Inverse Vaccines for Autoimmune Diseases
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inverse Vaccines for Autoimmune Diseases
This is Dr. Jeffrey Hubbell. He’s a molecular engineer, with a focus on immunotherapy, immune response, autoimmune diseases, and growth factor variants.
He’s held 88 patents, and was the recipient of the Society for Biomaterials’ Founders Award for his “long-term, landmark contributions to the discipline of biomaterials”, amongst other awards and honours that would make our article too long if we included them all.
And, his latest research has been about developing…
Inverse Vaccines
You may be thinking: “you mean diseases; he’s engineering diseases?”
And no, it’s not that. Here’s how it works:
Normally in the case of vaccine, it’s something to tell the body “hey, if you see something that looks like this, you should kill it on sight” and the body goes “ok, preparing countermeasures according to these specifications; thanks for the heads-up”
In the case of an inverse vaccine, it’s the inverse. It’s something to tell the body “hey, this thing you seem to think is a threat, it’s actually not, and you should leave it alone”.
Why this matters for people with autoimmune diseases
Normally, autoimmune diseases are treated in one or more of the following ways:
- Dampen the entire immune system (bad for immunity against actual diseases, obviously, and is part of why many immunocompromised people have suffered and died disproportionately from COVID, for example)
- Give up and find a workaround (a good example of this is Type 1 Diabetes, and just giving up on the pancreas not being constantly at war with itself, and living on exogenous insulin instead)
Neither of those are great.
What inverse vaccines do is offer a way to flag the attacked-in-error items as acceptable things to have in the body. Those might be things that are in our body by default, as in the case of many autoimmune diseases, or they may even be external items that should be allowed but aren’t, as in the case of gluten, in the context of Celiac disease.
The latest research is not yet accessible for free, alas, but you can read the abstract here:
Or if you prefer a more accessible pop-science approach, here’s a great explanatory article:
“Inverse vaccine” shows potential to treat multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases
Where can we get such inverse vaccines?
❝There are no clinically approved inverse vaccines yet, but we’re incredibly excited about moving this technology forward❞
~ Dr. Jeffrey Hubbell
But! Lest you be disappointed, you can get in line already, in the case of the Celiac disease inverse vaccine, if you’d like to be part of their clinical trial:
Click here to see if you are eligible to be part of their clinical trial
If you’re not up for that, or if your autoimmune disease is something else (most of the rest of their research is presently focusing on Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes), then:
- The phase 1 MS trial is currently active, estimated completion in summer 2024.
- They are in the process of submitting an investigational new drug (IND) application for Type 1 Diabetes
- This is the first step to starting clinical safety and efficacy trials
…so, watch this space!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
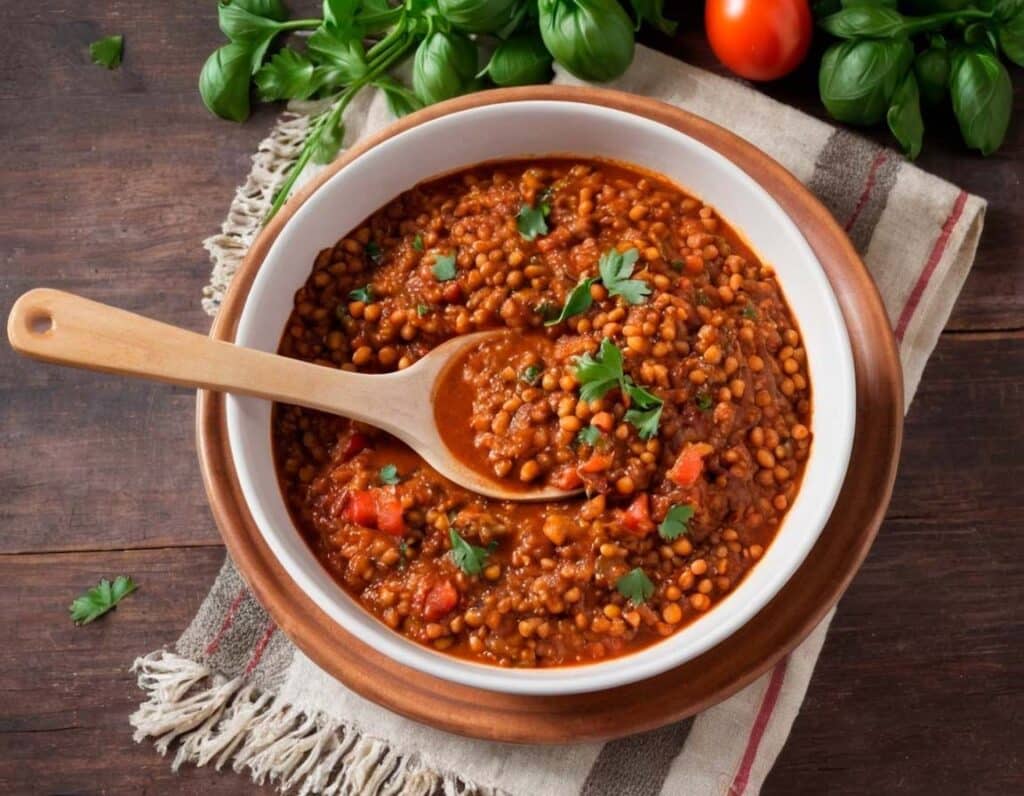
Hearty Healthy Ragù
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ragù is a traditional Italian meaty sauce with tomato, and is the base for a number of other Italian dishes. It can be enjoyed as-is, or with very minor modifications can be turned into a Bolognese sauce or a lasagna filling or various other things. Our variations from tradition are mainly twofold here: we’re using nutrition-packed lentils instead of meat (but with a couple of twists that make them meatier), and we’re not using wine.
Traditionally, red wine is used in a ragù (white wine if you want to make it into a Bolognese sauce, by the way), but with all we’re doing it’s not necessary. If you want to add a splash of wine, we’re not going to call that a healthy ingredient, but we’re also not the boss of you
You will need
- 1 large onion (or equivalent small ones), chopped roughly
- 1 bulb garlic (or to your heart’s content), chopped finely or crushed
- 4 large tomatoes, chopped (or 2 cans chopped tomatoes)
- 1 tube (usually about 7 oz) tomato purée
- 1 cup brown lentils (green lentils will do if you can’t get brown)
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp black pepper, cracked or coarse ground
- 1 bunch fresh basil, finely chopped (or 1 tbsp, freeze-dried)
- 1 bunch fresh oregano, finely chopped (or 1 tbsp, freeze-dried)
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (failing that, 1 tbsp yeast extract, yes, even if you don’t like it, we promise it won’t taste like it once it’s done; it just makes the dish meatier in taste and also adds vitamin B12)
- 1 tsp cumin, ground (note that this one was tsp, not tbsp like the others)
- 1 tsp MSG, or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- 4 cups water
- Olive oil for frying (ideally Extra Virgin, but so long as it’s at least marked virgin olive oil and not cut with other oils, that’s fine)
- Parsley, chopped, to garnish
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the lentils in a small saucepan, or if you have one, a rice cooker (the rice cooker is better; works better and requires less attention), adding the chia seeds, MSG or low sodium salt, and nutritional yeast (or yeast extract). as well as the cumin. Add 4 cups boiling water and turn on the heat to cook them. This will probably take about 15–20 minutes; you want the lentils to be soft; a tiny bit past al dente, but not so far as mushy.
2) Fry the onion in some olive oil in a big pan (everything is going in here eventually if the pan is big enough; if it isn’t, you’ll need to transfer to a bigger pan in a bit). Once they’re nearly done, throw in the garlic too. If the lentils aren’t done yet, take the onions and garlic off the heat while you wait. After a few times of doing this recipe, you’ll be doing everything like clockwork and it’ll all align perfectly.
3) Drain the lentils (if all the water wasn’t absorbed; again, after doing it a few times, you’ll just use the right amount of water for your apparatus) but don’t rinse them (remember you put seasonings in here!), and add them to the pan with the onions and garlic; add a splash more olive oil if necessary, and stir until all the would-be-excess fat is absorbed into the lentils.
Note: the excess fat to be absorbed by the lentils was a feature not a bug; we wanted a little fat in the lentils! Makes the dish meatier and tastier, as well as more nutrient-dense.
4) add the tomatoes and tomato purée, stirring them in thoroughly; add the basil and oregano too and stir those in as well. Set it on a low heat for at least 10–15 minutes, stirring occasionally to let the flavors blend.
(if you happen to be serving pasta with it, then the time it takes to boil water and cook the pasta is a good time for the flavors to do their thing)
5) take it off the heat, and add the parsley garnish. It’s done!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- What Is The Mediterranean Diet, Anyway?
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure ← one more reason for the brown lentils today
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal
- The Many Health Benefits of Garlic
- Olive Oil: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
We’re aware that very many of our readers are women, who do not have a prostate.
However, dear reader: if you do have one, and/or love someone who has one, this is a good thing to know about.
The prostate gland is a (hopefully) walnut-sized gland (it actually looks a bit like a walnut too), that usually sits just under the bladder.
See also: How to Locate Your Prostate*
*The scale is not great in these diagrams, but they’ll get the job done. Besides, everyone is different on the inside, anyway. Not in a “special unique snowflake” way, but in a “you’d be surprised how much people’s insides move around” way.
Fun fact: did you ever feel like your intestines are squirming? That’s because they are.
You can’t feel it most of the time due to the paucity of that kind of nervous sensation down there, but the peristaltic motion that they use to move food along them on the inside, also causes them push against the rest of your guts, on the outside of them. This is the exact same way that many snakes move about.
If someone has to perform an operation in that region, sometimes it will be necessary to hang the intestines on a special rack, to keep them in one place for the surgery.
What can go wrong?
There are two very common things that can go wrong with the prostate:
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH), otherwise known as an enlarged prostate
- Prostate cancer
For most men, the prostate gland continues to grow with age, which is how the former comes about so frequently.
For everyone, due to the nature of the mathematics involved in cellular mutation and replication, we will eventually get cancer if something else doesn’t kill us first.
- Prostate cancer affects 12% of men overall, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing each year thereafter.
- Prostate cancer can look like BPH in the early stages (and/or, an enlarged prostate can turn cancerous) so it’s important to not shrug off the symptoms of BPH.
How can BPH be avoided/managed?
There are prescription medications that can help reduce the size of the prostate, including testosterone blockers (such as spironolactone and bicalutamide) and 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride. Each have their pros and cons:
- Testosterone-blockers are the heavy-hitters, and work very well… but have more potential adverse side effects (your body is used to running on testosterone, after all)
- 5α-reductase inhibitors aren’t as powerful, but they block the conversion of free testosterone to dihydrogen testosterone (DHT), and it’s primarily DHT that causes the problems. By blocking the conversion of T to DHT, you may actually end up with higher serum testosterone levels, but fewer ill-effects. Exact results will vary depending on your personal physiology, and what else you are taking, though.
There are also supplements that can help, including saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil. Here’s a good paper that covers both:
We have recommended saw palmetto before for a variety of uses, including against BPH:
Too much or too little testosterone? This one supplement may fix that
You might want to avoid certain medications that can worsen BPH symptoms (but not actually the size of the prostate itself). They include:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (most modern antidepressants aren’t this kind; ask your pharmacist/doctor if unsure)
You also might want to reduce/skip:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
In all the above cases, it’s because of how they affect the bladder, not the prostate, but given their neighborliness, each thing affects the other.
What if it’s cancer? How do I know and what do I do?
The creator of the Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test has since decried it as “a profit-driven health disaster” that is “no better than a coin toss”, but it remains the first go-to of many medical services.
However, there’s a newer, much more accurate test, called the Prostate Screening Episwitch (PSE) test, which is 94% accurate, so you might consider asking your healthcare provider whether that’s an option:
The new prostate cancer blood test with 94 per cent accuracy
As for where to go from there, we’re out of space for today, but we previously reviewed a very good book about this, Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer, and we highly recommend it—it could easily be a literal lifesaver.
Share This Post
-
Lies I Taught in Medical School – by Dr. Robert Lufkin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There seems to be a pattern of doctors who practice medicine one way, get a serious disease personally, and then completely change their practice of medicine afterwards. This is one of those cases.
Dr. Lufkin here presents, on a chapter-by-chapter basis, the titularly promised “lies” or, in more legally compliant speak (as he acknowledges in his preface), flawed hypotheses that are generally taught as truths. In many cases, the “lie” is some manner of “xyz is normal and nothing to worry about”, and/or “there is nothing to be done about xyz; suck it up”.
The end result of the information is not complicated—enjoy a plants-forward whole foods low-carb diet to avoid metabolic diseases and all the other things to branch off from same (Dr. Lufkin makes a fair case for metabolic disease leading to a lot of secondary diseases that aren’t considered metabolic diseases per se). But, the journey there is actually important, as it answers a lot of questions that are much less commonly understood, and often not even especially talked-about, despite their great import and how they may affect health decisions beyond the dietary. Things like understanding the downsides of statins, or the statistical models that can be used to skew studies, per relative risk reduction and so forth.
Bottom line: this book gives the ins and outs of what can go right or wrong with metabolic health and why, and how to make sure you don’t sabotage your health through missing information.
Click here to check out Lies I Taught In Medical School, and arm yourself with knowledge!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
5 Steps To Quit Sugar Easily
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sugar is one of the least healthy things that most people consume, yet because it’s so prevalent, it can also be tricky to avoid at first, and the cravings can also be a challenge. So, how to quit it?
Step by step
Dr. Mike Hansen recommends the following steps:
- Be aware: a lot of sugar consumption is without realizing it or thinking about it, because of how common it is for there to be added sugar in things we might purchase ready-made, even supposedly healthy things like yogurts, or easy-to-disregard things like condiments.
- Recognize sugar addiction: a controversial topic, but Dr. Hansen comes down squarely on the side of “yes, it’s an addiction”. He wants us to understand more about the mechanics of how this happens, and what it does to us.
- Reduce gradually: instead of going “cold turkey”, he recommends we avoid withdrawal symptoms by first cutting back on liquid sugars like sodas, juices, and syrups, before eliminating solid sugar-heavy things like candy, sugar cookies, etc, and finally the more insidious “why did they put sugar in this?” added-sugar products.
- Find healthy alternatives: simple like-for-like substitutions; whole fruits instead of juices/smoothies, for example. 10almonds tip: stuffing dates with an almond each makes it very much like eating chocolate, experientially!
- Manage cravings: Dr. Hansen recommends distraction, and focusing on upping other healthy habits such as hydration, exercise, and getting more vegetables.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Mythbusting The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
State Regulators Know Health Insurance Directories Are Full of Wrong Information. They’re Doing Little to Fix It.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for The Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this one in your inbox.
Series: America’s Mental Barrier:How Insurers Interfere With Mental Health Care
- Extensive Errors: Many states have sought to make insurers clean up their health plans’ provider directories over the past decade. But the errors are still widespread.
- Paltry Penalties: Most state insurance agencies haven’t issued a fine for provider directory errors since 2019. When companies have been penalized, the fines have been small and sporadic.
- Ghostbusters: Experts said that stricter regulations and stronger fines are needed to protect insurance customers from these errors, which are at the heart of so-called ghost networks.
These highlights were written by the reporters and editors who worked on this story.
To uncover the truth about a pernicious insurance industry practice, staffers with the New York state attorney general’s office decided to tell a series of lies.
So, over the course of 2022 and 2023, they dialed hundreds of mental health providers in the directories of more than a dozen insurance plans. Some staffers pretended to call on behalf of a depressed relative. Others posed as parents asking about their struggling teenager.
They wanted to know two key things about the supposedly in-network providers: Do you accept insurance? And are you accepting new patients?
The more the staffers called, the more they realized that the providers listed either no longer accepted insurance or had stopped seeing new patients. That is, if they heard back from the providers at all.
In a report published last December, the office described rampant evidence of these “ghost networks,” where health plans list providers who supposedly accept that insurance but who are not actually available to patients. The report found that 86% of the listed mental health providers who staffers had called were “unreachable, not in-network, or not accepting new patients.” Even though insurers are required to publish accurate directories, New York Attorney General Letitia James’ office didn’t find evidence that the state’s own insurance regulators had fined any insurers for their errors.
Shortly after taking office in 2021, Gov. Kathy Hochul vowed to combat provider directory misinformation, so there seemed to be a clear path to confronting ghost networks.
Yet nearly a year after the publication of James’ report, nothing has changed. Regulators can’t point to a single penalty levied for ghost networks. And while a spokesperson for New York state’s Department of Financial Services has said that “nation-leading consumer protections” are in the works, provider directories in the state are still rife with errors.
A similar pattern of errors and lax enforcement is happening in other states as well.
In Arizona, regulators called hundreds of mental health providers listed in the networks of the state’s most popular individual health plans. They couldn’t schedule visits with nearly 2 out of every 5 providers they called. None of those companies have been fined for their errors.
In Massachusetts, the state attorney general investigated alleged efforts by insurers to restrict their customers’ mental health benefits. The insurers agreed to audit their mental health provider listings but were largely allowed to police themselves. Insurance regulators have not fined the companies for their errors.
In California, regulators received hundreds of complaints about provider listings after one of the nation’s first ghost network regulations took effect in 2016. But under the new law, they have actually scaled back on fining insurers. Since 2016, just one plan was fined — a $7,500 penalty — for posting inaccurate listings for mental health providers.
ProPublica reached out to every state insurance commission to see what they have done to curb rampant directory errors. As part of the country’s complex patchwork of regulations, these agencies oversee plans that employers purchase from an insurer and that individuals buy on exchanges. (Federal agencies typically oversee plans that employers self-fund or that are funded by Medicare.)
Spokespeople for the state agencies told ProPublica that their “many actions” resulted in “significant accountability.” But ProPublica found that the actual actions taken so far do not match the regulators’ rhetoric.
“One of the primary reasons insurance commissions exist is to hold companies accountable for what they are advertising in their contracts,” said Dr. Robert Trestman, a leading American Psychiatric Association expert who has testified about ghost networks to the U.S. Senate Committee on Finance. “They’re not doing their job. If they were, we would not have an ongoing problem.”
Most states haven’t fined a single company for publishing directory errors since 2019. When they do, the penalties have been small and sporadic. In an average year, fewer than a dozen fines are issued by insurance regulators for directory errors, according to information obtained by ProPublica from almost every one of those agencies. All those fines together represent a fraction of 1% of the billions of dollars in profits made by the industry’s largest companies. Health insurance experts told ProPublica that the companies treat the fines as a “cost of doing business.”
Insurers acknowledge that errors happen. Providers move. They retire. Their open appointments get booked by other patients. The industry’s top trade group, AHIP, has told lawmakers that companies contact providers to verify that their listings are accurate. The trade group also has stated that errors could be corrected faster if the providers did a better job updating their listings.
But providers have told us that’s bogus. Even when they formally drop out of a network, they’re not always removed from the insurer’s lists.
The harms from ghost networks are real. ProPublica reported on how Ravi Coutinho, a 36-year-old entrepreneur from Arizona, had struggled for months to access the mental health and addiction treatment that was covered by his health plan. After nearly two dozen calls to the insurer and multiple hospitalizations, he couldn’t find a therapist. Last spring, he died, likely due to complications from excessive drinking.
Health insurance experts said that, unless agencies can crack down and issue bigger fines, insurers will keep selling error-ridden plans.
“You can have all the strong laws on the books,” said David Lloyd, chief policy officer with the mental health advocacy group Inseparable. “But if they’re not being enforced, then it’s kind of all for nothing.”
The problem with ghost networks isn’t one of awareness. States, federal agencies, researchers and advocates have documented them time and again for years. But regulators have resisted penalizing insurers for not fixing them.
Two years ago, the Arizona Department of Insurance and Financial Institutions began to probe the directories used by five large insurers for plans that they sold on the individual market. Regulators wanted to find out if they could schedule an appointment with mental health providers listed as accepting new patients, so their staff called 580 providers in those companies’ directories.
Thirty-seven percent of the calls did not lead to an appointment getting scheduled.
Even though this secret-shopper survey found errors at a lower rate than what had been found in New York, health insurance experts who reviewed Arizona’s published findings said that the results were still concerning.
Ghost network regulations are intended to keep provider listings as close to error-free as possible. While the experts don’t expect any insurer to have a perfect directory, they said that double-digit error rates can be harmful to customers.
Arizona’s regulators seemed to agree. In a January 2023 report, they wrote that a patient could be clinging to the “last few threads of hope, which could erode if they receive no response from a provider (or cannot easily make an appointment).”
Secret-shopper surveys are considered one of the best ways to unmask errors. But states have limited funding, which restricts how often they can conduct that sort of investigation. Michigan, for its part, mostly searches for inaccuracies as part of an annual review of a health plan. Nevada investigates errors primarily if someone files a complaint. Christine Khaikin, a senior health policy attorney for the nonprofit advocacy group Legal Action Center, said fewer surveys means higher odds that errors go undetected.
Some regulators, upon learning that insurers may not be following the law, still take a hands-off approach with their enforcement. Oregon’s Department of Consumer and Business Services, for instance, conducts spot checks of provider networks to see if those listings are accurate. If they find errors, insurers are asked to fix the problem. The department hasn’t issued a fine for directory errors since 2019. A spokesperson said the agency doesn’t keep track of how frequently it finds network directory errors.
Dave Jones, a former insurance commissioner in California, said some commissioners fear that stricter enforcement could drive companies out of their states, leaving their constituents with fewer plans to choose from.
Even so, staffers at the Arizona Department of Insurance and Financial Institutions wrote in the report that there “needs to be accountability from insurers” for the errors in their directories. That never happened, and the agency concealed the identities of the companies in the report. A department spokesperson declined to provide the insurers’ names to ProPublica and did not answer questions about the report.
Since January 2023, Arizonans have submitted dozens of complaints to the department that were related to provider networks. The spokesperson would not say how many were found to be substantiated, but the department was able to get insurers to address some of the problems, documents obtained through an open records request show.
According to the department’s online database of enforcement actions, not a single one of those companies has been fined.
Sometimes, when state insurance regulators fail to act, attorneys general or federal regulators intervene in their stead. But even then, the extra enforcers haven’t addressed the underlying problem.
For years, the Massachusetts Division of Insurance didn’t fine any company for ghost networks, so the state attorney general’s office began to investigate whether insurers had deceived consumers by publishing inaccurate directories. Among the errors identified: One plan had providers listed as accepting new patients but no actual appointments were available for months; another listed a single provider more than 10 times at different offices.
In February 2020, Maura Healey, who was then the Massachusetts attorney general, announced settlements with some of the state’s largest health plans. No insurer admitted wrongdoing. The companies, which together collect billions in premiums each year, paid a total of $910,000. They promised to remove providers who left their networks within 30 days of learning about that decision. Healey declared that the settlements would lead to “unprecedented changes to help ensure patients don’t have to struggle to find behavioral health services.”
But experts who reviewed the settlements for ProPublica identified a critical shortcoming. While the insurers had promised to audit directories multiple times a year, the companies did not have to report those findings to the attorney general’s office. Spokespeople for Healey and the attorney general’s office declined to answer questions about the experts’ assessments of the settlements.
After the settlements were finalized, Healey became the governor of Massachusetts and has been responsible for overseeing the state’s insurance division since she took office in January 2023. Her administration’s regulators haven’t brought any fines over ghost networks.
Healey’s spokesperson declined to answer questions and referred ProPublica to responses from the state’s insurance division. A division spokesperson said the state has taken steps to strengthen its provider directory regulations and streamline how information about in-network providers gets collected. Starting next year, the spokesperson said that the division “will consider penalties” against any insurer whose “provider directory is found to be materially noncompliant.”
States that don’t have ghost network laws have seen federal regulators step in to monitor directory errors.
In late 2020, Congress passed the No Surprises Act, which aimed to cut down on the prevalence of surprise medical bills from providers outside of a patient’s insurance network. Since then, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, which oversees the two large public health insurance programs, has reached out to every state to see which ones could handle enforcement of the federal ghost network regulations.
At least 15 states responded that they lacked the ability to enforce the new regulation. So CMS is now tasked with watching out for errors in directories used by millions of insurance customers in those states.
Julie Brookhart, a spokesperson for CMS, told ProPublica that the agency takes enforcement of the directory error regulations “very seriously.” She said CMS has received a “small number” of provider directory complaints, which the agency is in the process of investigating. If it finds a violation, Brookhart said regulators “will take appropriate enforcement action.”
But since the requirement went into effect in January 2022, CMS hasn’t fined any insurer for errors. Brookhart said that CMS intends to develop further guidelines with other federal agencies. Until that happens, Brookhart said that insurers are expected to make “good-faith” attempts to follow the federal provider directory rules.
Last year, five California lawmakers proposed a bill that sought to get rid of ghost networks around the state. If it passed, AB 236 would limit the number of errors allowed in a directory — creating a cap of 5% of all providers listed — and raise penalties for violations. California would become home to one of the nation’s toughest ghost network regulations.
The state had already passed one of America’s first such regulations in 2015, requiring insurers to post directories online and correct inaccuracies on a weekly basis.
Since the law went into effect in 2016, insurance customers have filed hundreds of complaints with the California Department of Managed Health Care, which oversees health plans for nearly 30 million enrollees statewide.
Lawyers also have uncovered extensive evidence of directory errors. When San Diego’s city attorney, Mara Elliott, sued several insurers over publishing inaccurate directories in 2021, she based the claims on directory error data collected by the companies themselves. Citing that data, the lawsuits noted that error rates for the insurers’ psychiatrist listings were between 26% and 83% in 2018 and 2019. The insurers denied the accusations and convinced a judge to dismiss the suits on technical grounds. A panel of California appeals court judges recently reversed those decisions; the cases are pending.
The companies have continued to send that data to the DMHC each year — but the state has not used it to examine ghost networks. California is among the states that typically waits for a complaint to be filed before it investigates errors.
“The industry doesn’t take the regulatory penalties seriously because they’re so low,” Elliott told ProPublica. “It’s probably worth it to take the risk and see if they get caught.”
California’s limited enforcement has resulted in limited fines. Over the past eight years, the DMHC has issued just $82,500 in fines for directory errors involving providers of any kind. That’s less than one-fifth of the fines issued in the two years before the regulation went into effect.
A spokesperson for the DMHC said its regulators continue “to hold health plans accountable” for violating ghost network regulations. Since 2018, the DMHC has discovered scores of problems with provider directories and pushed health plans to correct the errors. The spokesperson said that the department’s oversight has also helped some customers get reimbursed for out-of-network costs incurred due to directory errors.
“A lower fine total does not equate to a scaling back on enforcement,” the spokesperson said.
Dr. Joaquin Arambula, one of the state Assembly members who co-sponsored AB 236, disagreed. He told ProPublica that California’s current ghost network regulation is “not effectively being enforced.” After clearing the state Assembly this past winter, his bill, along with several others that address mental health issues, was suddenly tabled this summer. The roadblock came from a surprising source: the administration of the state’s Democratic governor.
Officials with the DMHC, whose director was appointed by Gov. Gavin Newsom, estimated that more than $15 million in extra funding would be needed to carry out the bill’s requirements over the next five years. State lawmakers accused officials of inflating the costs. The DMHC’s spokesperson said that the estimate was accurate and based on the department’s “real experience” overseeing health plans.
Arambula and his co-sponsors hope that their colleagues will reconsider the measure during next year’s session. Sitting before state lawmakers in Sacramento this year, a therapist named Sarah Soroken told the story of a patient who had called 50 mental health providers in her insurer’s directory. None of them could see her. Only after the patient attempted suicide did she get the care she’d sought.
“We would be negligent,” Soroken told the lawmakers, “if we didn’t do everything in our power to ensure patients get the health care they need.”
Paige Pfleger of WPLN/Nashville Public Radio contributed reporting.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Online Reaction Tests & Women’s Cognitive Health (Test Yours!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A team of researchers have looked into the use of online reaction tests (in which, for example, one clicks whenever a certain prompt is shown, or for more of a cognitive challenge, one presses a numerical key when the corresponding digit is shown) to cognitive health in women at different ages.
Why women? To quote the man who had the honor of being the first-listed author on the study (something that happens mysteriously often in science),
❝Women have long been under-represented in healthy aging research, despite making up more than half the population. We developed an easy way to measure cognitive function in the home, without the need for individuals to travel to clinics or receive home visits. Our research shows that testing of cognitive function in the home largely acceptable, easy and convenient❞
About that convenience: they used data from the UK Women’s Cohort Study, which involved over 35,000 British women, and then specifically focused on a follow-up study of 768 participants aged 48–85.
Of the two kinds of online reaction tests we described up top, they used the numerical kind. The participants also filled in a questionnaire about their personal traits (demographic data, mostly, though things like self-reported level of health literacy, and how they would rate their overall health).
What they found
The findings included:
- Younger women were more likely to participate, with participation rates dropping from 89% at age 45 to 44% at age 65.
- Each higher level of education increased the likelihood of volunteering by 7%.
- Women who rated themselves as having “high” intelligence were 19% more likely to participate than those who considered themselves of “average” intelligence.
- Women with lower self-reported health literacy made fewer errors, possibly due to taking longer to decide on answers—consistent with findings from older adults.
You can read the full paper itself here: Health literacy in relation to web-based measurement of cognitive function in the home: UK Women’s Cohort Study
Why this matters
We wrote, a little while ago, about the use of online games (of a specific kind) to improve cognitive function:
Synergistic Brain-Training: Let The Games Begin (But It Matters What Kind) ← the good news is, these are very accessible too
When it comes to rapid and/but correct reactions, this becomes really critical:
How (And Why) To Train Your Pre-Frontal Cortex ← Dr. Sandra Chapman advocates strongly for this, and it’s closely related to working memory and the ability to focus
Want to test yours?
Here are two ways to do it (now, for free, without needing to sign up for anything; the tests are right there on the page):
- HumanBenchmark.com’s Reaction Time Test ← this one’s just a “click when the red panel turns green” test, but the merit here is that it compares your scores to a very large dataset of other people
- Keypress Reaction Time Test ← this one’s the kind that was used in the study, and requires pressing the correct numerical key when the corresponding digit is shown on the screen. You can make it easier or harder by restricting or increasing the range of numbers it uses (default setting is to use the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: