Water Bath + More Cookbook for Beginners – by Sarah Roslin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whether you want to be prepared for the next major crisis that shuts down food supply chains, or just learn a new skill, this book provides the tools!
Especially beneficial if you also grow your own vegetables, but even you just buy those… Home-canned food is healthy, contains fewer additives and preservatives, and costs less in the long run.
Roslin teaches an array of methods, including most importantly:
- fermentation and pickling
- water bath canning, and
- pressure canning.
As for what’s inside? She covers not just vegetables, but also fruit, seafood, meat… Basically, anything that can be canned.
The book explains the tools and equipment you will need as well as how to perform it safely—as well as common mistakes to avoid!
Lest we be intimidated by the task of acquiring appropriate equipment, she also walks us through what we’ll need in that regard too!
Last but not least, there’s also a (sizeable) collection of simple, step-by-step recipes, catering to a wide variety of tastes.
Bottom line: a highly valuable resource that we recommend heartily.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Topping Up Testosterone?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Testosterone Drop
Testosterone levels decline amongst men over a certain age. Exactly when depends on the individual and also how we measure it, but the age of 45 is a commonly-given waypoint for the start of this decline.
(the actual start is usually more like 20, but it’s a very small decline then, and speeds up a couple of decades later)
This has been called “the male menopause”, or “the andropause”.
Both terms are a little misleading, but for lack of a better term, “andropause” is perhaps not terrible.
Why “the male menopause” is misleading:
To call it “the male menopause” suggests that this is when men’s menstruation stops. Which for cis men at the very least, is simply not a thing they ever had in the first place, to stop (and for trans men it’s complicated, depending on age, hormones, surgeries, etc).
Why “the andropause” is misleading:
It’s not a pause, and unlike the menopause, it’s not even a stop. It’s just a decline. It’s more of an andro-pitter-patter-puttering-petering-out.
Is there a better clinical term?
Objectively, there is “late-onset hypogonadism” but that is unlikely to be taken up for cultural reasons—people stigmatize what they see as a loss of virility.
Terms aside, what are the symptoms?
❝Andropause or late-onset hypogonadism is a common disorder which increases in prevalence with advancing age. Diagnosis of late-onset of hypogonadism is based on presence of symptoms suggestive of testosterone deficiency – prominent among them are sexual symptoms like…❞
…and there we’d like to continue the quotation, but if we list the symptoms here, it won’t get past a lot of filters because of the words used. So instead, please feel free to click through:
Source: Andropause: Current concepts
Can it be safely ignored?
If you don’t mind the sexual symptoms, then mostly, yes!
However, there are a few symptoms we can mention here that are not so subjective in their potential for harm:
- Depression
- Loss of muscle mass
- Increased body fat
Depression kills, so this does need to be taken seriously. See also:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
(the above is a guide to managing depression, in yourself or a loved one)
Loss of muscle mass means being less robust against knocks and falls later in life
Loss of muscle mass also means weaker bones (because the body won’t make bones stronger than it thinks they need to be, so bone will follow muscle in this regard—in either direction)
See also:
- Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
- Protein vs Sarcopenia
- Fall Special (How to Proof Yourself Against Falls)
Increased body fat means increased risk of diabetes and heart disease, as a general rule of thumb, amongst other problems.
Will testosterone therapy help?
That’s something to discuss with your endocrinologist, but for most men whose testosterone levels are lower than is ideal for them, then yes, taking testosterone to bring them [back] to “normal” levels can make you happier and healthier (though it’s certainly not a cure-all).
See for example:
Testosterone Therapy Improves […] and […] in Hypogonadal Men
(Sorry, we’re not trying to be clickbaity, there are just some words we can’t use without encountering software problems)
Here’s a more comprehensive study that looked at 790 men aged 65 or older, with testosterone levels below a certain level. It looked at the things we can’t mention here, as well as physical function and general vitality:
❝The increase in testosterone levels was associated with significantly increased […] activity, as assessed by the Psychosexual Daily Questionnaire (P<0.001), as well as significantly increased […] desire and […] function.
The percentage of men who had an increase of at least 50 m in the 6-minute walking distance did not differ significantly between the two study groups in the Physical Function Trial but did differ significantly when men in all three trials were included (20.5% of men who received testosterone vs. 12.6% of men who received placebo, P=0.003).
Testosterone had no significant benefit with respect to vitality, as assessed by the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Fatigue scale, but men who received testosterone reported slightly better mood and lower severity of depressive symptoms than those who received placebo❞
Source: Effects of Testosterone Treatment in Older Men
We strongly recommend, by the way, when a topic is of interest to you to read the paper itself, because even the extract above contains some subjectivity, for example what is “slightly better”, and what is “no significant benefit”.
That “slightly better mood and lower severity of depressive symptoms”, for example, has a P value of 0.004 in their data, which is an order of magnitude more significant than the usual baseline for significance (P<0.05).
And furthermore, that “no significant benefit with respect to vitality” is only looking at either the primary outcome aggregated goal or the secondary FACIT score whose secondary outcome had a P value of 0.06, which just missed the cut-off for significance, and neglects to mention that all the other secondary outcome metrics for men involved in the vitality trial were very significant (ranging from P=0.04 to P=0.001)
Click here to see the results table for the vitality trial
Will it turn me into a musclebound angry ragey ‘roidmonster?
Were you that kind of person before your testosterone levels declined? If not, then no.
Testosterone therapy seeks only to return your testosterone levels to where they were, and this is done through careful monitoring and adjustment. It’d take a lot more than (responsible) endocrinologist-guided hormonal therapy to turn you into Marvel’s “Wolverine”.
Is testosterone therapy safe?
A question to take to your endocrinologist because everyone’s physiology is different, but a lot of studies do support its general safety for most people who are prescribed it.
As with anything, there are risks to be aware of, though. Perhaps the most critical risk is prostate cancer, and…
❝In a large meta-analysis of 18 prospective studies that included over 3500 men, there was no association between serum androgen levels and the risk of prostate cancer development
For men with untreated prostate cancer on active surveillance, TRT remains controversial. However, several studies have shown that TRT is not associated with progression of prostate cancer as evidenced by either PSA progression or gleason grade upstaging on repeat biopsy.
Men on TRT should have frequent PSA monitoring; any major change in PSA (>1 ng/mL) within the first 3-6 months may reflect the presence of a pre-existing cancer and warrants cessation of therapy❞
Those are some select extracts, but any of this may apply to you or your loved one, we recommend to read in full about this and other risks:
Risks of testosterone replacement therapy in men
See also: Prostate Health: What You Should Know
Beyond that… If you are prone to baldness, then taking testosterone will increase that tendency. If that’s a problem for you, then it’s something to know about. There are other things you can take/use for that in turn, so maybe we’ll do a feature on those one of these days!
For now, take care!
Share This Post
-
Are You Stuck Playing These Three Roles in Love?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The psychology of Transactional Analysis holds that our interpersonal dynamics can be modelled in the following fashion:
The roles
- Child: vulnerable, trusting, weak, and support-seeking
- Parent: strong, dominant, responsible—but also often exhausted and critical
- Adult: balanced, thoughtful, creative, and kind
Ideally we’d be able to spend most of our time in “Adult” mode, and occasionally go into “Child” or “Parent” mode when required, e.g. child when circumstances have rendered us vulnerable and we need help; parent when we need to go “above and beyond” in the pursuit of looking after others. That’s all well and good and healthy.
However, in relationships, often it happens that partners polarize themselves and/or each other, with one shouldering all of the responsibility, and the other willfully losing their own agency.
The problem lies in that either role can be seductive—on the one hand, it’s nice to be admired and powerful and it’s a good feeling to look after one’s partner; on the other hand, it’s nice to have someone who will meet your every need. What love and trust!
Only, it becomes toxic when these roles stagnate, and each forgets how to step out of them. Each can become resentful of the other (for not pulling their weight, on one side, and for not being able to effortlessly solve all life problems unilaterally and provide endlessly in both time and substance, on the other), digging in to their own side and exacerbating the less healthy qualities.
As to the way out? It’s about self-exploration and mutual honesty—and mutual support:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Further reading
While we haven’t (before today) written about TA per se, we have previously written about AT (Attachment Theory), and on this matter, the two can overlap, where certain attachment styles can result in recreating parent/child/adult dynamics:
How To Leverage Attachment Theory In Your Relationship ← this is about understanding and recognizing attachment styles, and then making sure that both you and your partner(s) are armed with the necessary knowledge and understanding to meet each other’s needs.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Creatine, Genomic Screening, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In this week’s health news…
Creatine: no difference vs control at 5g/day
A study found, as the title suggests, no difference between creatine and placebo, at the usual dose of 5g/day, while doing a supervised resistance training program.
This was a 12-week trial, and in the first week, the creatine group put on an average of 0.5kg more lean (i.e. not fat) body mass than the control group, however, as this quickly equalized after the first week, it is assumed that the brief extra weight gain was water weight (creatine promotes water retention, especially in the initial phase).
However, it is still possible that it may promote weight gain at higher doses.
This study was done with adult participants under the age of 50; we’ve noted before that it is generally young people who use creatine for bodybuilding, so in principle, this should have been ideal for that, but it wasn’t.
Read in full: Sports supplement creatine makes no difference to muscle gains, trial finds
Related: Creatine’s Brain Benefits Increase With Age ← this, on the other hand, does work—but only for older adults.
Genomics & disease risk: what to know
In a recent study evaluation, 175,500 participants were screened, and 1 in 30 received medically important genetic results. More than 90% of those found to have a genetic risk were previously unaware of it.
This is important, because most current genetic risk assessment for patients is based on personal and family history, which often misses a lot of data due to barriers to care or lack of family history.
Genomic screening helps close these gaps:
Read in full: Genomic screening is important in identifying disease risk, study finds
Related: Do You Have A Personalized Health Plan? (Here’s How)
FDA-Approved Antivirals (Not Vaccines) Ineffective Against H5N1
The H5N1 avian influenza outbreak is now rife amongst dairy farms, with the virus found in cows’ milk and infecting farmworkers. Researchers studied potential treatments, revealing two FDA-approved antivirals (baloxavir and oseltamivir) were generally ineffective in treating severe H5N1 infections.
Oral infections per raw milk consumption, were the most severe and hardest to treat, and the virus spread quickly to the blood and brain (when the infection is respiratory, it is much slower to spread from the respiratory tract).
It wasn’t a complete loss, though:
- Eye infections were better controlled with baloxavir, achieving a 100% survival rate compared to 25% with oseltamivir.
- For nasal infections, baloxavir reduced viral levels better but still allowed the virus to reach the brain. Survival rates were 75% for baloxavir and 50% for oseltamivir.
The researchers in question are urging preventative measures as being of critical importance, given the difficulty of treatment:
Read in full: Current antivirals likely less effective against severe infection caused by bird flu virus in cows’ milk
Related: Bird Flu: Children At High Risk; Older Adults Not So Much
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Total Recovery – by Dr. Gary Kaplan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, know: Dr. Kaplan is an osteopath, and as such, will be mostly approaching things from that angle. That said, he is also board certified in other things too, including family medicine, so he’s by no means a “one-trick pony”, nor are there “when your only tool is a hammer, everything starts to look like a nail” problems to be found here. Instead, the scope of the book is quite broad.
Dr. Kaplan talks us through the diagnostic process that a doctor goes through when presented with a patient, what questions need to be asked and answered—and by this we mean the deeper technical questions, e.g. “what do these symptoms have in common”, and “what mechanism was at work when the pain become chronic”, not the very basic questions asked in the initial debriefing with the patient.
He also asks such questions (and questions like these get chapters devoted to them) as “what if physical traumas build up”, and “what if physical and emotional pain influence each other”, and then examines how to interrupt the vicious cycles that lead to deterioration of one’s condition.
The style of the book is very pop-science and often narrative in its presentation, giving lots of anecdotes to illustrate the principles. It’s a “sit down and read it cover-to-cover” book—or a chapter a day, whatever your preferred pace; the point is, it’s not a “dip directly to the part that answers your immediate question” book; it’s not a textbook or manual.
Bottom line: a lot of this work is about prompting the reader to ask the right questions to get to where we need to be, but there are many illustrative possible conclusions and practical advices to be found and given too, making this a useful read if you and/or a loved one suffers from chronic pain.
Click here to check out Total Recovery, and solve your own mysteries!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
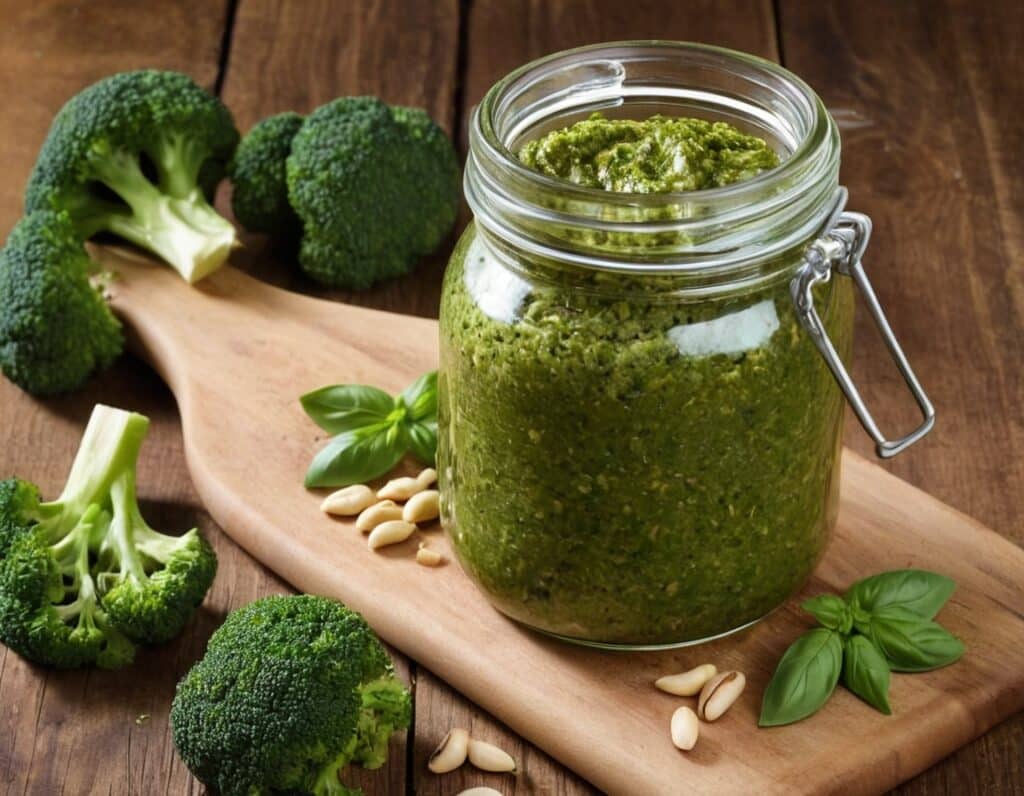
Superfood Broccoli Pesto
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cruciferous vegetables have many health benefits of their own (especially: a lot of anticancer benefits). But, it can be hard to include them in every day’s menu, so this is just one more way that’ll broaden your options! It’s delicious mixed into pasta, or served as a dip, or even on toast.
You will need
- 4 cups small broccoli florets
- 1 cup fresh basil leaves
- ½ cup pine nuts
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 3 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red pepper flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Steam the broccoli for 3–5 minutes. Allow to cool.
2) Blend the pine nuts, garlic, lemon juice, and nutritional yeast.
3) Add the broccoli, basil, olive oil, black pepper, red pepper, and MSG or salt, and blend in the food processor again until well-combined.
4) Serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Broccoli vs Cauliflower – Which is Healthier?
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Herbs for (Evidence-Based) Health & Healing ← Basil features here! It’s easy to think that medicinal herbs have to be some kind of arcane obscurity, but it’s often not so.
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← Black pepper, red pepper, and garlic all feature here
- All About Olive Oil: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Some Friendships Last And Others Don’t
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Friendships matter a lot, playing a significant role in our wellbeing, physical as well as mental. They bring additional meaning to our lives, help us cope with setbacks, and hopefully will be at our side through the highs and lows of life. And yet, for something that’s in principle good for everyone involved, there can be problems:
Friend to the end?
Firstly, some people find it harder to make (and then further deepen) friendships with others, which can be for a whole host of reasons.
Approaching new people can feel intimidating, but it’s a common struggle. Research shows that people often underestimate how much others enjoy their company, a phenomenon known as the “liking gap.” By reminding ourselves that others are likely to appreciate our presence and expecting to be well-received (the “acceptance prophecy”), we can approach social interactions with greater confidence.
As relationships grow, they often deepen through companionship and closeness:
- Companionship arises from shared hobbies, interests, or values, and it builds rapport.
- Closeness involves sharing thoughts, feelings, and experiences, which can build intimacy together.
An important key to these is consistency, which—whether through regular chats, honoring plans, or showing support—helps strengthen bonds, even in long-distance friendships (something often considered a barrier to closeness).
Even the strongest friendships can face challenges, of course. Conflicts may arise from a lack of support during difficult moments, or worse, betrayal. Or it could all be a misunderstanding. These situations are best addressed through honest, non-judgmental conversations. Avoiding defensiveness or accusations, and instead focusing on sharing feelings and understanding the other person’s perspective, can turn these tough discussions into opportunities for growth and stronger connections.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: