Wheat Belly, Revised & Expanded Edition – by Dr. William Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This review pertains to the 2019 edition of the book, not the 2011 original, which will not have had all of the same research.
We are told, by scientific consensus, to enjoy plenty of whole grains as part of our diet. So, what does cardiologist Dr. William Davis have against wheat?
Firstly, not all grains are interchangeable, and wheat—in particular, modern strains of wheat—cannot be described as the same as the wheat of times past.
While this book does touch on the gluten aspect (and Celiac disease), and notes that modern wheat has a much higher gluten content than older strains, most of this book is about other harms that wheat can do to us.
Dr. Davis explores and explains the metabolic implications of wheat’s unique properties on organs such as our pancreas, liver, heart, and brain.
The book does also have recipes and meal plans, though in this reviewer’s opinion they were a little superfluous. Wheat is not hard to cut out unless you are living in a food desert or are experiencing food poverty, in which case, those recipes and meal plans would also not help.
Bottom line: this book, filled with plenty of actual science, makes a strong case against wheat, and again, mostly for reasons other than its gluten content. You might want to cut yours down!
Click here to check out Wheat Belly, and see if skipping the wheat could be good for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
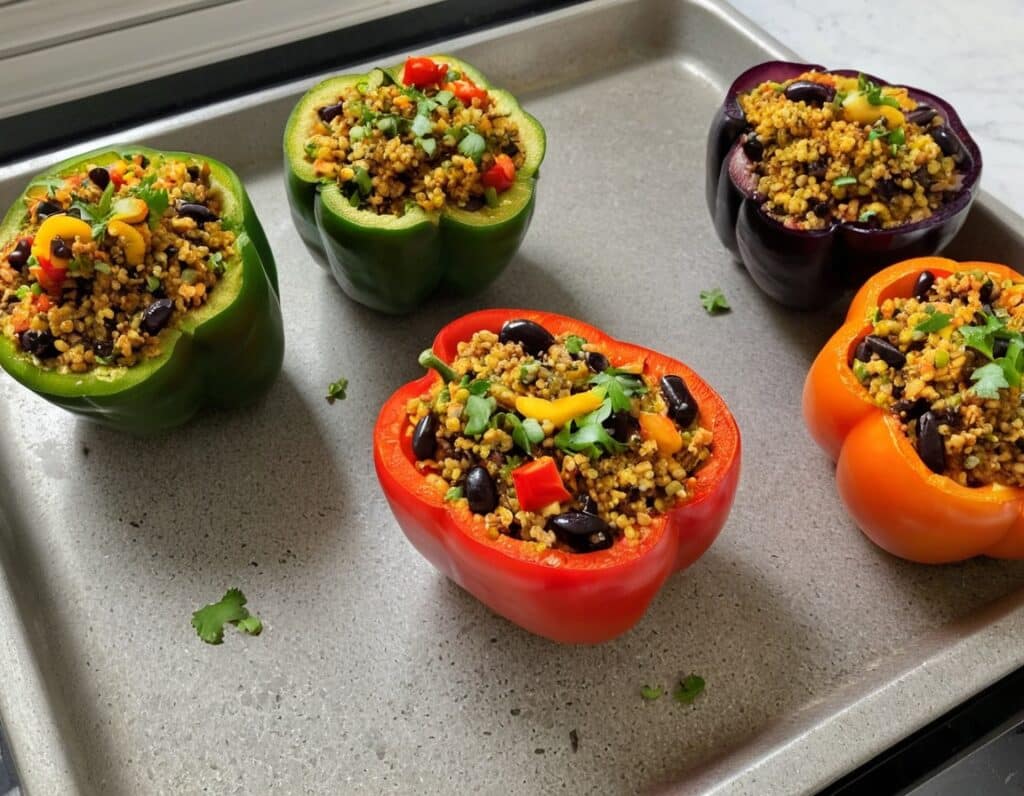
Protein-Stuffed Bell Peppers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hot, tasty, meaty, and vegan! You can have it all. And with this recipe, you’ll want to err on the side of overcatering, because everyone will want some. As for healthiness, we’ve got lycopene, lutein and a stack of other carotenoids, a plethora of other polyphenols, and a veritable garden party of miscellaneous phytochemicals otherwise categorized. It’s full of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, relatively low-fat but the fats present are healthy. It’s antidiabetic, anti-CVD, anticancer, antineurodegeneration, and basically does everything short of making you sing well too.
You will need
- 4 large bell peppers, tops sliced open and innards removed (keep the tops; we will put them back on later)
- 1 cup quinoa, rinsed
- 1 can black beans, drained and rinsed
- 1 small zucchini (diced)
- 1 small eggplant (diced)
- 1 small red onion (finely chopped)
- ½ bulb garlic, minced*
- 1 tbsp tomato paste
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp dried basil
- 2 tsp dried thyme
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
*we always try to give general guidelines with regard to garlic, but the reality is it depends on the size and strength of your local garlic, which we cannot account for, as well as your personal taste. Same situation with hot peppers of various kinds. This writer (it’s me, hi) would generally use about 2x the garlic and pepper advised in our recipes. All we can say is: follow your heart!
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the quinoa with the chia seeds, and cook as per normal cooking of quinoa (i.e. bring to a boil and then simmer for about 15 minutes until cooked and fluffy). Drain and rinse (carefully, without losing the chia seeds; use a sieve).
2) Heat your grill to a high heat. Combine the zucchini, eggplant, onion, garlic, and olive oil in a big bowl and mix well, ensuring an even distribution of the oil. Now also add the herbs and spices (including the MSG or salt) and mix well again. Put them all to grill for about 5 minutes, turning as necessary.
3) Heat your oven to a high heat. Take the grilled vegetables and combine them in a bowl with the quinoa-and-chia, and the black beans, as well as the tomato paste. Mix everything well. Spoon the mixture generously into the bell peppers, replacing the tops (it can be loosely), and bake for about 5–10 minutes, keeping an eye on them; you want them to be lightly charred, but not a burnt offering.
4) Serve! This dish works well as a light lunch or as part of a larger spread.
(before going in the oven with lids replaced to keep moisture in)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- A Spectrum Of Specialties: Which Color Bell Peppers To Pick?
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value: If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Sciatica Exercises & Home Treatment – by Dr. George Best
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Best is a doctor of chiropractic, but his work here is compelling. He starts by giving an overview of the relevant anatomy, and then the assorted possible causes of sciatica, before moving on to the treatments.
As is generally the case for chiropractic, nothing here will be “cured”, but it will give methods for ongoing management to keep you pain-free—which in the case of sciatica, is usually the single biggest thing that most people suffering from it most dearly want.
We get to read a lot about self-massage and exercises, of the (very well-evidenced; about the most well-evidenced thing there is for back pain) McKenzie technique exercises, as well as assorted acupressure-based techniques that are less well-evidenced but have good anecdotal support.
He also writes about preventing sciatica—which if you already have it, that doesn’t mean it’s too late; it just means, in that case do these things (along with the aforementioned exercises) to gradually reverse the harm done and get back to where you were pre-sciatica.
Lastly, he does also speak on when signs might point to your problems being beyond the scope of this book, and seeking professional examination if you haven’t already.
The style throughout is straight to the point, informative, and instructional. There is zero fluff or padding, and no sensationalization. There are diagrams and illustrative photos where appropriate.
Bottom line: if you have, or fear the threat of, sciatica, then this is an excellent book to have and use its exercises.
Click here to check out Sciatica Exercises & Home Treatment, and live pain-free!
Share This Post
-
Better Than BMI
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
BMI is a very flawed system, and there are several more useful ways of measuring our bodies. Let’s take a look at them!
What’s wrong with BMI?
Oof, what isn’t wrong with BMI?
In short, it was developed as a demographic-based tool to specifically chart the weight-related health of working-age European white men a little under 200 years ago.
This means that if you are, perchance, not a working-age European white man in 1830 or so, then it’s not so useful. It’d be like first establishing height norms based on NBA basketball players, and then applying it to the general population, and thus coming to the conclusion that someone who is 6’2″ is very short.
In long, we did a deep-dive into it here, and in particular what things go dangerously wrong when it’s applied to women, non-white people, athletic people, pregnant people, people under 16 or over 65 and more:
When BMI Doesn’t Quite Measure Up
What we usually recommend instead
For heart disease risk and diabetes risk both, waist circumference is a much more universally reliable indicator. And since those two things tend to affect a lot of other health risks, it becomes an excellent starting point for being aware of many aspects of health.
Pregnancy will still throw off waist circumference a little (measure below the bump, not around it!), but it will nevertheless be more helpful than BMI even then, as it becomes necessary to just increase the numbers a little, according to gestational month and any confounding factors e.g. twins, triplets, etc. Ask your obstetrician about this, as it’s beyond the scope of our article today!
As to what’s considered a risk:
- Waist circumference of more than 35 inches for women
- Waist circumference of more than 40 inches for men
These numbers are considered applicable across demographics of age, ethnicity, and lifestyle.
Bonus extra measurement based on the above
Important also is waist to hip ratio.
How to calculate it:
- measure your waist circumference
- measure your hip circumference
- divide the first measurement by the second one
Because it’s a ratio, it doesn’t matter what units you use (e.g. inches, cm, etc) so long as you use the same units for both measurements.
The World Health Organization offers the following chart:
Health risk Women Men Low 0.80 or lower 0.95 or lower Moderate 0.81–0.85 0.96–1.0 High 0.86 or higher 1.1 or higher Source: Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation
This is especially relevant for cardiovascular disease risk:
…and also holds true for all-cause mortality:
Waist-Hip-Ratio as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in High-Functioning Older Adults
An ancient contender that’s still more useful than BMI
Remember Archimedes? The (perhaps apocryphal) story of his “Eureka” moment in the bathtub when he realized that water displacement could be used to measure the volume of an irregular shape?
Just like Archimedes (who, the story goes, had been hired to determine the composition of a crown that might or might not have been pure gold), we can use this method to determine body composition, because we have references for how much a given volume of a given substance will weigh, so combing what we know about a body’s weight and volume will tell us about its composition in ways that neither metric could give us alone.
Indeed, it’s one of the commonly-mentioned flaws of BMI that muscle weighs more than fat, and Archimedes’ method not only avoids that problem, but also, actually turns that knowledge (muscle weighs more than fat) to our advantage.
It’s called “hydrostatic weighing” now:
You may be wondering: what about bones? Or internal organs?
The fact is that those are slightly confounding factors that do get in the way of a truly accurate analysis, but the variation in how much one person’s skeleton weighs vs another’s, or one person’s set of organs weigh than another’s, is too small to make an important difference to the health implications.
Lastly…
Hydrostatic weighing isn’t the only way to work out how much of our body is made of fat; if you have for example a smart scale at home (like this one) that tells you your body fat percentage, that is an estimate based on bioelectrical impedance analysis.
It’s less accurate than the hydrostatic method, but easier to do at home!
As to what percentages are “best”, healthy body fat percentages are (assuming normal hormones) generally considered to be in the range of 20–25% for women and 15–20% for men.
You can read more about this here:
Is A Visible Six-Pack Obtainable Regardless Of Genetic Predisposition?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Soy Beans vs Kidney Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing soy beans to kidney beans, we picked the soy.
Why?
In terms of macros, soy has 2x the protein, while kidney beans have nearly 3x the carbs and very slightly more fiber. Ratio-wise, the “very slightly more fiber” does not offset the “nearly 3x the carbs” when it comes to glycemic index (though both are still good, really, but this is a head-to-head so the comparison is relevant), and 2x the protein is also quite a bonus, so this category’s an easy win for soy.
In the category of vitamins, soy beans have more of vitamins A, B2, B6, C, E, K, and choline, while kidney beans have more of vitamins B3, B5, and B9, thus making for a 7:3 win for soy.
When it comes to minerals, soy beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while kidney beans are not higher in any mineral. Another clear win for soy.
Adding up the three strong wins for soy, makes for an overall easy win for soy. Still, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tofu to seitan, we picked the tofu.
Why?
This one is not close!
In terms of macros, seitan does have about 2x the protein, but it also has 6x the carbs and 6x the sodium of tofu, as well as less fiber than tofu.. So we’ll call it a tie on macros. But…
Seitan is also much more processed than tofu, as tofu has usually just been fermented and possibly pressed (depending on kind). Seitan, in contrast, is processed gluten that has been extracted from wheat and usually had lots of things happen to it on the way (depending on kind).
About that protein… Tofu is a complete protein, meaning it has all of the essential amino acids. Seitain, meanwhile, is lacking in lysine.
When it comes to vitamins and minerals, again tofu easily comes out on top; tofu has 5x the calcium, similar iron, more magnesium, 2x the phosphorous, 150% of the potassium, and contains several other nutrients that seitan doesn’t, such as folate and choline.
So, easy winning for tofu across the board on micronutrients.
Tofu is also rich in isoflavones, antioxidant phytonutrients, while seitan has no such benefits.
So, another win for tofu.
There are two reasons you might choose seitan:
- prioritizing bulk protein above all other health considerations
- you are allergic to soy and not allergic to gluten
If neither of those things are the case, then tofu is the healthier choice!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Tempeh vs Tofu – Which is Healthier? ← tempeh is, nutritionally speaking, tofu but better. Of course on a culinary level, there are many recipes where tofu will work and tempeh wouldn’t, though.
- Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Citicoline: Better Than Dietary Choline?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Citicoline: Better Than Dietary Choline?
Citicoline, also known as cytidine diphosphate-choline (or CDP-Choline, to its friends, or cytidine 5′-diphosphocholine if it wants to get fancy) is a dietary supplement that the stomach can metabolize easily for all the brain’s choline needs. What are those needs?
Choline is an essential nutrient. We technically can synthesize it, but only in minute amounts, far less than we need. Choline is a key part of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, as well as having other functions in other parts of the body.
As for citicoline specifically… it appears to do the job better than dietary sources of choline:
❝Intriguing data, showing that on a molar mass basis citicoline is significantly less toxic than choline, are also analyzed.
It is hypothesized that, compared to choline moiety in other dietary sources such as phosphatidylcholine, choline in citicoline is less prone to conversion to trimethylamine (TMA) and its putative atherogenic N-oxide (TMAO).
Epidemiological studies have suggested that choline supplementation may improve cognitive performance, and for this application citicoline may be safer and more efficacious.❞
Source: Citicoline: A Superior Form of Choline?
Great! What does it do?
What doesn’t it do? When it comes to cognitive function, anyway, citicoline covers a lot of bases.
Short version: it improves just about every way a brain’s healthy functions can be clinically measured. From cognitive improvements in all manner of tests (far beyond just “improves memory” etc; also focus, alertness, verbal fluency, logic, computation, and more), to purely neurological things like curing tinnitus (!), alleviating mobility disorders, and undoing alcohol-related damage.
One of the reasons it’s so wide in its applications, is that it has a knock-on effect to other systems in the brain, including the dopaminergic system.
Long version: Citicoline: pharmacological and clinical review, 2022 update
(if you don’t want to sit down for a long read, we recommend skimming to the charts and figures, which are very elucidating even alone)
Spotlight study in memory
For a quick-reading example of how it helps memory specifically:
Keeping dementia at bay
For many older people looking to improve memory, it’s less a matter of wanting to perform impressive feats of memory, and more a matter of wanting to keep a sharp memory throughout our later years.
Dr. Maria Bonvicini et al. looked into this:
❝We selected seven studies including patients with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease or post-stroke dementia
All the studies showed a positive effect of citicoline on cognitive functions. Six studies could be included in the meta-analysis.
Overall, citicoline improved cognitive status, with pooled standardized mean differences ranging from 0.56 (95% CI: 0.37-0.75) to 1.57 (95% CI: 0.77-2.37) in different sensitivity analyses❞
The researchers concluded “yes”, and yet, called for more studies, and of higher quality. In many such studies, the heterogeneity of the subjects (often, residents of nursing homes) can be as much a problem (unclear whether the results will be applicable to other people in different situations) as it is a strength (fewer confounding variables).
Another team looked at 47 pre-existing reviews, and concluded:
❝The review found that citicoline has been proven to be a useful compound in preventing dementia progression.
Citicoline has a wide range of effects and could be an essential substance in the treatment of many neurological diseases.
Its positive impact on learning and cognitive functions among the healthy population is also worth noting.❞
Source: Application of Citicoline in Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review
The dopamine bonus
Remember how we said that citicoline has a knock-on effect on other systems, including the dopaminergic system? This means that it’s been studied (and found meritorious) for alleviating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease:
❝Patients with Parkinson’s disease who were taking citicoline had significant improvement in rigidity, akinesia, tremor, handwriting, and speech.
Citicoline allowed effective reduction of levodopa by up to 50%.
Significant improvement in cognitive status evaluation was also noted with citicoline adjunctive therapy.❞
Source: Citicoline as Adjuvant Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Where to get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: