection of other drugs, like antidepressants and muscle relaxants) as a potential means to an end worth exploring, but he doesn’t expect them to be the best choice for everyone, and nor does he expect them to be a cure-all. Neither should we. He also advises being mindful of the drawbacks and potential complications of these drugs, too.
Interventions
Sometimes, surgery is the right choice. Sometimes it isn’t. Often, it will change a life—one way or the other. Similar to with medications, Dr. Ravindran is very averse to a “one size fits all” approach here. See also:
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
Neuroscience and stress management
Often a lot of the distress of pain is not just the pain itself, but the fear associated with it. Will it get worse if I move wrong or eat the wrong thing? How long will it last? Will it ever get better? Will it get worse if I do nothing?. Dr. Ravindran advises tackling this, with the same level of importance as the pain itself. Here’s a good start:
Stress, And Building Psychological Resilience
Diet and the microbiome
Many chronic illnesses are heavily influenced by this, and Dr. Ravindran’s respect for lifestyle medicine comes into play here. While diet might not fix all our ills, it certainly can stop things from being a lot worse. Beyond the obvious “eat healthily” (Mediterranean diet being a good starting point for most people), he also advises doing elimination tests where appropriate, to screen out potential flare-up triggers. You also might consider:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
Sleep
“Get good sleep” is easy advice for those who are not in agonizing pain that sometimes gets worse from staying in the same position for too long. Nevertheless, it is important, and foundational to good health. So it’s important to explore—whatever limitations one might realistically have—what can be done to improve it.
If you can only sleep for a short while at a time, you may get benefit from this previous main feature of ours:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
Exercise and movement
The trick here is to move little and often; without overdoing it, but without permitting loss of mobility either. See also:
The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Therapies of the mind and body
This is about taking a holistic approach to one’s wellness. In Dr. Ravindran’s words:
❝Mind-body therapies are often an extremely sensitive topic about which people hold very strong opinions and sometimes irrational beliefs.
Some, like reiki and spiritual therapy and homeopathy, have hardly any scientific evidence to back them up, while others like yoga, hypnosis, and meditation/mindfulness are mainstream techniques with many studies showing the benefits, but they all work for certain patients.❞
In other words: evidence-based is surely the best starting point, but if you feel inclined to try something else and it works for you, then it works for you. And that’s a win.
Want to know more?
You might like his book…
The Pain-Free Mindset: 7 Steps to Taking Control and Overcoming Chronic Pain
He also has a blog and a podcast.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Vaccines and cancer: The myth that won’t die
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Two recent studies reported rising cancer rates among younger adults in the U.S. and worldwide. This prompted some online anti-vaccine accounts to link the studies’ findings to COVID-19 vaccines.
But, as with other myths, the data tells a very different story.
What you need to know
- Baseless claims that COVID-19 vaccines cause cancer have persisted online for several years and gained traction in late 2023.
- Two recent reports finding rising cancer rates among younger adults are based on pre-pandemic cancer incidence data. Cancer rates in the U.S. have been on the rise since the 1990s.
- There is no evidence of a link between COVID-19 vaccination and increased cancer risk.
False claims about COVID-19 vaccines began circulating months before the vaccines were available. Chief among these claims was misinformed speculation that vaccine mRNA could alter or integrate into vaccine recipients’ DNA.
It does not. But that didn’t prevent some on social media from spinning that claim into a persistent myth alleging that mRNA vaccines can cause or accelerate cancer growth. Anti-vaccine groups even coined the term “turbo cancer” to describe a fake phenomenon of abnormally aggressive cancers allegedly linked to COVID-19 vaccines.
They used the American Cancer Society’s 2024 cancer projection—based on incidence data through 2020—and a study of global cancer trends between 1999 and 2019 to bolster the false claims. This exposed the dishonesty at the heart of the anti-vaccine messaging, as data that predated the pandemic by decades was carelessly linked to COVID-19 vaccines in viral social media posts.
Some on social media cherry-pick data and use unfounded evidence because the claims that COVID-19 vaccines cause cancer are not true. According to the National Cancer Institute and American Cancer Society, there is no evidence of any link between COVID-19 vaccines and an increase in cancer diagnosis, progression, or remission.
Why does the vaccine cancer myth endure?
At the root of false cancer claims about COVID-19 vaccines is a long history of anti-vaccine figures falsely linking vaccines to cancer. Polio and HPV vaccines have both been the target of disproven cancer myths.
Not only do HPV vaccines not cause cancer, they are one of only two vaccines that prevent cancer.
In the case of polio vaccines, some early batches were contaminated with simian virus 40 (SV40), a virus that is known to cause cancer in some mammals but not humans. The contaminated batches were discovered, and no other vaccine has had SV40 contamination in over 60 years.
Follow-up studies found no increase in cancer rates in people who received the SV40-contaminated polio vaccine. Yet, vaccine opponents have for decades claimed that polio vaccines cause cancer.
Recycling of the SV40 myth
The SV40 myth resurfaced in 2023 when vaccine opponents claimed that COVID-19 vaccines contain the virus. In reality, a small, nonfunctional piece of the SV40 virus is used in the production of some COVID-19 vaccines. This DNA fragment, called the promoter, is commonly used in biomedical research and vaccine development and doesn’t remain in the finished product.
Crucially, the SV40 promoter used to produce COVID-19 vaccines doesn’t contain the part of the virus that enters the cell nucleus and is associated with cancer-causing properties in some animals. The promoter also lacks the ability to survive on its own inside the cell or interact with DNA. In other words, it poses no risk to humans.
Over 5.6 billion people worldwide have received COVID-19 vaccines since December 2020. At that scale, even the tiniest increase in cancer rates in vaccinated populations would equal hundreds of thousands of excess cancer diagnoses and deaths. The evidence for alleged vaccine-linked cancer would be observed in real incidence, treatment, and mortality data, not social media anecdotes or unverifiable reports.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it’s time to tell the meat to beat it…
Meat in general, and red meat and processed meat in particular, have been associated with so many health risks, that it’s very reasonable to want to reduce, if not outright eliminate, our meat consumption.
First, in case anyone’s wondering “what health risks?”
The aforementioned culprits tend to turn out to be a villain in the story of every second health-related thing we write about here. To name just a few:
- Processed Meat Consumption and the Risk of Cancer: A Critical Evaluation of the Constraints of Current Evidence from Epidemiological Studies
- Red Meat Consumption (Heme Iron Intake) and Risk for Diabetes and Comorbidities?
- Health Risks Associated with Meat Consumption: A Review of Epidemiological Studies
- Associations of Processed Meat, Unprocessed Red Meat, Poultry, or Fish Intake With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality
- Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010-2020) evidences
Seasoned subscribers will know that we rarely go more than a few days without recommending the very science-based Mediterranean Diet which studies find beneficial for almost everything we write about. The Mediterranean Diet isn’t vegetarian per se—by default it consists of mostly plants but does include some fish and a very small amount of meat from land animals. But even that can be improved upon:
- A Pesco-Mediterranean Diet With Intermittent Fasting
- Mediterranean, vegetarian and vegan diets as practical outtakes of EAS and ACC/AHA recommendations for lowering lipid profile
- A Mediterranean Low-Fat Vegan Diet to Improve Body Weight and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Randomized, Cross-over Trial
So that’s the “why”; now for the “how”…
It’s said that with a big enough “why” you can always find a “how”, but let’s make things easy!
Meatless Mondays
One of the biggest barriers to many people skipping the meat is “what will we even eat?”
The idea of “Meatless Mondays” means that this question need only be answered once a week, and in doing that a few Mondays in a row, you’ll soon find you’re gradually building your repertoire of meatless meals, and finding it’s not so difficult after all.
Then you might want to expand to “meat only on the weekends”, for example.
Flexitarian
This can be met with derision, “Yes and I’m teetotal, apart from wine”, but there is a practical aspect here:
The idea is “I will choose vegetarian options, unless it’s really inconvenient for me to do so”, which wipes out any difficulty involved.
After doing this for a while, you might find that as you get more used to vegetarian stuff, it’s almost never inconvenient to eat vegetarian.
Then you might want to expand it to “I will choose vegan options, unless it’s really inconvenient for me to do so”
Like-for-like substitutions
Pretty much anything that can come from an animal, one can get a plant-based version of it nowadays. The healthiness (and cost!) of these substitutions can vary, but let’s face it, meat is neither the healthiest nor the cheapest thing out there these days either.
If you have the money and don’t fancy leaping to lentils and beans, this can be a very quick and easy zero-effort change-over. Then once you’re up and running, maybe you can—at your leisure—see what all the fuss is about when it comes to tasty recipes with lentils and beans!
That’s all we have time for today, but…
We’re thinking of doing a piece making your favorite recipes plant-based (how to pick the right substitutions so the meal still tastes and “feels” the same), so let us know if you’d like that? Feel free to mention your favorite foods/meals too, as that’ll help us know what there’s a market for!
You can do that by hitting reply to any of our emails, or using the handy feedback widget at the bottom!
Curious to know more while you wait?
Check out: The Vegan Diet: A Complete Guide for Beginners ← this is a well-sourced article from Healthline, who—just like us—like to tackle important health stuff in an easy-to-read, well-sourced format
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
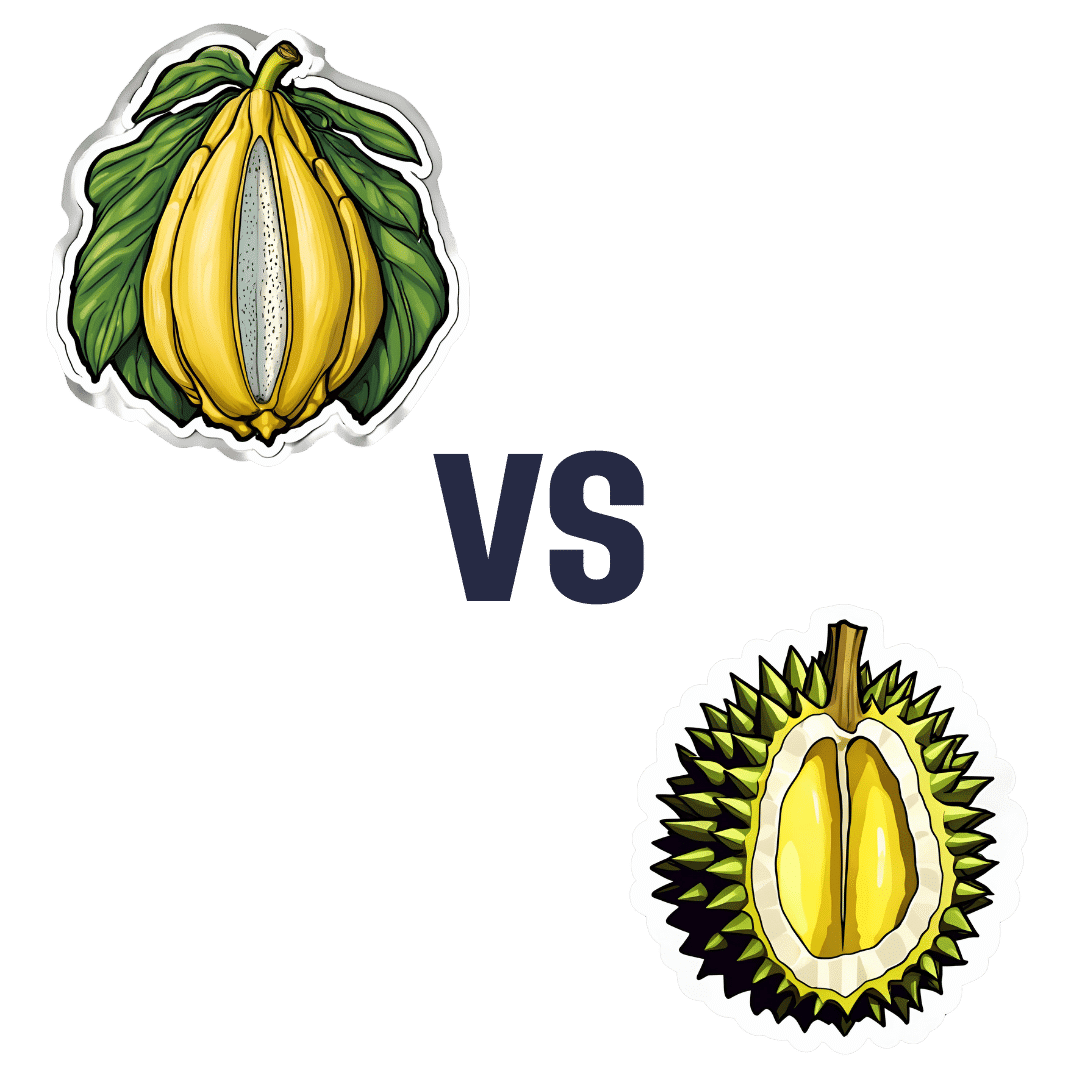
Jackfruit vs Durian – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing jackfruit to durian, we picked the durian.
Why?
Durian may look and smell like it has come directly from Hell, but there’s a lot of goodness in there!
First, let’s talk macros: jackfruit and durian are both unusually high in protein, for fruits. That said, jackfruit does have slightly more protein—but durian has more than 2x the fiber, for only slightly more carbs, so we call this section a win for durian.
Like most fruits, these two are an abundance source of vitamins; jackfruit has more of vitamins A and E, while durian has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B9, and C. Another win for durian.
When it comes to minerals, jackfruit has more calcium, while durian has more copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. We don’t usually measure this one as there’s not much in most foods (unless added in artificially), but durian is also high in sulfur, specifically in “volatile sulfur compounds”, which account for some of its smell, and are—notwithstanding the alarming name—harmless. In any case, mineral content is another win for durian.
These three things add up to one big win for durian.
There is one thing to watch out for, though: durian inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase, which the body uses to metabolize alcohol. So, we recommend you don’t drink-and-durian, as it can increase the risk of alcohol poisoning, and even if alcohol consumption is moderate, it’ll simply stay in your system for longer, doing more damage while it’s there. Of course, it is best to simply avoid drinking alcohol regardless, durian or no durian, but the above is good to know for those who do imbibe.
A final word on durians: if you haven’t had it before, or had it and it was terrible, then know: much like a banana or an avocado, durian has a rather brief “ideal ripeness” phase for eating. It should be of moderate firmness; neither tough nor squishy. It should not have discolored spikes, nor should it have little holes in, nor be leaking fluid, and it should not smell of sweat and vinegar, although it should smell like sulfurous eggs, onions, and cheese. Basically, if it smells like a cheese-and-onion omelette made in Hell, it’s probably good. If it smells like something that died and then was kept warm in someone’s armpit for a day, it’s probably not. The best way to have a good first experience with a durian is to enjoy one with someone who knows and enjoys durians, as they will be able to pick one that’s right, and will know if it’s not (durian-sellers may not necessarily have your best interests at heart, and may seek to palm off over-ripe durians on people who don’t know better).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: