What Happens Every Day When You Quit Sugar For 30 Days
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that sugar isn’t exactly a health food, but it can be hard to quit. How long can cravings be expected to last, and when can we expect to see benefits? Today’s video covers the timeline in a realistic yet inspiring fashion:
What to expect on…
Day 1: expect cravings and withdrawal symptoms including headaches, fatigue, mood swings, and irritability—as well as tiredness, without the crutch of sugar.
Days 2 & 3: more of the same, plus likely objections from the gut, since your Candida albicans content will not be enjoying being starved of its main food source.
Days 4–7: reduction of the above symptoms, better energy levels, improved sleep, and likely the gut will be adapting or have adapted.
Days 8–14: beginning of weight loss, clearer skin, improved complexion; taste buds adapt too, making foods taste sweeter. Continued improvement in energy and focus, as well.
Days 15–21: more of the same improvements, plus the immune system will start getting stronger around now. But watch out, because there may still be some cravings from time to time.
Days 22–30: all of the above positive things, few or no cravings now, and enhanced metabolic health as a whole.
For more specificity on each of these stages, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How (And Why) To Train Your Pre-Frontal Cortex
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Chapman’s Keys For Mental Focus
This is Dr. Sandra Chapman; she’s a cognitive neuroscientist, on a mission to, in her words, further our understanding of:
- what makes the brain stronger, faster and last longer
- what enhances human cognitive capacity, and
- what enhances the underlying brain systems across the lifespan.
To this end, she’s also the founder and Chief Director of the Center For Brain Health, where she has worked on her mission for the past 25 years (clocking up hundreds of peer-reviewed publications to her name), as well as being a professor of Behavioral and Brain Sciences at UT Dallas.
What does she want us to know?
Get your brain into gear
When it comes to your brainpower, it is “use it or lose it”, but it is also perfectly possible to use it and lose it.
Why?
Very often, what we are using our brains for is high-strain, low-yield stuff, such as multitasking, overthinking, or overthinking while multitasking. And to make it worse, we often do it without sufficient rest.
This is the equivalent of owning a Ferrari but trying to drive it in second and third gear at once by switching between the two as rapidly as possible. And doing that for 18 hours each day.
Suffice it to say, you’ll be going nowhere quickly.
An alternative “use” of brainpower is low-strain, low-yield stuff, such as having to pay close attention to a boring conversation. It’s enough to stop your mind from doing anything else, but not enough to actually stimulate you.
This is the equivalent of owning a Ferrari but keeping it idling. The wear and tear is minimal this time, but you’re not actually going anywhere either.
Better, of course, are the other two quadrants:
- low-strain, high-yield: consistently using our brain in relatively non-taxing ways that encourage its development
- high-strain, high-yield: here the Ferrari metaphor definitely fails, because unlike cars, our bodies (including our brains) are machines that benefit from judicious regular progressive overloading (but just by a bit, and with adequate recovery time between overloads).
See also: 12 Weeks To Measurably Boost Your Brain
How to do the “low-strain, low-yield” part
When it comes to “what’s the most important part of the brain to help in the face of cognitive decline?” the usual answer is either to focus on memory (hippocampi) or language (various parts, but for example Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area), since people most fear losing memory, and language is very important both socially and practically.
Those are indeed critical, and we at 10almonds stand by them, but Dr. Chapman (herself having originally trained as speech and language pathologist!) makes a strong case for adding a third brain part to the list.
Specifically, she advocates for strengthening the pre-frontal cortex, which is responsible for inhibition, task-switching, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. If that seems like a lot, do remember it’s a whole cortex and not one of the assorted important-but-small brain bits we mentioned above.
How? She has developed training programs for this, based on what she calls Strategic Memory Advanced Reasoning Tactics (SMART), to support support attention, planning, judgment and emotional management.
You can read more about those programs here:
Center For Brain Health | Our Programs
Participation in those is mostly not free, however, if you join their…
Center For Brain Health | BrainHealth Project
…then they will periodically invite you to join pilot programs, research programs, and the like, which will either be free or they-pay-you affairs—because this is how science is done, and you can read about yourself (anonymized, of course) later in peer-reviewed papers of the kind we often cite here.
If you’re not interested in any of that though, we will say that according to Dr. Chapman, the keys are:
Inhibition: be conscious of this function of your brain, and develop it. This is the function of your brain that stops you from making mistakes—or put differently: stops you from saying/doing something stupid.
Switching: do this consciously; per “I am now doing this task, now I am switching to this other task”, rather than doing the gear-grinding thing we discussed earlier
Working memory: this is effectively your brain’s RAM. Unlike the RAM of a computer (can be enhanced by adding another chip or replacing with a bigger chip), our brain’s RAM can be increased by frequent use, and especially by judicious use of progressive overloading (with rests between!) which we’ll discuss in the high-strain, high-yield section.
Flexibility: this is about creative problem-solving, openness to new ideas, and curiosity
See also: Curiosity Kills The Neurodegeneration
How to do the “high-strain, high-yield” part
Delighting this chess-playing writer, Dr. Chapman recommends chess. Although, similar games such as go (a Chinese game that looks simpler than chess but actually requires more calculation) work equally well too.
Why?
Games like chess and go cause structural changes that are particularly helpful, in terms of engaging in such foundational tasks as learning, abstract reasoning, problem-solving and self-control:
Chess Practice as a Protective Factor in Dementia
Basically, it checks (so to speak) a lot of boxes, especially for the pre-frontal cortex. Some notes:
- Focusing on the game is required for brain improvement; simply pushing wood casually will not do it. Ideally, calculating several moves ahead will allow for strong working memory use (because to calculate several moves ahead, one will have to hold increasingly many possible positions in the mind while doing so).
- The speed of play must be sufficiently slow as to allow not only for thinking, but also for what in chess is called “blunder-checking”, in other words, having decided on one’s move, pausing to consider whether it is a mistake, and actively trying to find evidence that it is. This is the crucial “inhibition habit”, and when one does it reflexively, one will make fewer mistakes. Tying this to dementia, see for example how one of the common symptoms of dementia is falling for scams that one wouldn’t have previously. How did cognitive decline make someone naïve? It didn’t, per se; it just took away their ability to, having decided what to do, pause to consider whether it was a mistake, and actively trying to find evidence that it is.
- That “conscious switching” that we talked about, rather than multitasking? In chess, there is a difference between strategy and tactics. Don’t worry about what that difference is for now (learn it if you want to take up chess), but know that strong players will only strategize while it is their opponent’s turn, and only calculate (tactics) while it is their own turn. It’s very tempting to flit constantly between one and the other, but chess requires players to have the mental discipline be able to focus on one task or the other and stick with that task until it’s the appointed time to switch.
If you feel like taking up chess, this site (and related app, if you want it) is free (it’s been funded by voluntary donations for a long time now) and good and even comes with free tuition and training tools: LiChess.org
Here’s another site that this writer (hi, it’s me) personally uses—it has great features too, but many are paywalled (I’m mostly there just because I’ve been there nearly since its inception, so I’m baked into the community now): Chess.com
Want to know more?
You might like this book by Dr. Chapman, which we haven’t reviewed yet but it did inform large parts of today’s article:
Make Your Brain Smarter: Increase Your Brain’s Creativity, Energy, and Focus – by Dr. Sandra Chapman
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Sleep Solution – by Dr. Chris Winter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book’s blurb contains a bold claim:
❝If you want to fix your sleep problems, Internet tips and tricks aren’t going to do it for you. You need to really understand what’s going on with your sleep—both what your problems are and how to solve them.❞
So, how well does it deliver, on the strength of being a whole book rather than an Internet article?
Well, for sure we wouldn’t have the room to include all the information that Dr. Winter does, in one of our main feature articles here (we’d need to spread it out over several weeks, at least).
He examines very thoroughly what is going on with sleep, sleep disturbance, and sleep deprivation. What’s going on with the different phases of sleep (far more than your phone’s sleep app will), and how imbalances in these can cause problems.
While the usual sleep hygiene tips do get a mention, he broadly assumes we know that part already. Instead, he focuses on aligning as many components as possible of our rich and interesting circadian rhythm. Yes, even if that means clawing our way out of insomnia and/or a bad sleep schedule (or lack of coherent sleep schedule) first. He gives plenty of practical advice on how to do that.
Bottom line: if you’d like to more deeply understand sleep, what is or isn’t wrong with yours, and how you can fix it, this book is a great resource.
Click here to check out The Sleep Solution, and enjoy the benefits of better rest!
Share This Post
-
The Kindness Method – by Shahroo Izadi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Shahroo Izadi here covers everything from alcohol addiction to procrastination to weight loss. It’s a catch-all handbook for changing your habits—in general, and/or in whatever area of your life you most feel you want or need to.
She herself went from yo-yo dieting to a stable healthy lifestyle, and wants to share with us how she did it. So she took what worked for her, organized and dilstilled it, and named it “the kindness method”, which…
- promotes positivity not in a “head in the sand” sense but rather: you have strengths, let’s find them and use them
- offers many exploratory exercises to help you figure out what’s actually going to be best for you
- plans support in advance—you’re going to be your own greatest ally here
Basically it’s about:
- being kind to yourself rather than setting yourself up to fail, and “judging a fish by how well it can climb a tree”
- being kind to yourself by being compassionate towards your past self and moving on with lessons learned
- being kind to yourself by getting things in order for your future self, because you need to treat your future self like a loved one
In fact, why not buy a copy of this book as a gift for your future self?
Click Here To Order Your Copy of “The Kindness Method” on Amazon Today!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Butter vs Plant Oils: What The Latest Evidence Shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve done some relevant head-to-head comparisons before in our “This or That” section:
- Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Sesame Oil vs Almond Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Sunflower Oil vs Canola Oil – Which is Healthier?
- Margarine vs Butter – Which is Healthier
- Butter vs Ghee – Which is Healthier?
We also did a deeper-dive into butter vs margarine:
Butter vs Margarine – Mythbusting Edition ← this one clears up a lot of misinformation about both butter and margarine
As well as: Saturated Fats: What’s The Truth? Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
So, we’re not coming into this one today unawares, and/but it’s an interesting comparison we haven’t directly written about before: butter vs plant oils in general
The Study
It was a JAMA Internal Medicine cohort study, which followed 221,054 adults (average age 56 at the start of the study, with a standard deviation of 7 years from that age) for up to 33 years.
Why “up to”? Because not everybody survived the study.
Specifically, 50,932 deaths were recorded, including 12,241 from cancer and 11,240 from cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Participants were categorized into quartiles based on butter or plant-based oil intake, and…
- The highest quartile (i.e. the 25% of people who consumed the most) butter intake linked to a 15% higher total mortality.
- The highest quartile (i.e. the 25% of people who consumed the most) plant-based oil intake linked to a 16% lower total mortality.
But, if those are the opposite ends of the spectrum, what about smaller differences?
Every 10g/day increase in consumption of plant-based oils yielded…
- 11% lower cancer mortality.
- 6% lower CVD mortality.
Meanwhile, 10g/day increase in butter consumption yielded…
- 12% higher cancer mortality.
- 17% higher CVD mortality.
These benefits must have a cap (after all, one cannot just drink liters of olive oil per day for for a 3400% decrease in mortality), but that cap was not ascertained, because there was no group drinking liters of plant oils per day, not even for science.
However, in the realm of small changes, substituting even 10g/intake of total butter with an equivalent amount of plant-based oils yielded 17% lower total mortality.
You can read the study in full, here: Butter and Plant-Based Oils Intake and Mortality
“So, what about the surely great difference between seed oils and olive oil?”
Compared the the vast gaping statistical chasm that lay between the results of butter and the results of plant oils, which plant oil one chooses doesn’t make a huge difference, iff one isn’t consuming a large amount—the important thing was skipping butter in favor of a plant oil of some kind.
Note also that, for example, deep-frying a starchy food like potatoes will cause the resultant fries (or such), even if not visibly oily, to now have about 10–15% of their original weight in water, replaced with oil. So, 100g (about 3oz) of fries may have around 10-15g oil. Obviously, this does depend on the cut and other factors, but that’s a ballpark figure.
Here’s a lengthier discussion about seed oils than we have room for today:
If you’re worried about inflammation, stop stressing about seed oils and focus on the basics ← in other words, yes it counts, but there are other things that count a lot more, such that if you’re paying attention to the other things, the fact that you sprayed your wok with a little canola oil before stir-frying those vegetables isn’t going to make a meaningful difference.
An as for olive oil? It’s a famously healthy oil, and certainly a candidate for the top spot along with avocado oil*:
All About Olive Oil ← we talk lipids, polyphenols, virginity, and more!
*…and it’s worth noting that these two oils’ (excellent) lipids profiles are very similar, meaning that the main factor between them is that olive oil usually retains vitamins that avocado oil doesn’t.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Plum vs Persimmon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing plum to persimmon, we picked the plum.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, persimmon has 3x the carbs for only the same amount of fiber, on account of which plum has the lower glycemic index, so we’ll go with plum here, though your opinion could vary.
In terms of vitamins, it’s much less subjective: plums have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, E, K, and choline, while persimmon has more vitamin C. So, unless you have scurvy, plums will be the best choice for most people.
In the category of minerals, plums have more copper, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while persimmon has more calcium, iron, phosphorus, and potassium—thus, a 4:4 tie on minerals.
Adding up the sections gives an overall win for plums, but of course, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
PS: plums have an extra bonus too; check out the link below…
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← plums kill cancer cells while sparing healthy ones
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
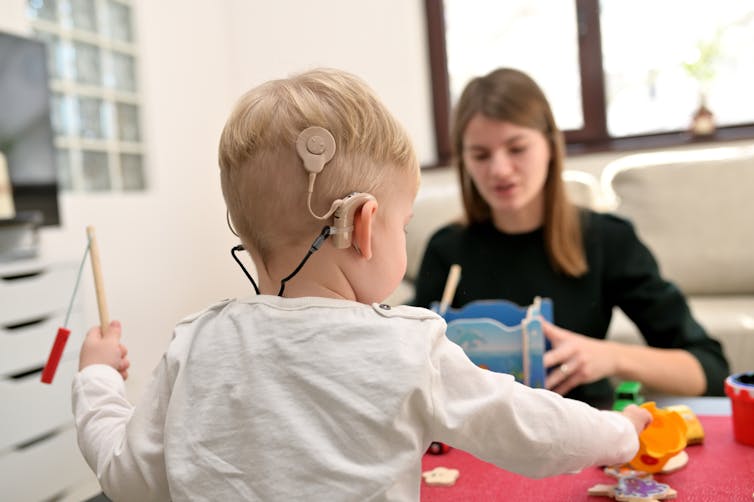
Hearing loss is twice as common in Australia’s lowest income groups, our research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around one in six Australians has some form of hearing loss, ranging from mild to complete hearing loss. That figure is expected to grow to one in four by 2050, due in a large part to the country’s ageing population.
Hearing loss affects communication and social engagement and limits educational and employment opportunities. Effective treatment for hearing loss is available in the form of communication training (for example, lipreading and auditory training), hearing aids and other devices.
But the uptake of treatment is low. In Australia, publicly subsidised hearing care is available predominantly only to children, young people and retirement-age people on a pension. Adults of working age are mostly not eligible for hearing health care under the government’s Hearing Services Program.
Our recent study published in the journal Ear and Hearing showed, for the first time, that working-age Australians from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are at much greater risk of hearing loss than those from higher socioeconomic backgrounds.
We believe the lack of socially subsidised hearing care for adults of working age results in poor detection and care for hearing loss among people from disadvantaged backgrounds. This in turn exacerbates social inequalities.
Population data shows hearing inequality
We analysed a large data set called the Household, Income and Labour Dynamics in Australia (HILDA) survey that collects information on various aspects of people’s lives, including health and hearing loss.
Using a HILDA sub-sample of 10,719 working-age Australians, we evaluated whether self-reported hearing loss was more common among people from lower socioeconomic backgrounds than for those from higher socioeconomic backgrounds between 2008 and 2018.
Relying on self-reported hearing data instead of information from hearing tests is one limitation of our paper. However, self-reported hearing tends to underestimate actual rates of hearing impairment, so the hearing loss rates we reported are likely an underestimate.
We also wanted to find out whether people from lower socioeconomic backgrounds were more likely to develop hearing loss in the long run.
Hearing care is publicly subsidised for children.
mady70/ShutterstockWe found people in the lowest income groups were more than twice as likely to have hearing loss than those in the highest income groups. Further, hearing loss was 1.5 times as common among people living in the most deprived neighbourhoods than in the most affluent areas.
For people reporting no hearing loss at the beginning of the study, after 11 years of follow up, those from a more deprived socioeconomic background were much more likely to develop hearing loss. For example, a lack of post secondary education was associated with a more than 1.5 times increased risk of developing hearing loss compared to those who achieved a bachelor’s degree or above.
Overall, men were more likely to have hearing loss than women. As seen in the figure below, this gap is largest for people of low socioeconomic status.
Why are disadvantaged groups more likely to experience hearing loss?
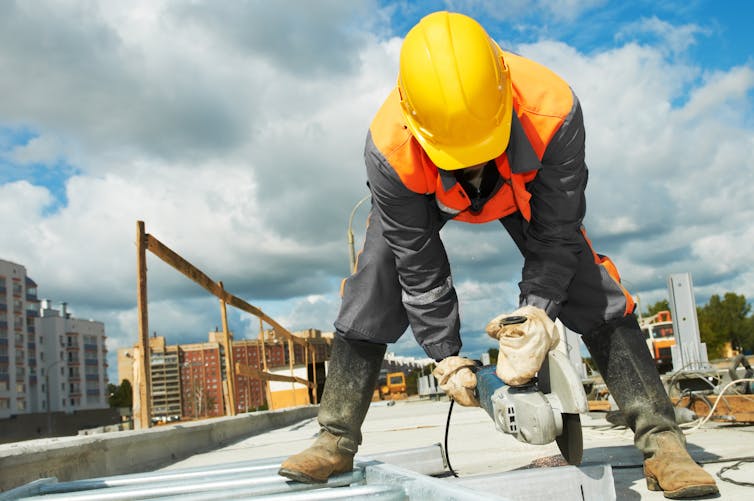
There are several possible reasons hearing loss is more common among people from low socioeconomic backgrounds. Noise exposure is one of the biggest risks for hearing loss and people from low socioeconomic backgrounds may be more likely to be exposed to damaging levels of noise in jobs in mining, construction, manufacturing, and agriculture.
Lifestyle factors which may be more prevalent in lower socioeconomic communities such as smoking, unhealthy diet, and a lack of regular exercise are also related to the risk of hearing loss.
Finally, people with lower incomes may face challenges in accessing timely hearing care, alongside competing health needs, which could lead to missed identification of treatable ear disease.
Why does this disparity in hearing loss matter?
We like to think of Australia as an egalitarian society – the land of the fair go. But nearly half of people in Australia with hearing loss are of working age and mostly ineligible for publicly funded hearing services.
Hearing aids with a private hearing care provider cost from around A$1,000 up to more than $4,000 for higher-end devices. Most people need two hearing aids.
Hearing loss might be more common in low income groups because they’re exposed to more noise at work.
Dmitry Kalinovsky/ShutterstockLack of access to affordable hearing care for working-age adults on low incomes comes with an economic as well as a social cost.
Previous economic analysis estimated hearing loss was responsible for financial costs of around $20 billion in 2019–20 in Australia. The largest component of these costs was productivity losses (unemployment, under-employment and Jobseeker social security payment costs) among working-age adults.
Providing affordable hearing care for all Australians
Lack of affordable hearing care for working-age adults from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may significantly exacerbate the impact of hearing loss among deprived communities and worsen social inequalities.
Recently, the federal government has been considering extending publicly subsidised hearing services to lower income working age Australians. We believe reforming the current government Hearing Services Program and expanding eligibility to this group could not only promote a more inclusive, fairer and healthier society but may also yield overall cost savings by reducing lost productivity.
All Australians should have access to affordable hearing care to have sufficient functional hearing to achieve their potential in life. That’s the land of the fair go.
Mohammad Nure Alam, PhD Candidate in Economics, Macquarie University; Kompal Sinha, Associate Professor, Department of Economics, Macquarie University, and Piers Dawes, Professor, School of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: