Natural Remedies and Foods for Osteoarthritis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Natural solutions for osteoarthritis. Eg. Rosehip tea, dandelion root tea. Any others??? What foods should I absolutely leave alone?❞
We’ll do a main feature on arthritis (in both its main forms) someday soon, but meanwhile, we recommend eating for good bone/joint health and against inflammation. To that end, you might like these main features we did on those topics:
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of (collagen for bone and joint health)
- The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis (eating for bone health generally)
- Keep Inflammation At Bay (dietary tips for minimizing inflammation—also, our all-time most popular article to date!)
Of these, probably the last one is the most critical, and also will have the speediest effects if implemented.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

The Brain As A Work-In-Progress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
And The Brain Goes Marching On!

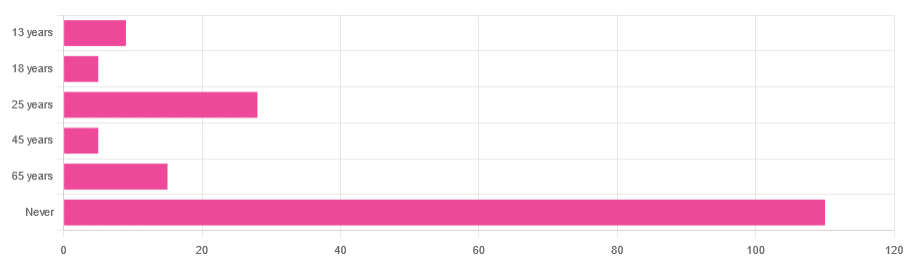
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you “when does the human brain stop developing?” and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 64% of people said “Never”
- About 16% of people said “25 years”
- About 9% of people said “65 years”
- About 5% of people said “13 years”
- About 3% of people said “18 years”
- About 3% of people said “45 years”
Some thoughts, before we get into the science:
An alternative wording for the original question was “when does the human brain finish developing”; the meaning is the same but the feeling is slightly different:
- “When does the human brain stop developing?” focuses attention on the idea of cessation, and will skew responses to later ages
- When does the human brain finish developing?” focuses on attention on a kind of “is it done yet?” and will skew responses to earlier ages
Ultimately, since we had to chose one word or another, we picked the shortest one, but it would have been interesting if we could have done an A/B test, and asked half one way, and half the other way!
Why we picked those ages
We picked those ages as poll options for reasons people might be drawn to them:
- 13 years: in English-speaking cultures, an important milestone of entering adolescence (note that the concept of a “teenager” is not precisely universal as most languages do not have “-teen” numbers in the same way; the concept of “adolescent” may thus be tied to other milestones)
- 18 years: age of legal majority in N. America and many other places
- 25 years: age popularly believed to be when the brain is finished developing, due to a study that we’ll talk about shortly (we guess that’s why there’s a spike in our results for this, too!)
- 45 years: age where many midlife hormonal changes occur, and many professionals are considered to have peaked in competence and start looking towards retirement
- 65 years: age considered “senior” in much of N. America and many other places, as well as the cut-off and/or starting point for a lot of medical research
Notice, therefore, how a lot of things are coming from places they really shouldn’t. For example, because there are many studies saying “n% of people over 65 get Alzheimer’s” or “n% of people over 65 get age-related cognitive decline”, etc, 65 becomes the age where we start expecting this—because of an arbitrary human choice of where to draw the cut-off for the study enrollment!
Similarly, we may look at common ages of legal majority, or retirement pensions, and assume “well it must be for a good reason”, and dear reader, those reasons are more often economically motivated than they are biologically reasoned.
So, what does the science say?
Our brains are never finished developing: True or False?
True! If we define “finished developing” as “we cease doing neurogenesis and neuroplasticity is no longer in effect”.
Glossary:
- Neurogenesis: the process of creating new brain cells
- Neuroplasticity: the process of the brain adapting to changes by essentially rebuilding itself to suit our perceived current needs
We say “perceived” because sometimes neuroplasticity can do very unhelpful things to us (e.g: psychological trauma, or even just bad habits), but on a biological level, it is always doing its best to serve our overall success as an organism.
For a long time it was thought that we don’t do neurogenesis at all as adults, but this was found to be untrue:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
Summary of conclusions of the above: we’re all growing new brain cells at every age, even if we be in our 80s and with Alzheimer’s disease, but there are things we can do to enhance our neurogenic potential along the way.
Neuroplasticity will always be somewhat enhanced by neurogenesis (after all, new neurons get given jobs to do), and we reviewed a great book about the marvels of neuroplasticity including in older age:
Our brains are still developing up to the age of 25: True or False?
True! And then it keeps on developing after that, too. Now this is abundantly obvious considering what we just talked about, but see what a difference the phrasing makes? Now it makes it sound like it stops at 25, which this statement doesn’t claim at all—it only speaks for the time up to that age.
A lot of the popular press about “the brain isn’t fully mature until the age of 25” stems from a 2006 study that found:
❝For instance, frontal gray matter volume peaks at about age 11.0 years in girls and 12.1 years in boys, whereas temporal gray matter volume peaks at about age at 16.7 years in girls and 16.2 years in boys. The dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex, important for controlling impulses, is among the latest brain regions to mature without reaching adult dimensions until the early 20s.❞
Source: Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Adolescent Brain
There are several things to note here:
- The above statement is talking about the physical size of the brain growing
- Nowhere does he say “and stops developing at 25”
However… The study only looked at brains up to the age of 25. After that, they stopped looking, because the study was about “the adolescent brain” so there has to be a cut-off somewhere, and that was the cut-off they chose.
This is the equivalent of saying “it didn’t stop raining until four o’clock” when the reality is that four o’clock is simply when you gave up on checking.
The study didn’t misrepresent this, by the way, but the popular press did!
Another 2012 study looked at various metrics of brain development, and found:
- Synapse overproduction into the teens
- Cortex pruning into the late 20s
- Prefrontal pruning into middle age at least (they stopped looking)
- Myelination beyond middle age (they stopped looking)
Source: Experience and the developing prefrontal cortex ← check out figure 1, and make sure you’re looking at the human data not the rat data
So how’s the most recent research looking?
Here’s a 2022 study that looked at 123,984 brain scans spanning the age range from mid-gestation to 100 postnatal years, and as you can see from its own figure 1… Most (if not all) brain-things keep growing for life, even though most slow down at some point, they don’t stop:
Brain charts for the human lifespan ← check out figure 1; don’t get too excited about the ventricular volume column as that is basically “brain that isn’t being a brain”. Do get excited about the rest, though!
Want to know how not to get caught out by science being misrepresented by the popular press? Check out:
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
Take care!
Share This Post

What happens when I stop taking a drug like Ozempic or Mounjaro?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
Drugs like Ozempic are very effective at helping most people who take them lose weight. Semaglutide (sold as Wegovy and Ozempic) and tirzepatide (sold as Zepbound and Mounjaro) are the most well known in the class of drugs that mimic hormones to reduce feelings of hunger.
But does weight come back when you stop using it?
The short answer is yes. Stopping tirzepatide and semaglutide will result in weight regain in most people.
So are these medications simply another (expensive) form of yo-yo dieting? Let’s look at what the evidence shows so far.
It’s a long-term treatment, not a short course
If you have a bacterial infection, antibiotics will help your body fight off the germs causing your illness. You take the full course of medication, and the infection is gone.
For obesity, taking tirzepatide or semaglutide can help your body get rid of fat. However it doesn’t fix the reasons you gained weight in the first place because obesity is a chronic, complex condition. When you stop the medications, the weight returns.
Perhaps a more useful comparison is with high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. Treatment for hypertension is lifelong. It’s the same with obesity. Medications work, but only while you are taking them. (Though obesity is more complicated than hypertension, as many different factors both cause and perpetuate it.)

Obesity drugs only work while you’re taking them. KK Stock/Shutterstock Therefore, several concurrent approaches are needed; taking medication can be an important part of effective management but on its own, it’s often insufficient. And in an unwanted knock-on effect, stopping medication can undermine other strategies to lose weight, like eating less.
Why do people stop?
Research trials show anywhere from 6% to 13.5% of participants stop taking these drugs, primarily because of side effects.
But these studies don’t account for those forced to stop because of cost or widespread supply issues. We don’t know how many people have needed to stop this medication over the past few years for these reasons.
Understanding what stopping does to the body is therefore important.
So what happens when you stop?
When you stop using tirzepatide or semaglutide, it takes several days (or even a couple of weeks) to move out of your system. As it does, a number of things happen:
- you start feeling hungry again, because both your brain and your gut no longer have the medication working to make you feel full

When you stop taking it, you feel hungry again. Stock-Asso/Shutterstock - blood sugars increase, because the medication is no longer acting on the pancreas to help control this. If you have diabetes as well as obesity you may need to take other medications to keep these in an acceptable range. Whether you have diabetes or not, you may need to eat foods with a low glycemic index to stabilise your blood sugars
- over the longer term, most people experience a return to their previous blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as the weight comes back
- weight regain will mostly be in the form of fat, because it will be gained faster than skeletal muscle.
While you were on the medication, you will have lost proportionally less skeletal muscle than fat, muscle loss is inevitable when you lose weight, no matter whether you use medications or not. The problem is, when you stop the medication, your body preferentially puts on fat.
Is stopping and starting the medications a problem?
People whose weight fluctuates with tirzepatide or semaglutide may experience some of the downsides of yo-yo dieting.
When you keep going on and off diets, it’s like a rollercoaster ride for your body. Each time you regain weight, your body has to deal with spikes in blood pressure, heart rate, and how your body handles sugars and fats. This can stress your heart and overall cardiovascular system, as it has to respond to greater fluctuations than usual.
Interestingly, the risk to the body from weight fluctuations is greater for people who are not obese. This should be a caution to those who are not obese but still using tirzepatide or semaglutide to try to lose unwanted weight.
How can you avoid gaining weight when you stop?
Fear of regaining weight when stopping these medications is valid, and needs to be addressed directly. As obesity has many causes and perpetuating factors, many evidence-based approaches are needed to reduce weight regain. This might include:
- getting quality sleep
- exercising in a way that builds and maintains muscle. While on the medication, you will likely have lost muscle as well as fat, although this is not inevitable, especially if you exercise regularly while taking it

Prioritise building and maintaining muscle. EvMedvedeva/Shutterstock - addressing emotional and cultural aspects of life that contribute to over-eating and/or eating unhealthy foods, and how you view your body. Stigma and shame around body shape and size is not cured by taking this medication. Even if you have a healthy relationship with food, we live in a culture that is fat-phobic and discriminates against people in larger bodies
- eating in a healthy way, hopefully continuing with habits that were formed while on the medication. Eating meals that have high nutrition and fibre, for example, and lower overall portion sizes.
Many people will stop taking tirzepatide or semaglutide at some point, given it is expensive and in short supply. When you do, it is important to understand what will happen and what you can do to help avoid the consequences. Regular reviews with your GP are also important.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Natasha Yates, General Practitioner, PhD Candidate, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post

Stick with It – by Dr. Sean Young
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us know the theory when it comes to building new habits and/or replacing old ones, and maybe we even implement those ideas. So why is our success rate still not as high as we think it should be?
Dr. Sean Young is here to do science to it!
This book comes with advice and explanations that rely a lot less on “that sounds reasonable” and a lot more on “in this recent high-quality study, researchers found…”
And, at 10almonds, we love that. We’re all for trying new things that sound reasonable in general… but we definitely prefer when there’s a stack of solid science to point to, and that’s the kind of thing we recommend!
Dr. Young is big on using that science to find ways to trick our brains and get them working the way we want.
Each chapter has lots of science, lots of explanations, and lots of actionable step-by-step advice.
Bottom line: if you’re all over “Atomic Habits”, this one’s the science-based heavy-artillery for your practical neurohacking.
Share This Post
Related Posts

Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes – by Ginger Vieira
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you or a loved one has Type 1 Diabetes, you’ll know that exercise can be especially frustrating…
- If you don’t do it, you risk weight gain and eventual insulin resistance.
- If you do it, you risk dangerous hypos, or perhaps hypers if you took off your pump or skipped a bolus.
Unfortunately, the popular medical advice is “well, just do your best”.
Ginger Vieira is Type 1 Diabetic, and writes with 20+ experience of managing her diabetes while being a keen exerciser. As T1D folks out there will also know, comorbidities are very common; in her case, fibromyalgia was the biggest additional blow to her ability to exercise, along with an underactive thyroid. So when it comes to dealing with the practical nuts and bolts of things, she (while herself observing she’s not a doctor, let alone your doctor) has a lot more practical knowledge than an endocrinologist (without diabetes) behind a desk.
Speaking of nuts and bolts, this book isn’t a pep talk.
It has a bit of that in, but most of it is really practical information, e.g: using fasted exercise (4 hours from last meal+bolus) to prevent hypos, counterintuitive as that may seem—the key is that timing a workout for when you have the least amount of fast-acting insulin in your body means your body can’t easily use your blood sugars for energy, and draws from your fat reserves instead… Win/Win!
That’s just one quick tip because this is a 1-minute review, but Vieira gives:
- whole chapters, with example datasets (real numbers)
- tech-specific advice, e.g. pump, injection, etc
- insulin-specific advice, e.g. fast vs slow, and adjustments to each in the context of exercise
- timing advice re meal/bolus/exercise for different insulins and techs
- blood-sugar management advice for different exercise types (aerobic/anaerobic, sprint/endurance, etc)
…and lots more that we don’t have room to mention here
Basically… If you or a loved one has T1D, we really recommend this book!
Order a copy of “Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Ageless Aging – by Maddy Dychtwald
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Maddy Dychtwald, herself 73, has spent her career working in the field of aging. She’s not a gerontologist or even a doctor, but she’s nevertheless been up-to-the-ears in the industry for decades, mostly as an organizer, strategist, facilitator, and so forth. As such, she’s had her finger on the pulse of the healthy longevity movement for a long time.
This book was written to address a problem, and the problem is: lifespan is increasing (especially for women), but healthspan has not been keeping up the pace.
In other words: people (especially women) are living longer, but often with more health problems along the way than before.
And mostly, it’s for lack of information (or sometimes: too much competing incorrect information).
Fortunately, information is something that a woman in Dychtwald’s position has an abundance of, because she has researchers and academics in many fields on speed-dial and happy to answer her questions (we get a lot of input from such experts throughout the book—which is why this book is so science-based, despite the author not being a scientist).
The book answers a lot of important questions beyond the obvious “what diet/exercise/sleep/supplements/etc are best for healthy aging” (spoiler: it’s quite consistent with the things we recommend here, because guess what, science is science), questions like how best to prepare for this that or the other, how to get a head start on preventative healthcare for some things, how to avoid being a burden to our families (one can argue that families are supposed to look after each other, but still, it’s a legitimate worry for many, and understandably so), and even how to balance the sometimes conflicting worlds of health and finances.
Unlike many authors, she also talks about the different kinds of aging, and tackles each of them separately and together. We love to see it!
Bottom line: this book is a very good one-stop-shop for all things healthy aging. It’s aimed squarely at women, but most advice goes for men the same too, aside from the section on hormones and such.
Click here to check out Ageless Aging, and plan your future!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Can You Get Addicted To MSG, Like With Sugar?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Hello, I love your newsletter 🙂 Can I have a question? While browsing through your recepies, I realised many contained MSG. As someone based in Europe, I am not used to using MSG while cooking (of course I know that processed food bought in supermarket containes MSG). There is a stigma, that MSG is not particulary healthy, but rather it should be really bad and cause negative effects like headaches. Is this true? Also, can you get addicted to MSG, just like you get addicted to sugar? Thank you :)❞
Thank you for the kind words, and the interesting questions!
Short answer: no and no 🙂
Longer answer: most of the negative reputation about MSG comes from a single piece of satire written in the US in the 1960s, which the popular press then misrepresented as a genuine concern, and the public then ran with, mostly due to racism/xenophobia/sinophobia specifically, given the US’s historically not fabulous relations with China, and the moniker of “Chinese restaurant syndrome”, notwithstanding that MSG was first isolated in Japan, not China, more than 100 years ago.
The silver lining that comes out of this is that because of the above, MSG has been one of the most-studied food additives in recent decades, with many teams of scientists in many countries trying to determine its risks and not finding any (except insofar as anything in extreme quantities can kill you, including water or oxygen).
You can read more about this and other* myths about MSG, here:
Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
*such as pertaining to gluten sensitivity, which in reality MSG has no bearing on whatsoever as it does not contain gluten and is not even made of the same basic stuff; gluten being a protein made of (amongst other things) the amino acid glutamine, not a glutamate salt. Glutamate is as closely related to gluten as cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) is to cyanide (the famous poison).
PS: if you didn’t click the above link to read that article, then 1) we really do recommend it 2) we did some LD50 calculations there and looked at available research, and found that for someone of this writer’s (very medium) size, eating 1kg of MSG at once is sufficient to cause toxicity, and injecting >250g of MSG may cause heart problems. So we don’t recommend doing that.
However, ½ tsp in a recipe that gives multiple portions is not going to get you anywhere close to the danger zone, unless you consume that entire meal by yourself hundreds of times per day. And if you do, the MSG is probably the least of your concerns.
(2 tsp of cassia cinnamon, however, is enough to cause coumarin toxicity; for this reason we recommend Ceylon (or “True” or “Sweet”) cinnamon in our recipes, as it has almost undetectable levels of coumarin)
With regard to your interesting question about addiction, first of all let’s speak briefly about sugar addiction:
Sugar addiction is, by broad scientific consensus, agreed-upon as an extant thing that does exist, and contemporary research is more looking into the “hows” and “whys” and “whats” rather than the “whether”. It is a somewhat complicated topic, because it’s halfway between what science would usually consider a chemical addiction, and what science would usually consider a behavioral addiction:
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
The reasonable prevailing hypothesis, therefore, is that sugar simply has two moderate mechanisms of addiction, rather than one strong one.
The biochemical side of sugar addiction comes from the body’s metabolism of sugar, so this cannot be a thing for MSG, because there is nothing to metabolize in the same sense of the word (MSG being an inorganic compound with zero calories).
People can crave salt, especially when deficient in it, and MSG does contain sodium (it’s what the “S” stands for), but it contains a little under ⅓ of the sodium that table salt does (sodium chloride in whatever form, be it sea salt, rock salt, or such):
MSG vs. Salt: Sodium Comparison ← we do molecular calculations here!
Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier? ← this one for a head-to-head
However, even craving salt does not constitute an addiction; nobody is shamefully hiding their rock salt crystals under their bed and getting a fix when they feel low, and nor does withdrawal cause adverse side effects, except insofar as (once again) a person deficient in salt will crave salt.
Finally, the only other way we know of that one might wonder if MSG could be addictive, is about glutamate and glutamate receptors. The glutamate in MSG is the same glutamate (down to the atoms) as the glutamate formed if one consumes tomatoes in the presence of salt, and triggers the same glutamate receptors in the same way. We have the same number of receptors either way, and uptake is exactly the same (because again, it’s exactly the same chemical) so there is a maximum to how strong this effect can be, and that maximum is the same whatever the source of the glutamate was.
In this respect, if MSG is addictive, then so is a tomato salad with a pinch of salt: it’s not—it’s just tasty.
We haven’t cited papers in today’s article, but it’s just because we cited them already in the articles we linked, and so we avoided doubling up. Most of them are in that first link we gave 🙂
One final note
Technically anyone can develop a sensitivity to anything, so in theory someone could develop a sensitivity to MSG, just like they could for any other ingredient. Our usual legal/medical disclaimer applies.
However, it’s certainly not a common trigger, putting it well below common allergens like nuts (or less common allergens like, say, bananas), not even in the same league as common intolerances such as gluten, and less worthy of health risk warnings than, say, spinach (high in oxalates; fine for most people but best avoided if you have kidney problems).
The reason we use it in the recipes we use it in, is simply because it’s a lower-sodium alternative to salt, and while it contains a (very) tiny bit less sodium than low-sodium salt (which itself has about ⅓ the sodium of regular salt), it has more of a flavor-enhancing effect, such that one can use half as much, for a more than sixfold total sodium reduction. Which for most of us in the industrialized world, is beneficial.
Want to try some?
If today’s article has inspired you to give MSG a try, here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: