The China Study – by Dr. T Colin Campbell and Dr. Thomas M. Campbell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not the newest book we’ve reviewed (originally published 2005; this revised and expanded edition 2016), but it is a seminal one.
You’ve probably heard it referenced, and maybe you’ve wondered what the fuss is about. Now you can know!
The titular study itself was huge. We tend to think “oh there was one study” and look to discount it, but it literally looked at the population of China. That’s a large study.
And because China is relatively ethnically homogenous, especially per region, it was easier to isolate what dietary factors made what differences to health. Of course, that did also create a limitation: follow-up studies would be needed to see if the results were the same for non-Chinese people. But even for the rest of us (this reviewer is not Chinese), it already pointed science in the right direction. And sure enough, smaller follow-up studies elsewhere found the same.
But enough about the research; what about the book? This is a book review, not a research review, after all.
The book itself is easy for a lay reader to understand. It explains how the study was conducted (no small feat), and how the data was examined. It also discusses the results, and the conclusions drawn from those results.
In light of all this, it also offers simple actionable advices, on how to eat to avoid disease in general, and cancer in particular. In especially that latter case, one take-home conclusion was: get more of your protein from plants for a big reduction in cancer risk, for example.
Bottom line: this book is an incredible blend of “comprehensive” and “readable” that we don’t often find in the same book! It contains not just a lot of science, but also an insight into how the science works, on a research level. And, of course, its results and conclusions have strong implications for all our lives.
Click here to check out The China Study, to know more about it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
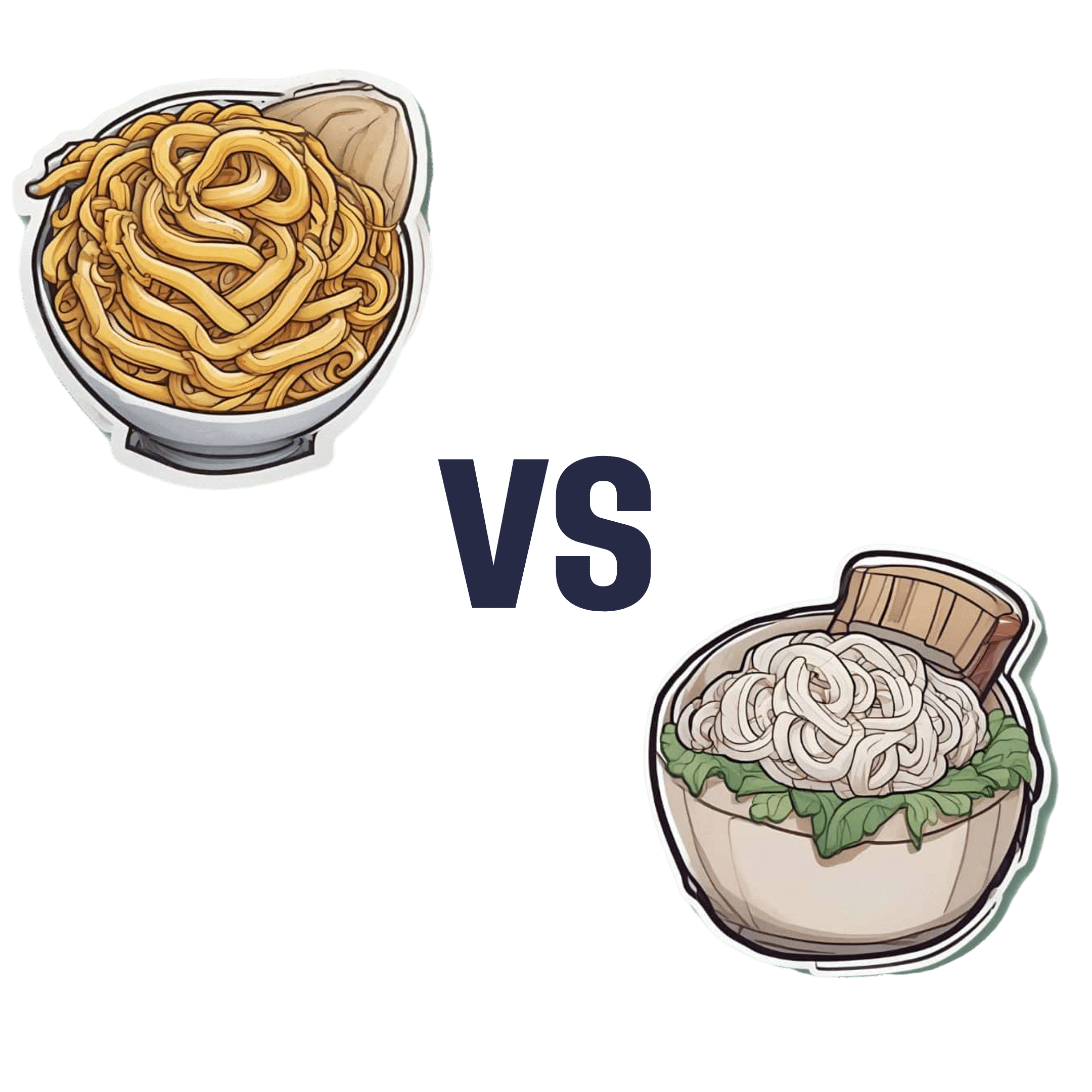
Egg Noodles vs Rice Noodles – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing egg noodles to rice noodles, we picked the egg noodles.
Why?
It was close—these are both quite mediocre foods. They’re neither amazing for the health nor appalling for the health (in moderation). They are both relatively low in nutrients, but they are also low in anti-nutrients, i.e. things that have a negative effect on the health.
Their mineral profiles are similar; both are a source of selenium, manganese, phosphorus, copper, and iron. Not as good as many sources, but not devoid of nutrients either.
Their vitamin profiles are both pitiful; rice noodles have trace amounts of various vitamins, and egg noodles have only slightly more. While eggs themselves are nutritious, the processing has robbed them of much of their value.
In terms of macros, egg noodles have a little more fat (but the fats are healthier) and rice noodles have a lot more carbs, so this is the main differentiator, and is the main reason we chose the egg noodles over the rice noodles. Both have a comparable (small) amount of protein.
In short:
- They’re comparable on minerals, and vitamins here are barely worth speaking about (though egg noodles do have marginally more)
- Egg noodles have a little more fat (but the fats are healthier)
- Rice noodles have a lot more carbs (with a moderately high glycemic index, which is relatively worse—if you eat them with vegetables and fats, then that’ll offset this, but we’re judging the two items on merit, not your meal)
Learn more
You might like this previous main feature of ours:
Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Blue Zones, Second Edition – by Dan Buettner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat beans & greens, take walks, have a purpose; you can probably list off the top of your head some of the “advices from Blue Zones”, so what makes this book stand out?
This is perhaps one of the most thoughtful investigations; the author (a National Geographic researcher) toured and researched all the Blue Zones, took many many notes (we get details), and asked a lot of questions that others skipped.
For example, a lot of books about the Blue Zones mention the importance of community—but they don’t go into much detail of what that looks like… And they certainly don’t tend to explain what we should do about it.
And that’s because community is often viewed as environmental in a way that we can’t control. If we want to take supplements, eat a certain way, exercise, etc, we can do all those things alone if we want. But if we want community? We’re reliant on other people—and that’s a taboo in the US, and US-influenced places.
So, one way this book excels is in describing how exactly people foster community in the Blue Zones (hint: the big picture—the form of the community—is different in each place, but the individual actions taken are similar), with particular attention to the roles actively taken on by the community elders.
In a similar vein, “reduce stress” is good, but what mindsets and mechanisms do they use that are still reproducible if we are not, for example, Okinawan farmers? Again, Buettner delivers in spades.
Bottom line: this is the Blue Zones book that digs deeper than others, and makes the advices much more applicable no matter where we live.
Click here to check out The Blue Zones, and build these 9 things into your life!
Share This Post
-
I lost weight and my period stopped. How are weight and menstruation linked?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may have noticed that changes in weight are sometimes accompanied by changes in your period.
But what does one really have to do with the other?
Maintaining a healthy weight is key to regular menstruation. Here’s why – and when to talk to your doctor.
The role of hormones
The menstrual cycle – including when you bleed and ovulate – is regulated by a balance of hormones, particularly oestrogen.
The ovaries are connected to the brain through a hormonal signalling system. This acts as a kind of “chain of command” of hormones controlling the menstrual cycle.
The brain produces a key hormone, called the gonadotropin-releasing hormone, in the hypothalamus. It stimulates the release of other hormones which tell the ovaries to produce oestrogen and release a mature egg (ovulation).
But the release of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone depends on oestrogen levels and how much energy is available to the body. Both of these are closely related to body weight.
Oestrogen is primarily produced in the ovaries, but fat cells also produce oestrogen. This is why weight – and more specifically body fat – can affect menstruation.
Fat cells produce oestrogen, a hormone with a key role in the menstrual cycle. Halfpoint/Shutterstock Can being underweight affect my period?
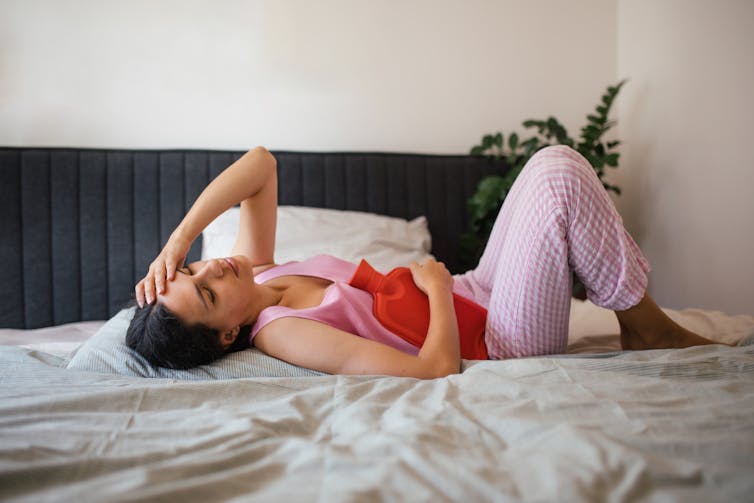
The body prioritises conserving energy. When reserves are low it stops anything non-essential, such as reproduction.
This can happen when you are underweight, or suddenly lose weight. It can also happen to people who undertake intense exercise or have inadequate nutrition.
The stress sends the hypothalamus into survival mode. As a result, the body lowers its production of the hormones important to ovulation, including oestrogen, and stops menstruation.
Being chronically underweight means not having enough energy available to support reproduction, which can lead to menstrual irregularities including amenorrhea (no periods at all).
This results in very low oestrogen levels and can cause potentially serious health risks, including infertility and bone loss.
Missing periods is not always a cause for concern. But a chronic lack of energy availability can be, if not addressed. The two are linked, meaning understanding your period and being aware of any prolonged changes is important.
How about being overweight?
Higher body fat can elevate oestrogen levels.
When you’re overweight your body stores extra energy in fat cells, which produce oestrogen and other hormones and can cause inflammation in the body. So, if you have a lot of fat cells, your body produces an excess of these hormones. This can affect normal functioning of the uterus lining (endometrium).
Excess oestrogen and inflammation can interfere in the feedback system to the brain and stop ovulation. As a result, you may have irregular or missed periods.
It can also lead to pain (dysmenorrhea) and heavier bleeding (menorrhagia).
Being overweight can sometimes worsen premenstrual syndrome as well. One study found for every 1 kg increase in height (m²) in body mass index (BMI), the risk of premenstrual syndrome went up by 3%. Women with a BMI over 27.5 kg/m² had a much higher risk than those with a BMI under 20 kg/m².
What else might be going on?
Sometimes weight changes are linked to hormonal balances that indicate an underlying condition.
For example, people with polycystic ovary syndrome may gain weight or find it hard to lose weight because they have a hormonal imbalance, including higher levels of testosterone.
The syndrome is also associated with irregular periods and heavy bleeding. So, if you notice these symptoms, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor.
Similarly, weight changes and irregular periods in midlife might signal the start of perimenopause, the period before menopause (when your periods stop altogether).
Changes in weight and your period could be a sign of menopause approaching. Sabrina Bracher/Shutterstock When should I worry?
Small changes in when your period comes or how long it lasts are usually harmless.
Similarly, slight fluctuations in weight won’t usually have a significant impact on your period – or the changes may be so subtle you don’t notice them.
But regular menstruation is an important marker of female health. Sometimes changes in flow, regularity or the pain you experience can indicate there’s something else going on.
If you notice changes and they don’t feel right to you, speak to a health care provider.
Mia Schaumberg, Associate Professor in Physiology, School of Health, University of the Sunshine Coast and Laura Pernoud, PhD Candidate in Women’s Health, School of Health, University of the Sunshine Coast
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Kiwi vs Grapefruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi to grapefruit, we picked the kiwi.
Why?
In terms of macros, kiwi has nearly 2x the protein, slightly more carbs, and 2x the fiber; both fruits are low glycemic index foods, however.
When it comes to vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins B3, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while grapefruit has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, and B5. An easy win for kiwi.
In the category of minerals, kiwi is higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while grapefruit is not higher in any minerals. So, no surprises for guessing which wins this category.
One thing that grapefruit is a rich source of: furanocoumarin, which can inhibit cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme and P-glycoptrotein transporters in the intestine and liver—slowing down their drug metabolism capabilities, thus effectively increasing the bioavailability of many drugs manifold.
This may sound superficially like a good thing (improving bioavailability of things we want), but in practice it means that in the case of many drugs, if you take them with (or near in time to) grapefruit or grapefruit juice, then congratulations, you just took an overdose. This happens with a lot of meds for blood pressure, cholesterol (including statins), calcium channel-blockers, anti-depressants, benzo-family drugs, beta-blockers, and more. Oh, and Viagra, too. Which latter might sound funny, but remember, Viagra’s mechanism of action is blood pressure modulation, and that is not something you want to mess around with unduly. So, do check with your pharmacist to know if you’re on any meds that would be affected by grapefruit or grapefruit juice!
All in all, adding up the categories makes for an overwhelming total win for kiwis.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← kiwi is top of the list!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
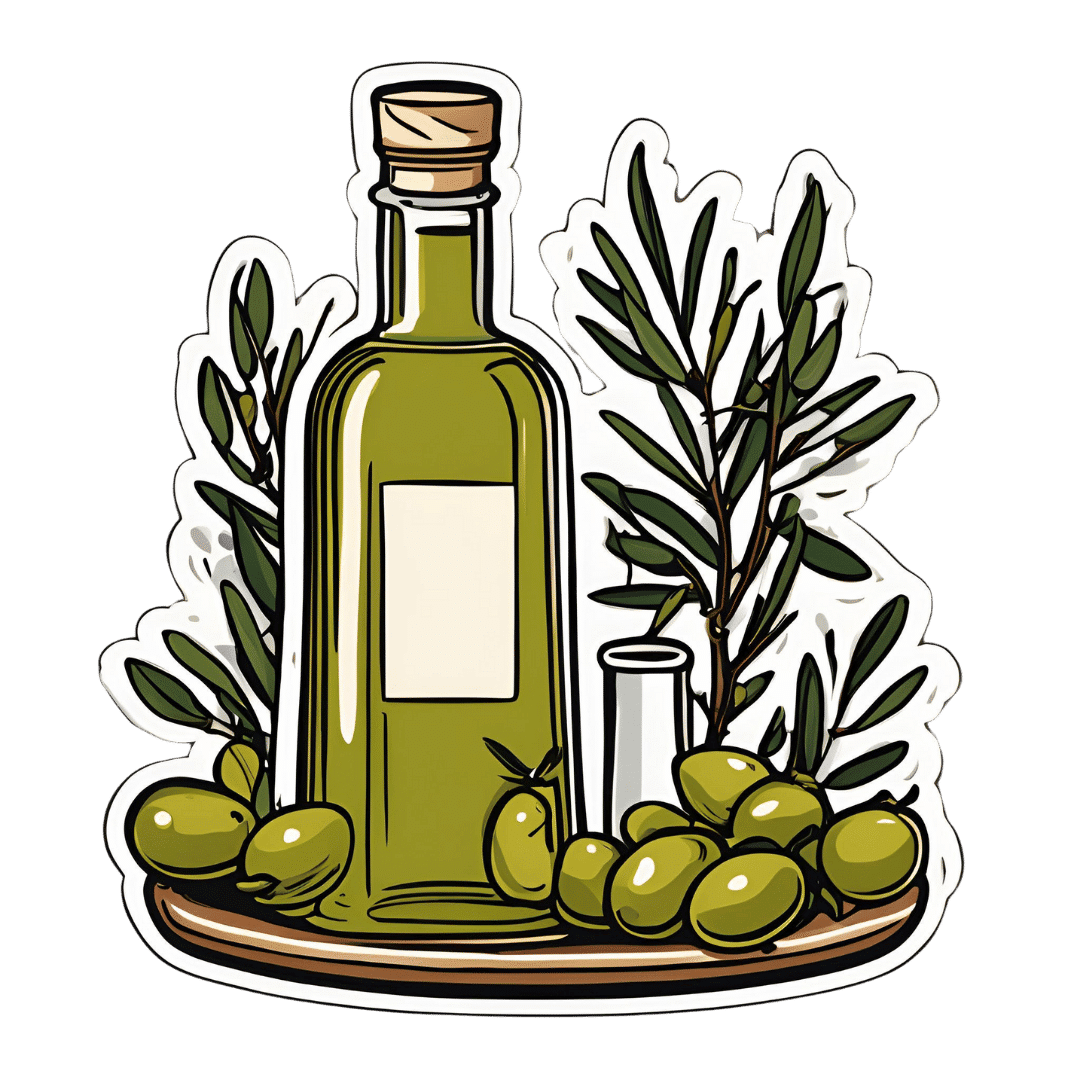
All About Olive Oil
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Skip the video & tell more about olive oil please.❞
We love requests!
We can’t really do anti-requests (e.g. “skip the video”) because for every one person who doesn’t care for one particular element of the newsletter, there will be thousands who do—and indeed, the video segment is a popular one, so it will certainly remain.
However! Let us reassure you that you personally are not obliged to watch the video if you don’t want to 🙂 In fact, our general hope with 10almonds is that there will be at least one feature that is of value to each reader, each day.
Writer’s note: I’m a very bookish person, and in honesty do not love videos personally either. You know what I do love though? Olive oil. So let’s get onto that 😎
Why olive oil?
Let’s quickly address the taste/culinary side of things first, and then spend more time on the health aspects. Olive oil’s strong punchy flavor (as oils go, anyway) makes it a big winner with those of us who love strong punchy flavors. However, it does mean that it can overwhelm some more delicate dishes if one isn’t careful, meaning that it’s not perfect for everything all the time.
Healthwise, olive oil is one of the healthiest oils around, along with avocado oil. In fact, we compared them previously:
Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
…and it’s worth noting that their (excellent) lipids profiles are very similar, meaning that the main factor between them is that olive oil usually retains vitamins that avocado oil doesn’t.
Meanwhile, another popular contender for “healthy oil” is coconut oil, but this doesn’t have nearly as unambiguously good a lipids profile, because of coconut oil’s high saturated fat content—though lauric acid can have a cardioprotective effect, so the jury is out on that one:
Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil – Which is Healthier?
Interestingly, this article from The Conversation considered seed oils (canola, sunflower, sesame) to be next-best options:
I can’t afford olive oil. What else can I use?
…but it’s worth noting that the way those seed oils are made varies a lot from country to country, and can affect their health impact considerably.
It’s not just about the fats
Olives, especially green olives with their stronger more pungent flavor, are rich in assorted polyphenols that have many health-giving properties:
Black Olives vs Green Olives – Which is Healthier
…and olive oil is almost always made from green olives. Note that while we picked black olives in the above comparison, that’s mainly because green olives are “cured” for longer and thus are much higher in sodium… Which, guess what, isn’t in olive oil, so with olive oil we can enjoy all of the polyphenols with almost none of the sodium!
Let’s talk virginity
When it comes to olive oil, definitely not everything labelled as olive oil in the supermarket is of the same quality. Mostly, however, it’s not whether it’s “extra virgin” (i.e. the oil from the first mechanical pressing) or not that actually makes the biggest health difference, so much as that olive oils are often adulterated with other cheaper oils, so it’s important to check labels for that, even when they say “extra virgin”, in case it’s something like:
a blend of
EXTRA VIRGIN OLIVE OIL
and other oilsWe talk about this, and the various different levels of quality of olive oil and how you can tell them apart for yourself in the supermarket (and be wise to the ways they may try to trick you), here:
What to enjoy it with?
Olive oil is the single largest source of fat in the Mediterranean diet, and by that we mean not just “food that is eaten in the Mediterranean”, but rather, the well-defined dietary approach that has for a long time now been considered “the gold standard” of what a healthy diet looks like, scientifically. You can read more about what is and isn’t included in the definition, here:
Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← what isn’t it good for!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Anti-Viral Gut – by Dr. Robynne Chutkan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people get a virus and feel terrible for a few days; other people get the same virus and die. Then there are some who never even get it at all despite being in close proximity with the other two. So, what’s the difference?
Dr. Robynne Chutkan outlines the case for the difference not being in the virus, but in the people. And nor is it a matter of mysterious fate, but rather, a matter of the different levels of defenses (or lack thereof) that we each have.
The key, she explains, is in our microbiome, and the specific steps to make sure that ours is optimized and ready to protect us. The book goes beyond “eat prebiotics and probiotics”, though, and goes through other modifiable factors, based on data from this pandemic and the last one a hundred years ago. We also learn about the many different kinds of bacteria that live in our various body parts (internal and external), because as it turns out, our gut microbiome (however important; hence the title) isn’t the only relevant microbiome when it comes to whether or not a given disease will take hold or be eaten alive on the way in.
The style is very polished—Dr. Chutkan is an excellent educator who makes her points clearly and comprehensibly without skimping on scientific detail.
Bottom line: if you’d like your chances of surviving any given virus season to not be left to chance, then this is a must-read book.
Click here to check out The Anti-Viral Gut, and make your body a fortress!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: