The Science of Nutrition – by Rhiannon Lambert
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While there are a lot of conflicting dietary approaches out there, the science itself is actually fairly cohesive in most regards. This book does a lot of what we do here at 10almonds, and presents the science in a clear fashion without having any particular agenda to push.
The author is a nutritionist (BSc, MSc, RNutr) and therefore provides an up-to-date evidence-based approach for eating.
As a result, the only part of this book that brings it down in this reviewer’s opinion is the section on Intermittent Fasting. Being not strictly about nutrition, she has less expertise on that topic, and it shows.
The information is largely presented in double-page spreads each answering a particular question. Because of this, and the fact there are colorful graphic representations of information too, we do recommend the print version over Kindle*.
Bottom line: if you like the notion of real science being presented in a clear and simple fashion (we like to think our subscribers do!), then you’ll surely enjoy this book.
Click here to check out the Science of Nutrition, and get a clear overview!
*Writer’s note: I realize I’ve two days in a row recommended this (yesterday because there are checkboxes to check, worksheets to complete, etc), but it’s not a new trend; just how it happened to be with these two books. I love my Kindle dearly, but sometimes print has the edge for one reason or another!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
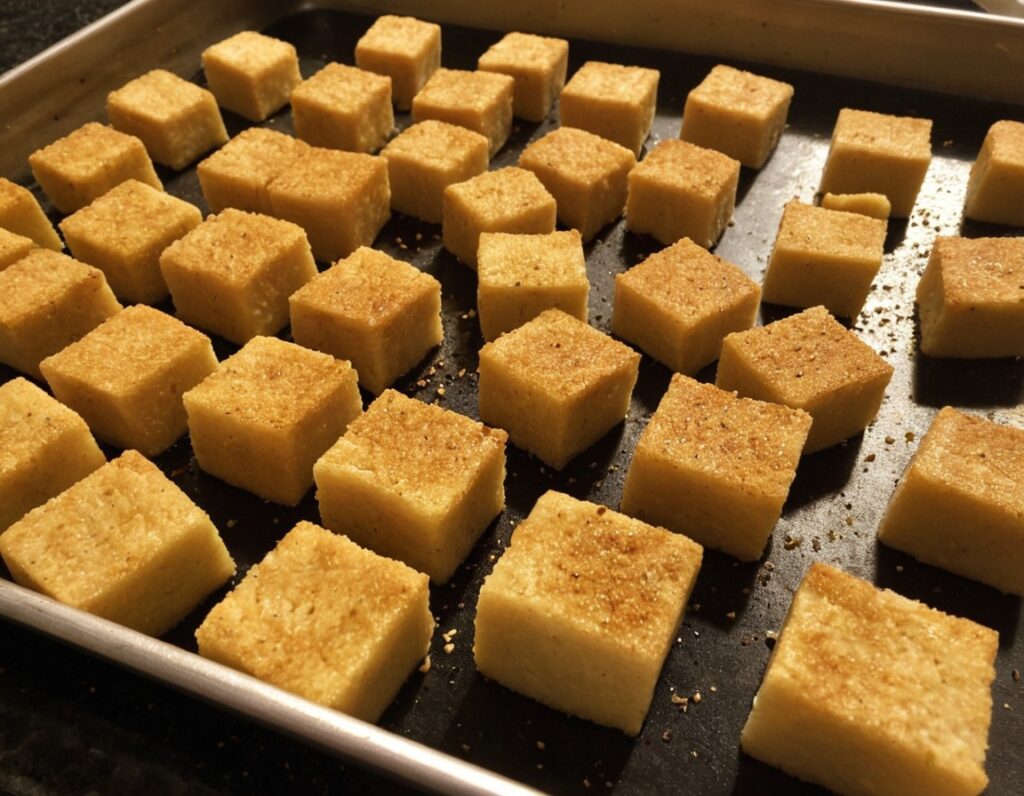
Basic Baked Tofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One of the main criticisms of tofu is that it is tasteless. Well, so is flour, but you’re not supposed to eat it plain, and the same goes for tofu. It’s a blank canvas that you get to decide what to do with—not to mention, it’s a canvas that’s very high in protein, and is a complete protein too, containing all essential amino acids. Anyway, here’s a starter recipe that elevates tofu from “nutrition” to “nutritious tasty snack”!
We were going to do a fancier recipe today, but considered that it might be judicious to cover this basic element first, that can be incorporated into a larger recipe later, a bit like we have done with recipes such as our Tasty Versatile Rice, and Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese (amongst others).
You will need
- 1 block of extra-firm tofu; these are quite standardized in size; it should be about 12oz; don’t worry if it’s a little more or less.
- 2 tbsp arrowroot powder (or potato starch if you don’t have arrowroot)
- 1½ tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: ½ tsp garlic powder
- Optional: ½ tsp ground turmeric
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 425ºF / 220ºC.
2) Press the tofu for about 15 minutes (to remove excess moisture), using a tofu press if you have one. If you don’t, then here is an example product on Amazon, or alternatively, you can go with the time-honored tradition of cutting the tofu lengthways into slabs, and wrapping it in a lint-free kitchen towel or muslin cloth, and pressing it with heavy books. We don’t recommend pressing for more than about 15 minutes, as you are going to bake the tofu so you don’t want it too dry going in.
3) Cut the tofu into cubes. Size is up to you, but half-inch cubes are very respectable.
4) Combine the tofu cubes in a big bowl with the oil and seasonings, including the nutritional yeast but not the arrowroot powder or potato starch yet. You will need to toss them gently (very gently; they are fragile!) to combine.
5) Add the arrowroot powder or potato starch, and again toss gently to combine. We do this last, because it would stop the other things from sticking properly if we did it earlier.
6) Arrange the tofu on a baking tray lined with baking paper, in a single layer so that the cubes don’t touch. Bake for 15 minutes, turn them over, and bake for a further 15 minutes on the other side. They should now be golden and crisp, but if they’re not, just give them a little more time.
7) Serve as a snack, or set aside for whatever else you’re going to do with them in a larger more complex recipe.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Yes, you still need to use sunscreen, despite what you’ve heard on TikTok
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Summer is nearly here. But rather than getting out the sunscreen, some TikTokers are urging followers to chuck it out and go sunscreen-free.
They claim it’s healthier to forgo sunscreen to get the full benefits of sunshine.
Here’s the science really says.
Karolina Grabowska/Pexels How does sunscreen work?
Because of Australia’s extreme UV environment, most people with pale to olive skin or other risk factors for skin cancer need to protect themselves. Applying sunscreen is a key method of protecting areas not easily covered by clothes.
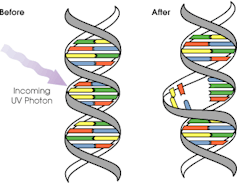
Sunscreen works by absorbing or scattering UV rays before they can enter your skin and damage DNA or supportive structures such as collagen.
When UV particles hit DNA, the excess energy can damage our DNA. This damage can be repaired, but if the cell divides before the mistake is fixed, it causes a mutation that can lead to skin cancers.
The energy from a particle of UV (a photon) causes DNA strands to break apart and reconnect incorrectly. This causes a bump in the DNA strand that makes it difficult to copy accurately and can introduce mutations. NASA/David Herring The most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Melanoma is less common, but is the most likely to spread around the body; this process is called metastasis.
Two in three Australians will have at least one skin cancer in their lifetime, and they make up 80% of all cancers in Australia.
Around 99% of skin cancers in Australia are caused by excessive exposure to UV radiation.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation also affects the appearance of your skin. UVA rays are able to penetrate deep into the skin, where they break down supportive structures such as elastin and collagen.
This causes signs of premature ageing, such as deep wrinkling, brown or white blotches, and broken capillaries.
Sunscreen can help prevent skin cancers
Used consistently, sunscreen reduces your risk of skin cancer and slows skin ageing.
In a Queensland study, participants either used sunscreen daily for almost five years, or continued their usual use.
At the end of five years, the daily-use group had reduced their risk of squamous cell carcinoma by 40% compared to the other group.
Ten years later, the daily use group had reduced their risk of invasive melanoma by 73%
Does sunscreen block the health-promoting properties of sunlight?
The answer is a bit more complicated, and involves personalised risk versus benefit trade-offs.
First, the good news: there are many health benefits of spending time in the sun that don’t rely on exposure to UV radiation and aren’t affected by sunscreen use.
Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not all light. Ron Lach/Pexels Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not visible light or infrared light (which we feel as heat). And importantly, some of the benefits of sunlight are obtained via the eyes.
Visible light improves mood and regulates circadian rhythm (which influences your sleep-wake cycle), and probably reduces myopia (short-sightedness) in children.
Infrared light is being investigated as a treatment for several skin, neurological, psychiatric and autoimmune disorders.
So what is the benefit of exposing skin to UV radiation?
Exposing the skin to the sun produces vitamin D, which is critical for healthy bones and muscles.
Vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly common among Australians, peaking in Victoria at 49% in winter and being lowest in Queensland at 6% in summer.
Luckily, people who are careful about sun protection can avoid vitamin D deficiency by taking a supplement.
Exposing the skin to UV radiation might have benefits independent of vitamin D production, but these are not proven. It might reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis or cause release of a chemical that could reduce blood pressure. However, there is not enough detail about these benefits to know whether sunscreen would be a problem.
What does this mean for you?
There are some benefits of exposing the skin to UV radiation that might be blunted by sunscreen. Whether it’s worth foregoing those benefits to avoid skin cancer depends on how susceptible you are to skin cancer.
If you have pale skin or other factors that increase you risk of skin cancer, you should aim to apply sunscreen daily on all days when the UV index is forecast to reach 3.
If you have darker skin that rarely or never burns, you can go without daily sunscreen – although you will still need protection during extended times outdoors.
For now, the balance of evidence suggests it’s better for people who are susceptible to skin cancer to continue with sun protection practices, with vitamin D supplementation if needed.
Katie Lee, PhD Candidate, Dermatology Research Centre, The University of Queensland and Rachel Neale, Principal research fellow, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
I’m So Effing Tired – by Dr. Amy Shah
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s easy sometimes to feel like we know more or less what we should be doing… If only we had the energy to get going!
- We know we want a better diet… But we don’t have the time/energy to cook so will go for the quickest option even when it’s not the best?
- We know we should exercise… But feel we just need to crash out on the couch for a bit first?
- We would dearly love to get better sleep… But our responsibilities aren’t facilitating that?
…and so on. Happily, Dr. Amy Shah is here with ways to cut through the Gordian Knot that is this otherwise self-perpetuating cycle of exhaustion.
Most of the book is based around tackling what Dr. Shah calls “the energy trifecta“:
- Hormone levels
- Immune system
- Gut health
You’ll note (perhaps with relief) that none of these things require an initial investment of energy that you don’t have… She’s not asking you to hit the gym at 5am, or magically bludgeon your sleep schedule into its proper place, say.
Instead, what she gives is practical, actionable, easy changes that don’t require much effort, to gently slide us back into the fast lane of actually having energy to do stuff!
In short: if you’ve ever felt like you’d like to implement a lot of very common “best practice” lifestyle advice, but just haven’t had the energy to get going, there’s more value in this handbook than in a thousand motivational pep talks.
Click here to check out “I’m So Effing Tired” and get on a better track of life!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
This Is Your Brain on Music – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Music has sometimes been touted as having cognitive benefits, by its practice and even by the passive experience of it. But what’s the actual science of it?
Dr. Levitin, an accomplished musician and neuroscientist, explores and explains.
We learn about how music in all likelihood allowed our ancestors to develop speech, something that set us apart (and ahead!) as a species. How music was naturally-selected-for in accordance with its relationship with health. How processing music involves almost every part of the brain. How music pertains specifically to memory. And more.
As a bonus, as well as explaining a lot about our brain, this book offers those of us with limited knowledge of music theory a valuable overview of the seven main dimensions of music, too.
Bottom line: if you’d like to know more about the many-faceted relationship between music and cognitive function, this is a top-tier book about such.
Click here to check out “This Is Your Brain On Music”, and learn more about yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vodka vs Beer – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing vodka to beer, we picked the vodka.
Why?
As you might have guessed, neither are exactly healthy. But one of them is relatively, and we stress relatively, less bad than the other.
In the category of nutrients, vodka is devoid of nutrients, and beer has small amounts of some vitamins and minerals—but the amounts are so small, that you would need to drink yourself to death before benefiting from them meaningfully. And while beer gets touted as “liquid bread”, it really isn’t. A thousand years ago it will have been a lot less alcoholic and more carby, but even then, it wasn’t a health product aside from that it provided a way of making potentially contaminated water safer to drink.
In the category of carbohydrates, vodka nominally has none, due to the distillation process, and beer has some. Glycemic index websites often advise that the GI of beers, wines, and spirits can’t be measured as their carb content is not sufficient to get a meaningful sample, but diabetes research tells a more useful story:
Any alcoholic drink will generally cause a brief drop in blood sugars, followed by a spike. This happens because the liver prioritises metabolizing alcohol over producing glycogen, so it hits pause on the sugar metabolism and then has a backlog to catch up on. In the case of alcoholic drinks that have alcohol and carbs, this will be more pronounced—so this means that the functional glycemic load of beer is higher.
That’s a point in favor of vodka.
Additionally, in terms of the alcohol content, correctly-distilled vodka’s alcohol is pure ethanol, while beer will contain an amount of methanol that will vary per beer, but an illustrative nominal figure could be about 16mg/L. Methanol is more harmful than ethanol.
So that’s another point in favor of vodka.
Once again, neither drink is healthy; both are distinctly unhealthy. But unit for unit, beer is the least healthy of the two, making vodka the lesser of two evils.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Can We Drink To Good Health? (answer: we cannot, but this was about alcohol’s proposed heart-healthy benefits)
- Guinness Is Good For You* (it isn’t, but this was the long-time slogan and marketing campaign that fooled many)
- How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Eat To Lose Belly Fat (3 Stages)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Belly fat is easier to gain than it is to lose, and it’s absolutely something that needs more attention in the kitchen than in the gym. Here’s one way of doing it:
By the numbers
First note: this video is by a man, and judging by the numbers mentioned, assumes that the viewer is also a man. An end goal of 10% body fat is a little on the low side for men, and would be dangerous for women. The magic 15% mark that he mentions as being a point where various metabolic things change, is more like 20% for women. All assuming normal hormones, of course, since it is hormones that direct this.
Healthy body fat percentages are (assuming normal hormones) in the range of 20–25% for women and 15–20% for men.
With that in mind…
The idea of this approach is to lose enough weight that your body gets rid of even the most awkward bits (e.g: visceral belly fat, which will often be the last to get used) before, if desired, then maintaining at a slightly higher body fat percentage.
- Stage 1: count calories (we don’t usually recommend this at 10almonds, but he does, so we’re reporting it here) and use your weight in pounds multiplied by 12 to give your daily calorie target. Make the majority of your diet foods that have a large volume:calorie ratio, such as fruits and vegetables, in order to feel full without overloading your metabolism. He has an interesting method of calculating a protein target; instead of the usual “1g/kg of body weight”, he says 1g per cm of height. Doing this consistently should get you to 15% body fat (so, 20%, for women).
- Stage 2: start counting fat intake too, and aim for 20–25% of your daily calories as fat. Continue, aside from that, with what you were doing in Stage 1. Doing this consistently should get you to 12% body fat (so, about 17%, for women). Being under the usual healthy level for a while should allow your body to start getting rid of visceral fat.
- Stage 3: track everything, levelling up your precision (no more “this little thing doesn’t count”), and planning ahead when it comes to social events etc. Doing this consistently should yet you to 10% body fat (so, about 15%, for women). This stage has a good chance of making most people miserable, so if that happens, consider the benefits of going back to the healthier 15% body fat (men) or 20% (women).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← without calorie-counting! We prefer this 😉
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: