Tinnitus: Quieting The Unwanted Orchestra In Your Ears
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tinnitus—When a “minor” symptom becomes disruptive
Tinnitus (typically: ringing in the ears) is often thought of less as a condition in and of itself, and more a symptom related to other hearing-related conditions. Paradoxically, it can be associated with hearing loss as well as with hyperacusis (hearing supersensitivity, which sounds like a superpower, but can be quite a problem too).
More than just ringing
Tinnitus can manifest not just as ringing, but also as whistling, hissing, pulsing, buzzing, hooting, and more.
For those who don’t suffer from this, it can seem very trivial; for those who do… Sometimes it can seem trivial too!
But sometimes it’s hard to carry on a conversation when at random moments it suddenly sounds like someone is playing a slide-whistle directly into your earhole, or like maybe a fly got stuck in there.
It’s distracting, to say the least.
What causes it?
First let’s note, tinnitus can be acute or chronic. So, some of these things may just cause tinnitus for a while, whereas some may give you tinnitus for life. In some cases, it depends on how long the thing in question persisted for.
A lot of things can cause it, but common causes include:
- Noise exposure (e.g. concerts, some kinds of industrial work, war)
- High blood pressure
- Head/neck injuries
- Ear infection
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g. Type 1 Diabetes, Lupus, Multiple Sclerosis)
So what can be done about it?
Different remedies will work (or not) for different people, depending on the cause and type of tinnitus.
Be warned also: some things that will work for one person’s tinnitus will make another person’s worse, so you might need to try a degree of experimentation and some of it might not be fun!
That in mind, here are some things you might want to try if you haven’t already:
- Earplugs or noise-canceling headphones—while tinnitus is an internal sound, not external, it often has to do with some part(s) of your ears being unduly sensitive, so giving them less stimulus may ease the tinnitus that occurs in reaction to external noise.
- A great option (that this writer uses personally and considers a life-changer) is silicon earplugs that live in a little case on a keyring when not in use—no more heart-racing fleeing from supermarket checkout boops or pedestrian crossing bips or traffic noises or babies crying or (etc)
- White noise—if you also have hyperacusis, a lower frequency range will probably not hurt the way a higher range might. If you don’t also have hyperacusis, you have more options here and this is a popular remedy. Either way, white noise outperforms “relaxing” soundscapes.
- Hearing aids—counterintuitively, for some people whose tinnitus has developed in response to hearing loss, hearing aids can help bring things “back to normal” and eliminate tinnitus in the process.
- Customized sound machines—if you have the resources to get fancy, science currently finds this to be best of all. They work like white noise, but are tailored to your specific tinnitus.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cupping: How It Works (And How It Doesn’t)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Good Health By The Cup?
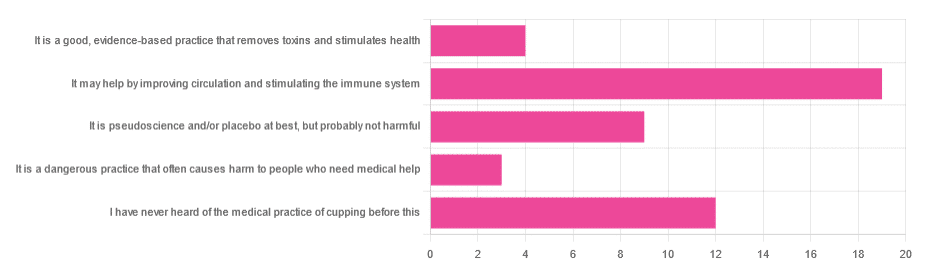
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of cupping (the medical practice), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 40% said “It may help by improving circulation and stimulating the immune system”
- About 26% said “I have never heard of the medical practice of cupping before this”
- About 19% said “It is pseudoscience and/or placebo at best, but probably not harmful
- About 9% said “It is a good, evidence-based practice that removes toxins and stimulates health”
- About 6% said “It is a dangerous practice that often causes harm to people who need medical help”
So what does the science say?
First, a quick note for those unfamiliar with cupping: it is the practice of placing a warmed cup on the skin (open side of the cup against the skin). As the warm air inside cools, it reduces the interior air pressure, which means the cup is now (quite literally) a suction cup. This pulls the skin up into the cup a little. The end result is visually, and physiologically, the same process as what happens if someone places the nozzle of a vacuum cleaner against their skin. For that matter, there are alternative versions that simply use a pump-based suction system, instead of heated cups—but the heated cups are most traditional and seem to be most popular. See also:
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health | Cupping
It is a dangerous practice that often causes harm to people who need medical help: True or False?
False, for any practical purposes.
- Directly, it can (and usually does) cause minor superficial harm, much like many medical treatments, wherein the benefits are considered to outweigh the harm, justifying the treatment. In the case of cupping, the minor harm is usually a little bruising, but there are other risks; see the link we gave just above.
- Indirectly, it could cause harm by emboldening a person to neglect a more impactful treatment for their ailment.
But, there’s nothing for cupping akin to the “the most common cause of death is when someone gets a vertebral artery fatally severed” of chiropractic, for example.
It is a good, evidence-based practice that removes toxins and stimulates health: True or False?
True and False in different parts. This one’s on us; we included four claims in one short line. But let’s look at them individually:
- Is it good? Well, those who like it, like it. It legitimately has some mild health benefits, and its potential for harm is quite small. We’d call this a modest good, but good nonetheless.
- Is it evidence-based? Somewhat, albeit weakly; there are some papers supporting its modest health claims, although the research is mostly only published in journals of alternative medicine, and any we found were in journals that have been described by scientists as pseudoscientific.
- Does it remove toxins? Not directly, at least. There is also a version that involves making a small hole in the skin before applying the cup, the better to draw out the toxins (called “wet cupping”). This might seem a little medieval, but this is because it is from early medieval times (wet cupping’s first recorded use being in the early 7th century). However, the body’s response to being poked, pierced, sucked, etc is to produce antibodies, and they will do their best to remove toxins. So, indirectly, there’s an argument.
- Does it stimulate health? Yes! We’ll come to that shortly. But first…
It is pseudoscience and/or placebo at best, but probably not harmful: True or False?
True in that its traditionally-proposed mechanism of action is a pseudoscience and placebo almost certainly plays a strong part, and also in that it’s generally not harmful.
On it being a pseudoscience: we’ve talked about this before, but it bears repeating; just because something’s proposed mechanism of action is pseudoscience, doesn’t necessarily mean it doesn’t work by some other mechanism of action. If you tell a small child that “eating the rainbow” will improve their health, and they believe this is some sort of magical rainbow power imbuing them with health, then the mechanism of action that they believe in is a pseudoscience, but eating a variety of colorful fruit and vegetables will still be healthy.
In the case of cupping, its proposed mechanism of action has to do withbalancing qi, yin and yang, etc (for which scientific evidence does not exist), in combination with acupuncture lore (for which some limited weak scientific evidence exists). On balancing qi, yin and yang etc, this is a lot like Europe’s historically popular humorism, which was based on the idea of balancing the four humors (blood, yellow bile, black bile, phlegm). Needless to say, humorism was not only a pseudoscience, but also eventually actively disproved with the advent of germ theory and modern medicine. Cupping therapy is not more scientifically based than humorism.
On the placebo side of things, there probably is a little more to it than that; much like with acupuncture, a lot of it may be a combination of placebo and using counter-irritation, a nerve-tricking method to use pain to reduce pain (much like pressing with one’s nail next to an insect bite).
Here’s one of the few studies we found that’s in what looks, at a glance, to be a reputable journal:
Cupping therapy and chronic back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis
It may help by improving circulation and stimulating the immune system: True or False?
True! It will improve local circulation by forcing blood into the area, and stimulate the immune system by giving it a perceived threat to fight.
Again, this can be achieved by many other means; acupuncture (or just “dry needling”, which is similar but without the traditional lore), a cold shower, and/or exercise (and for that matter, sex—which combines exercise, physiological arousal, and usually also foreign bodies to respond to) are all options that can improve circulation and stimulate the immune system.
You can read more about using some of these sorts of tricks for improving health in very well-evidenced, robustly scientific ways here:
The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Why is ADHD so often misdiagnosed as anxiety in women?❞
A great question! A short and slightly flippant answer could be “it’s the medical misogyny”:
Women and Minorities Bear the Brunt of Medical Misdiagnosis
…and if you’d like to learn more in-depth about this, we recommend this excellent book:
Unwell Women: Misdiagnosis and Myth in a Man-Made World – by Dr. Elinor Cleghorn ← you can read our review here
However, in this case there is more going on too!
Part of this is because ADHD is, like many psychiatric issues, a collection of symptoms that may or may not all always be present. Since clinical definitions are decided by clinicians, rather than some special natural law of the universe, sometimes this results in “several small conditions in a trenchcoat”, and if one symptom is or isn’t present, it can make things look quite different:
What’s The Difference Between ADD and ADHD?
There are two things at hand here: as in the above example, there’s the presence or absence of hyperactivity, but also, that “attention deficit”?
It’s often not really a deficit of attention, so much as the attention is going somewhere else—an example of naming psychiatric disorders for how they affect other people, rather than the person in question.
Sidenote: personality disorders really get the worst of this!
“You have a deep insecurity about never being good enough, and you constantly mess up in your attempt to overcompensate? You may have Evil Bastard Disorder!”
“You have a crippling fear of abandonment and that you are fundamentally unloveable, so you do all you can to try to keep people close? You must have Manipulative Bitch Disorder!”
etc
See also: Why Everyone You Don’t Like Is A Narcissist
In the case of ADHD and anxiety and women, a lot of this comes down to how the redirection of focus is perceived:
❝For some time, it has been held that women with ADHD are more likely to internalize symptoms and become anxious and depressed and to suffer emotional dysregulation❞
This internalization of symptoms, vs the externalization more generally perceived in boys and men, is more likely to be seen as anxiety.
Double standards also abound for social reasons, e.g:
- He is someone who thinks ten steps ahead and covers all bases
- She is anxious and indecisive and unable to settle on one outcome
Here’s a very good overview of how this double-standard makes its way into diagnostic processes, along with other built-in biases:
Miss. Diagnosis: A Systematic Review of ADHD in Adult Women
Want to learn more?
We’ve reviewed quite a few books about ADHD, but if we had to pick one to spotlight, we’d recommend this one:
The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults – by L. William Ross-Child, MLC
Enjoy! And while we have your attention… Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Share This Post
-
Getting Your Messy Life In Order
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Getting Your Messy Life In Order
We’ve touched on this before by recommending the book, but today we’re going to give an overview of the absolute most core essentials of the “Getting Things Done” method. If you’re unfamiliar, this will be enough to get you going. If you’re already familiar, this may be a handy reminder!
First, you’ll need:
- A big table
- A block of small memo paper squares—post-it note sized, but no need to be sticky.
- A block of A4 printer paper
- A big trash bag
Gathering everything
Gather up not just all your to-dos, but: all sources of to-dos, too, and anything else that otherwise needs “sorting”.
Put them all in one physical place—a dining room table may have enough room. You’ll need a lot of room because you’re going to empty our drawers of papers, unopened (or opened and set aside) mail. Little notes you made for yourself, things stuck on the fridge or memo boards. Think across all areas of your life, and anything you’re “supposed” to do, write it down on a piece of paper. No matter what area of your life, no matter how big or small.
Whether it’s “learn Chinese” or “take the trash out”, write it down, one item per piece of paper (hence the block of little memo squares).
Sorting everything
Everything you’ve gathered needs one of three things to happen:
- You need to take some action (put it in a “to do” pile)
- You may need it later sometime (put it in a “to file” pile)
- You don’t need it (put it in the big trash bag for disposal)
What happens next will soothe you
- Dispose of the things you put for disposal
- File the things for filing in a single alphabetical filing system. If you don’t have one, you’ll need to get one, so write that down and add it to the “to do” pile.
- You will now process your “to dos”
Processing the “to dos”
The pile you have left is now your “inbox”. It’s probably huge; later it’ll be smaller, maybe just a letter-tray on your desk.
Many of your “to dos” are actually not single action items, they’re projects. If something requires more than one step, it’s a project.
Take each item one-by-one. Do this in any order; you’re going to do this as quickly as possible! Now, ask yourself: is this a single-action item that I could do next, without having to do something else first?
- If yes: put it in a pile marked “next action”
- If no: put it in a pile marked “projects”.
Take a sheet of A4 paper and fold it in half. Write “Next Action” on it, and put your pile of next actions inside it.
Take a sheet of A4 paper per project and write the name of the project on it, for example “Learn Chinese”, or “Do taxes”. Put any actions relating to that project inside it.
Likely you don’t know yet what the first action will be, or else it’d be in your “Next Action” pile, so add an item to each project that says “Brainstorm project”.
Processing the “Next Action” pile
Again you want to do this as quickly as possible, in any order.
For each item, ask yourself “Do I care about this?” If the answer is no, ditch that item, and throw it out. That’s ok. Things change and maybe we no longer want or need to do something. No point in hanging onto it.
For each remaining item, ask yourself “can this be done in under 2 minutes?”.
- If yes, do it, now. Throw away the piece of paper for it when you’re done.
- If no, ask yourself:”could I usefully delegate this to someone else?” If the answer is yes, do so.
If you can’t delegate it, ask yourself: “When will be a good time to do this?” and schedule time for it. A specific, written-down, clock time on a specific calendar date. Input that into whatever you use for scheduling things. If you don’t already use something, just use the calendar app on whatever device you use most.
The mnemonic for the above process is “Do/Defer/Delegate/Ditch”
Processing projects:
If you don’t know where to start with a project, then figuring out where to start is your “Next Action” for that project. Brainstorm it, write down everything you’ll need to do, and anything that needs doing first.
The end result of this is:
- You will always, at any given time, have a complete (and accessible) view of everything you are “supposed” to do.
- You will always, at any given time, know what action you need to take next for a given project.
- You will always, when you designate “work time”, be able to get straight into a very efficient process of getting through your to-dos.
Keeping on top of things
- Whenever stuff “to do something with/about” comes to you, put it in your physical “inbox” place—as mentioned, a letter-tray on a desk should suffice.
- At the start of each working day, quickly process things as described above. This should be a small daily task.
- Once a week, do a weekly review to make sure you didn’t lose sight of something.
- Monthly, quarterly, and annual reviews can be a good practice too.
How to do those reviews? Topic for another day, perhaps.
Or:
Check out the website / Check out GTD apps / Check out the book
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Progesterone Menopausal HRT: When, Why, And How To Benefit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Progesterone doesn’t get talked about as much as other sex hormones, so what’s its deal? Dr. Heather Hirsch explains:
Menopausal progesterone
Dr. Hirsch considers progesterone essential for menopausal women who are taking estrogen and have an intact uterus, to keep conditions at bay such as endometriosis or even uterine cancer.
However, she advises it is not critical in those without a uterus, unless there was a previous case of one of the above conditions.
10almonds addition: on the other hand, progesterone can still be beneficial from a metabolic and body composition standpoint, so do speak with your endocrinologist about it.
As an extra bonus: while not soporific (it won’t make you sleepy), taking progesterone at night will improve the quality of your sleep once you do sleep, so that’s a worthwhile thing for many!
Dr. Hirsch also discusses the merits of continuous vs cyclic use; continuous maintains the above sleep benefits, for example, while cyclic use can help stabilize menstrual patterns in late perimenopause and early menopause.
For more on these things, plus discussion of different types of progesterone, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
- What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
- HRT: Bioidentical vs Animal – A Tale Of Two Approaches
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Food For Life Cookbook – by Dr. Tim Spector
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Spector’s “Food For Life”, and while that was more of an “explanatory science” book, this one takes that science (reiterating it more briefly this time, by way of introduction) and makes a cookbook of it.
The nutritional emphasis in these recipes is on two things: maximizing fiber, and maximizing plant diversity. The recipes are not all vegan or even vegetarian, but they are plant-centric, and if the reader is vegetarian/vegan, then substitutions are easy to make.
The recipes themselves are simple without being boring, and are easy to follow, with full-page photos to accompany them. The science parts are very clear, accessible, and pop-science in style.
Bottom line: if you’d like to incorporate more fiber and more plants into your diet without it being a burden, this book is great for that.
Click here to check out the Food For Life Cookbook, and get cooking for life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Five Invitations – by Frank Ostaseski
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book covers exactly what its subtitle promises, and encourages the reader to truly live life fully, something that Ostaseski believes cannot be done in ignorance of death.
Instead, he argues from his experience of decades working at a hospice, we must be mindful of death not only to appreciate life, but also to make the right decisions in life—which means responding well to what he calls, as per the title of this book, “the five invitations”.
We will not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Don’t wait; do the important things now
- Welcome everything; push away nothing
- Bring your whole self to the experience
- Find a place in the middle of things
- Cultivate a “don’t know” mind
Note, for example, that “do the important things now” requires knowing what is important. For example, ensuring a loved one knows how you feel about them, might be more important than scratching some item off a bucket list. And “push away nothing” does mean bad things too; rather, of course try to make life better rather than worse, but accept the lessons and learnings of the bad too, and see the beauty that can be found in contrast to it. Enjoying the fullness of life without getting lost in it; carrying consciousness through the highs and lows. And yes, approaching the unknown (which means not only death, but also the large majority of life) with open-minded curiosity and wonder.
The style of the book is narrative and personal, without feeling like a collection of anecdotes, but rather, taking the reader on a journey, prompting reflection and introspection along the way.
Bottom line: if you’d like to minimize the regrets you have in life, this book is a fine choice.
Click here to check out The Five Invitations, and answer with a “yes” to the call of life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: