Apple Cider Vinegar vs Balsamic Vinegar – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple cider vinegar to balsamic vinegar, we picked the apple cider vinegar.
Why?
It’s close! And it’s a simple one today and they’re both great. Taking either for blood-sugar-balancing benefits is fine, as it’s the acidity that has this effect. But:
- Of the two, balsamic vinegar is the one more likely to contain more sugars, especially if it’s been treated in any fashion, and not by you, e.g. made into a glaze or even a reduction (the latter has no need to add sugar, but sometimes companies do because it is cheaper—so we recommend making your own balsamic vinegar reduction at home)
- Of the two, apple cider vinegar is the one more likely to contain “the mother”, that is to say, the part with extra probiotic benefits (but if the vinegar has been filtered, it won’t have this—it’s just more common to be able to find unfiltered apple cider vinegar, since it has more popular attention for its health benefits than balsamic vinegar does)
So, two wins for apple cider vinegar there.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Apple Cider Vinegar vs Apple Cider Vinegar Gummies – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Marathons in Mid- and Later-Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
We had several requests pertaining to veganism, meatless mondays, and substitutions in recipes—so we’re going to cover those on a different day!
As for questions we’re answering today…
Q: Is there any data on immediate and long term effects of running marathons in one’s forties?
An interesting and very specific question! We didn’t find an overabundance of studies specifically for the short- and long-term effects of marathon-running in one’s 40s, but we did find a couple of relevant ones:
The first looked at marathon-runners of various ages, and found that…
- there are virtually no relevant running time differences (p<0.01) per age in marathon finishers from 20 to 55 years
- the majority of middle-aged and elderly athletes have training histories of less than seven years of running
From which they concluded:
❝The present findings strengthen the concept that considers aging as a biological process that can be considerably speeded up or slowed down by multiple lifestyle related factors.❞
See the study: Performance, training and lifestyle parameters of marathon runners aged 20–80 years: results of the PACE-study
The other looked specifically at the impact of running on cartilage, controlled for age (45 and under vs 46 and older) and activity level (marathon-runners vs sedentary people).
The study had the people, of various ages and habitual activity levels, run for 30 minutes, and measured their knee cartilage thickness (using MRI) before and after running.
They found that regardless of age or habitual activity level, running compressed the cartilage tissue to a similar extent. From this, it can be concluded that neither age nor marathon-running result in long-term changes to cartilage response to running.
Or in lay terms: there’s no reason that marathon-running at 40 should ruin your knees (unless you are doing something wrong).
That may or may not have been a concern you have, but it’s what the study looked at, so hey, it’s information.
Here’s the study: Functional cartilage MRI T2 mapping: evaluating the effect of age and training on knee cartilage response to running
Q: Information on [e-word] dysfunction for those who have negative reactions to [the most common medications]?
When it comes to that particular issue, one or more of these three factors are often involved:
- Hormones
- Circulation
- Psychology
The most common drugs (that we can’t name here) work on the circulation side of things—specifically, by increasing the localized blood pressure. The exact mechanism of this drug action is interesting, albeit beyond the scope of a quick answer here today. On the other hand, the way that they work can cause adverse blood-pressure-related side effects for some people; perhaps you’re one of them.
To take matters into your own hands, so to speak, you can address each of those three things we just mentioned:
Hormones
Ask your doctor (or a reputable phlebotomy service) for a hormone test. If your free/serum testosterone levels are low (which becomes increasingly common in men over the age of 45), they may prescribe something—such as testosterone shots—specifically for that.
This way, it treats the underlying cause, rather than offering a workaround like those common pills whose names we can’t mention here.
Circulation
Look after your heart health; eat for your heart health, and exercise regularly!
Cold showers/baths also work wonders for vascular tone—which is precisely what you need in this matter. By rapidly changing temperatures (such as by turning off the hot water for the last couple of minutes of your shower, or by plunging into a cold bath), your blood vessels will get practice at constricting and maintaining that constriction as necessary.
Psychology
[E-word] dysfunction can also have a psychological basis. Unfortunately, this can also then be self-reinforcing, if recalling previous difficulties causes you to get distracted/insecure and lose the moment. One of the best things you can do to get out of this catch-22 situation is to not worry about it in the moment. Depending on what you and your partner(s) like to do in bed, there are plenty of other equally respectable options, so just switch track!
Having a conversation about this in advance will probably be helpful, so that everyone’s on the same page of the script in that eventuality, and it becomes “no big deal”. Without that conversation, misunderstandings and insecurities could arise for your partner(s) as well as yourself (“aren’t I desirable enough?” etc).
So, to recap, we recommend:
- Have your hormones checked
- Look after your circulation
- Make the decision to have fun!
Share This Post
-
Science-backed ways to take care of your mental health this winter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The colder, darker months can take a toll on well-being. Two out of five U.S. adults say their mental health worsens in the winter. Plus, about five percent of U.S. adults experience seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a type of depression induced by seasonal changes that typically begins when the weather gets colder and there’s less daylight.
Fortunately, there are science-backed lifestyle changes that can make this time of year more tolerable. Here’s how to take care of your mental health this winter.
Exercise regularly
When you exercise, your body releases endorphins, or “feel-good” chemicals that can improve your mood. A 2024 review of studies found that exercise—particularly walking, jogging, yoga, and strength training—can reduce symptoms of depression.
Before starting a new exercise routine, talk to your health care provider about the types of exercise that may work best for you.
Get outside
While getting outside during the colder months may feel challenging, time outdoors—especially in nature—has been shown to decrease stress, depression, and anxiety. Plus, sunlight helps your body make vitamin D, which may improve your energy and mood.
You can reap the benefits of nature no matter where you live.
“Cities can be very energetic and exciting but also can contribute to both conscious and unconscious stress from the sensory overload and challenges of maneuvering in those spaces,” said Jodie M. Smith, a Mayo Clinic nurse practitioner, in a 2024 Mayo Clinic article. “If you live in an urban environment, exploring to find even a small natural reprieve can be extremely beneficial.”
Prioritize sleep
Inadequate sleep has been linked to depression and anxiety. Taking steps to improve the quality and duration of your sleep can help you become more resilient against stressors.
You can improve your sleep by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day; avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and large meals before bed; keeping your bedroom cool and dark; and limiting exposure to distressing media in the evening.
Practice gratitude
Research suggests that people who practice gratitude are less likely to experience depression. It can also help you make lifestyle changes that improve your well-being overall.
“Practicing gratitude may also make someone a bit more motivated to take care of their health,” said Tyler VanderWeele, co-director of the Initiative on Health, Spirituality, and Religion at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, in a 2024 Harvard Health Publishing article. “Maybe they’re more likely to show up for medical appointments or exercise. It may also help with relationships and social support, which we know contribute to health.”
Add more gratitude to your life by sharing what you’re grateful for with others or keeping a gratitude journal.
Spend quality time with loved ones
“Social isolation and loneliness have a serious impact on physical and mental health, quality of life, and longevity,” according to the World Health Organization, with effects comparable to other risk factors like smoking.
Research shows that people who have close confidants are more satisfied with their lives and less likely to experience depression. Even after holiday gatherings have ended, schedule time with friends and family to stay positive and feel supported.
Limit cell phone use
Social media use and “doomscrolling” inflammatory news headlines are both associated with anxiety and depression across age groups, especially in teens.
“Excessive social media use is associated with behaviors, such as poor sleep, increased social comparisons, impact on learning, and exposure to cyberbullying and negative content, that could contribute to the worsening of depressive symptoms,” Dr. Carol Vidal, an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, said in a Hopkins Medicine article.
Minimize the time you and your family members spend on your phones by pausing notifications, keeping your phone out of reach when you’re preparing for sleep, using a “grayscale” setting to make scrolling less enticing, and finding phone-free hobbies to enjoy.
Light therapy
Light therapy is one treatment for people who have been diagnosed with SAD. It involves sitting in front of a bright light box for 30 to 45 minutes per day to increase light exposure.
This treatment may not be right for people who take certain medications or have eye diseases. Talk to your health care provider about whether light therapy is right for you and what type of light box you should use.
Seek professional support
If your mental health over the winter interferes with your daily functioning, seek help from a therapist, support group, or mental health hotline. Find resources here.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
A New Tool For Bone Regeneration
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to rebuilding bones, one of the tools in the orthopedic surgeon’s toolbox is bone grafts. This involves, to oversimplify it a bit, gluing particles of bone to where bone needs rebuilding. However, this comes with problems, most notably:
- that the bone tissue and the adhesive “glue” need to be prepared separately and mixed in situ, which is fiddly, to say the least
- that the resultant mixture mixed in situ will usually be unevenly mixed, resulting in weak bonding and degradation over time
- having any more of one part or the other in any given site means that bone regeneration and adhesion become a “pick one” matter, when both are critically needed
You may be wondering: why can’t they mix them before putting them in?
And the answer is: because then either the glue will set the bone prematurely (and now we have a clump of bone outside of the body which is not what we wanted), or else the glue will have issues with setting in situ, and now we have bone tissue running down the inside of someone’s leg and setting somewhere else, which is also not what we want.
These kinds of problems may seem a little more “arts and crafts” than “orthopedic surgery”, but they are the kind of nitty-gritty real-life real challenges that actually get in the way of healing patients’ bones.
The new solution
Biomaterial research scientists have developed an injectable hydrogel (containing all the necessary ingredients* that uses light to achieve cross-linking of bone particles and mineralization without any of the above being necessary. In again oversimplified terms: they inject the hydrogel where it’s needed, and then irradiate the site with harmless visible light which instantly sets it in place. As to how the light gets in there: it’s just very shiny, like candling an egg to see inside, or like how you can still approximately see bright light even with your eyes closed.
*alginate (natural polysaccharide derived from brown algae), RGD peptide-containing mussel** adhesive protein, calcium ions, phosphonodiols, and a photoinitiator.
**unclear whether this would trigger a shellfish allergy. Probably kosher per “פיקוח נפש” and Talmud Yoma 85b, but we are a health science newsletter, not Talmudic scholars, so please talk to your Rabbi. Probably halal per Qur’an 5:4 and failing that, the same principle as previously mentioned, expressed in Qur’an 5:3 and 6:119, but once again, your humble writer here is no Mufti, so please talk to your Imam. As for if you are vegetarian or vegan, then that is for you to decide whether to take a “medications with animal ingredients are unfortunate but necessary” stance, as most do. This vegan writer would (she’d grumble about it, though, and at least try to find an acceptable alternative first).
Back to the more general practicalities…
How it works, in less oversimplified terms:
❝The coacervate-based formulation, which is immiscible in water, ensures that the hydrogel retains its shape and position after injection into the body. Upon visible light irradiation, cross-linking occurs, and amorphous calcium phosphate, which functions as a bone graft material, is simultaneously formed. This eliminates the need for separate bone grafts or adhesives, enabling the hydrogel to provide both bone regeneration and adhesion.❞
“That’s great, but I was hoping for something I can do right now, ideally at home”
If getting glued back together was not on your bucket list, that’s understandable. There’s still a lot you can do for bone density; here’s a quick overview:
- Get it checked. Yes, this first, if you haven’t already! You want a basis for comparison later. Book a bone density scan. See for example this case study with bone density scans at each end: 21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!)
- Enjoy a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D yes, but be aware that you can have too much of a good thing, and doing so will result in more harm than good, including (paradoxically) for your bones. See: Vitamin D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
- Enjoy a diet rich is phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium, which things are also necessary for bone health, and in which people are much more likely to be deficient (especially magnesium). If you’re going to supplement, then there are very big difference in the efficacy of different kinds of magnesium supplement (brace yourself; the cheapest and most common kind barely does anything at all). See: Which Magnesium? (And: When?)
- Enjoy a diet rich in high quality protein—collagen is very useful, but if you want a plant-based approach, don’t worry, our body can and will make it for yourself if you give it a hand—and vitamin C to help its absorption, as well as glycine if you’re going the no-animals route. See: Collagen For Bones: We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of and: The Sweet Truth About Glycine: Making Your Collagen Work Better
- Consider medication, if your bone density is already lower than what it should be. There are meds to stop further deterioration, and different meds to encourage your body to rebuild bone. However, there are downsides to each of them: Which Osteoporosis Medication, If Any, Is Right For You?
- While we’re on the topic of medications, consider bioidentical HRT if you are female and not otherwise producing your own estrogen and progesterone in adequate quantities to maintain your skeletal integrity: HRT: A Tale Of Two Approaches
- Look after your gut too! So much starts there: Is Your Gut Leading You Into Osteoporosis? Bacterioides Vulgatus & Bone Health
- Lastly, exercise, but exercise right, because with insufficient resistance exercise your bones will not “think” they need to remain strong, and with the wrong kind of resistance exercise, you could break/compress your bones if they are already weak, so check out: Osteoporosis & Exercises: Which To Do (And Which To Avoid)
Too much information?
If that was too much information all at once, then we recommend this as your one-stop article:
The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
Want more information?
We are but a humble newsletter and can only include so much per day, but we highly recommend this book we reviewed a little while back, which goes into everything in a lot more detail than we can here:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Smart Woman’s Guide to Breast Cancer – by Dr. Jenn Simmons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot more to breast cancer care than “check your breasts regularly”. Because… And then what? “Go see a doctor” obviously, but it’s a scary prospect with a lot of unknowns.
Dr. Simmons demystifies these unknowns, from both her position as an oncologist (and breast surgeon) and also her position as a breast cancer survivor herself.
What she found, upon getting to experience the patient side of things, was that the system is broken in ways she’d never considered before as a doctor.
This book is the product of the things she’s learned both within her field, and elsewhere because of realizing the former’s areas of shortcoming.
She gives a step-by-step guide, from diagnosis onwards, advising taking as much as possible into one’s own hands—especially in the categories of information and action. She also explains the things that make the biggest difference to cancer outcomes when it comes to eating, sleeping, and so forth, the best attitude to have to be neither despairing and giving up, nor overconfident and complacent.
She does also talk complementary therapies, be they supplements or more out-of-the-box approaches and the evidence for them where applicable, as well as doing some high-quality mythbusting about more prescription-based considerations such as HRT.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one have a breast cancer diagnosis, or you just prefer knowing this sort of thing than not, then this book is a top-tier “insider’s guide”.
Click here to check out the Smart Woman’s Guide To Breast Cancer, and take control!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Resistance Beyond Weights
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resistance, Your Way
We’ve talked before about the importance of resistance training:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And we’ve even talked about how to make resistance training more effective:
(High Intensity Interval Training, but make it High Intensity Resistance Training)
Which resistance training exercises are best?
There are two reasonable correct answers here:
- The resistance training exercises that you will actually do (because it’s no good knowing the best exercise ever if you’re not going to do it because it is in some way offputting to you)
- The resistance training exercises that will prevent you from getting a broken bone in the event of some accident or incident
This latter is interesting, because when people think resistance training, the usually immediate go-to exercises are often things like the bench press, or the chest machine in the gym.
But ask yourself: how often do we hear about some friend or relative who in their old age has broken their humerus?
It can happen, for sure, but it’s not as often as breaking a hip, a tarsal (ankle bones), or a carpal (wrist bones).
So, how can we train to make those bones strong?
Strong bones grow under strong muscles
When archaeologists dig up a skeleton from a thousand years ago, one of the occupations that’s easy to recognize is an archer. Why?
An archer has an unusual frequent exercise: pushing with their left arm while pulling with their right arm. This will strengthen different muscles on each side, and thus, increase bone density in different places on each arm. The left first metacarpal and right first and second metacarpals and phalanges are also a giveaway.
This is because: one cannot grow strong muscles on weak bones (or else the muscles would just break the bones), so training muscles will force the body to strengthen the relevant bones.
So: if you want strong bones, train the muscles attached to those bones
This answers the question of “how am I supposed to exercise my hips” etc.
Weights, bodyweight, resistance bands
If you go to the gym, there’s a machine for everything, and a member of gym staff will be able to advise which of their machines will strengthen which muscles.
If you train with free weights at home:
- Wrist curls (forearm supported and stationary, lifting a dumbbell in your hand, palm-upwards) will strengthen the wrist
- The farmer’s walk (carrying a heavy weight in each hand) will also strengthen your wrist
- A modified version of this involves holding the weight with just your fingertips, and then raising and lowering it by curling and uncurling your fingers)
- Lateral leg raises (you will need ankle-weights for this) will strengthen your ankles and your hips, as will hip abductions (as in today’s featured video), especially with a weight attached.
- Ankle raises (going up on your tip-toes and down again, repeat) while holding weights in your hands will strengthen your ankles
If you don’t like weights:
- Press-ups will strengthen your wrists
- Fingertip press-ups are even better: to do these, do your press-ups as normal, except that the only parts of your hands in contact with the ground are your fingertips
- This same exercise can be done the other way around, by doing pull-ups
- And that same “even better” works by doing pull-ups, but holding the bar only with one’s fingertips, and curling one’s fingers to raise oneself up
- Lateral leg raises and hip abductions can be done with a resistance band instead of with weights. The great thing about these is that whereas weights are a fixed weight, resistance bands will always provide the right amount of resistance (because if it’s too easy, you just raise your leg further until it becomes difficult again, since the resistance offered is proportional to how much tension the band is under).
Remember, resistance training is still resistance training even if “all” you’re resisting is gravity!
If it fells like work, then it’s working
As for the rest of preparing to get older?
Check out:
Training Mobility Ready For Later Life
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Walking can prevent low back pain, a new study shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
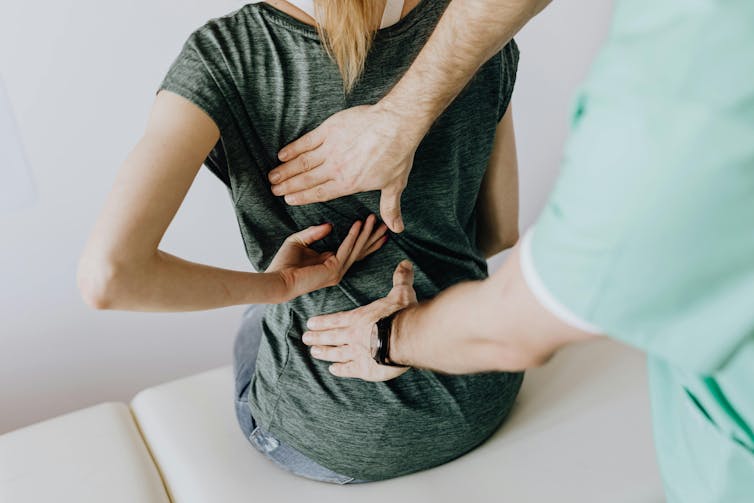
Do you suffer from low back pain that recurs regularly? If you do, you’re not alone. Roughly 70% of people who recover from an episode of low back pain will experience a new episode in the following year.
The recurrent nature of low back pain is a major contributor to the enormous burden low back pain places on individuals and the health-care system.
In our new study, published today in The Lancet, we found that a program combining walking and education can effectively reduce the recurrence of low back pain.
PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock The WalkBack trial
We randomly assigned 701 adults who had recently recovered from an episode of low back pain to receive an individualised walking program and education (intervention), or to a no treatment group (control).
Participants in the intervention group were guided by physiotherapists across six sessions, over a six-month period. In the first, third and fifth sessions, the physiotherapist helped each participant to develop a personalised and progressive walking program that was realistic and tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
The remaining sessions were short check-ins (typically less than 15 minutes) to monitor progress and troubleshoot any potential barriers to engagement with the walking program. Due to the COVID pandemic, most participants received the entire intervention via telehealth, using video consultations and phone calls.
Low back pain can be debilitating. Karolina Kaboompics/Pexels The program was designed to be manageable, with a target of five walks per week of roughly 30 minutes daily by the end of the six-month program. Participants were also encouraged to continue walking independently after the program.
Importantly, the walking program was combined with education provided by the physiotherapists during the six sessions. This education aimed to give people a better understanding of pain, reduce fear associated with exercise and movement, and give people the confidence to self-manage any minor recurrences if they occurred.
People in the control group received no preventative treatment or education. This reflects what typically occurs after people recover from an episode of low back pain and are discharged from care.
What the results showed
We monitored the participants monthly from the time they were enrolled in the study, for up to three years, to collect information about any new recurrences of low back pain they may have experienced. We also asked participants to report on any costs related to their back pain, including time off work and the use of health-care services.
The intervention reduced the risk of a recurrence of low back pain that limited daily activity by 28%, while the recurrence of low back pain leading participants to seek care from a health professional decreased by 43%.
Participants who received the intervention had a longer average period before they had a recurrence, with a median of 208 days pain-free, compared to 112 days in the control group.
In our study, regular walking appeared to help with low back pain. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock Overall, we also found this intervention to be cost-effective. The biggest savings came from less work absenteeism and less health service use (such as physiotherapy and massage) among the intervention group.
This trial, like all studies, had some limitations to consider. Although we tried to recruit a wide sample, we found that most participants were female, aged between 43 and 66, and were generally well educated. This may limit the extent to which we can generalise our findings.
Also, in this trial, we used physiotherapists who were up-skilled in health coaching. So we don’t know whether the intervention would achieve the same impact if it were to be delivered by other clinicians.
Walking has multiple benefits
We’ve all heard the saying that “prevention is better than a cure” – and it’s true. But this approach has been largely neglected when it comes to low back pain. Almost all previous studies have focused on treating episodes of pain, not preventing future back pain.
A limited number of small studies have shown that exercise and education can help prevent low back pain. However, most of these studies focused on exercises that are not accessible to everyone due to factors such as high cost, complexity, and the need for supervision from health-care or fitness professionals.
On the other hand, walking is a free, accessible way to exercise, including for people in rural and remote areas with limited access to health care.
Walking has a variety of advantages. Cast Of Thousands/Shutterstock Walking also delivers many other health benefits, including better heart health, improved mood and sleep quality, and reduced risk of several chronic diseases.
While walking is not everyone’s favourite form of exercise, the intervention was well-received by most people in our study. Participants reported that the additional general health benefits contributed to their ongoing motivation to continue the walking program independently.
Why is walking helpful for low back pain?
We don’t know exactly why walking is effective for preventing back pain, but possible reasons could include the combination of gentle movements, loading and strengthening of the spinal structures and muscles. It also could be related to relaxation and stress relief, and the release of “feel-good” endorphins, which block pain signals between your body and brain – essentially turning down the dial on pain.
It’s possible that other accessible and low-cost forms of exercise, such as swimming, may also be effective in preventing back pain, but surprisingly, no studies have investigated this.
Preventing low back pain is not easy. But these findings give us hope that we are getting closer to a solution, one step at a time.
Tash Pocovi, Postdoctoral research fellow, Department of Health Sciences, Macquarie University; Christine Lin, Professor, Institute for Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney; Mark Hancock, Professor of Physiotherapy, Macquarie University; Petra Graham, Associate Professor, School of Mathematical and Physical Sciences, Macquarie University, and Simon French, Professor of Musculoskeletal Disorders, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: