The Other Significant Others – by Rhaina Cohen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we get older, it’s a function of statistics that increasingly many of us are divorced or widowed. While some will—after whatever time seems right to them—get back into dating, what about those of us who decide that we won’t?
Rhaina Cohen explores the importance of friendship, mutual support, and (Platonic!) closeness and yes, even kinds of intimacy (for that too can be Platonic!) as we go on.
Even from a purely evolutionary approach, we are fundamentally social creatures, and while as individuals we may exist on a spectrum from reclusive to extroverted, we all thrive better when we at least have access to community and friends.
The style of the book is easy-reading and exploratory, and is very compelling as a call-to-arms for those who may wish to give/receive support to/from those with whom we are not necessarily sleeping.
Because at the end of the day, why should sex and/or romance be a required feature for legal protections? Aren’t we adults who can make our own decisions about whom we trust to care for us?
Bottom line: if you’re happily partnered and expect to pre-decease your partner, this book might not be directly important for you (it might for your partner, though). Everyone else? This book may be important at some point. That point might even be now already; only you know.
Click here to check out The Other Significant Others, and make your own choices in life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
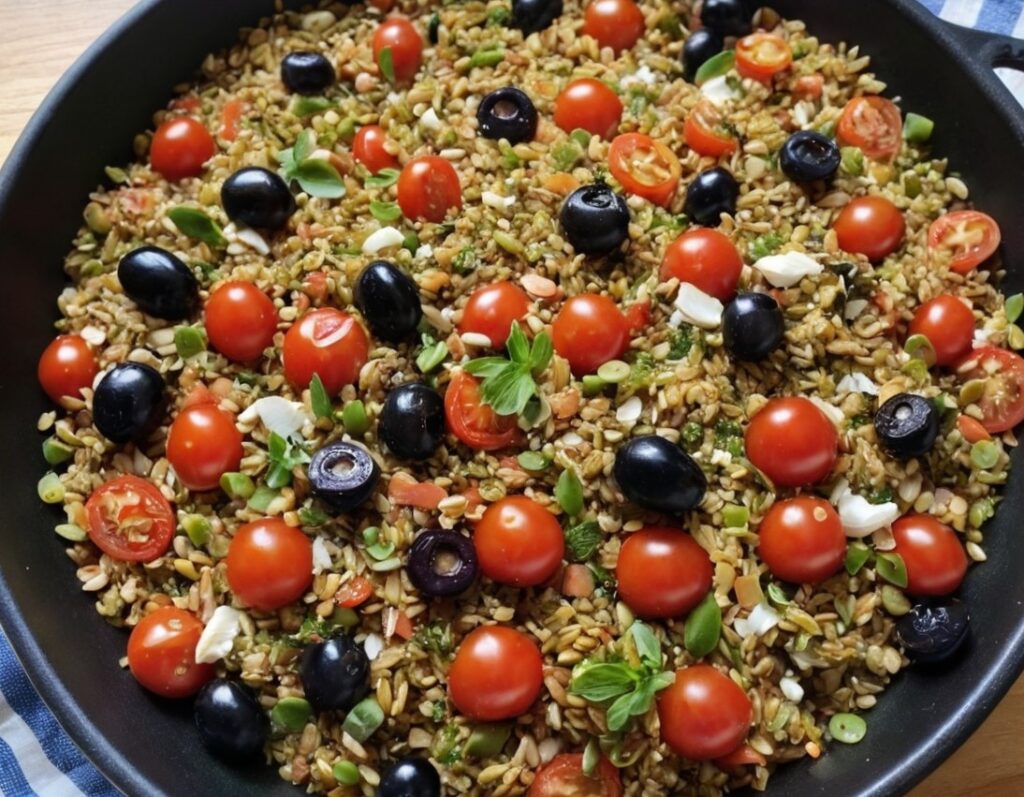
Freekeh Tomato Feast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber-dense freekeh stars in this traditional Palestinian dish, and the whole recipe is very gut-healthy, not to mention delicious and filling, as well as boasting generous amounts of lycopene and other phytonutrients:
You will need
- 1 cup dried freekeh (if avoiding gluten, substitute a gluten-free grain, or pseudograin such as buckwheat; if making such a substitution, then also add 1 tbsp nutritional yeast—for the flavor as well as the nutrients)
- 1 medium onion, thinly sliced
- 1 2oz can anchovies (if vegan/vegetarian, substitute 1 can kimchi)
- 1 14oz can cherry tomatoes
- 1 cup halved cherry tomatoes, fresh
- ½ cup black olives, pitted
- 1 5oz jar roasted peppers, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 sprig fresh thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Place a heavy-based (cast iron, if you have it) sauté pan over a medium heat. Add some olive oil, then the onion, stirring for about 5 minutes.
2) Add the anchovies, herbs and spices (including the garlic), and stir well to combine. The anchovies will probably soon melt into the onion; that’s fine.
3) Add the canned tomatoes (but not the fresh), followed by the freekeh, stirring well again to combine.
4) Add 2 cups boiling water, and simmer with the lid on for about 40 minutes. Stir occasionally and check the water isn’t getting too low; top it up if it’s getting dry and the freekeh isn’t tender yet.
5) Add the fresh chopped cherry tomatoes and the chopped peppers from the jar, as well as the olives. Stir for just another 2 minutes, enough to let the latest ingredients warm through.
6) Serve, adding a garnish if you wish:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Are plant-based burgers really bad for your heart? Here’s what’s behind the scary headlines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re hearing a lot about ultra-processed foods and the health effects of eating too many. And we know plant-based foods are popular for health or other reasons.
So it’s not surprising new research out this week including the health effects of ultra-processed, plant-based foods is going to attract global attention.
And the headlines can be scary if that research and the publicity surrounding it suggests eating these foods increases your risk of heart disease, stroke or dying early.
Here’s how some media outlets interpreted the research. The Daily Mail ran with:
Vegan fake meats are linked to increase in heart deaths, study suggests: Experts say plant-based diets can boost health – but NOT if they are ultra-processed
The New York Post’s headline was:
Vegan fake meats linked to heart disease, early death: study
But when we look at the study itself, it seems the media coverage has focused on a tiny aspect of the research, and is misleading.
So does eating supermarket plant-based burgers and other plant-based, ultra-processed foods really put you at greater risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death?
Here’s what prompted the research and what the study actually found.
Nina Firsova/Shutterstock Remind me, what are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods undergo processing and reformulation with additives to enhance flavour, shelf-life and appeal. These include everything from packet macaroni cheese and pork sausages, to supermarket pastries and plant-based mince.
There is now strong and extensive evidence showing ultra-processed foods are linked with an increased risk of many physical and mental chronic health conditions.
Although researchers question which foods should be counted as ultra-processed, or if all of them are linked to poorer health, the consensus is that, generally, we should be eating less of them.
We also know plant-based diets are popular. These are linked with a reduced risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke, cancer and diabetes. And supermarkets are stocking more plant-based, ultra-processed food options.
How about the new study?
The study looked for any health differences between eating plant-based, ultra-processed foods compared to eating non-plant based, ultra-processed foods. The researchers focused on the risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease and stroke) and deaths from it.
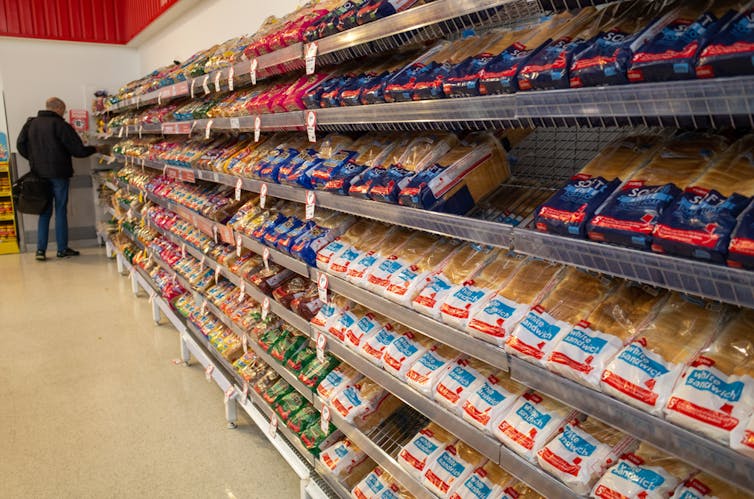
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods in this study included mass-produced packaged bread, pastries, buns, cakes, biscuits, cereals and meat alternatives (fake meats). Ultra-processed foods that were not plant-based included milk-based drinks and desserts, sausages, nuggets and other reconstituted meat products.
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank. This is a large biomedical database that contains de-identified genetic, lifestyle (diet and exercise) and health information and biological samples from half a million UK participants. This databank allows researchers to determine links between this data and a wide range of diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
They used data from nearly 127,000 people who provided details of their diet between 2009 and 2012. The researchers linked this to their hospital records and death records. On average, the researchers followed each participant’s diet and health for nine years.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods included in this study included packaged supermarket bread. doublelee/Shutterstock What did the study find?
With every 10% increase of total energy from plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods there was an associated 5% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke) and a 12% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
But for every 10% increase in plant-sourced, non-ultra-processed foods consumed there was an associated 7% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
The researchers found no evidence for an association between all plant-sourced foods (whether or not they were ultra-processed) and either an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease or dying from it.
This was an observational study, where people recalled their diet using questionnaires. When coupled with other data, this can only tell us if someone’s diet is associated with a particular risk of a health outcome. So we cannot say that, in this case, the ultra-processed foods caused the heart disease and deaths from it.
Why has media coverage focused on fake meats?
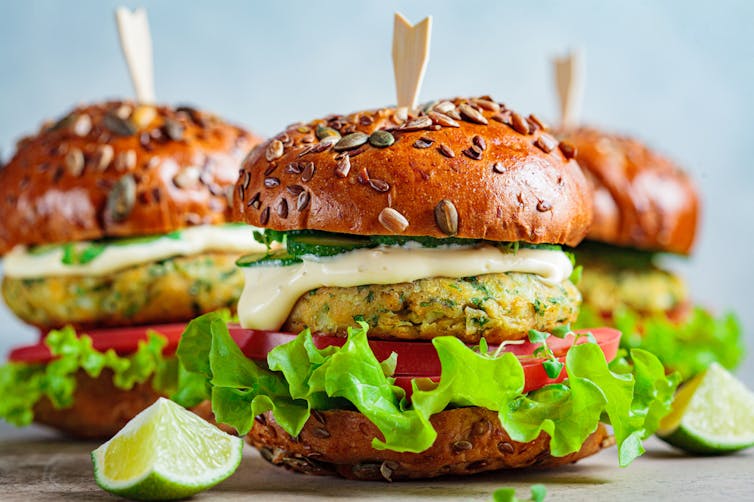
Much of the media coverage has focused on the apparent health risks associated with eating fake meats, such as sausages, burgers, nuggets and even steaks.
These are considered ultra-processed foods. They are made by deconstructing whole plant foods such as pea, soy, wheat protein, nuts and mushrooms, and extracting the protein. They are then reformulated with additives to make the products look, taste and feel like traditional red and white meats.
However this was only one type of plant-based, ultra-processed food analysed in this study. This only accounted for an average 0.2% of the dietary energy intake of all the participants.
Compare this to bread, pastries, buns, cakes and biscuits, which are other types of plant-based, ultra-processed foods. These accounted for 20.7% of total energy intake in the study.
This image was at the top of the media release. Screenshot/Imperial It’s hard to say why the media focused on fake meat. But there is one clue in the media release issued to promote the research.
Although the media release did not mention the words “fake meat”, an image of plant-based burgers, sausages and meat balls or rissoles featured prominently.
The introduction of the study itself also mentions plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods, such as sausages, nuggets and burgers.
So it’s no wonder people can be confused.
Does this mean fake meats are fine?
Not necessarily. This study analysed the total intake of plant-based, ultra-processed foods, which included fake meats, albeit a very small proportion of people’s diets.
From this study alone we cannot tell if there would be a different outcome if someone ate large amounts of fake meats.
In fact, a recent review of fake meats found there was not enough evidence to determine their impact on health.
We also need more recent data to reflect current eating patterns of fake meats. This study used dietary data collected from 2009 to 2012, and fake meats have become more popular since.
What if I really like fake meat?
We have known for a while that ultra-processed foods can harm our health. This study tells us that regardless if an ultra-processed food is plant-based or not, it may still be harmful.
We know fake meat can contain large amounts of saturated fats (from coconut or palm oil), salt and sugar.
So like other ultra-processed foods, they should be eaten infrequently. The Australian Dietary Guidelines currently recommends people should only consume foods like this sometimes and in small amounts.
Are some fake meats healthier than others?
Check the labels and nutrition information panels. Look for those lowest in fat and salt. Burgers and sausages that are a “pressed cake” of minced ingredients such as nuts, beans and vegetables will be preferable to reformulated products that look identical to meat.
You can also eat whole plant-based protein foods such as legumes. These include beans, lentils, chickpeas and soy beans. As well as being high in protein and fibre, they also provide essential nutrients such as iron and zinc. Using spices and mushrooms alongside these in your recipes can replicate some of the umami taste associated with meat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Being Mortal – by Dr. Atul Gawande
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Maybe you want to “live forever or die trying”, and that’s an understandable goal… But are you prepared for “or die trying” being the outcome?
This is not a cheerful book, if you’re anything like this reviewer, you will need a little towel or something to mop up the tears while you read. But it’s worth it.
Dying is one thing; fighting for life is even generally considered a noble endeavor. Suffering alone isn’t fun, losing independence can feel humiliating, and seeing someone who was always a tower of strength, now a frail shadow of their former self, reduced to begging for something that they’re “not allowed”, can be worse.
Do we want that for ourselves? For our loved ones? Can there be a happy medium between that, and the alternative to indeed “go gentle into that good night”?
Dr. Gawande, a surgeon well-acquainted with death and dying, thinks so. But it involves work on our part, and being prepared for hard decisions.
- What is most important to us, and what tradeoffs are we willing to make for it?
- What, even, is actually an option to us with the resources available?
- Can we make peace with a potentially bad lot? And… Should we?
- When is fighting important, and when is it self-destructive?
These (and others) are all difficult questions posed by Dr. Gawande, but critical ones.
We don’t usually quote other people’s reviews when reviewing books here, but let’s consider the following words from the end of a long review on Amazon:
❝If “dying as we lived” is some kind of standard for how we should go, then maybe alone and medicalized makes some sense right now after all.❞
Bottom line: we all deserve better than that. And if we don’t take the time to think about what’s most important, then time will take it from us. This very insightful book may not have all the answers, but it has the questions, and it can help a lot in exploring them and deciding what matters most to us in the end, really.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Wandering Mind – by Dr. Michael Corballis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our mind’s tendency to wander can be a disability, but could it also be a superpower? Dr. Corballis makes the case for such.
While many authors focus on, well, how to focus, Dr. Corballis argues in this book that our wandering imagination can be more effective at problem-solving and creative tasks, than a focused, blinkered mind.
The book’s a quick read (184 pages of quite light reading), and yet still quite dense with content. He takes us on a tour of the brain, theory of mind, the Default Mode Network (where a lot of the brain’s general ongoing organization occurs), learning, memory, forgetting, and creativity.
Furthermore, he cites (and explains) studies showing what kinds of “breaks” from mental work allow the wandering mind to do its thing at peak efficiency, and what kinds of breaks are counterproductive. Certainly this has practical applications for all of us!
Bottom line: if you’d like to be less frustrated by your mind’s tendency to wander, this is a fine book to show how to leverage that trait to your benefit.
Click here to check out The Wandering Mind, and set yours onto more useful tracks!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ozempic Helps People Walk Further
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s often a catch-22 when it comes to exercise: it’s important for good health, and/but people with ill health usually cannot exercise much.
A recent (published today, at time of writing, the 29th of March 2025, never let it be said we don’t bring you the very most up-to-date health science!) study by Dr. Neda Rasouli et al. has shown there is a possible way through that catch-22, depending on the nature of the illness.
This study followed 792 people across 112 outpatient clinical trial sites in 20 countries in North America, Asia, and Europe, with type 2 diabetes and peripheral artery disease.
What they found
Patients taking semaglutide (specifically, 1mg Ozempic) enjoyed a 21% median increase in walking distance, as well as some bonus benefits, namely:
- Weight reduction: the semaglutide group saw a greater reduction in body weight (–4.1 kg; P < 0 .0001)
- HbA1c levels: semaglutide lowered HbA1c by 1 percentage point (P < 0.0001)
- Blood pressure: systolic blood pressure decreased by 3.2 mmHg (P = 0.0042)
You may be wondering what that “P =” means: it’s the probability of this occurring by random chance, on a scale from zero (impossible outcome) to 1 (unavoidable outcome).
For example:
“We hypothesized that singing the happy birthday song before tossing a coin would result in it landing on heads. We sang the happy birthday song and tossed the coin; it landed on heads (P = 0.5)”
In science, generally speaking anything with a probability of under 0.05 (expressed as: “P < 0.05”) is considered a statistically significant result.
All this to say, the cited figures of, for example, P < 0.0001, are very significant indeed.
On which note, that 21% median increase in walking distance? P < 0.0004.
As for side effects? Serious adverse events related to the drug occurred in 1% of the semaglutide group vs 2% in the placebo group. So, that seems quite safe indeed.
You can find the paper itself here:
Want to learn more?
Check out:
- The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, & Move More
- Walking… Better.
- 5 Ways To Naturally Boost The “Ozempic Effect”
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Building Psychological Resilience (Without Undue Hardship)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s The Worst That Could Happen?
When we talk about the five lifestyle factors that make the biggest difference to health, stress management would be a worthy addition as number six. We haven’t focused explicitly on that for a while, so let’s get ready to start the New Year on a good footing…
You’re not going to have a stress-free 2024
What a tender world that would be! Hopefully your stressors will be small and manageable, but rest assured, things will stress you.
And that’s key: “rest assured”. Know it now, prepare for it, and build resilience.
Sounds grim, doesn’t it? It doesn’t have to be, though.
When the forecast weather is cold and wet, you’re not afraid of it when you have a warm dry house. When the heating bill comes for that warm dry house, you’re not afraid of it when you have money to pay it. If you didn’t have the money and the warm dry house, the cold wet weather could be devastating to you.
The lesson here is: we can generally handle what we’re prepared for.
Negative visualization and the PNS
This is the opposite of what a lot of “think and grow rich”-style gurus would advise. And indeed, it’s not helpful to slide into anxious worrying.
If you do find yourself spiralling, here’s a tool for getting out of that spiral:
RAIN: an intervention for dealing with difficult emotions
For now, however, we’re going to practice Radical Acceptance.
First, some biology: you may be aware that your Central Nervous System (CNS) branches into the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) and the Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS).
The PNS is the part that cues our body to relax, and suppresses our fight/flight response. We’re going to activate it.
Activating the PNS is easy for most people in comfortable circumstances (e.g., you are not currently exposed to stressful stimuli). It may well be activated already, and if it’s not, a few deep breaths is usually all it takes.
If you’d like a quick and easy Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) technique, here you go:
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
Activating the PNS is hard for most people in difficult circumstances (e.g., you either are currently exposed to stressful stimuli, or you are in one of the emotional spirals we discussed earlier).
However, we can trick our bodies and brains by—when we are safe and unstressed—practicing imagining those stressful stimuli. Taking a moment to not just imagine it experientially, but immersively. This, in CBT and DBT, is the modern equivalent to the old samurai who simply accepted, before battle, that they were already dead—and thus went into battle with zero fear of death.
A less drastic example is the zen master who had a favorite teacup, and feared it would get broken. So he would tell himself “the cup is already broken”. One day, it actually broke, and he simply smiled ruefully and said “Of course”.
How this ties together: practice the mindfulness-based stress reduction we linked above, while imagining the things that do/would stress you the most.
Since it’s just imagination, this is a little easier than when the thing is actually happening. Practicing this way means that when and if the thing actually happens (an unfortunate diagnosis, a financial reversal, whatever it may be), our CNS is already well-trained to respond to stress with a dose of PNS-induced calm.
You can also leverage hormesis, a beneficial aspect of (in this case, optional and chosen by you) acute stress:
Dr. Elissa Epel | The Stress Prescription
Psychological resilience training
This (learned!) ability to respond to stress in an adaptive fashion (without maladaptive coping strategies such as unhelpful behavioral reactivity and/or substance use) is a key part of what in psychology is called resilience:
And yes, the CBT/DBT/MBSR methods we’ve been giving you are the evidence-based gold standard.
Only the best for 10almonds subscribers! 😎
❝That was helpful, but not cheery; can we finish the year on a cheerier note?❞
We can indeed:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: