How To Regrow Receding Gums
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One of the problems with the human form is that our teeth evolved to last us for the whole of our life, with plenty of room to spare before our eventual death at the ripe old age of about 35 on average. Dr. Ellie Phillips advises those of us who might be a bit older than that, on how we can avoid becoming “too long in the tooth”—in other words, how to keep our gums, and thus our teeth, in place and healthy.
Getting to the root of the problem
The single biggest cause of gum recession is an acidic environment in the mouth, which harms teeth and gums alike. This acidic environment is produced not merely by consuming acid foods or drinks, but also (and much more often, and more problematically) by sugary foods and drinks, which are not necessarily themselves acidic, but they feed bacteria that release acids as a by-product of their metabolism. If we consume an acidic food or drink, it’s there for a moment, but if we then salivate and/or take a drink of water, it’s pretty much gone in a few seconds. But those bacteria when we feed them sugar? They are there to stay unless we do something more about them than just drink some water.
Other contributing factors to gum recession include teeth grinding, and (ironically) certain oral care products, especially many artificial teeth whiteners.
In case you were wondering: no, brushing will not* generally cause or even worsen gum recession, but flossing can exacerbate it if it’s already underway.
*unless, of course, you are using one of the whiteners we mentioned above
What to do about it: Dr. Phillips recommends:
- use a moderately firm toothbrush to massage gums and promote blood flow
- avoid acidic oral products and homemade remedies even if they’re not acidic but can be caustic, such as baking soda
- rebuild your gums’ and teeth’s protective biofilm (yes, there are “good bacteria” that are supposed to be there) with proper brushing
- avoid cleanings that are more intensive than brushing—skip flossing until your gums have recovered, too
- adjust your diet to avoid acids and (especially) sugars
10almonds note: she also recommends the use of xylitol to promote a healthy oral environment; we don’t recommend that, as while it may be great for the teeth, studies have found it to be bad for the heart.
For more on all of her advices and a bit more of the science of it, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing Without Flossing?
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← including the miswak “chewing stick”, which even outperformed toothbrushes in clinical trials, by biochemically altering the composition of the saliva while gently cleaning like a toothbrush.
- Fluoride Toothpaste vs Non-Fluoride Toothpaste – Which is Healthier?
- Non-Alcohol Mouthwash vs Alcohol Mouthwash – Which is Healthier?
- Xylitol vs Erythritol – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
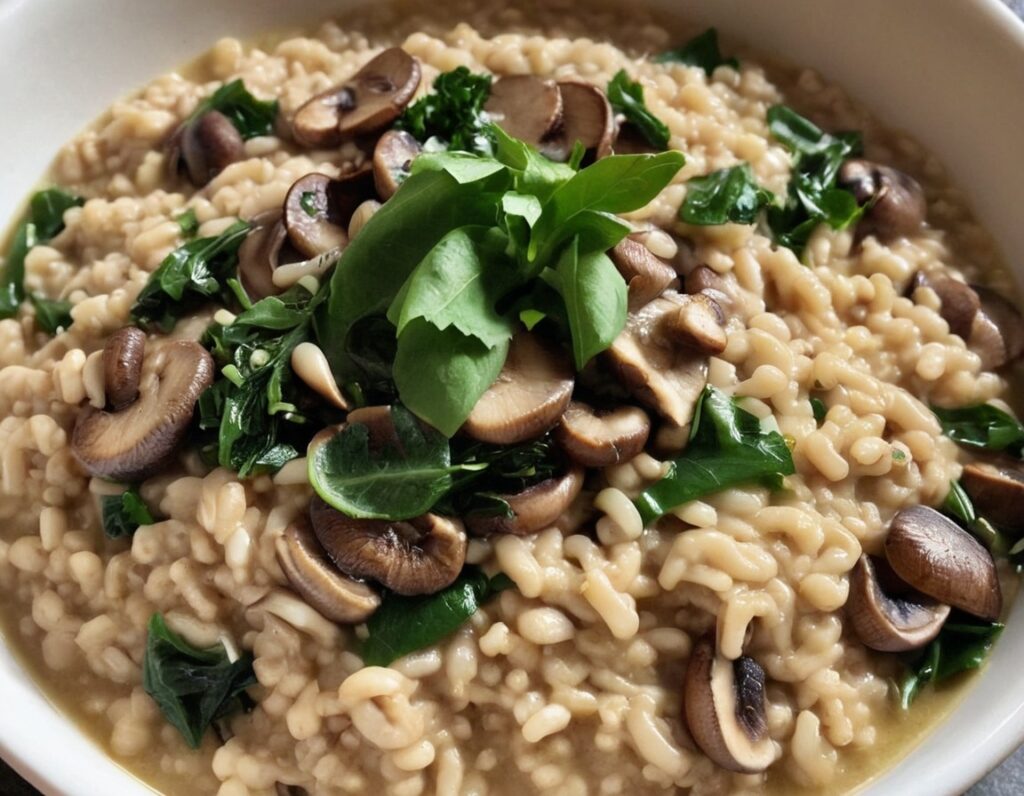
Luxurious Longevity Risotto
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pearl barley is not only tasty and fiber-rich, but also, it contains propionic acid, which lowers cholesterol. The fiber content also lowers cholesterol too, of course, by the usual mechanism. The dish’s health benefits don’t end there, though; check out the science section at the end of the recipe!
You will need
- 2 cups pearl barley
- 3 cups sliced chestnut mushrooms
- 2 onions, finely chopped
- 6 large leaves collard greens, shredded
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 8 spring onions, sliced
- 1½ quarts low-sodium vegetable stock
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp MSG or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- 1 tsp rosemary
- 1 tsp thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
- Optional garnish: fresh basil leaves
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a large sauté pan; add the onions and garlic and cook for 5 minutes; add the mushrooms and cook for another 5 minutes.
2) Add the pearl barley and a cup of the vegetable stock. Cook, stirring, until the liquid is nearly all absorbed, and add more stock every few minutes, as per any other risotto. You may or may not use all the stock you had ready. Pearl barley takes longer to cook than rice, so be patient—it’ll be worth the wait!
Alternative: an alternative is to use a slow cooker, adding a quart of the stock at once and coming back about 4 hours later—thus, it’ll take a lot longer, but will require minimal/no supervision.
3) When the pearl barley has softened, become pearl-like, and the dish is taking on a creamy texture, stir in the rest of the ingredients. Once the greens have softened, the dish is done, and it’s time to serve. Add the garnish if using one:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Magic Of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Study Tips for Exam Season?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’ve Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
Q: Any study tips as we approach exam season? A lot of the productivity stuff is based on working life, but I can’t be the only student!
A: We’ve got you covered:
- Be passionate about your subject! We know of no greater study tip than that.
- Find a willing person and lecture them on your subject. When one teaches, two learn!
- Your mileage may vary depending on your subject, but, find a way of studying that’s fun to you!
- If you can get past papers, get as many as you can, and use those as your “last minute” studying in the week before your exam(s). This will prime you for answering exam-style questions (and leverage state-dependent memory). As a bonus, it’ll also help ease any anxiety, because by the time of your exam it’ll be “same old, same old”!
Share This Post
-
Plant vs Animal Protein
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
Some people will obviously have strong ideological opinions here—for vegetarians and vegans, it’s no question, and for meat-eaters, it’s easy to be reactive to that and double-down on the bacon. But, we’re a health science newsletter, so we’ll be sticking to the science.
Which is better, healthwise?
First, it depends on how you go about it. Consider these options:
- A piece of salmon
- A steak
- A hot dog
- A hot dog, but plant-based
- Textured soy protein (no additives)
- Edamame (young soy) beans
Three animal-based protein sources, three plant-based. We could render the competition simple (but very unfair) by pitting the hotdog against the edamame beans, or the plant-based hot dog against the piece of salmon. So let’s kick this off by saying:
- There are good and bad animal-based protein sources
- There are good and bad plant-based protein sources
Whatever you choose, keep that in mind while you do. Less processed is better in either case. And if you do go for red meat, less is better, period.
Picking the healthiest from each, how do the nutritional profiles look?
They look good in both cases! One factor of importance is that in either case, our bodies will reduce the proteins we consume to their constituent amino acids, and then rebuild them into the specific proteins we actually need. Our bodies will do that regardless of the source, because we are neither a salmon nor a soybean, for example.
We need 20 specific amino acids, for our bodies to make the proteins we will use in our bodies. Of these, 9 are considered “essential”, meaning we cannot synthesize them and must get them from our diet,
Animal protein sources contain all 9 of those (just like we do). Plant based sources often don’t, individually, but by eating soy for example (which does contain them all) and/or getting multiple sources of protein from different plants, the 9 can be covered quite easily with little thought, just by having a varied diet.
Meats are #1!
- They’re number 1 for nutritional density
- They’re number 1 for health risks, too
So while plant-based diet adherents may need to consume more varied things to get all the nutrients necessary, meat-eaters won’t have that problem.
Meat-eaters will instead have a different problem, of more diet-related health risks, e.g.
- Cardiovascular disease
- Metabolic disorders
- Cancers
So again, if eating (especially processed and/or red) meat, moderation is good. The Mediterranean Diet that we so often recommend, by default contains small amounts of lean animal protein.
Which is better for building muscle?
Assuming a broadly healthy balanced diet, and getting sufficient protein from your chosen source, they’re pretty equal:
- Vegan and Omnivorous High Protein Diets Support Comparable Daily Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis Rates and Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy in Young Adults
- A mycoprotein-based high-protein vegan diet supports equivalent daily myofibrillar protein synthesis rates compared with an isonitrogenous omnivorous diet in older adults: a randomised controlled trial
(both studies showed that both dietary approaches yielded results that showed no difference in muscle synthesis between the two)
The bottom line is…
Healthwise, what’s more important than whether you get your protein from animals or plants is that you eat foods that aren’t processed, and are varied.
And if you want to do a suped-up Mediterranean Diet with less red meat, you might want to try:
A Pesco-Mediterranean Diet With Intermittent Fasting: JACC Review Topic of the Week
^This is from a review in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, and in few words, they recommend it very highly
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Great Cholesterol Myth, Revised and Expanded – by Dr. Jonny Bowden and Dr. Stephen Sinatra
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The topic of cholesterol, and saturated fat for that matter, is a complex and often controversial one. How does this book treat it?
With strong opinions, is how—but backed by good science. The authors, a nutritionist and a cardiologist, pull no punches about outdated and/or cherry-picked science, and instead make the case for looking at what, statistically speaking, appear to be the real strongest risk factors.
So, are they advocating for Dave Asprey-style butter-guzzling, or “the carnivore diet”? No, no they are not. Those things remain unhealthy, even if they give some short-term gains (of energy levels, weight loss, etc).
They do advocate, however, for enjoying saturated fats in moderation, and instead of certain polyunsaturated seed oils that do far worse. They also advocate strongly for avoiding sugar, stress, and (for different reasons) statins (in most people’s cases).
They also demystify in clear terms, and often with diagrams and infographics, the various kinds of fats and their components, broken down in far more detail than any other pop-science source this reviewer has seen.
Bottom line: if you want to take a scientific approach to heart health, this book can help you to focus on what will actually make the biggest difference.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Egg Noodles vs Soba Noodles – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing egg noodles to soba noodles, we picked the soba.
Why?
First of all, for any unfamiliar, soba noodles are made with buckwheat. Buckwheat, for any unfamiliar, is not wheat and does not contain gluten; it’s just the name of a flowering plant that gets used as though a grain, even though it’s technically not.
In terms of macros, egg noodles have slightly more protein 2x the fat (of which, some cholesterol) while soba noodles have very slightly more carbs and 3x the fiber (and, being plant-based, no cholesterol). Given that the carbs are almost equal, it’s a case of which do we care about more: slightly more protein, or 3x the fiber? We’re going with 3x the fiber, and so are calling this category a win for soba.
In the category of vitamins, egg noodles have more of vitamins A, B12, C, D, E, K, and choline, while soba noodles have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9. That’s a 6:6 tie. One could argue that egg noodles’ vitamins are the ones more likely to be a deficiency in people, but on the other hand, soba noodles’ vitamins have the greater margins of difference. So, still a tie.
When it comes to minerals, egg noodles have more calcium and selenium, while soba noodles have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. So, this one’s not close; it’s an easy win for soba noodles.
Adding up the sections makes for a clear win for soba noodles, but by all means, enjoy moderate portions of either or both (unless you are vegan or allergic to eggs, in which case, skip the egg noodles and just enjoy the soba!).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Egg Noodles vs Rice Noodles – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Avoid Self-Hatred & Learn To Love Oneself More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Alain de Botton gives a compassionate, but realistic, explanation in this video:
The enemy within
Or rather, the collaborator within. Because there’s usually first an enemy without—those who are critical of us, who consider that we are bad people in some fashion, and may indeed get quite colorful in their expressions of this.
Sometimes, their words will bounce straight off us; sometimes, their words will stick. So what’s the difference, and can we do anything about it?
The difference is: when their words stick, it’s usually because on some level we believe their words may be true. That doesn’t mean they necessarily are true!
They could be (and it would be a special kind of hubris to assume no detractor could ever find a valid criticism of us), but very often the reason we have that belief, or at least that fear/insecurity, is simply because it was taught to us at an early age, often by harsh words/actions of those around us; perhaps our parents, perhaps our schoolteachers, perhaps our classmates, and so forth.
The problem—and solution—is that we learn emotions much the same way that we learn language; only in part by reasoned thought, and rather for the most part, by immersion and repetition.
It can take a lot of conscious self-talk to undo the harm of decades of unconscious self-talk based on what was probably a few years of external criticisms when we were small and very impressionable… But, having missed the opportunity to start fixing this sooner, the next best time to do it is now.
We cannot, of course, simply do what a kind friend might do and expect any better results; if a kind friend tells us something nice that we do not believe is true, then however much they mean it, we’re not going to internalize it. So instead, we must simply chip away at those unhelpful longstanding counterproductive beliefs, and simply build up the habit of viewing ourselves in a kinder light.
For more on all this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Escape From The Clutches Of Shame
- To Err Is Human; To Forgive, Healthy
- How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: