Dr. Greger’s Anti-Aging Eight
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Greger’s Anti-Aging Eight
This is Dr. Michael Greger. We’ve featured him before: Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
This time, we’re working from his latest book, the excellent “How Not To Age”, which we reviewed all so recently. It is very information-dense, but we’re going to be focussing on one part, his “anti-aging eight”, that is to say, eight interventions he rates the most highly to slow aging in general (other parts of the book pertained to slowing eleven specific pathways of aging, or preserving specific bodily functions against aging, for example).
Without further ado, his “anti-aging eight” are…
- Nuts
- Greens
- Berries
- Xenohormesis & microRNA manipulation
- Prebiotics & postbiotics
- Caloric restriction / IF
- Protein restriction
- NAD+
As you may have noticed, some of these are things might appear already on your grocery shopping list; others don’t seem so “household”. Let’s break them down:
Nuts, greens, berries
These are amongst the most nutrient-dense and phytochemical-useful parts of the diet that Dr. Greger advocates for in his already-famous “Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen”.
For brevity, we’ll not go into the science of these here, but will advise you: eat a daily portion of nuts, a daily portion of berries, and a couple of daily portions of greens.
Xenohormesis & microRNA manipulation
You might, actually, have these on your grocery shopping list too!
Hormesis, you may recall from previous editions of 10almonds, is about engaging in a small amount of eustress to trigger the body’s self-strengthening response, for example:
Xenohormesis is about getting similar benefits, second-hand.
For example, plants that have been grown to “organic” standards (i.e. without artificial pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers) have had to adapt to their relatively harsher environment by upping their levels of protective polyphenols and other phytochemicals that, as it turns out, are as beneficial to us as they are to the plants:
Hormetic Effects of Phytochemicals on Health and Longevity
Additionally, the flip side of xenohormesis is that some plant compounds can themselves act as a source of hormetic stress that end up bolstering us. For example:
In essence, it’s not just that it has anti-oxidant effect; it also provides a tiny oxidative-stress immunization against serious sources of oxidative stress—and thus, aging.
MicroRNA manipulation is, alas, too complex to truly summarize an entire chapter in a line or two, but it has to do with genetic information from the food that we eat having a beneficial or deleterious effect to our own health:
Diet-derived microRNAs: unicorn or silver bullet?
A couple of quick takeaways (out of very many) from Dr. Greger’s chapter on this is to spring for the better quality olive oil, and skip the cow’s milk:
- Impact of Phenol-Enriched Virgin Olive Oils on the Postprandial Levels of Circulating microRNAs Related to Cardiovascular Disease
- MicroRNA exosomes of pasteurized milk: potential pathogens of Western diseases
Prebiotics & Postbiotics
We’re short on space, so we’ll link you to a previous article, and tell you that it’s important against aging too:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
An example of how one of Dr. Greger’s most-recommended postbiotics helps against aging, by the way:
- The mitophagy activator urolithin A is safe and induces a molecular signature of improved mitochondrial and cellular health in humans
- Urolithin A improves muscle strength, exercise performance, and biomarkers of mitochondrial health in a randomized trial in middle-aged adults
(Urolithin can be found in many plants, and especially those containing tannins)
See also: How to Make Urolithin Postbiotics from Tannins
Caloric restriction / Intermittent fasting
This is about lowering metabolic load and promoting cellular apoptosis (programmed cell death; sounds bad; is good) and autophagy (self-consumption; again, sounds bad; is good).
For example, he cites the intermittent fasters’ 46% lower risk of dying in the subsequent years of follow-up in this longitudinal study:
For brevity we’ll link to our previous IF article, but we’ll revisit caloric restriction in a main feature on of these days:
Fasting Without Crashing? We sort the science from the hype!
Dr. Greger favours caloric restriction over intermittent fasting, arguing that it is easier to adhere to and harder to get wrong if one has some confounding factor (e.g. diabetes, or a medication that requires food at certain times, etc). If adhered to healthily, the benefits appear to be comparable for each, though.
Protein restriction
In contrast to our recent main feature Protein vs Sarcopenia, in which that week’s featured expert argued for high protein consumption levels, protein restriction can, on the other hand, have anti-aging effects. A reminder that our body is a complex organism, and sometimes what’s good for one thing is bad for another!
Dr. Greger offers protein restriction as a way to get many of the benefits of caloric restriction, without caloric restriction. He further notes that caloric restriction without protein restriction doesn’t decrease IGF-1 levels (a marker of aging).
However, for FGF21 levels (these are good and we want them higher to stay younger), what matters more than lowering proteins in general is lowering levels of the amino acid methionine—found mostly in animal products, not plants—so the source of the protein matters:
For example, legumes deliver only 5–10% of the methionine that meat does, for the same amount of protein, so that’s a factor to bear in mind.
NAD+
This is about nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+ to its friends.
NAD+ levels decline with age, and that decline is a causal factor in aging, and boosting the levels can slow aging:
Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The In Vivo Evidence
Can we get NAD+ from food? We can, but not in useful quantities or with sufficient bioavailability.
Supplements, then? Dr. Greger finds the evidence for their usefulness lacking, in interventional trials.
How to boost NAD+, then? Dr. Greger prescribes…
Exercise! It boosts levels by 127% (i.e., it more than doubles the levels), based on a modest three-week exercise bike regimen:
Skeletal muscle NAMPT is induced by exercise in humans
Another study on resistance training found the same 127% boost:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Marine Collagen Worth Taking?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Questions and Answers at 10almonds
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
This newsletter has been growing a lot lately, and so have the questions/requests, and we love that! In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
I wanted to ask if you think marine collagen is decent to take. I’ve heard a lot of bad press about it
We don’t know what you’ve heard, but generally speaking it’s been found to be very beneficial to bones, joints, and skin! We wrote about it quite recently on a “Research Review Monday”:
Share This Post
-
Pear vs Peach – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pears to peaches, we picked the peaches.
Why?
Both are great! But peaches are exceptional in some ways that pears just can’t match up to:
In terms of macros, pears have more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which results in an approximately equal glycemic index. Thus, we’ll say that pears win this round by virtue of being the nutritionally denser option.
Looking at the vitamins, pears have (slightly) more of vitamins B6, B9, and K, while peaches have (much) more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, C, E, and choline—thus sweeping this category easily for peaches.
In the category of minerals, pears have more calcium and copper, while peaches have more iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. This time, the margins of difference for each mineral are comparably low (i.e. pears are close behind peaches on all those minerals), but still, by strength of numbers, it’s a clear win for peaches.
When it comes to polyphenols, not only do peaches have more, but also, they have anticancer properties that pears don’t—see our link below for more about that!
Meanwhile, adding up the sections makes for an overall win for peaches, but as ever when it comes to fruits, by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← peaches in the #2 spot! They induce cell death in cancer cells while sparing healthy ones
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
What is mitochondrial donation? And how might it help people have a healthy baby one day?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mitochondria are tiny structures in cells that convert the food we eat into the energy our cells need to function.
Mitochondrial disease (or mito for short) is a group of conditions that affect this ability to generate the energy organs require to work properly. There are many different forms of mito and depending on the form, it can disrupt one or more organs and can cause organ failure.
There is no cure for mito. But an IVF procedure called mitochondrial donation now offers hope to families affected by some forms of mito that they can have genetically related children free from mito.
After a law to allow mitochondrial donation in Australia was passed in 2022, scientists are now preparing for a clinical trial to see if mitochondrial donation is safe and works.
Jonathan Borba/Pexels What is mitochondrial disease?
There are two types of mitochondrial disease.
One is caused by faulty genes in the nuclear DNA, the DNA we inherit from both our parents and which makes us who we are.
The other is caused by faulty genes in the mitochondria’s own DNA. Mito caused by faulty mitochondrial DNA is passed down through the mother. But the risk of disease is unpredictable, so a mother who is only mildly affected can have a child who develops serious disease symptoms.
Mitochondrial disease is the most common inherited metabolic condition affecting one in 5,000 people.
Some people have mild symptoms that progress slowly, while others have severe symptoms that progress rapidly. Mito can affect any organ, but organs that need a lot of energy such as brain, muscle and heart are more often affected than other organs.
Mito that manifests in childhood often involves multiple organs, progresses rapidly, and has poor outcomes. Of all babies born each year in Australia, around 60 will develop life-threatening mitochondrial disease.
What is mitochondrial donation?
Mitochondrial donation is an experimental IVF-based technique that offers people who carry faulty mitochondrial DNA the potential to have genetically related children without passing on the faulty DNA.
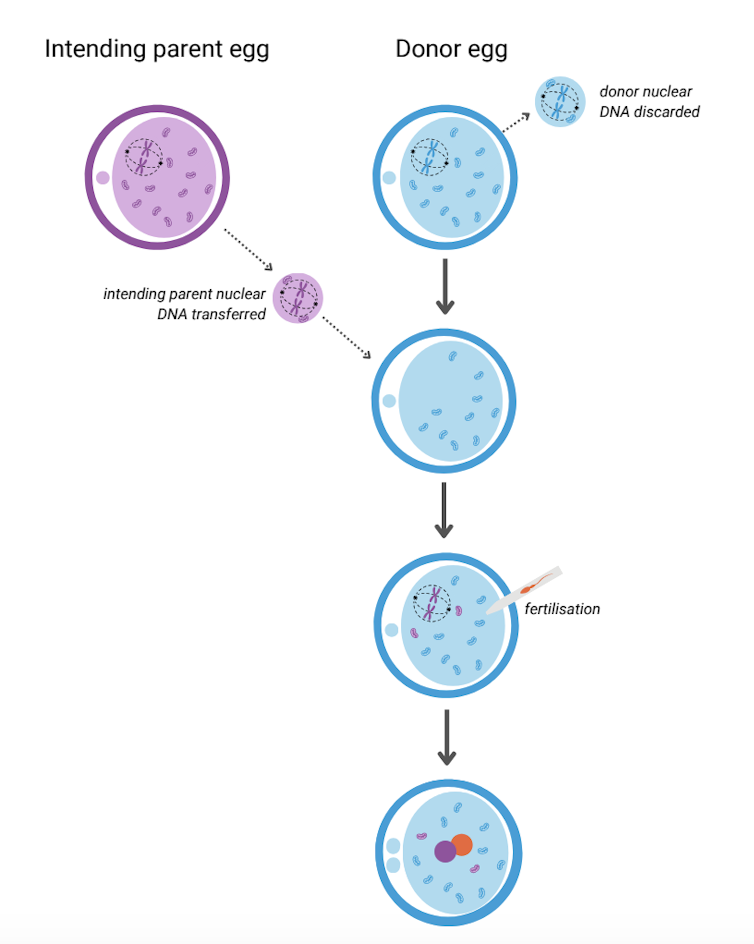
It involves removing the nuclear DNA from the egg of someone who carries faulty mitochondrial DNA and inserting it into a healthy egg donated by someone not affected by mito, which has had its nuclear DNA removed.
The donor egg (in blue) has had its nuclear DNA removed. Author provided The resulting egg has the nuclear DNA of the intending parent and functioning mitochondria from the donor. Sperm is then added and this allows the transmission of both intending parents’ nuclear DNA to the child.
A child born after mitochondrial donation will have genetic material from the three parties involved: nuclear DNA from the intending parents and mitochondrial DNA from the egg donor. As a result the child will likely have a reduced risk of mito, or no risk at all.
The procedure removes the faulty DNA to reduce the chance of it passing on to the baby. Josh Willink/Pexels This highly technical procedure requires specially trained scientists and sophisticated equipment. It also requires both the person with mito and the egg donor to have hormone injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. The eggs are then retrieved in an ultrasound-guided surgical procedure.
Mitochondrial donation has been pioneered in the United Kingdom where a handful of babies have been born as a result. To date there have been no reports about whether they are free of mito.
Maeve’s Law
After three years of public consultation The Mitochondrial Donation Law Reform (Maeve’s Law) Bill 2021 was passed in the Australian Senate in 2022, making mitochondrial donation legal in a research and clinical trial setting.
Maeve’s law stipulates strict conditions including that clinics need a special licence to perform mitochondrial donation.
To make sure mitochondrial donation works and is safe before it’s introduced into Australian clinical practice, the law also specifies that initial licences will be issued for pre-clinical and clinical trial research and training.
We’re expecting one such licence to be issued for the mitoHOPE (Healthy Outcomes Pilot and Evaluation) program, which we are part of, to perfect the technique and conduct a clinical trial to make sure mitochondrial donation is safe and effective.
Before starting the trial, a preclinical research and training program will ensure embryologists are trained in “real-life” clinical conditions and existing mitochondrial donation techniques are refined and improved. To do this, many human eggs are needed.
The need for donor eggs
One of the challenges with mitochondrial donation is sourcing eggs. For the preclinical research and training program, frozen eggs can be used, but for the clinical trial “fresh” eggs will be needed.
One possible source of frozen eggs is from people who have stored eggs they don’t intend to use.
A recent study looked at data on the outcomes of eggs stored at a Melbourne clinic from 2012 to 2021. Over the ten-year period, 1,132 eggs from 128 patients were discarded. No eggs were donated to research because the clinics where the eggs were stored did not conduct research requiring donor eggs.
However, research shows that among people with stored eggs, the number one choice for what to do with eggs they don’t need is to donate them to research.
This offers hope that, given the opportunity, those who have eggs stored that they don’t intend to use might be willing to donate them to mitochondrial donation preclinical research.
As for the “fresh” eggs needed in the future clinical trial, this will require individuals to volunteer to have their ovaries stimulated and eggs retrieved to give those people impacted by mito a chance to have a healthy baby. Egg donors may be people who are friends or relatives of those who enter the trial, or it might be people who don’t know someone affected by mito but would like to help them conceive.
At this stage, the aim is to begin enrolling participants in the clinical trial in the next 12 to 18 months. However this may change depending on when the required licences and ethics approvals are granted.
Karin Hammarberg, Senior Research Fellow, Global and Women’s Health, School of Public Health & Preventive Medicine, Monash University; Catherine Mills, Professor of Bioethics, Monash University; Mary Herbert, Professor, Anatomy & Developmental Biology, Monash University, and Molly Johnston, Research fellow, Monash Bioethics Centre, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Chew On This… But Don’t Swallow − by Dr. Blanche Grube & Anita Vasquez-Tibau
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Blanche Grube is a dentist with over 40 years of experience, and Anita Vasquez-Tibau is a well-respected research scientist with many peer-reviewed publications to her name, and both have lectured extensively.
So, what do they want us to know?
It’s mostly about the iatrogenic (i.e., caused by treatment) harm done by many common conventional dental practices (including dental mercury amalgams, metal crowns, root canals, implants, and even braces), and how we can avoid such, and enjoy better treatment instead.
After an introductory overview of the basics (and also where her own work came from in the first place, namely, her own root canals that were established as largely responsible for her leukemia), the largest part of the book is practical advice, laid out practically. What things come with what risks, what things get advertised differently than they really are, and which way to go in the case of unenviable situations where one must choose the “least bad” option out of a bunch of bad options.
Lastly, she discusses a range of solutions that can help side-step most problems, provided one implements them early. The good news is, they are “do these small things every day” recommendations, not “get this prophylactic surgical treatment” options. And yes, they are beyond the obvious of good dental hygiene, though she does cover that too.
The style is in part narrative, in part explanatory, and/but very readable throughout.
Bottom line: if you love having teeth and/but don’t love going to the dentist, this book will help you take good care of yourself, and also mean you can safely and informedly advocate for yourself if you do find yourself in the dentist’s office.
Click here to check out Chew On This… But Don’t Swallow, and protect your teeth!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Easing Lower Back Pain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lower back pain often originates from an unexpected culprit: your pelvis. Similar to how your psoas can contribute to lower back pain, when your pelvis tilts forward due to tight hip flexors, it can misalign your spine, leading to discomfort and pain. As WeShape shows us in the below video, one simple stretch can help realign your pelvis and significantly ease lower back pain.
Why Your Pelvis Matters
Sitting for long periods causes your hip flexors to shorten, leading to an anterior pelvic tilt. This forward tilt puts pressure on your spine and SI joint, causing pain and discomfort in the lower back. To help resolve this, you can work on correcting your pelvic alignment, helping to significantly reduce this pressure and alleviate related pain. And no, this doesn’t require any spinal cord stimulation.
Easy Variations for All
A lot of you recognise the stretch in this video; it’s quite a well-known kneeling stretch. But, unlike other guides, WeShape also provides a fantastic variation for those who aren’t mobile enough for the kneeling variation
So, if you can’t comfortably get down on the ground, WeShape outlines a brilliant standing variation. So, regardless of your mobility, there’s an option for you!
See both variations here:
Excited to reduce your lower back pain? We hope so! Let us know if you have any tips that you’d like to share with us.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dealing With Hearing Loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hearing is important, not only for convenience, but also for cognitive health—as an inability to participate in what for most people is an important part of social life, has been shown to accelerate cognitive decline:
14 Powerful Strategies To Prevent Dementia ← one of them is looking after your hearing
To this end, we’ve written before about ways to retain (or at least slow the loss of) your hearing, here:
But, what if, despite our best efforts, your hearing is declining regardless, or is already impaired in some way?
Working with the hand we’ve been dealt
So, your hearing is bad and/or deteriorating. Assuming you’ve ruled out possibilities of fixing it, the next step is how to manage this new state of affairs.
One thing to seriously consider, sooner than you think you need to, is using hearing aids. This is because they will not only help you in the obvious practical way, but also, they will slow the associated decline of the parts of your brain that process the language you hear:
ACHIEVE study finds hearing aids cut cognitive decline by 48%
…and here’s the paper itself:
Furthermore, hearing aid use can significantly reduce all-cause mortality:
Your ears are not the only organs
Remember, today’s about dealing with hearing loss, not preventing it (for preventing it, see the second link we dropped up top).
With this in mind: do not underestimate the usefulness of learning to lipread.
Lipreading is not a panacea; it has its limitations:
- You can’t lipread an audio-only phonecall, or a podcast, or the radio
- You can’t lipread a video call if the video quality is poor
- You can’t lipread if someone is wearing a mask (as in many healthcare settings)
- You can’t lipread multiple people at once; you have to choose whose mouth to watch (or at least, you will miss the first word(s) each time while switching)
- You can’t lipread during sex if your/their face is somewhere else (may seem like a silly example, but actually communication can be important in sex, and the number of times this writer has had to say “Say again?” in intimate moments is ridiculous)
However, it can also make a huge difference the rest of the time, and can even be a superpower in times/places when other people’s hearing is nullified, such as a noisy environment, or a video call in which someone’s mic isn’t working.
The good news is, it’s really very easy to learn to lipread. There are many valid ways (often involving consciously memorizing mouth-shapes from charts, and then putting them together one by one to build a vocabulary), but this writer recommends a more organic, less effort-intensive approach:
- Choose a video of someone who speaks clearly, and for which video you already know what is being said (such as by using subtitles first, or a transcript, or perhaps the person is delivering a famous speech or reciting a poem that you know well, or it’s your favorite movie that you’ve watched many times).
- Now watch it with the sound off (assuming you do normally have some hearing; if you don’t, then you’re probably ahead of the game here) and just pay close attention to the lips. Do this on repeat; soon you’ll be able to “hear” the sounds as you see them made.
- Now choose a video of someone who speaks clearly, for which video you do not already know what is being said. You’ll probably only get parts of it at first; that’s ok.
- Now learn the rest of what they said in that video (by reading a transcript or such), and use it like you used the first video.
- Now repeat steps 3 and 4 until you are lipreading most people easily unless there is some clear obfuscation preventing you.
This process should not take long, as there are only about 44 phonemes (distinct sounds) in English, and once you’ve learned them, you’re set. If you speak more languages, those same 44 phonemes should cover most of most of them, but if not, just repeat the above process with the next language.
Remember, if you have at least some hearing, then most of the time your lipreading and your hearing are going to be working together, and neither will be as strong without the other—but if necessary, well-practised lipreading can indeed often stand in for hearing when hearing isn’t available.
A note on sign language:
Sign language is great, and cool, and useful. However, it’s only as useful as the people who know it, which means that it’s top-tier in the Deaf community (where people will dodge hearing-related cognitive decline entirely, because their social interaction is predominantly signed rather than spoken), and can be useful with close friends or family members who learn it (or at least learn some), but isn’t as useful in most of the wider world when people don’t know it. But if you do want to learn it, don’t let that hold you back—be the change you want to see!
Most of our readers are American, so here’s a good starting place for American Sign Language ← this is a list of mostly-free resources
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: