Eat More, Live Well – by Dr. Megan Rossi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Often, eating healthily can feel restrictive. Don’t eat this, skip that, eliminate the other. Where is the joy?
Dr. Megan Rossi brings a scientific angle on positive dieting, that is to say, looking at what to add, rather than what to subtract. Now, the idea isn’t to have sugar-laden chocolate cake with berries on top and call it a net positive because of the berries, though. Rather, Dr. Rossi lays out how to include as many diverse vegetables and fruits as possible, with tasty recipes so that we’re too busy with those to crave junk food.
Speaking of recipes, there are 80, and they are easy to follow. She describes them as “plant-based”, and by this what she really means is “plant-centric” or such; she does include the use of some animal products.
This is important to note, because general convention is to use “plant-based” to mean functionally vegan, but being about the food rather than the ideology; a relevant distinction in both society and science. In the case of this book, it’s neither, but it is very healthy.
Bottom line: if you’d like to introduce more healthy diversity to your diet, rather than eating the same three fruits and five vegetables, but you’re not sure how, this book will get you where you need to be.
Click here to check out Eat More, Live Well, and diversify your diet!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healing Spices – by Dr. Bharat Aggarwal & Debora Yost
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is exactly what the subtitle promises it to be, and more. It’s actually herbs and spices, but definitely mostly spices, and includes the kinds found in even the smallest supermarket, to some you might not have heard of, and might need to order online.
We are treated to an explanation of the health-giving properties of each (and any potential contraindications), as well as the culinary properties, many tables of what goes with what and how and why, and even recipes to use them in. For the more adventurous, there’s even advice on how to grow, prepare, and store each of them.
An extra benefit is that everything is cross-linked such that you can look things up by spice or by health condition or by flavor profile, and find what you need and what’ll go with it.
The style is simple and informational, clearly laid-out in encyclopedic form.
Bottom line: this book should be in your kitchen (or related nearby kitchen-book-place).
Click here to check out Healing Spices, and advance your culinary repertoire!
Share This Post
-
Meals That Heal – by Dr. Carolyn Williams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inflammation is implicated as a contributory or casual factor in almost all chronic diseases (and still exacerbates the ones in which it’s not directly implicated causally), so if there’s one area of health to focus on with one’s diet, then reducing inflammation is a top candidate.
This book sets about doing exactly that.
You may be wondering whether, per the book’s subtitle, they can really all be done in 30 minutes or under. The answer is: no, not unless you have a team of sous-chefs to do all the prep work for you, and line up everything mise-en-place style for when you start the clock. If you do have that team of sous-chefs working for you, then you can probably do most of them in under 30 minutes. If you don’t have that team, then budget about an hour in total, sometimes less, sometimes more, depending on the recipe.
The recipes themselves are mostly Mediterranean-inspired, though you might want to do a few swaps where the author has oddly recommended using seed oils instead of olive oil, or plant milk in place of where she has used dairy milk in a couple of “recipes” for smoothies. You might also want to be a little more generous with the seasonings, if you’re anything like this reviewer.
Bottom line: if you’re looking for an anti-inflammatory starter cookbook, you could do worse than this. You could probably do better, too, such as starting with The Inflammation Spectrum – by Dr. Will Cole.
Alternatively, click here if you want to check out Meals That Heal, and dive straight in!
Share This Post
-
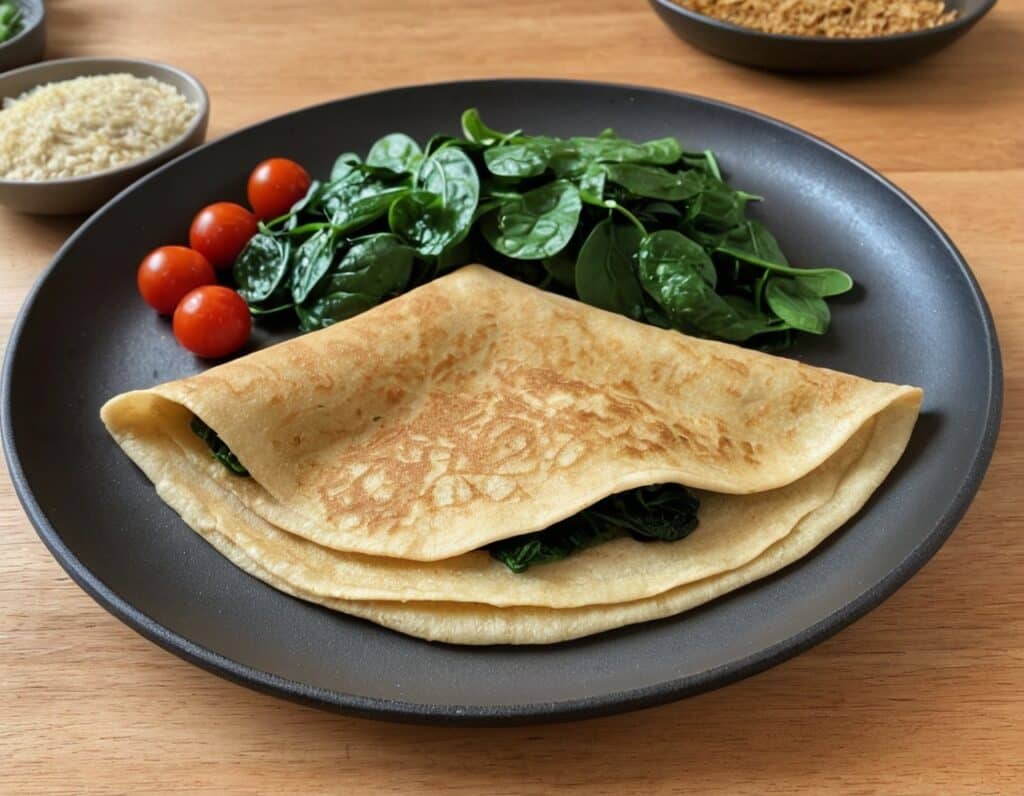
Savory Protein Crêpe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pancakes have a bad reputation healthwise, but they don’t have to be so. Here’s a very healthy crêpe recipe, with around 20g of protein per serving (which is about how much protein most people’s body’s can use at one sitting) and a healthy dose of fiber too:
You will need
Per crêpe:
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend oat milk for this)
- 2 oz chickpea flour (also called garbanzo bean flour, or gram flour)
- 1 tsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp ras el-hanout (optional but tasty and contains an array of beneficial phytochemicals)
- 1 tsp dried mixed herbs
- ⅛ tsp MSG or ¼ tsp low-sodium salt
For the filling (also per crêpe):
- 6 cherry tomatoes, halved
- Small handful baby spinach
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix the dry crêpe ingredients in a bowl, and then stir in the milk, whisking to mix thoroughly. Leave to stand for at least 5 minutes.
2) Meanwhile, heat a little olive oil in a skillet, add the tomatoes and fry for 1 minute, before adding the spinach, stirring, and turning off the heat. As soon as the spinach begins to wilt, set it aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil either in the same skillet (having been carefully wiped clean) or a crêpe pan if you have one, and pour in a little of the batter you made, tipping the pan so that it coats the pan evenly and thinly. Once the top is set, jiggle the pan to see that it’s not stuck, and then flip your crêpe to finish on the other side.
If you’re not confident of your pancake-tossing skills, or your pan isn’t good enough quality to permit this, you can slide it out onto a heatproof chopping board, and use that to carefully turn it back into the pan to finish the other side.
4) Add the filling to one half of the crêpe, and fold it over, pushing down at the edges with a spatula to make a seal, cooking for another 30 seconds or so. Alternatively, you can just serve a stack of crêpes and add the filling at the table, folding or rolling per personal preference:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Should Men Over 50 Get PSA?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Loved the information on prostate cancer. Do recommend your readers get a PSA or equivalent test annually for over 50 yr old men.❞
(This is about: Prostate Health: What You Should Know)
Yep, or best yet, the much more accurate PSE test! But if PSA test is what’s available, it’s a lot better than nothing. And, much as it’s rarely the highlight of anyone’s day, a prostate exam by a suitably qualified professional is also a good idea.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cannabis & Heart Attacks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For many, cannabis use has taken the place that alcohol used to have when it comes to wanting a “downer”, that is to say, a drug that relaxes us as opposed to stimulating us.
Indeed, it is generally considered safer than alcohol ← however this is not a strong claim, because alcohol is much more dangerous than one would think given its ubiquity and (in many places, at least) social acceptability.
We’ve talked a bit about cannabis use before, in its various forms, for example:
Cannabis Myths vs Reality ← a very good starting point for the curious
And one specifically about the use of THC gummies (THC is the psychoactive compound in cannabis, i.e. it’s the chemical that gets people high, as opposed to CBD, which is not psychoactive) as a sleep aid:
Sweet Dreams Are Made of THC (Or Are They?)
And for those skipping the THC, we’ve also written about CBD use, including:
CBD Oil: What Does The Science Say? and Do CBD Gummies Work?
So, about cannabis and heart attacks
Alcohol is a relaxant, and yet it can contribute to heart disease (amongst many other things, of course):
Can We Drink To Good Health? ← this is mostly about red wine’s putative heart health benefits, how the idea got popularized, and how it doesn’t stand up to scrutiny when actually looking at the evidence.
And cannabis, another relaxant? Not so good either!
New research has shown that cannabis users have a higher risk of heart attacks, even among younger and otherwise healthy individuals. This is based on analyzing data from 4,636,628 relatively healthy adults.
Specifically, the data showed that even young healthy cannabis users get:
- Sixfold increased risk of heart attack
- Fourfold increased risk of ischemic stroke
- Threefold increased risk of cardiovascular death, heart attack, or stroke
We mention the otherwise “relatively healthy” nature of the participants, because it’s important to note that less healthy people (who were perhaps using cannabis to self-medicate for some serious condition) were not included in the dataset, as it’d skew the data unhelpfully and it’d make the risk look a lot higher than the risk levels we mentioned above.
The mechanisms by which cannabis affects heart health are not fully understood, but hypotheses include:
- Disrupting heart rhythm regulation
- Increasing oxygen demand in the heart muscle
- Causing endothelial dysfunction, which affects blood vessel function
Further, heart attack risk peaked one hour after cannabis use, and while this doesn’t prove causality, it certainly doesn’t make cannabis look safe.
You can read the paper in its entirety here:
Want a safer way to relax?
We recommend:
- No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
- Meditation Games That You’ll Actually Enjoy
- Which Style Of Yoga Is Best For You?
- 7 Kinds Of Rest When Sleep Is Not Enough
- Better Sex = Longer Life (Here’s How)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
7 Tips To Burn Fat & Build Muscle At The Same Time
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cori Lefkowith, of “Redefining Strength” and “Strong At Any Age” fame, has her formula to share:
Know your priorities
We’ll not keep the 7 tips a mystery; they are:
- Determine your primary goal: decide whether your main focus is losing fat while building muscle or building muscle while trimming up. This choice will influence your calorie intake, macros, and cardio approach.
- Start tracking: spend 7–14 days logging your current food intake, including calories, protein, carbs, and fats, without taking any particular action to change them yet. Understanding your baseline will help tailor your diet and exercise plan.
- Prioritize strength training: focus on strength work over cardio to build muscle. Avoid turning strength sessions into cardio by rushing between sets—allow adequate rest for muscle progression.
- Center your meals on protein: adjust your protein intake based on your primary goal. For fat loss while gaining muscle, aim for 40-45% of calories from protein. For building muscle while losing fat, aim for 30-40% protein, with attention to maintaining sufficient carbs.
- Set your calories: after adjusting protein, fine-tune your calorie intake. However, make only small changes (e.g. 100 calories up or down) and reassess every 2–3 weeks to avoid extreme deficits or surpluses.
- Adjust your cardio: prioritize strength training but use walking as low-impact cardio. Avoid excessive cardio that may hinder muscle gains, and use strategic HIIT sessions if needed.
- Ditch the scale: avoid using the scale as your sole measure of progress. Instead, rely on measurements, progress photos, and how your clothes fit to track body recomposition effectively.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Can You Gain Muscle & Lose Fat At The Same Time? ← we got this question in our Q&A day not long back, and here was our answer. We went for a less numbers-based approach, and a more principles-based approach. Both ways work, so by all means pick whichever method you personally find better suits how you like to do things!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: