Superfood Soba Noodle Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This Japanese dish is packed with nutrients and takes very little preparation time, involving only one cooked ingredient, and a healthy one at that!
You will need
- 8 oz dried soba noodles
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp avocado oil
- 2 tsp soy sauce
- ¼ cucumber, cut into thin batons (don’t peel it first)
- ½ carrot, grated (don’t peel it first)
- 6 cherry tomatoes, halved (you wouldn’t peel these, right? Please don’t)
- ½ red onion, finely sliced (ok, this one you can peel first! Please do)
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tsp crushed red chili flakes
- Garnish: fresh parsley, chopped
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the soba noodles (boil in water for 10 mins or until soft). Rinse with cold water (which lowers the glycemic index further, and also we want them cold anyway) and set aside.
2) Make the dressing by blending the garlic, avocado oil, and soy cauce. Set it aside.
3) Assemble the salad by thoroughly but gently mixing the noodles with the cucumber, carrot, tomatoes, and onion. Add the dressing, the chia seeds, and the chili flakes, and toss gently to combine.
4) Serve, adding the parsley garnish.
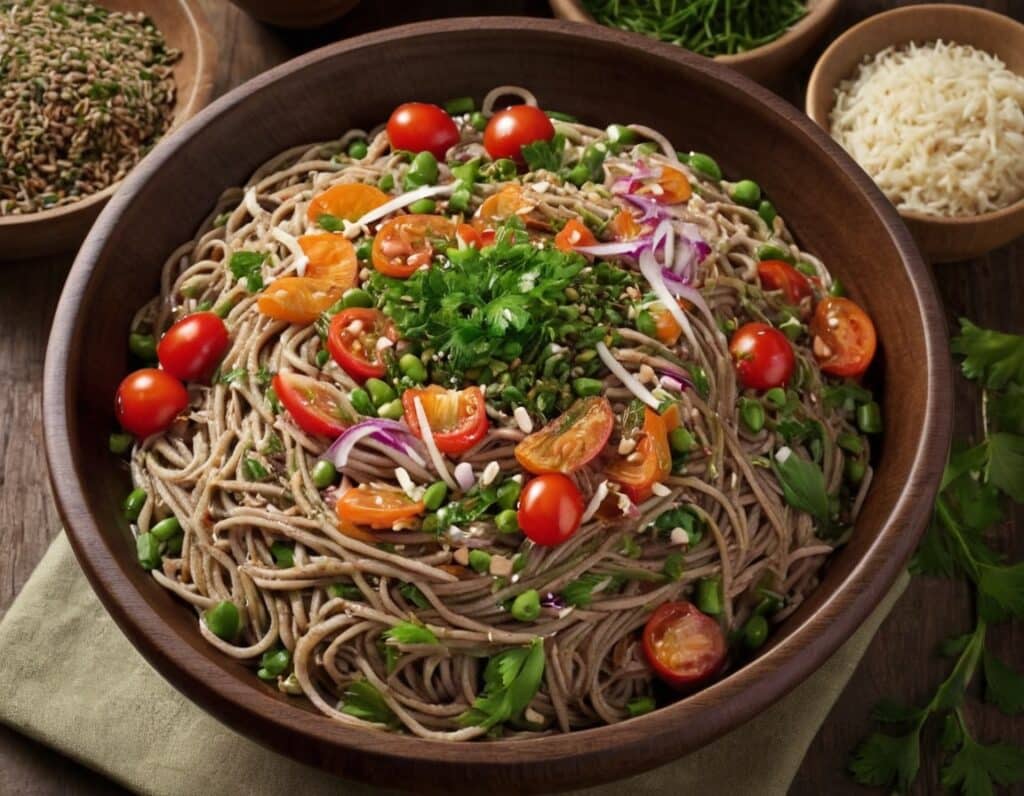

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Rice vs Buckwheat – Which is Healthier? ← soba noodles are made from buckwheat, which by the way is also a good source of rutin, which can strengthen blood vessel walls against damage, reducing the risk of atheroma
- Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Coca-Cola vs Diet Coke – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Coca-Cola to Diet Coke, we picked the Diet Coke.
Why?
While the Diet Coke is bad, the Coca-Cola has mostly the same problems plus sugar.
The sugar in a can of Coca-Cola is 39g high-fructose corn syrup (the worst kind of sugar yet known to humanity), and of course it’s being delivered in liquid form (the most bioavailable way to get, which in this case, is bad).
To put those 39g into perspective, the daily recommended amount of sugar is 36g for men or 25g for women, according to the AHA.
The sweetener in Diet Coke is aspartame, which has had a lot of health risk accusations made against it, most of which have not stood up to scrutiny, and the main risk it does have is “it mimics sugar too well” and it can increase cravings for sweetness, and therefore higher consumption of sugars in other products. For this reason, the World Health Organization has recommended to simply reduce sugar intake without looking to artificial sweeteners to help.
Nevertheless, aspartame has been found safe (in moderate doses; the upper tolerance level would equate to more than 20 cans of diet coke per day) by food safety agencies ranging from the FDA to the EFSA, based on a large body of science.
Other problems that Diet Coke has are present in Coca-Cola too, such as its acidic nature (bad for tooth enamel) and gassy nature (messes with leptin/ghrelin balance).
Summary: the Diet Coke is relatively less unhealthy, but is still bad in numerous ways, and remains best avoided.
Read more:
Share This Post
-
Exercise Less, Move More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Exercise Less, Move More
Today we’re talking about Dr. Rangan Chatterjee. He’s a medical doctor with decades of experience, and he wants us all to proactively stay in good health, rather than waiting for things to go wrong.
Great! What’s his deal?
Dr. Chatterjee advises that we take care of the following four pillars of good health:
- Relaxation
- Food
- Movement
- Sleep
And, they’re not in this order at random. Usually advice starts with diet and exercise, doesn’t it?
But for Dr. Chatterjee, it’s useless to try to tackle diet first if one is stressed-to-death by other things. As for food next, he knows that a good diet will fuel the next steps nicely. Speaking of next steps, a day full of movement is the ideal setup to a good night’s sleep—ready for a relaxing next day.
Relaxation
Here, Dr. Chatterjee advises that we go with what works for us. It could be meditation or yoga… Or it could be having a nice cup of tea while looking out of the window.
What’s most important, he says, is that we should take at least 15 minutes per day as “me time”, not as a reward for when we’ve done our work/chores/etc, but as something integrated into our routine, preferably early in the day.
Food
There are no grand surprises here: Dr. Chatterjee advocates for a majority plant-based diet, whole foods, and importantly, avoiding sugar.
He’s also an advocate of intermittent fasting, but only so far as is comfortable and practicable. Intermittent fasting can give great benefits, but it’s no good if that comes at a cost of making us stressed and suffering!
Movement
This one’s important. Well, they all are, but this one’s particularly characteristic to Dr. Chatterjee’s approach. He wants us to exercise less, and move more.
The reason for this is that strenuous exercise will tend to speed up our metabolism to the point that we will be prompted to eat high calorie quick-energy foods to compensate, and when we do, our body will rush to store that as fat, understanding (incorrectly) that we are in a time of great stress, because why else would we be exerting ourselves that much?
Instead, he advocates for building as much natural movement into our daily routine as possible. Walking more, taking the stairs, doing the gardening/housework.
That said, he does also advise some strength-training on a daily basis—bodyweight exercises like squats and lunges are top of his list.
Sleep
Here, aside from the usual “sleep hygiene” advices (dark cool room, fresh bedding, etc), he also advises we do as he does, and take an hour before bedtime as a purely wind-down time. In gentle lighting, perhaps reading (not on a bright screen!), for example.
Ready to start the next day, relaxed and ready to go.
If you’d like to know more about Dr. Chatterjee’s approach…
You can check out his:
If you don’t know where to start, we recommend the blog! It has a lot of guests there too, including Wim Hof, Gabor Maté, Mindy Pelz, and come to think of it, a lot of other people we’ve also featured ideas from previously!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Savory Protein Crêpe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pancakes have a bad reputation healthwise, but they don’t have to be so. Here’s a very healthy crêpe recipe, with around 20g of protein per serving (which is about how much protein most people’s body’s can use at one sitting) and a healthy dose of fiber too:
You will need
Per crêpe:
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend oat milk for this)
- 2 oz chickpea flour (also called garbanzo bean flour, or gram flour)
- 1 tsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp ras el-hanout (optional but tasty and contains an array of beneficial phytochemicals)
- 1 tsp dried mixed herbs
- ⅛ tsp MSG or ¼ tsp low-sodium salt
For the filling (also per crêpe):
- 6 cherry tomatoes, halved
- Small handful baby spinach
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix the dry crêpe ingredients in a bowl, and then stir in the milk, whisking to mix thoroughly. Leave to stand for at least 5 minutes.
2) Meanwhile, heat a little olive oil in a skillet, add the tomatoes and fry for 1 minute, before adding the spinach, stirring, and turning off the heat. As soon as the spinach begins to wilt, set it aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil either in the same skillet (having been carefully wiped clean) or a crêpe pan if you have one, and pour in a little of the batter you made, tipping the pan so that it coats the pan evenly and thinly. Once the top is set, jiggle the pan to see that it’s not stuck, and then flip your crêpe to finish on the other side.
If you’re not confident of your pancake-tossing skills, or your pan isn’t good enough quality to permit this, you can slide it out onto a heatproof chopping board, and use that to carefully turn it back into the pan to finish the other side.
4) Add the filling to one half of the crêpe, and fold it over, pushing down at the edges with a spatula to make a seal, cooking for another 30 seconds or so. Alternatively, you can just serve a stack of crêpes and add the filling at the table, folding or rolling per personal preference:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Best 4 Pool Exercises to Strengthen Your Core & Tone Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of people don’t love working on their core strength, but exercising in the pool can make it a lot more enjoyable, as well as minimizing risk of injury.
Dr Alyssa Kuhn, arthritis specialist, also advises “being in the water also helps to control for balance and can offload the joints so they aren’t as painful”:
The gentlest exercise
The specific exercises she recommends are:
Wood Chops
Stagger your feet, clasp your hands, and submerge them in the water. Now, move your hands diagonally from one side to the other. This engages your core and balance using water resistance. Perform 10–20 reps per side, exhaling on the hardest part.
Front Kick with Opposite Arm Press
Kick one leg forward while pushing the opposite arm out or overhead—higher kicks increase difficulty by requiring more balance. If balance isn’t sufficient for you yet, hold onto the pool wall if needed. Either way, engage the core to lift the leg. Do 20–30 reps alternating sides.
Wall Push-Ups
Place your hands on the pool wall, shoulder-width apart. Keep feet together and hips slightly tucked for core engagement. Next, move your chest toward the wall and push back while maintaining a straight body—avoid arching your back. Do 10–20 reps.
Arm Circles
Stand with your feet wider than shoulder-width. Clasp your hands, extend your arms, and submerge them in the water. Make large circular motions for resistance training. This can be done with straight or bent arms for different difficulty levels. Do 10–20 circles in each direction.
For more on each of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Osteoporosis & Exercises: Which To Do (And Which To Avoid)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
This Book May Save Your Life – by Dr. Karan Rajan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The title is a bold sell, but the book does include a lot of information about what can go wrong in your body, and how those things can be avoided.
What it’s not: a reiteration of Dr. Michael Greger’s “How Not To Die“. It’s not dense medical information, and it doesn’t cite papers at a rate of ten per page.
What it is: an easy-reading tour guide of the human body and its many quirks and foibles, and how we can leverage those to our benefit. On which note…
Hopefully, your insides will never see the light of day, but this author is a general surgeon and as such, is an experienced and well-qualified tour guide. Here, we learn about everything from the long and interesting journey through our gut, to the unique anatomical features and liabilities of the brain. From the bizarre oddities of the genitals, to things most people don’t know about the process of death.
The style of the book is very casual, with lots of short sections (almost mini chapters-within-chapters, really) making for very light reading—and certainly enjoyable reading too, unless you are inclined to squeamishness.
Bottom line: in honesty, the book is more informative than it is instructional, though it does contain the promised health tips too. With that in mind, it’s a very enjoyable and educational read, and we do recommend it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No, your aches and pains don’t get worse in the cold. So why do we think they do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s cold and wet outside. As you get out of bed, you can feel it in your bones. Your right knee is flaring up again. That’ll make it harder for you to walk the dog or go to the gym. You think it must be because of the weather.
It’s a common idea, but a myth.
When we looked at the evidence, we found no direct link between most common aches and pains and the weather. In the first study of its kind, we found no direct link between the temperature or humidity with most joint or muscle aches and pains.
So why are so many of us convinced the weather’s to blame? Here’s what we think is really going on.
fongbeerredhot/Shutterstock Weather can be linked to your health
The weather is often associated with the risk of new and ongoing health conditions. For example, cold temperatures may worsen asthma symptoms. Hot temperatures increase the risk of heart problems, such as arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat), cardiac arrest and coronary heart disease.
Many people are also convinced the weather is linked to their aches and pains. For example, two in every three people with knee, hip or hand osteoarthritis say cold temperatures trigger their symptoms.
Musculoskeletal conditions affect more than seven million Australians. So we set out to find out whether weather is really the culprit behind winter flare-ups.
What we did
Very few studies have been specifically and appropriately designed to look for any direct link between weather changes and joint or muscle pain. And ours is the first to evaluate data from these particular studies.
We looked at data from more than 15,000 people from around the world. Together, these people reported more than 28,000 episodes of pain, mostly back pain, knee or hip osteoarthritis. People with rheumatoid arthritis and gout were also included.
We then compared the frequency of those pain reports between different types of weather: hot or cold, humid or dry, rainy, windy, as well as some combinations (for example, hot and humid versus cold and dry).
Bad back on a cold day? We wanted to know if the weather was really to blame. Pearl PhotoPix/Shutterstock What we found
We found changes in air temperature, humidity, air pressure and rainfall do not increase the risk of knee, hip or lower back pain symptoms and are not associated with people seeking care for a new episode of arthritis.
The results of this study suggest we do not experience joint or muscle pain flare-ups as a result of changes in the weather, and a cold day will not increase our risk of having knee or back pain.
In order words, there is no direct link between the weather and back, knee or hip pain, nor will it give you arthritis.
It is important to note, though, that very cold air temperatures (under 10°C) were rarely studied so we cannot make conclusions about worsening symptoms in more extreme changes in the weather.
The only exception to our findings was for gout, an inflammatory type of arthritis that can come and go. Here, pain increased in warmer, dry conditions.
Gout has a very different underlying biological mechanism to back pain or knee and hip osteoarthritis, which may explain our results. The combination of warm and dry weather may lead to increased dehydration and consequently increased concentration of uric acid in the blood, and deposition of uric acid crystals in the joint in people with gout, resulting in a flare-up.
Why do people blame the weather?
The weather can influence other factors and behaviours that consequently shape how we perceive and manage pain.
For example, some people may change their physical activity routine during winter, choosing the couch over the gym. And we know prolonged sitting, for instance, is directly linked to worse back pain. Others may change their sleep routine or sleep less well when it is either too cold or too warm. Once again, a bad night’s sleep can trigger your back and knee pain.
Likewise, changes in mood, often experienced in cold weather, trigger increases in both back and knee pain.
So these changes in behaviour over winter may contribute to more aches and pains, and not the weather itself.
Believing our pain will feel worse in winter (even if this is not the case) may also make us feel worse in winter. This is known as the nocebo effect.
When it’s cold outside, we may be less active. Anna Nass/Shutterstock What to do about winter aches and pains?
It’s best to focus on risk factors for pain you can control and modify, rather than ones you can’t (such as the weather).
You can:
- become more physically active. This winter, and throughout the year, aim to walk more, or talk to your health-care provider about gentle exercises you can safely do at home, with a physiotherapist, personal trainer or at the pool
- lose weight if obese or overweight, as this is linked to lower levels of joint pain and better physical function
- keep your body warm in winter if you feel some muscle tension in uncomfortably cold conditions. Also ensure your bedroom is nice and warm as we tend to sleep less well in cold rooms
- maintain a healthy diet and avoid smoking or drinking high levels of alcohol. These are among key lifestyle recommendations to better manage many types of arthritis and musculoskeletal conditions. For people with back pain, for example, a healthy lifestyle is linked with higher levels of physical function.
Manuela Ferreira, Professor of Musculoskeletal Health, Head of Musculoskeletal Program, George Institute for Global Health and Leticia Deveza, Rheumatologist and Research Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: