Metabolic Health Roadmap – by Brenda Wollenberg
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The term “roadmap” is often used in informative books, but in this case, Wollenberg (a nutritionist with decades of experience) really does deliver what can very reasonably be described as a roadmap:
She provides chapters in the form of legs of a journey [to better metabolic health], and those legs are broadly divided into an “information center” to deliver new information, a “rest stop” for reflection, “roadwork” to guide the reader through implementing the information we just learned, in a practical fashion, and finally “traveller assistance” to give additional support / resources, as well as any potential troubleshooting, etc.
The information and guidance within are all based on very good science; a lot is what you will have read already about blood sugar management (generally the lynchpin of metabolic health in general), but there’s also a lot about leveraging epigenetics for our benefit, rather than being sabotaged by such.
There’s a little guidance that falls outside of nutrition (sleep, exercise, etc), but for the most part, Wollenberg stays within her own field of expertise, nutrition.
The style is idiosyncratic; it’s very clear that her goal is providing the promised roadmap, and not living up to any editor’s wish or publisher’s hope of living up to industry standard norms of book formatting. However, this pays off, because her delivery is clear and helpful while remaining personable and yet still bringing just as much actual science, and this makes for a very pleasant and informative read.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your metabolic health, as well as get held-by-the-hand through your health-improvement journey by a charming guide, this is very much the book for you!
Click here to check out the Metabolic Health Roadmap, and start taking steps!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Put Your Feet Up! (Against A Wall, For 20 Minutes)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Feel free to browse our articles while you do
Here are 10 good reasons to give it a try; there are another 10 in the short (3:18) video:
- Improves blood circulation
- Improves blood pressure
- Relaxes the body as a whole
- Alleviates lower back tension
- Eases headaches and migraines
- Reduces knee pain
- Relieves swelling in feet and ankles
- Improves lymphatic flow
- Stretches the hamstrings (and hip flexors, if you do it wide)
- Helps quiet the mind
As for the rest…
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
PS: about that circulation… As a general rule of thumb, anything that slightly confuses the heart (anatomically, not romantically) will tend to have a beneficial effect, in moderation. This goes for being upside-down (as is partly the case here), and also for high-intensity interval training (HIIT):
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
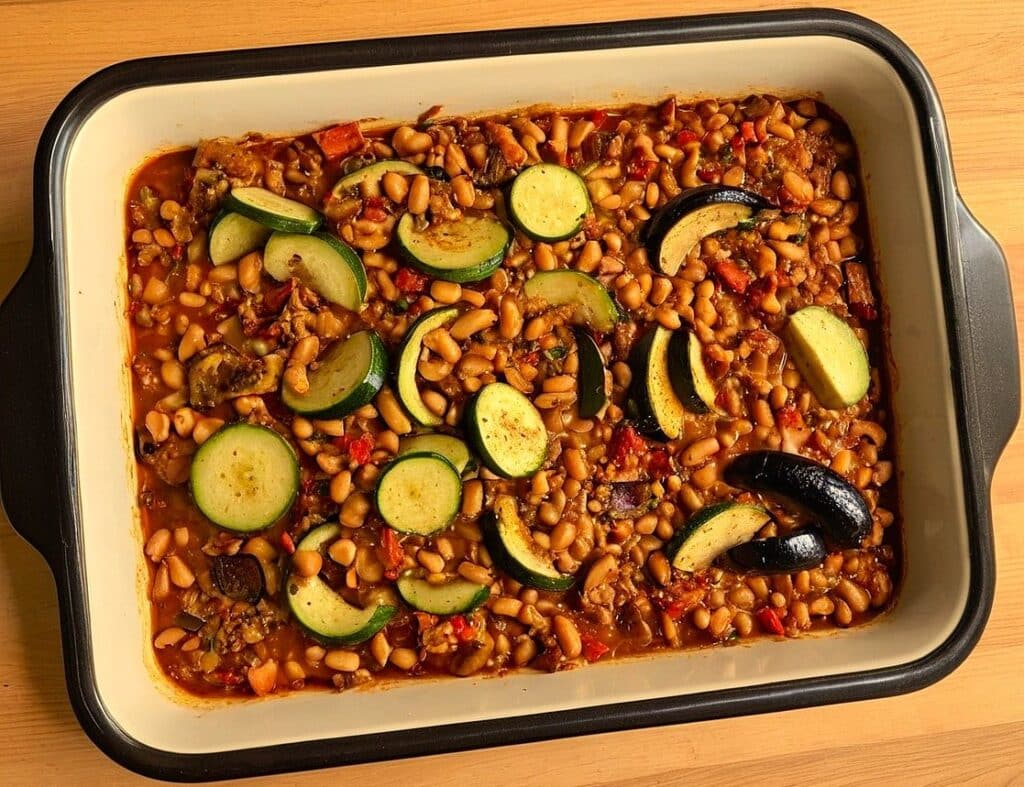
Oven-Roasted Ratatouille
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a supremely low-effort, high-yield dish. It’s a nutritional tour-de-force, and very pleasing to the tastebuds too. We use flageolet beans in this recipe; they are small immature kidney beans. If they’re not available, using kidney beans or really any other legume is fine.
You will need
- 2 large zucchini, sliced
- 2 red peppers, sliced
- 1 large eggplant, sliced and cut into semicircles
- 1 red onion, thinly sliced
- 2 cans chopped tomatoes
- 2 cans flageolet beans, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups same, cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp balsamic vinegar
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp red chili pepper flakes (omit or adjust per your heat preferences)
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Mixed herbs, per your preference. It’s hard to go wrong with this one, but we suggest leaning towards either basil and oregano or rosemary and thyme. We also suggest having some finely chopped to go into the dish, and some held back to go on the dish as a garnish.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃.
2) Mix all the ingredients (except the tomatoes and herbs) in a big mixing bowl, ensuring even distribution.
2) Add the tomatoes. The reason we didn’t add these before is because it would interfere with the oil being distributed evenly across the vegetables.
3) Transfer to a deep-walled oven tray or an ovenproof dish, and roast for 30 minutes.
4) Stir, add the chopped herbs, stir again, and return to the oven for another 30 minutes.
5) Serve (hot or cold), adding any herb garnish you wish to use.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Diabetes Drugs That Can Cut Asthma Attacks By 70%
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Asthma, obesity, and type 2 diabetes are closely linked, with the latter two greatly increasing asthma attack risk.
While bronchodilators / corticosteroids can have immediate adverse effects due to sympathetic nervous system activation, and lasting adverse effects due to the damage it does to metabolic health, diabetes drugs, on the other hand, can improve things with (for most people) fewer unwanted side effects.
Great! Which drugs?
Metformin, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs).
Specifically, researchers have found:
- Metformin is associated with a 30% reduction in asthma attacks
- GLP-1RAs are associated with a 40% reduction in asthma attacks
…and yes, they stack, making for a 70% reduction in the case of people taking both. Furthermore, the results are independent of weight, glycemic control, or asthma phenotype.
In terms of what was counted, the primary outcome was asthma attacks at 12-month follow-up, defined by oral corticosteroid use, emergency visits, hospitalizations, or death.
The effect of metformin on asthma attacks was not affected by BMI, HbA1c levels, eosinophil count, asthma severity, or sex.
Of the various extra antidiabetic drugs trialled in this study, only GLP-1 receptor agonists showed a further and sustained reduction in asthma attacks.
Here’s the study itself, hot off the press, published on Monday:
JAMA Int. Med. | Antidiabetic Medication and Asthma Attacks
“But what if I’m not diabetic?”
Good news:
More than half of all US adults are eligible for semaglutide therapy ← this is because they’ve expanded the things that semaglutide (the widely-used GLP-1 receptor agonist drug) can be prescribed for, now going beyond just diabetes and/or weight loss 😎
And metformin, of course, is more readily available than semaglutide, so by all means speak with your doctor/pharmacist about that, if it’s of interest to you.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
When You “Can’t Complain”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Bone To Pick… Up And Then Put Back Where We Found It
In today’s Psychology Sunday feature, we’re going to be flipping the narrative on gratitude, by tackling it from the other end.
We have, by the way, written previously about gratitude, and what mistakes to avoid, in one of our pieces on positive psychology:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
“Can’t complain”
Your mission, should you choose to accept it (and come on, who doesn’t like a challenge?) is to go 21 days without complaining (to anyone, including yourself, about anything). If you break your streak, that’s ok, just start again!
Why?
Complaining is (unsurprisingly) inversely correlated with happiness, in a self-perpetuating cycle:
Pet Peeves and Happiness: How Do Happy People Complain?
And if a stronger motivation is required, there’s a considerable inverse correlation between all-cause happiness and all-cause mortality, even when potential confounding factors (e.g., chronic health conditions, socioeconomic status, etc) are controlled for, and especially as we get older:
Investing in Happiness: The Gerontological Perspective
How?
You may have already formulated some objections by this point, for example:
- Am I supposed to tell my doctor/therapist “I’m fine thanks; how are you?”
- Some things are worthy of complaint; should I be silent?
But both of these issues (communication, and righteousness) have answers:
On communication:
There is a difference between complaining, and giving the necessary information in answer to a question—or even volunteering such information.
For example, when our site went down yesterday, some of you wrote to us to let us know the links weren’t working. There is a substantive difference (semantic, ontological, and teleological) between:
- ❝The content was great but the links in “you may have missed” did not work.❞ ← a genuine piece of feedback we received (thank you!)
- ❝Wasted my time, couldn’t read your articles! Unsubscribing, and I hope your socks get wet tomorrow!❞ ← nobody said this; our subscribers are lovely (thank you)
- Note that the former wasn’t a complaint, it was genuinely helpful feedback, without which we might not have noticed the problem and fixed it.
- The latter was a complaint, and also (like many complaints) didn’t even address the actual problem usefully.
What makes it a complaint or not is not the information conveyed, but the tone and intention. So for example:
“You’ve only done half the job I asked you to!” → “Thank you for doing the first half of this job, could you please do the other half now?”
Writer’s anecdote: my washing machine needs a part replaced; the part was ordered two weeks ago and I was told it would take a week to arrive. It’s been two weeks, so tomorrow I will not complain, but I will politely ask whether they have any information about the delay, and a new estimated time of arrival. Because you know what? Whatever the delay is, complaining won’t make it arrive last week!
On righteousness:
Indeed, some things are very worthy of complaint. But are you able to effect a solution by complaining? If not, then it’s just hot air. And venting isn’t without its own merits (we touched on the benefits of emotional catharsis recently), but that should be a mindful choice when you choose to do that, not a matter of reactivity.
Complaining is a subset of criticizing, and criticizing can be done without the feeling and intent of complaining. However, it too should definitely be measured and considered, responsive, not reactive. This itself could be the topic for another main feature, but for now, here’s a Psychology Today article that at least explains the distinction in more words than we have room for here:
React vs Respond: What’s the difference?
This, by the way, also goes the same for engaging in social and political discourse. It’s easy to get angry and reactive, but it’s good to take a moment to pick your battles, and by all means fight for what you believe in, and/but also do so responsively rather than reactively.
Not only will your health thank you, but you’re also more likely to “win friends and influence people” and all that!
What gets measured, gets done
Find a way of tracking your streak. There are apps for that, like this one, or you could find a low-tech method you prefer.
Bonus tip: if you do mess up and complain, and you realize as you’re doing it, take a moment to take a breath and correct yourself in the moment.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
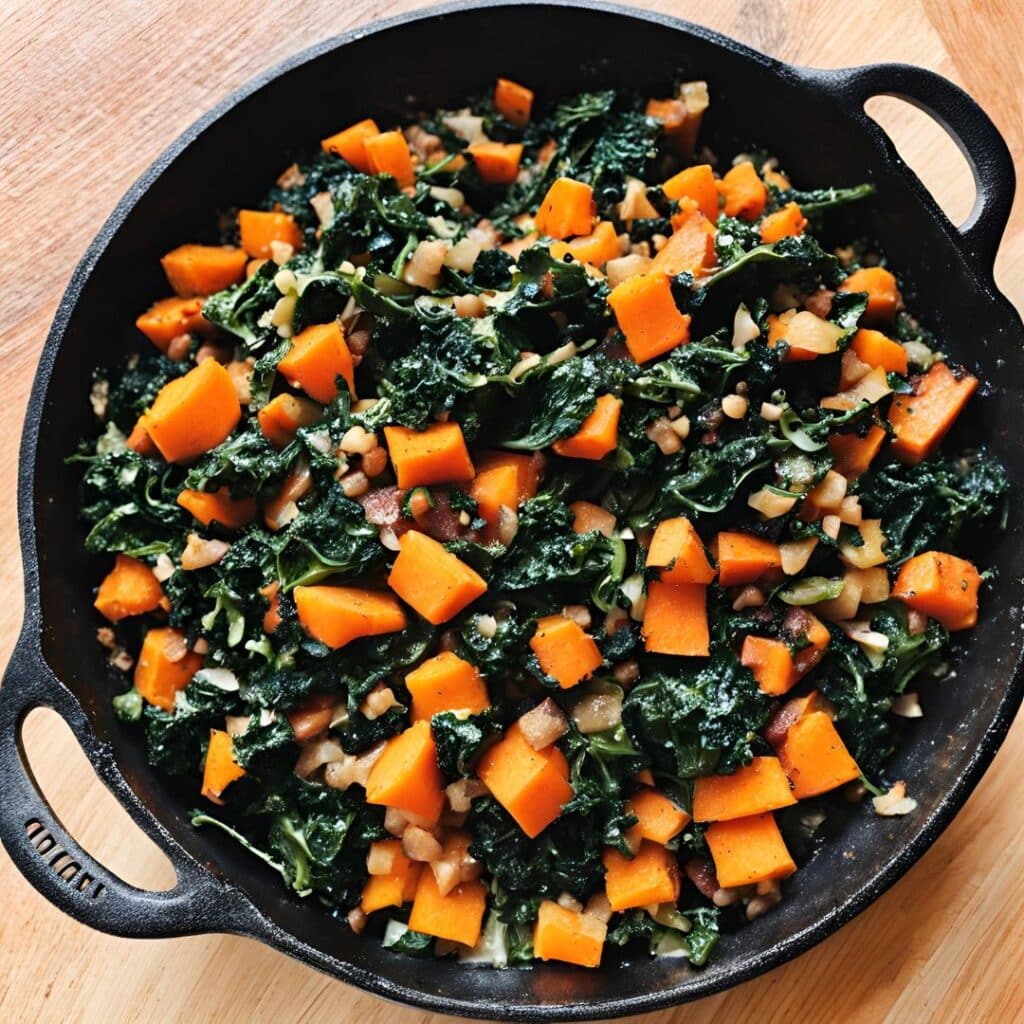
Cavolo Nero & Sweet Potato Hash
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
🎶 Sweet potato hash? It’s a seasonal smash… Catches on in a flash… Let’s do the hash 🎶
You will need
- 6 oz cavolo nero, tough stems removed, chopped
- 1 large sweet potato, diced
- 1 large red onion, finely chopped
- 1 parsnip, grated
- 1 small red pepper, chopped
- 4 oz baby portobello mushrooms, chopped
- ½ cup fresh or thawed peas
- ¼ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp dried rosemary
- 1 tsp dried thyme (dried for convenience; fresh is also fine if you have it)
- 1 tsp red chili flakes (dried for convenience; fresh is also fine if you have it)
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 425℉ / 220℃.
2) Toss the diced sweet potato in 1 tbsp olive oil, as well as the nutritional yeast, ground turmeric, black pepper, and MSG/salt, ensuring an even distribution. Roast in the oven on a lined baking tray, for 30 minutes, turning at least once to get all sides of the potato. When it is done, remove from the oven and set aside.
3) Heat a little oil in a sauté pan or large skillet (either is fine; we’re not adding liquids today), and fry the onion, parsnip, and pepper until softened, which should take about 5 minutes (this is one reason why we grated the parsnip; the other is for the variation in texture).
4) Add the garlic, mushrooms, herbs, and chili flakes, and cook for a further 1 minute, while stirring.
5) Add the cavolo nero and peas, stir until the cavolo nero begins to wilt, and then…
6) Add the roasted sweet potato; cook for about 5 more minutes, pressing down with the spatula here and there to mash the ingredients together.
7) Turn the hash over when it begins to brown on the bottom, to lightly brown the other side too.
8) Serve hot.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
- Ergothioneine: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hawthorn For The Heart (& More)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hawthorn, The Heart-Healthy Helper
Hawthorn, a berry of the genus Crataegus (there are many species, but they seem to give more or less the same benefits), has been enjoyed for hundreds of years, if not thousands, as a herbal remedy for many ailments, mostly of the cardiovascular, digestive, and/or endocrine systems:
Crataegus pinnatifida: Chemical Constituents, Pharmacology, and Potential Applications
Antioxidant & Anti-inflammatory
Like most berries, it’s full of helpful polyphenols, with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Indeed, as Dr. Nabavi et al. wrote,
❝Crataegus monogyna Jacq. (hawthorn) is one of the most important edible plants of the Rosaceae family and is also used in traditional medicine.
Growing evidence has shown that this plant has various interesting physiological and pharmacological activities due to the presence of different bioactive natural compounds.
In addition, scientific evidence suggests that the toxicity of hawthorn is negligible. ❞
Read in full: Polyphenolic Composition of Crataegus monogyna Jacq.: From Chemistry to Medical Applications
While “the toxicity of hawthorn is negligible” may be reasonably considered a baseline for recommending an edible plant, it’s still important as just that: a baseline. It’s good to know that berries are safe, after all!
More positively, about those antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties:
This one was a mouse study, but it’s important as it about modulating liver injury after being fed a high fructose diet.
In other words: it a) helps undo the biggest cause of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, b) logically, likely guards against diabetes also (by the same mechanism)
Anti-Diabetes Potential
Curious about that latter point, we looked for studies, and found, for example:
- Hypoglycemic effect of hawthorn in type II diabetes mellitus rat model
- Molecular Mechanisms of Hawthorn Extracts in Multiple Organs Disorders in Underlying of Diabetes: A Review
- Modulation of GPC-4 and GPLD1 serum levels by improving glycemic indices in type 2 diabetes: Resistance training and hawthorn extract intervention
Noteworthily, those studies are from the past couple of years, which is probably why we’re not seeing many human trials for this yet—everything has to be done in order, and there’s a lengthy process between each.
We did find some human trials with hawthorn in diabetes patients, for example:
…but as you see, that’s testing not its antidiabetic potential, so far demonstrated only in mice and rats (so far as we could find), but rather its blood pressure lowering effects, using diabetic patients as a sample.
Blood pressure benefits
Hawthorn has been studied specifically for its hypotensive effect, for example:
As an extra bonus, did you notice in the conclusion,
❝Furthermore, a trend towards a reduction in anxiety (p = 0.094) was also observed in those taking hawthorn compared with the other groups.
These findings warrant further study, particularly in view of the low dose of hawthorn extract used.❞
…it seems that not a lot more study has been done yet, but that is promising too!
Other blood metrics
So, it has antidiabetic and antihypertensive benefits, what of blood lipids?
Hawthorn Fruit Extract Elevates Expression of Nrf2/HO-1 and Improves Lipid Profiles
And as for arterial plaque?
here it was tested alongside another herb, and performed well (also against placebo).
In summary…
Hawthorn (Crataegus sp.) is…
- a potent berry containing many polyphenols with good antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- looking promising against diabetes, but research for this is still in early stages
- found to have other cardioprotective effects (antihypertensive, improves lipid profiles), too
- considered to have negligible toxicity
Where can I get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: