Plant-Based Alternatives for Meat Recipes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝How about providing a plant-based alternative when you post meat-based recipes? I appreciate how much you advocate for veggie diets and think offering an alternative with your recipes would support that❞
Glad you’re enjoying! And yes, we do usually do that. But: pardon, we missed one (the Tuna Steak with Protein Salad) because it’d be more than a simple this-for-that substitution, we didn’t already have an alternative recipe up (as with the salmon recipes such as the Chili Hot-Bedded Salmon and Thai Green Curry Salmon Burgers).
Our recipes, by the way, will tend towards being vegan, vegetarian, or at least pescatarian. This is for several reasons:
- Good science suggests the best diet for general purpose good health is one that is mostly plants, with optional moderate amounts of fermented dairy products, fish, and/or eggs.
- Your writer here (it’s me, hi) has been vegan for many years, transitioning to such via pescatarianism and ovo-lacto vegetarianism, and so the skill of cooking meat is least fresh in my memory, meaning I’d not be confident writing about that, especially as cooking meat has the gravest health consequences for messing it up.
Note on biases: notwithstanding this writer being vegan, we at 10almonds are committed to reporting the science as it stands with no agenda besides good health. Hence, there will continue to be unbiased information about animal products’ health considerations, positive as well as negative.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
…as well as, of course, some animal-based classics from our archives including:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of & Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
Finishing with one for the vegans though, you might enjoy:
Which Plant Milk? We Compare 6 Of The Most Popular
Some previous articles you might enjoy meanwhile:
- Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
- Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
- What Does Lion’s Mane Actually Do, Anyway?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Protein vs Sarcopenia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein vs Sarcopenia
This is Dr. Gabrielle Lyon. A medical doctor, she’s board-certified in family medicine, and has also engaged in research and clinical practice in the fields of geriatrics and nutritional sciences.
A quick note…
We’re going to be talking a bit about protein metabolism today, and it’s worth noting that Dr. Lyon personally is vehemently against vegetarianism/veganism, and considers red meat to be healthy.
Scientific consensus on the other hand, holds that vegetarianism and veganism are fine for most people if pursued in an informed and mindful fashion, that white meat and fish are also fine for most people, and red meat is simply not.
If you’d like a recap on the science of any of that:
- Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Diversity is Key
- Do We Need Animal Products to be Healthy?
Nevertheless, if we look at the science that she provides, the advice is sound when applied to protein in general and without an undue focus on red meat.
How much protein is enough?
In our article linked above, we gave 1–2g/kg/day
Dr. Lyons gives the more specific 1.6g/kg/day for adults older than 40 (this is where sarcopenia often begins!) and laments that many sources offer 0.8g/kg.
To be clear, that “per kilogram” means per kilogram of your bodyweight. For Americans, this means dividing lbs by 2.2 to get the kg figure.
Why so much protein?
Protein is needed to rebuild not just our muscles, but also our bones, joint tissues, and various other parts of us:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Additionally, our muscles themselves are important for far more than just moving us (and other things) around.
As Dr. Lyon explains: sarcopenia, the (usually age-related) loss of muscle mass, does more than just make us frail; it also messes up our metabolism, which in turn messes up… Everything else, really. Because everything depends on that.
This is because our muscles themselves use a lot of our energy, and/but also store energy as glycogen, so having less of them means:
- getting a slower metabolism
- the energy that can’t be stored in muscle tissue gets stored somewhere else (like the liver, and/or visceral fat)
So, while for example the correlation between maintaining strong muscles and avoiding non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may not be immediately obvious, it is clear when one follows the metabolic trail to its inevitable conclusion.
Same goes for avoiding diabetes, heart disease, and suchlike, though those things are a little more intuitive.
How can we get so much protein?
It can seem daunting at first to get so much protein if you’re not used to it, especially as protein is an appetite suppressant, so you’ll feel full sooner.
It can especially seem daunting to get so much protein if you’re trying to avoid too many carbs, and here’s where Dr. Lyon’s anti-vegetarianism does have a point: it’s harder to get lean protein without meat/fish.
That said, “harder” does not mean “impossible” and even she acknowledges that lentils are great for this.
If you’re not vegetarian or vegan, collagen supplementation is a good way to make up any shortfall, by the way.
And for everyone, there are protein supplements available if we want them (usually based on whey protein or soy protein)
Anything else we need to do?
Yes! Eating protein means nothing if you don’t do any resistance work to build and maintain muscle. This can take various forms, and Dr. Lyon recommends lifting weights and/or doing bodyweight resistance training (calisthenics, Pilates, etc).
Here are some previous articles of ours, consistent with the above:
- Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
- Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise
- How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
- Exercises To Do (And Ones To Avoid) If You Have Osteoporosis
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Your Brain on Art – by Susan Magsamen & Ivy Ross
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The notion of art therapy is popularly considered a little wishy-washy. As it turns out, however, there are thousands of studies showing its effectiveness.
Nor is this just a matter of self-expression. As authors Magsamen and Ross explore, different kinds of engagement with art can convey different benefits.
That’s one of the greatest strengths of this book: “this form of engagement with art will give these benefits, according to these studies”
With benefits ranging from reducing stress and anxiety, to overcoming psychological trauma or physical pain, there’s a lot to be said for art!
And because the book covers many kinds of art, if you can’t imagine yourself taking paintbrush to canvas, that’s fine too. We learn of the very specific cognitive benefits of coloring in mandalas (yes, really), of sculpting something terrible in clay, or even just of repainting the kitchen, and more. Each thing has its set of benefits.
The book’s main goal is to encourage the reader to cultivate what the authors call an aesthetic mindset, which involves four key attributes:
- a high level of curiosity
- a love of playful, open-ended exploration
- a keen sensory awareness
- a drive to engage in creative activities
And, that latter? It’s as a maker and/or a beholder. We learn about what we can gain just by engaging with art that someone else made, too.
Bottom line: come for the evidence-based cognitive benefits; stay for the childlike wonder of the universe. If you already love art, or have thought it’s just “not for you”, then this book is for you.
Click here to check out Your Brain On Art, and open up whole new worlds of experience!
Share This Post
-
How To En-Joy Life (With Long-Term Benefits)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
New Year’s Dissolutions?
We have talked previously about:
The Science Of New Year’s Pre-Resolutions
…and here we are now at the end of the first week of January; how’s it going?
Hopefully, based on that article, it’s been going just great since December! For most people, statistically speaking, it hasn’t.
Around now is typically when many people enter the “bargaining” stage of New Year’s Resolutions, which at this point are often in serious danger of becoming New Year’s Dissolutions.
What’s important, really?
When trying to juggle potentially too many new items, it’s important to be able to decide where to focus one’s efforts in the case of needing to drop a ball or two.
First, the laziest way…
The path of least resistance
This is perhaps most people’s go-to. It, without too much thought, drops whatever feels most onerous, and continues with what seems easiest.
This is not a terrible approach, because what we enjoy, we will be more likely to continue. But it can be improved upon, while still getting that benefit.
Marie Kondo your
resolutionsvaluesInstead of throwing out the new habits that “don’t spark joy”, ask yourself:
“What brings me joy?”
…because often, the answer is something that’s a result of a thing that didn’t “spark joy” directly. Many things in life involve delayed gratification.
Let’s separate the [unwanted action] from the [wanted result] for a moment.
Rather than struggling on with something unpleasant for the hope of joy at the end of the rainbow, though, give yourself permission to improve the middle bit.
For example, if the idea of having lots of energy and good cardiovascular fitness is what prompted you to commit to those 6am runs each morning (but they’re not actually joyous in your experience), what would be more fun and still give you the same benefit?
Now that you know “having lots of energy and good CV fitness” is what sparks joy, not “getting up to run at 6am”, you can change lanes without pulling off the highway entirely.
Maybe a dance class will be more your speed, for example.
The key here is: you’ll have changed your resolution, without breaking it in any way that mattered
Want more ways to keep on track without burning out?
Who doesn’t? So, check out:
How To Keep On Keeping On… Long Term!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Securely Attached –
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of books on attachment theory are quite difficult to read. They’re often either too clinical with too much jargon that can feel like incomprehensible psychobabble, or else too wishy-washy and it starts to sound like a horoscope for psychology enthusiasts.
This one does it better.
The author gives us a clear overview and outline of attachment theory, with minimal jargon and/but clearly defined terms, and—which is a boon for anyone struggling to remember which general attachment pattern is which—color-codes everything consistently along the way. This is one reason that we recommend getting a print copy of the book, not the e-book.
The other reason to invest in the print copy rather than the e-book is the option to use parts of it as a workbook directly—though if preferred, one can simply take the prompts and use them, without writing in the book, of course.
It’s hard to say what the greatest value of this book is because there are two very strong candidates:
- Super-clear and easy explanation of Attachment Theory, in a way that actually makes sense and will stick
- Excellent actually helpful advice on improving how we use the knowledge that we now have of our own attachment patterns and those of others
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand Attachment Theory and apply it to your life, but have been put off by other presentations of it, this is the most user-friendly, no-BS version that this reviewer has seen.
Click here to check out Securely Attached, and upgrade your relationship(s)!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
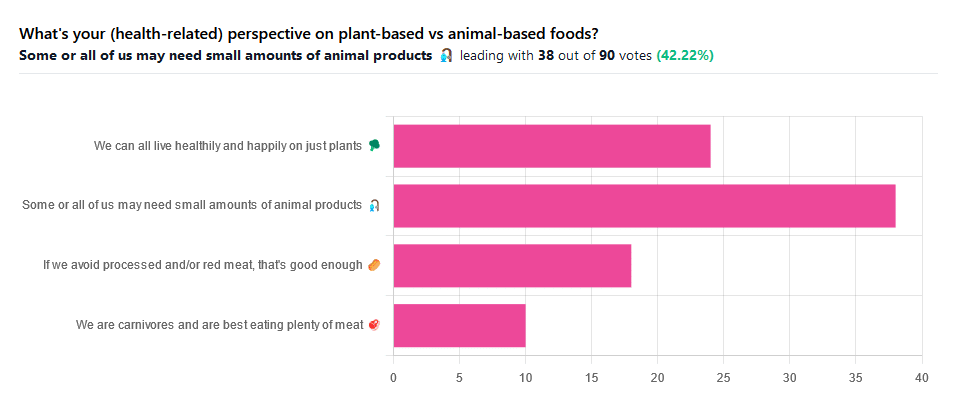
We asked you for your (health-related) perspective on plant-based vs anima-based foods, and got the above-pictured spread of answers.
“Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products” came out on top with more votes than the two more meat-eatery options combined, and the second most popular option was the hard-line “We can all live healthily and happily on just plants”.
Based on these answers, it seems our readership has quite a lot of vegans, vegetarians, and perhaps “flexitarians” who just have a little of animal products here and there.
Perhaps we should have seen this coming; the newsletter is “10almonds”, not “10 rashers of bacon”, after all.
But what does the science say?
We are carnivores and are best eating plenty of meat: True or False?
False. Let’s just rip the band-aid off for this one.
In terms of our anatomy and physiology, we are neither carnivores nor herbivores:
- We have a mid-length digestive tract (unlike carnivores and herbivores who have short and long ones, respectively)
- We have a mouthful of an assortment of teeth; molars and premolars for getting through plants from hard nuts to tough fibrous tubers, and we have incisors for cutting into flesh and (vestigial, but they’re there) canines that really serve us no purpose now but would have been a vicious bite when they were bigger, like some other modern-day primates.
- If we look at our closest living relatives, the other great apes, they are mostly frugivores (fruit-eaters) who supplement their fruity diet with a small quantity of insects and sometimes other small animals—of which they’ll often eat only the fatty organ meat and discard the rest.
And then, there’s the health risks associated with meat. We’ll not linger on this as we’ve talked about it before, but for example:
- Processed Meat Consumption and the Risk of Cancer: A Critical Evaluation of the Constraints of Current Evidence from Epidemiological Studies
- Red Meat Consumption (Heme Iron Intake) and Risk for Diabetes and Comorbidities?
- Health Risks Associated with Meat Consumption: A Review of Epidemiological Studies
- Associations of Processed Meat, Unprocessed Red Meat, Poultry, or Fish Intake With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality
- Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010-2020) evidences
If we avoid processed and/or red meat, that’s good enough: True or False?
True… Ish.
Really this one depends on one’s criteria for “good enough”. The above-linked studies, and plenty more like them, give the following broad picture:
- Red and/or processed meats are unequivocally terrible for the health in general
- Other mammalian meats, such as from pigs, are really not much better
- Poultry, on the other hand, the science is less clear on; the results are mixed, and thus so are the conclusions. The results are often barely statistically significant. In other words, when it comes to poultry, in the matter of health, the general consensus is that you can take it or leave it and will be fine. Some studies have found firmly for or against it, but the consensus is a collective scientific shrug.
- Fish, meanwhile, has almost universally been found to be healthful in moderation. You may have other reasons for wanting to avoid it (ethics, environmentalism, personal taste) but those things are beyond the scope of this article.
Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products: True or False?
True! With nuances.
Let’s divide this into “some” and “all”. Firstly, some people may have health conditions and/or other mitigating circumstances that make an entirely plant-based diet untenable.
We’re going light on quotations from subscriber comments today because otherwise this article will get a bit long, but here’s a great example that’s worth quoting, from a subscriber who voted for this option:
❝I have a rare genetic disease called hereditary fructose intolerance. It means I lack the enzyme, Aldolase B, to process fructose. Eating fruits and veggies thus gives me severe hypoglycemia. I also have anemia caused by two autoimmune diseases, so I have to eat meat for the iron it supplies. I also supplement with iron pills but the pills alone can’t fix the problem entirely.❞
And, there’s the thing. Popular vegan talking-points are very good at saying “if you have this problem, this will address it; if you have that problem, that will address it”, etc. For every health-related objection to a fully plant-based diet there’s a refutation… Individually.
But actual real-world health doesn’t work like that; co-morbidities are very common, and in some cases, like our subscriber above, one problem undermines the solution to another. Add a third problem and by now you really just have to do what you need to do to survive.
For this reason, even the Vegan Society’s definition of veganism includes the clause “so far as is possible and practicable”.
Now, as for the rest of us “all”.
What if we’re really healthy and are living in optimal circumstances (easy access to a wide variety of choice of food), can we live healthily and happily just on plants?
No—on a technicality.
Vegans famously need to supplement vitamin B12, which is not found in plants. Ironically, much of the B12 in animal products comes from the animals themselves being given supplements, but that’s another matter. However, B12 can also be enjoyed from yeast. Popular options include the use of yeast extract (e.g. Marmite) and/or nutritional yeast in cooking.
Yeast is a single-celled microorganism that’s taxonomically classified as a fungus, even though in many ways it behaves like an animal (which series of words may conjure an amusing image, but we mean, biologically speaking).
However, it’s also not technically a plant, hence the “No—on a technicality”
Bottom line:
By nature, humans are quite versatile generalists when it comes to diet:
- Most of us can live healthily and happily on just plants if we so choose.
- Some people cannot, and will require varying kinds (and quantities) of animal products.
- As for red and/or processed meats, we’re not the boss of you, but from a health perspective, the science is clear: unless you have a circumstance that really necessitates it, just don’t.
- Same goes for pork, which isn’t red and may not be processed, but metabolically it’s associated with the same problems.
- The jury is out on poultry, but it strongly appears to be optional, healthwise, without making much of a difference either way
- Fish is roundly considered healthful in moderation. Enjoy it if you want, don’t if you don’t.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
One Cause; Countless Aches
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Is The Cause?
Zac Cupples’ video (below) makes an appealing claim: 90% of movement issues and discomforts we experience daily come from one source: reduced joint space due to increased muscle tension.
For Cupples, this could be causing anything from knee pain to foot pain to ankle pain to hip pain to generalized joint pain to…pretty much any sort of pain.
So, why do we describe this as “appealing”?
Well, if there’s just one cause, that means there is only one thing to fix
Can This Be True?
Whilst we normally stray away from oversimplifications, we found Cupples’ example quite powerful.
Cupples defends his thesis by illustrating it with a simple wrist movement experiment: try moving your wrist in a circle with your palm open, and then do the same with your fist clenched.
Did you notice a difference?
When you clench your fist, movement (normally) becomes restricted and uncomfortable, illustrating how increased tension limits joint space.
It’s a powerful analogy for understanding our body’s mechanics.
So How Do We Fix It?
To combat issues with reduced joint space, Cupples proposes a three-step solution: reducing muscle tension, increasing range of motion in commonly limited areas, and enhancing movement efficiency. He delves into strategies for achieving these, including adopting certain positions and breathing techniques.
There are also some elements of strategic muscle engagement, but we’ll leave that to him to describe:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: