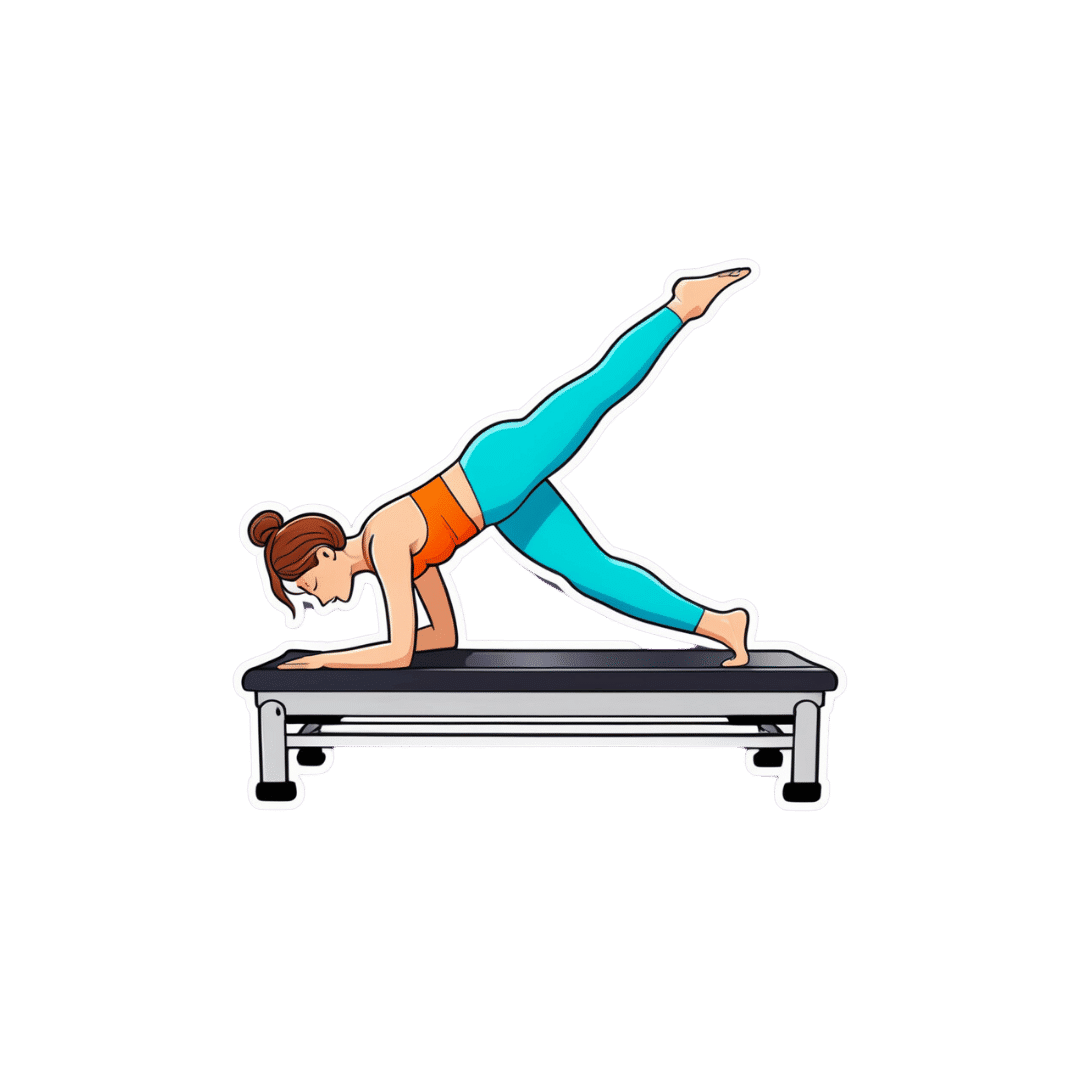
What is reformer pilates? And is it worth the cost?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Reformer pilates is steadily growing in popularity, with new studios opening regularly in major cities all over the world.
But what exactly is reformer pilates? And how does it compare with regular pilates and other types of exercise?
Classes aren’t cheap so let’s look at the potential benefits and drawbacks to help you decide if it’s right for you.
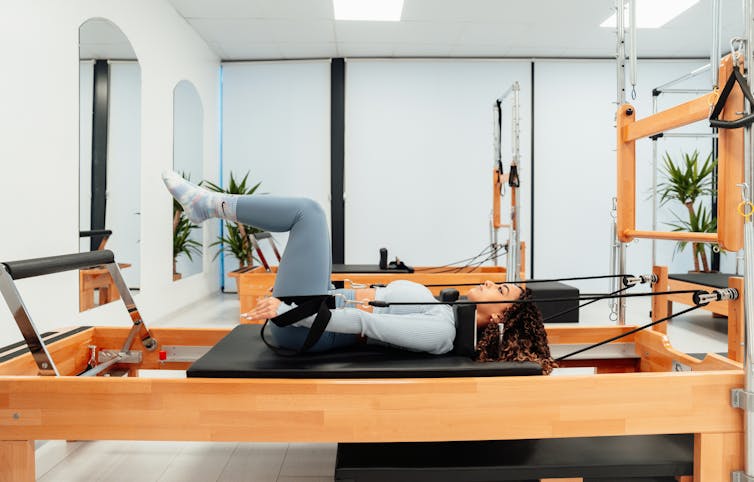

Pilates with special equipment
Pilates is a mode of exercise that focuses on core stability and flexibility, while also addressing muscular strength and endurance, balance and general fitness. At first glance, it might look a bit like yoga, with some more traditional weight training components thrown in.
Reformer pilates uses a piece of equipment called a “reformer”. This looks like a narrow bed that slides along a carriage, has straps to hold onto, and has adjustable springs that add resistance to movement. You perform pilates on the reformer to target specific muscle groups and movement patterns.
The reformer was first designed to help people recover from injuries. However, it has now become common for general fitness and even sports performance.
Unlike normal pilates, also known as “mat pilates”, which only uses your body weight, the reformer adds resistance, meaning you can change the difficulty according to your current level of fitness.
This not only provides a way to overload your muscles, but can make the exercise session more aerobically demanding, which has been proposed to improve cardiovascular fitness.
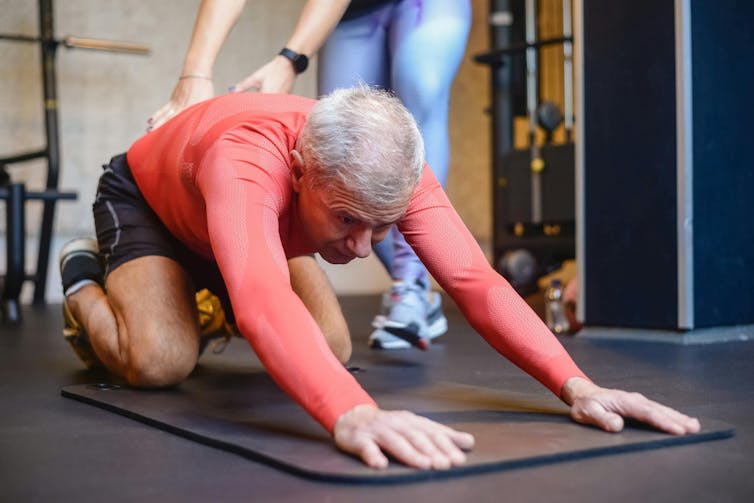

What are the benefits of reformer pilates?
Despite being around for decades, there is surprisingly little research looking at the benefits of reformer pilates. However, what we have seen so far suggests it has a similar effect to other modes of exercise.
Reformer pilates has been shown to help with weight loss, cause some small increases in muscle mass, and enhance cognitive function. All of these benefits are commonly seen when combining weight training and cardio into the same routine.
Similarly, among older adults, it has been shown to improve strength, enhance flexibility and may even reduce the risk of falling.
From a rehabilitation perspective, there is some evidence indicating reformer pilates can improve shoulder health and function, reduce lower back pain and increase flexibility.
Finally, there is some evidence suggesting a single session of reformer pilates can improve two key markers of cardiovascular health, being flow-mediated dilation and pulse wave velocity, while also improving cholesterol and insulin levels. This suggests reformer pilates could lead to long-term improvements in heart and metabolic health, although more research is needed to confirm this.
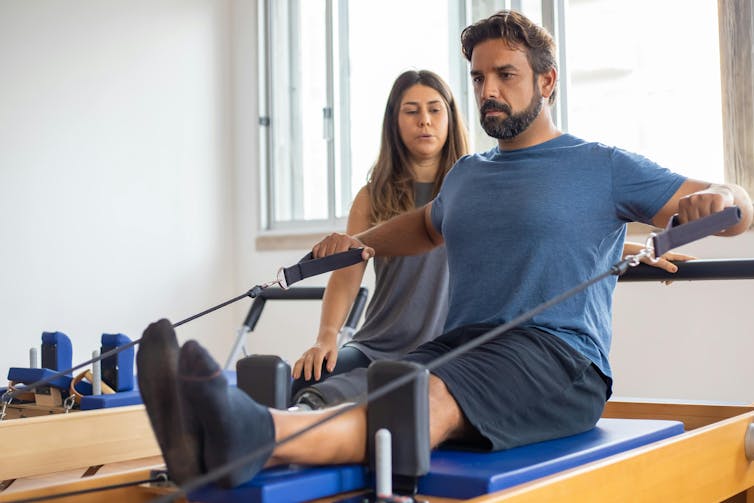

However, there are some key things to consider when discussing these benefits. Most of this research is quite exploratory and comes from a very small number of studies. So we do not know whether these findings will apply to everyone.
Very few studies compared reformer pilates to other types of exercise. Therefore, while it can improve most aspects of health and function, it’s unlikely reformer pilates provides the optimal mode of exercise for each individual component of physical fitness.
Traditional weight training, for example, will likely cause larger improvements in strength than reformer pilates. Similarly, stretching will probably make you more flexible. And running or cycling will make you fitter.
However, if you want a type of exercise that gives you broad overall health benefits, it could be a good option.
What are the downsides of reformer pilates
Reformer pilates is not for everyone.
First and foremost, classes can be expensive compared to other fitness options. You need to be doing at least two to three sessions per week of any type of exercise to maximise the benefits. So even if you can find a class for A$20 or $30, paying for two or three classes a week (or buying a weekly or monthly subscription) is a significant outlay.
Second, it’s not as accessible as other exercise. Even if you can afford it, not every town or suburb has a reformer pilates studio.

Third, the effectiveness of your workout is likely to be impacted by how competent your instructor is. There are a host of different pilates qualifications you can get in Australia, and some take much less time than others. With this in mind, it might be best to look for accredited pilates instructors, although this will further reduce the number of options you have available.
Finally, there is a learning curve. While you will get better over time, the exercise will likely be less effective during those first few weeks (or months) when you are getting used to the machine and the movements.
Is it right for you?
Reformer pilates can be a great addition to your fitness routine, especially if you’re looking for a low-impact way to build strength and flexibility.
But if you have more specific goals, you might need a more specific mode of exercise. For example, if you need to get stronger to improve your ability to manage your daily life, then strength training is probably your best bet. Likewise, if your goal is to run a marathon, you will get more specific benefits from running.
The cost and availability of reformer pilates make it less accessible for some people. With this in mind, if you are after similar benefits at a lower price point, mat pilates might be a better option. Not only does it have evidence suggesting it can improve strength and fitness, but it is something you can do at home if you find a good resource (YouTube could be a good starting point here).
Hunter Bennett, Lecturer in Exercise Science, University of South Australia; Jacinta Brinsley, Exercise Physiologist and Postdoctoral Researcher in the Alliance for Research in Nutrition, Exercise and Activity, University of South Australia, and Lewis Ingram, Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Natural Remedies and Foods for Osteoarthritis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Natural solutions for osteoarthritis. Eg. Rosehip tea, dandelion root tea. Any others??? What foods should I absolutely leave alone?❞
We’ll do a main feature on arthritis (in both its main forms) someday soon, but meanwhile, we recommend eating for good bone/joint health and against inflammation. To that end, you might like these main features we did on those topics:
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of (collagen for bone and joint health)
- The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis (eating for bone health generally)
- Keep Inflammation At Bay (dietary tips for minimizing inflammation—also, our all-time most popular article to date!)
Of these, probably the last one is the most critical, and also will have the speediest effects if implemented.
Share This Post
-
Super-Nutritious Shchi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today we have a recipe we’ve mentioned before, but now we have standalone recipe pages for recipes, so here we go. The dish of the day is shchi—which is Russian cabbage soup, which sounds terrible, and looks as bad as it sounds. But it tastes delicious, is an incredible comfort food, and is famous (in Russia, at least) for being something one can eat for many days in a row without getting sick of it.
It’s also got an amazing nutritional profile, with vitamins A, B, C, D, as well as lots of calcium, magnesium, and iron (amongst other minerals), and a healthy blend of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, plus an array of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals, and of course, water.
You will need
- 1 large white cabbage, shredded
- 1 cup red lentils
- ½ lb tomatoes, cut into eighths (as in: halve them, halve the halves, and halve the quarters)
- ½ lb mushrooms sliced (or halved, if they are baby button mushrooms)
- 1 large onion, chopped finely
- 1 tbsp rosemary, chopped finely
- 1 tbsp thyme, chopped finely
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp cumin, ground
- 1 tsp yeast extract
- 1 tsp MSG, or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- A little parsley for garnishing
- A little fat for cooking; this one’s a tricky and personal decision. Butter is traditional, but would make this recipe impossible to cook without going over the recommended limit for saturated fat. Avocado oil is healthy, relatively neutral in taste, and has a high smoke point for caramelizing the onions. Extra virgin olive oil is also a healthy choice, but not as neutral in flavor and does have a lower smoke point. Coconut oil has far too strong a taste and a low smoke point. Seed oils are very heart-unhealthy. All in all, avocado oil is a respectable choice from all angles except tradition.
Note: with regard to the seasonings, the above is a basic starting guide; feel free to add more per your preference—however, we do not recommend adding more cumin (it’ll overpower it) or more salt (there’s enough sodium in here already).
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the lentils until soft (a rice cooker is great for this, but a saucepan is fine); be generous with the water; we are making a soup, after all. Set them aside without draining.
2) Sauté the cabbage, and put it in a big stock pot or similar large pan (not yet on the heat)
3) Fry the mushrooms, and add them to the big pot (still not yet on the heat)
4) Use a stick blender to blend the lentils in the water you cooked them in, and then add to the big pot too.
5) Turn the heat on low, and if necessary, add more water to make it into a rich soup
6) Add the seasonings (rosemary, thyme, cumin, black pepper, yeast extract, MSG-or-salt) and stir well. Keep the temperature on low; you can just let it simmer now because the next step is going to take a while:
7) Caramelize the onion (keep an eye on the big pot, stirring occasionally) and set it aside
8) Fry the tomatoes quickly (we want them cooked, but just barely) and add them to the big pot
9) Serve! The caramelized onion is a garnish, so put a little on top of each bowl of shchi. Add a little parsley too.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- The Magic Of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Easily Digestible Vegetarian Protein Sources
- The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Problem With Active Listening
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The problem with active listening
Listening is an important skill to keep well-trained at any age. It’s important in romantic relationships, parent-child relationships, friendships, and more.
First, for any unfamiliar or hazy-of-memory: active listening is the practice of listening, actively. The “active” side of this comes in several parts:
- Asking helpful questions
- Giving feedback to indicate that the answer has been understood
- Prompting further information-giving
This can look like:
- A: How did you feel when that happened?
- B: My heart was racing and I felt panicked, it really shocked me
- A: It really shocked you?
- B: Yes, because it was so unexpected; I’d never imagined something like this happening
- A: You’d never expect something like that
- B: No, I mean, I had no reason to
And… As a superficial listening technique, it’s not terrible, and it has its place
But unfortunately, if it’s one’s only listening technique, one will very quickly start sounding like a Furby—that children’s toy from the 90s that allegedly randomly parroted fragments of things that had been said to it. In fact this was a trick of programming, but that’s beyond the scope of this article.
The point is: the above technique, if used indiscriminately and/or too often, starts to feel like talking to a very basic simulacrum.
Which is the opposite of feeling like being listened to!
A better way to listen
Start off similarly, but better.
Ask open questions, or otherwise invite sharing of information.
People can be resistant to stock phrases like “How did that make you feel?”, but this can be got around by simply changing it up, e.g.:
- “What was your reaction?” ← oblique but often elicits the same information
- “I’m not sure how I’d feel about that, in your shoes” ← not even a question, but shows active attention much better than the “mmhmm” noises of traditional active listening, and again prompts the same information
Express understanding… But better
People have been told “I understand” a lot, and often it’s code for “Stop talking”. So, avoid “I understand”. Instead, try:
- “I can understand that”
- “Understandable”
- “That makes sense”
Ask clarifying questions… Better
Sometimes, a clarifying question doesn’t have to have its own point, beyond prompting more sharing, and sometimes, an “open question” can be truly wide open, meaning that vaguer is better, such as:
- “Oh?”
- “How so?” ← this is the heavy artillery that can open up a lot
Know when to STFU
Something that good therapists (and also military interrogators) know: when to STFU
If someone is talking, don’t interrupt them. If you do, they might not start again, or might skip what they were going to say.
Interruption says “I think you’ve said all that needs to be said there”, or else, if the interruption was to ask one of the above questions, it says “you’re not doing a good enough job of talking”, and neither of those sentiments encourage people to share, nor do they make someone feel listened-to!
Instead, just listen. Passive listening has its place too! When there’s a break, then you can go to one of the above questions/prompts/expressions of understanding, as appropriate.
Judge not, lest they feel judged
Reserve judgement until the conversation is over, at the earliest. If asked for your judgement of some aspect, be as reassuring as you can. People feel listened-to when they don’t feel judged.
If they feel judged, conversely, they can often feel you didn’t listen properly, or else you’d be in agreement with them. So instead, just sit on it for as long as you can.
Note: that goes for positive judgements too! Sit on it. Expressing a positive judgement too soon can seem that you were simply eager to please, and can suggest insincerity.
If this seems simple, that’s because it is. But, try it, and see the difference.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Reduce Your Stroke Risk
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❝Each year in the U.S., over half a million people have a first stroke; however, up to 80% of strokes may be preventable.❞
~ American Stroke Association
Source: New guideline: Preventing a first stroke may be possible with screening, lifestyle changes
So, what should we do?
Some of the risk factors are unavoidable or not usefully avoidable, like genetic predispositions and old age, respectively (i.e. it is possible to avoid old age—by dying young, which is not a good approach).
Some of the risk factors are avoidable. Let’s look at the most obvious first:
You cannot drink to your good health
While overall, the World Health Organization has declared that “the only safe amount of alcohol is zero”, when it comes to stroke risk specifically, it seems that low consumption is not associated with stroke, while moderate to high consumption is associated with a commensurately increased risk of stroke:
Alcohol Intake as a Risk Factor for Acute Stroke
Note: there are some studies out there that say that a low to moderate consumption may decrease the risk compared to zero consumption. However, any such study that this writer has seen has had the methodological flaw of not addressing why those who do not drink alcohol, do not drink it. In many cases, someone who drinks no alcohol at all does so because either a) it would cause problems with some medication(s) they are taking, or b) they used to drink heavily, and quit. In either case, their reasons for not drinking alcohol may themselves be reasons for an increased stroke risk—not the lack of alcohol itself.
Smoke now = stroke later
This one is straightforward; smoking is bad for pretty much everything, and that includes stroke risk, as it’s bad for your heart and brain both, increasing stroke risk by 200–400%:
Smoking and stroke: the more you smoke the more you stroke
So, the advice here of course is: don’t smoke
Diet matters
The American Stroke Association’s guidelines recommend, just for a change, the Mediterranean Diet. This does not mean just whatever is eaten in the Mediterranean region though, and there are specifically foods that are included and excluded, and the ratios matter, so here’s a run-down of what the Mediterranean Diet does and doesn’t include:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← what isn’t it good for?!
You can outrun stroke
Or out-walk it; that’s fine too. Most important here is frequency of exercise, more than intensity. So basically, getting those 150 minutes moderate exercise per week as a minimum.
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less & Move More
Which is good, because it means we can get a lot of exercise in that doesn’t feel like “having to do” exercise, for example:
Do You Love To Go To The Gym? No? Enjoy These “No-Exercise Exercises”!
Your brain needs downtime too
Your brain (and your heart) both need you to get good regular sleep:
Sleep Disorders in Stroke: An Update on Management
We sometimes say that “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain” (because the heart feeds the brain, and also ultimately clears away detritus), and that’s true here too, so we might also want to prioritize sleep regularity over other factors, even over duration:
How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration ← this is about adverse cardiovascular events, including ischemic stroke
Keep on top of your blood pressure
High blood pressure is a very modifiable risk factor for stroke. Taking care of the above things will generally take care of this, especially the DASH variation of the Mediterranean diet:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
However, it’s still important to actually check your blood pressure regularly, because sometimes an unexpected extra factor can pop up for no obvious reason. As a bonus, you can do this improved version of the usual blood pressure test, still using just a blood pressure cuff:
Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
Consider GLP-1 receptor agonists (or…)
GLP-1 receptor agonists (like Ozempic et al.) seem to have cardioprotective and neuroprotective (thus: anti-stroke) activity independent of their weight loss benefits:
Of course, GLP-1 RAs aren’t everyone’s cup of tea, and they do have their downsides (including availability, cost, and the fact benefits reverse themselves if you stop taking them), so if you want a similar effect from a natural approach, there are some foods that work on the body’s incretin responses in the same way as GLP-1 RAs do:
5 Foods That Naturally Mimic The “Ozempic Effect”
Better to know sooner rather than too late
Rather than waiting until one half of our face is drooping to know that there was a stroke risk, here are things to watch out for to know about it before it’s too late:
6 Signs Of Stroke (One Month In Advance)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sticky Jackfruit Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All the taste and experience of pulled pork, without the increased risk of cancer and metabolic disease. On the contrary, jackfruit introduces lots of fiber, vitamins, carotenoids, and flavanones. We’ll have to do a main feature about jackfruit sometime; it’s an unusual fruit especially for its protein content, but for now, let’s get cooking!
You will need
- 1 can (14oz/400g) green jackfruit, drained (the flesh will not, in fact, be green—this is referring to the fruit being unripe and thus still firm in texture, which is what we want. The outside of the fruit, which will not be in the can, will have been green)
- 1/4 red cabbage, thinly sliced
- 1/2 carrot, grated
- 6 mangetout, thinly sliced
- 2 tbsp mayonnaise (your preference what kind, and yes, vegan is fine too)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp gochujang paste (if you can’t find gochujang paste locally, you can either order it online (here it is on Amazon) or substitute with harissa paste, which is not the same—it uses different spices—but will do the same job here re texture, umami taste, and level of spiciness)
- 1 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tbsp balsamic vinegar
- 1 tsp apple cider vinegar
- 1 tsp garlic paste
- 1 tsp tomato paste
- 1 tsp ginger paste
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 3½ fl oz water
- 2 burger buns (unless you make them yourself, burger buns will probably not be healthy; you can, however, also look for small round wholemeal breads—the name of which varies far too much by region for us to try to get a catch-all name here—and use them in place of burger buns)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the garlic paste, ginger paste, tomato paste, gochujang paste, soy sauce, balsamic vinegar, and chili flakes in a saucepan
2) Boil the 3½ fl oz water we mentioned; add it to the saucepan, mixing well, turn on the heat and let it simmer for 5 minutes or until it is thick and sticky (it will thicken more as it cools, too, so don’t worry if it doesn’t seem thick enough yet). Set it aside.
3) Dry the jackfruit (using strong kitchen paper should be fine), add the olive oil to a skillet and bring it to a high heat; add the jackfruit and fry on both sides for a few minutes, until it looks cooked (remember, while this may look like animal meat, it’s not, so there’s no danger of undercooking here).
4) When the jackfruit looks a nice golden-brown, add two thirds of the sauce from the saucepan, and break apart the jackfruit a bit (this can be done with a wooden/bamboo spatula, so as to not damage your pan), When it all looks how you’d expect pulled jackfruit (or pulled pork) to look, take it off the heat.
5) Combine the carrot, cabbage, and mangetout in a small bowl, adding the apple cider vinegar and mixing well; this will be the coleslaw element
6) Mix the remaining sauce with the mayonnaise
7) (optional) toast the burger buns
8) Assemble the burgers; we recommend the following order: bottom bun, pulled jackfruit, coleslaw, gochujang mayo, top bun
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake, The Fun Way!
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
100 Hikes of a Lifetime – by Kate Siber
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is published by National Geographic, so you can imagine the quality of the photos throughout.
Inside, and after a general introduction and guide to gear and packing appropriately, it’s divided into continents, with a diverse array of “trips of a lifetime” for anyone who enjoys hiking.
It’s not a narrative book, rather, it is a guide, a little in the style of “Lonely Planet”, with many “know before you go” tips, information about the best time to go, difficult level, alternative routes if you want to get most of the enjoyment while having an easier time of it (or, conversely, if you want to see some extra sights along the way), and what to expect at all points.
Where the book really excels is in balancing inspiration with information. There are some books that make you imagine being in a place, but you’ll never actually go there. There are other books that are technical manuals but not very encouraging. This one does both; it provides the motivation and the “yes, you really can, here’s how” information that, between them, can actually get you packing and on your way.
Bottom line: if you yearn for breathtaking views and time in the great outdoors, but aren’t sure where to start, this will give you an incredible menu to choose from, and give you the tools to go about doing it.
Click here to check out 100 Hikes Of A Lifetime, and live it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: